Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lymphatic System: N-13 Group Members
Uploaded by
May Chelle ErazoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lymphatic System: N-13 Group Members
Uploaded by
May Chelle ErazoCopyright:
Available Formats
Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System is a network of tissues, vessels and organs that work
together to move a colorless, watery fluid called lymph back into your circulatory
system. The lymphatic system has two major functions which is the removing of
excess body fluids and from cellular/tissue waste products. Most of the waste
products are actually interstitial fluids which are the fluids in between cells and the
medium for cellular and waste transport. The interstitial fluid can be worn out and
can be replaced as another waste product to be brought to the lymph vessels. The
interstitial fluid consists of a water solvent containing sugars, salts, fatty acids,
amino acids, coenzymes, hormones, neurotransmitters, white blood cells and cell
waste-products.
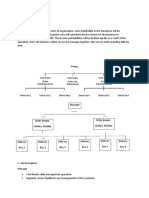
The Lymphatic System has three main components; the Lymphatic Blood
Vessels, Lymphoid Organs, and the Lymph Nodes. Falling under the component of
the Lymphatic Blood Vessels are the Lymphatic Capillaries which are tiny thin-
walled vessels. The second main component is the primary Lymphoid Organ
consisting of the bone marrow and thymus, while the secondary Lymphoid Organ
consists of the spleen, tonsils, Peyer’s Patch, and malt. Lastly, the third main
component are the Lymph Nodes which comprises with its sub-parts to be the
Afferent Lymphatic Vessel consisting of the sinuses and the Efferent Lymphatic
Vessel to be the hilus. Also consisting its sub-parts are the Medullary Cords in
which the B and T cells are categorized. Finally, the last four lymph node
compositions are the capsule, cortex, follicles, and the Germinal Centers.
N-13 Group Members:
Al Brian Sepulvida Altea A. Aya-on
Therese Yzabel Cloma Brandon Andrei U. Baldoman
Hector Emmanuel Go Maria Solima Nicole Estrada
May Chelle O. Erazo Mizpah Mae G. Geloca
Pearl Gem Rivas
You might also like
- Business Plan 1Document26 pagesBusiness Plan 1May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- A Research Paper Presented To TheDocument3 pagesA Research Paper Presented To TheMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- BODY Valiao SemiDocument38 pagesBODY Valiao SemiMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Areas: Areas of Occupational InterestDocument5 pagesAreas: Areas of Occupational InterestMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Claver National High School Senior High SchoolDocument3 pagesClaver National High School Senior High SchoolMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- FINAL Business PlanDocument53 pagesFINAL Business PlanMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Age Personal HygieneDocument4 pagesAge Personal HygieneMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Local Socio - Economic Profile (LSEP) - Barangay Panamaon, Loreto, Dinagat IslandsDocument11 pagesLocal Socio - Economic Profile (LSEP) - Barangay Panamaon, Loreto, Dinagat IslandsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Table of Content Business PalnDocument3 pagesTable of Content Business PalnMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Approval 1Document3 pagesApproval 1May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Management PlanDocument3 pagesManagement PlanMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument14 pagesAntimicrobial AgentsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderDocument6 pagesAssessing The Abdomen Basic Concept: Abdominal Assessment Is A Valuation of The Abdomen, Liver and BladderMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- CHN Daily ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCHN Daily ObjectivesMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Jesus: Prophet, Priest, and KingDocument2 pagesJesus: Prophet, Priest, and KingMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (Intro-Drug Calculation)Document46 pagesPharmacology (Intro-Drug Calculation)May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- What Is Your Impression About The Chosen People of GodDocument1 pageWhat Is Your Impression About The Chosen People of GodMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Home Visit OrientationDocument29 pagesHome Visit OrientationMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Playing Rules in BadmintonDocument3 pagesPlaying Rules in BadmintonMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Intrapartum Nursing RolesDocument1 pageIntrapartum Nursing RolesMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Formal LetterDocument1 pageFormal LetterMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Erazo, May Chelle O. BSN-N13Document7 pagesErazo, May Chelle O. BSN-N13May Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Log of Activities No. 2: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippines NursingDocument2 pagesLog of Activities No. 2: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippines NursingMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Home Visit Plan No. 1: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument7 pagesHome Visit Plan No. 1: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Initial Data Base Fro Ics CHNDocument16 pagesInitial Data Base Fro Ics CHNMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Home Visit Plan No. 1: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesHome Visit Plan No. 1: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument4 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)