Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blood Group and Genotype Compatibility: Info December 2013
Uploaded by
Aminu HassanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blood Group and Genotype Compatibility: Info December 2013
Uploaded by
Aminu HassanCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/303855977
Blood Group and Genotype Compatibility
Article in Info · December 2013
CITATIONS READS
0 200,985
1 author:
S.I.R. Okoduwa
School of Basic Medical Sciences, Babcock University, Ilishan-Remo Nigeria
57 PUBLICATIONS 524 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Enzymatic Conversion of waste Rice Husk through diluted acid pretreatment. View project
Appropriate Insulin Level for selecting animal model of Type 2 Diabetes View project
All content following this page was uploaded by S.I.R. Okoduwa on 08 June 2016.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
A Publication Series By
Infohealth Awareness Article SIRONigeria Global Limited
Health Article Vol 1, (2): Nov. 2013, pp 84-87
BLOOD GROUP AND GENOTYPE COMPATIBILITY
Okoduwa, S.I.R.
InfoHealth Awareness Unit, SIRONigeria Global Limited, Abuja-Nigeria
Accepted 13 December, 2013
What is Blood? Origin of Blood Group
Blood is the red liquid that circulates in the arteries and veins The two most significant blood group systems were
of humans and other vertebrate animals, carrying substances discovered by Karl Landsteiner during early experiments
such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and metabolic waste with blood transfusion: the ABO group in 1901 and in co-
products like carbon dioxide away from those same cells. operation with Alexander S. Wiener the Rhesus group in
1937.
Compositions of Blood
It is composed of solid corpuscle called blood cells Relevance of the Blood Group System
suspended in a liquid portion called plasma. The Plasma Blood groups have a hereditary basis and depend upon a
constitutes 55% of blood fluid, and it’s mostly water (92% series of alternative genes, a fact sometimes utilized in
by volume), and contains dissipated proteins, glucose, solving the problems of disputed parentage. They have been
mineral ions, hormones and carbon dioxide. The blood cells used in forensic science and were formerly used to
are: demonstrate impossibility of paternity (e.g., a type AB man
1. Red blood cells (erythrocytes) cannot be the father of a type O infant), but both of these
2. White blood cells (leukocytes) and uses are being replaced by genetic fingerprinting, which
3. Platelets (thrombocytes). provides greater certainty (Table 1).
Blood Group Table 1: Demonstration of Paternity Possibilities and
Blood group is the classification of blood based on the Impossibilities with Blood Group System
presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the Blood Group of Possible Impossible
surface of Red Blood Cells (RBCs). These antigens may be Couple Offspring offspring
A × A A ,O B , AB
proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids,
depending on the Blood Group System. Blood types are A × B A , B, AB O -- -
inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A A × O A , O B , AB
total of 32 human blood group systems have been recognized A × AB A , B , AB O
by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT).
B × B B , O A , AB
The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen;
they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with B × O B , O A , AB
+ and - denoting RhD status) B × AB A, B , AB O
O × O O A , B , AB
Okoduwa, S.I.R. is a Toxicologist/Medical Biochemist; and O × AB A , B O , AB
presently the Project Director of the Infohealth Awareness Group,
Abuja - Nigeria. AB × AB A , B , AB O
NOTE: Parents with blood group “AB” can’t possibly have
CORRESPONDENCE:
Tel: (+234) 08055-843-993; 0909-9640-143.
children with blood group “O” Also, Couple with Blood
Email: infohealth@sironigeria.com; group O × AB cannot possibly have children with either O
Website: http://sironigeria.com or AB.
Okoduwa, 2013 / Infohealth Awareness Article. Vol 1, No.2: PP 84-87
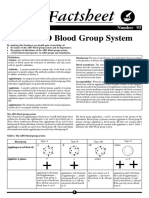
ABO Blood Group System individuals of any ABO blood group (i.e., A, B, O or AB). If
The ABO system is the most important blood-group system a patient in a hospital situation were to need a blood
in human-blood transfusion. The associated anti-A and anti- transfusion in an emergency, and if the time taken to process
B antibodies are usually immunoglobulin M, abbreviated the recipient's blood would cause a detrimental delay, O
IgM, antibodies (Table 2). ABO IgM antibodies are Negative blood can be issued. They are known as universal
produced in the first years of life by sensitization to donors.
environmental substances such as food, bacteria, and viruses.
An Rh D-Negative Patient who does not have any anti-D
Table 2: Illustration of the Genetic Make-up (Genotype and antibodies (never being previously sensitized to D-positive
Phenotype) of every Individual. RBCs) can receive a transfusion of D-positive blood once,
Phenotype Genotype but this would cause sensitization to the D antigen, and a
female patient would become at risk for hemolytic disease of
A IAIA or IAIO
the newborn (Figure 1). If a D-negative patient has
B IBIB or IBIO developed anti-D antibodies, a subsequent exposure to D-
AB IAIB positive blood would lead to a potentially dangerous
transfusion reaction. Rh D-positive blood should never be
O IOIO given to D-negative women of child bearing age or to
patients with D antibodies, so blood banks must conserve
The phenotype is the physical attribute, character or trait that Rh-negative blood for these patients. In extreme
is expressed in an individual. The genotype of an organism is circumstances, such as for a major bleed when stocks of D-
the inherited instructions it carries within its genetic code negative blood units are very low at the blood bank, D-
positive blood might be given to D-negative females above
Red Blood Cell compatibility child-bearing age or to Rh-negative males, providing that
Blood Group AB individuals have both A and B antigens on they did not have anti-D antibodies, to conserve D-negative
the surface of their RBCs and their blood plasma do not blood stock in the blood bank. The converse is not true; Rh
contain any antibodies against either A or B antigen. D-positive patients do not react to D negative blood (Figure
Therefore, an individual with type AB blood can receive 1)
blood from any group (with AB being preferable), but cannot
donate blood to any group other than AB. They are known as Rh Blood Group System
universal recipients. The Rh system is the second most significant blood-group
system in human-blood transfusion with currently 50
Blood Group A individuals have the A antigen on the antigens. The most significant Rh antigen is the D antigen,
surface of their RBCs, and blood serum containing IgM because it is the most likely to provoke an immune system
antibodies against the B antigen. Therefore, a group A response of the five main Rh antigens. It is common for D-
individual can receive blood only from individuals of groups negative individuals not to have any anti-D IgG or IgM
A or O (with A being preferable), and can donate blood to antibodies, because anti-D antibodies are not usually
individuals with type A or AB. produced by sensitization against environmental substances.
However, D-negative individuals can produce IgG anti-D
Blood Group B individuals have the B antigen on the antibodies following a sensitizing event: possibly a
surface of their RBCs, and blood serum containing IgM fetomaternal transfusion of blood from a fetus in pregnancy
antibodies against the A antigen. Therefore, a group B or occasionally a blood transfusion with D positive RBCs.
individual can receive blood only from individuals of groups Rh disease can develop in these cases.
B or O (with B being preferable), and can donate blood to
individuals with type B or AB. Rh INCOMPATIBILITY
What is Rhesus Factor?
Blood Group O (or blood group zero in some countries) It is a type protein found on red blood cells. If you have Rh
individuals do not have either A or B antigens on the surface factor, you're Rh-positive. If you don't have it, you're Rh-
of their RBCs, and their blood serum contains IgM anti-A negative. Rh factor is inherited (passed from parents to
and anti-B antibodies against the A and B blood group children through the genes). Most people are Rh-positive.
antigens. Therefore, a group O individual can receive blood
only from a group O individual, but can donate blood to
InfoHealth Awareness Article Vol 1 No 2 Nov. 2013 85
Okoduwa, 2013 / Infohealth Awareness Article. Vol 1, No.2: PP 84-87
Figure 1: Illustration of Occurrence of Rh Sensitization
Whether you have Rh factor doesn't affect your general How can an Rh-negative woman become sensitized? Rh-
health. However, it can cause problems during pregnancy. negative woman can become sensitized if she is pregnant
with a Rh-positive fetus. If a pregnant woman is Rh-
Rh Incompatibility is a condition that occurs during negative, her fetus can be Rh-positive only if the father is
pregnancy if a woman has Rh-negative blood and her baby Rh-positive. If both the mother and the father are Rh
has Rh-positive blood. negative, there is no chance the fetus will be Rh-positive and
no risk to the mother that she will be sensitized. If the
mother is Rh positive and the father is negative, sensitization
When does the Rh factor cause Problem?
does not occur (Table 3).
The Rh factor causes problems when a Rh-negative person’s
blood comes in contact with Rh-positive blood. If this
happens, the person with Rh-negative blood may become Table 3: Illustration of Rhesus Compatibility Match
sensitized. This means he or she produces antibodies that Father Mother Compatibility
fight against the Rh factor as if it were a harmful substance. Rh – Positive Rh – Positive Compatible
Once formed, these antibodies do not go away. Rh- Negative Rh- Negative Compatible
During pregnancy, the woman and fetus do not share blood Rh – Positive Rh – Negative Incompatible
systems. However, a small amount of blood from the fetus Rh – Negative Rh- Positive Compatible
can cross the placenta into the woman’s system. When this
happens, a small number of pregnant women with Rh-
negative blood carry an Rh-positive fetus will become When does Sensitization occur?
sensitized and make antibodies against the Rh factor. These These antibodies usually don't cause problems during a first
antibodies can attack and break down fetal Rh-positive red pregnancy. This is because the baby often is born before
blood cells. This causes hemolytic anaemia which can lead many of the antibodies develop. However, the antibodies
to a serious illness, brain damage, or even death of the fetus stay in your body once they have formed. Thus, Rh
or newborn. Hemolytic anemia is a condition in which red incompatibility is more likely to cause problems in second or
blood cells are destroyed faster than the body can replace later pregnancies (if the baby is Rh-positive).
them.
Genotype: The genotype of an organism is the inherited
Without enough red blood cells, your baby won't get enough instructions it carries within its genetic code. Genotype
oxygen. This can lead to serious problems. Severe hemolytic simply refers to hemoglobin gene constituents. Genes are
anemia may even be fatal to the child. always in pairs and overall expression depends whether
dominant, recessive or X-linked. So there is no problem
when one of the genes is abnormal e.g. AS, AC. This is
called a carrier state (sickle cell trait). Only when the two are
InfoHealth Awareness Article Vol 1 No 2 Nov. 2013 86
Okoduwa, 2013 / Infohealth Awareness Article. Vol 1, No.2: PP 84-87
abnormal then there is a great problem. The genotypes in sicklier among them. But why risk it? What if you're not so
humans are AA, AS, AC, SS. lucky? Can you forgive yourself when you end up having a
child with the sickle cell disease and put the child through
The great problem to avoid with genotype matchmaking for the agony the disease brings when you could have easily
intending couples is the Sickle cell disease. Intending avoided it?
couples must make sure to know their genotypes and be sure
it's compatible for marriage before going ahead to get
Compatible genotypes for marriage are: AA marries an AA.
married.
That's the best compatible. That way you save your future
children from having to worry about genotype compatibility
So who can you marry and who shouldn't you marry
based on Genotype compatibility? in future. This advocacy led to the formation of the
InfoHealth Awareness Group.
Someone with the genotype AA can marry across. That is
there's no risk of having a sicklier for a child even when he AA marries an AS. You'll end up with kids with AA and AS
or she marries an SS. But AA marrying an SS can only result which is good. But sometimes if you're not lucky all the kids
in AS children. There's no hope of having a child with the will be AS. Like my friend’s sister who is AA and married
genotype AA. But there's no danger either as illustrated in an AS and was expecting to have kids with genotype mostly
the Table 4. AA. But the last I heard two out of her 3 kids are AS; I'm not
sure what the genotype of her third child is. Like I've said
Table 4: Illustration of Genotype Compatibility Match. there's no problem having kids with AS except if eventually
Genotype Compatibility Remark the kids marry people with the genotype AS.
Rating
AA × AA 100% They can marry AS and AS should not marry. AS and SS shouldn't think of
marrying. And definitely SS and SS must not marry since
AA × AS 75% They can marry
there's absolutely no chance of escaping having a child with
AA × SS 50% They can marry the sickle cell disease.
AS × AS 25% Not Conclusion
recommended Rhesus factor does not constitute an absolute
AS × SS 0% Not contraindication why a Rh -ve woman should not marry a Rh
recommended
+ve man. Even in the few cases where sensitization occurs,
SS × SS 0% Not the affected child can still be effectively treated. There is a
recommended drug that can be used to prevent sensitization if the Rhesus
status of the couple is known initially. But as for AS
Someone with the genotype AS should only marry someone marrying an AS all in the name of “Love”, is a deliberate act
with the genotype AA because if AS marries AS there's one of destruction to the future generation. Let’s save our future
out of 4 chances (AS, AS, AA and SS) that they will have a generation by eradicating this abnormality in our society.
child with the sickle cell disease. Same applies when AC is
combined. AC and AS combine will produce AA, AS, AC, Before saying “ I do” know your blood group and genotype.
SC, the sickle cell disease will be SC. Help in preventing genetic diseases by marrying a partner of
compatible genotype. Determine the Rhesus status of every
Of course there are many cases where two abnormal was newly-born child. Consult your obstetrician during
combined that is an AS and AS or AC and AC or AC and AS pregnancy.
couples and had up to five or six children without a single
This article is an enlightenment seminar presentation to the Abuja Diocesan Youth during their Annual AYF Anniversary Week at CCA on
Friday 1st, November, 2013. Infohealth Awareness Article is a Copyright of InfoHealth Awareness Group, a Non-Profit Organisation aimed at
eradicating preventable diseases and hereditary disorders in Nigeria in order to have a Society of people living a healthier life.
© 2013 Infohealth Awareness Article. Alrights Reserved, Published By SIRONigeria Global Limited.
InfoHealth Awareness Article Vol 1 No 2 Nov. 2013 87
View publication stats
You might also like
- Genotype and Blood Group CompatibilityDocument5 pagesGenotype and Blood Group CompatibilityDo NothingNo ratings yet
- Rhesus Factor Incompatibility by Nwokolo ErnestDocument24 pagesRhesus Factor Incompatibility by Nwokolo Ernestagneschidimma27No ratings yet
- Blood GroupingDocument32 pagesBlood GroupingJaslir MendozaNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J Ijgg 20150301 12jshshahDocument12 pages10 11648 J Ijgg 20150301 12jshshahDiki MartikaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Abo Blood GroupDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Abo Blood Groupnidokyjynuv2100% (1)
- Blood Groups (1-2020) by DR Khaled A AbulfadleDocument7 pagesBlood Groups (1-2020) by DR Khaled A AbulfadleUzama Binu AliNo ratings yet
- Bio Project EditedDocument24 pagesBio Project Editedmisraadyasha6No ratings yet
- Blood Groups: HAP Unit 5thDocument31 pagesBlood Groups: HAP Unit 5thC RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Blood Groups: HAP Unit 5thDocument31 pagesBlood Groups: HAP Unit 5thSNEHASIS POLLEYNo ratings yet
- Resume of Blood TypeDocument6 pagesResume of Blood TypeAnster BrilianNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupDocument12 pagesBlood Groupalive computerNo ratings yet
- Blood Type - Wikipedia 08-26-2021Document14 pagesBlood Type - Wikipedia 08-26-2021michael_sr_44No ratings yet
- Blood Group MLDDocument5 pagesBlood Group MLDHarsheen KaurNo ratings yet
- Genotype and Blood Group CompatibilityDocument5 pagesGenotype and Blood Group CompatibilityajayranjithNo ratings yet
- Biology Project: C XIBDocument18 pagesBiology Project: C XIBPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Grouping Cbsebiology4uDocument10 pagesABO Blood Grouping Cbsebiology4usorojsahu85No ratings yet
- ABO Blood Grouping Cbsebiology4uDocument15 pagesABO Blood Grouping Cbsebiology4uanandbhanwalkar111No ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group System Is The Classification of Human Blood Based On TheDocument3 pagesABO Blood Group System Is The Classification of Human Blood Based On TheSidharthaBorahNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupsDocument38 pagesBlood GroupsVirendra JoshiNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Blood GroupDocument13 pagesBiology Investigatory Blood Groupanonymous user 345No ratings yet
- Abo Blood Group SystemDocument17 pagesAbo Blood Group SystemCSC LanjipadarNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Grouping Cbsebiology4uDocument14 pagesABO Blood Grouping Cbsebiology4uRahit BiswasNo ratings yet
- BLood GroupsDocument6 pagesBLood GroupsAhsanFarooqNo ratings yet
- PollinationDocument16 pagesPollinationR.KABILANNo ratings yet
- Blood Typing and Role It Plays in Preventing Adverse Reactions-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesBlood Typing and Role It Plays in Preventing Adverse Reactions-WPS OfficeAmina Isiaku SaniNo ratings yet
- Intro 7Document2 pagesIntro 7QUIZANA, Ceazairenee P.No ratings yet
- Topic Blood GroupsDocument5 pagesTopic Blood GroupsSeydou CisseNo ratings yet
- Blood TypingDocument9 pagesBlood TypingHuda BehroozNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigation ProjectDocument19 pagesBio Investigation ProjectMr StarkNo ratings yet
- Bhumika Biology ProjectDocument19 pagesBhumika Biology ProjectKiran DubeyNo ratings yet
- 2 4 6 Neuro 1 Sistem Penggolongan Darah 3 Maret 2013Document91 pages2 4 6 Neuro 1 Sistem Penggolongan Darah 3 Maret 2013sari antiNo ratings yet
- Facts Statistics Awareness Video Clip Related Topics Citation Discussion PrintDocument6 pagesFacts Statistics Awareness Video Clip Related Topics Citation Discussion PrintprasadNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupsDocument3 pagesBlood GroupsMian Talha KamalNo ratings yet
- Classical Genetics - ABO Blood GroupDocument2 pagesClassical Genetics - ABO Blood Groupprahashitha.s.2525No ratings yet
- Exercise 4 - Blood TypesDocument5 pagesExercise 4 - Blood TypesTricia RestriveraNo ratings yet
- 6 Blood PressureDocument13 pages6 Blood Pressurebertha tandiNo ratings yet
- Abobloodgroupsystem 170121130000Document31 pagesAbobloodgroupsystem 170121130000ashu pandeyNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument10 pagesBio Projectshwetanshu2109No ratings yet
- Bloodgroups 150424221954 Conversion Gate01Document38 pagesBloodgroups 150424221954 Conversion Gate01Endla SriniNo ratings yet
- ABO, H, and Lewis Blood Groups and Structurally Related AntigensDocument26 pagesABO, H, and Lewis Blood Groups and Structurally Related Antigenspro earnerNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chandra Sekhar-Oct-15Document5 pages1 - Chandra Sekhar-Oct-15Yana TaikiNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group SystemDocument14 pagesABO Blood Group SystemsankaiyahNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping 12thDocument17 pagesBlood Grouping 12thPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Medical Biotech Lab ReportDocument10 pagesMedical Biotech Lab ReportarasoNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Is Generally The Process of Receiving Blood Products IntoDocument3 pagesBlood Transfusion Is Generally The Process of Receiving Blood Products IntoMaverick RodriguezNo ratings yet
- AssignmentLab7 RodriguezDocument2 pagesAssignmentLab7 RodriguezRAZELLE JOY CATIAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- BLMOD TYPES and COMPATIBILITYDocument3 pagesBLMOD TYPES and COMPATIBILITYBiswaroopBiswasNo ratings yet
- LabbiologyDocument3 pagesLabbiologyapi-266034924No ratings yet
- BLOOD GROUPS TYPING - PowerpointDocument38 pagesBLOOD GROUPS TYPING - PowerpointJoy SNo ratings yet
- 95 Blood USDocument8 pages95 Blood USElaf Hassan AlsalemNo ratings yet
- The Blood StudentDocument6 pagesThe Blood StudentIustina Ioana0% (1)
- 95 Blood USDocument8 pages95 Blood USElaf Hassan AlsalemNo ratings yet
- Atvbaha 119 313658Document10 pagesAtvbaha 119 313658Sumeet TripathiNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group SystemDocument3 pagesABO Blood Group SystemSawan ShahNo ratings yet
- Abibakar Sheikaden Ismail 2019Document5 pagesAbibakar Sheikaden Ismail 2019Shafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- BORJA Genetics Lab Exercise 6 Multiple Alleles and ABO Blood Groups in HumansDocument5 pagesBORJA Genetics Lab Exercise 6 Multiple Alleles and ABO Blood Groups in Humansbry uyNo ratings yet
- LAB 3 - Blood TypingDocument8 pagesLAB 3 - Blood TypingCodespher3No ratings yet
- Ltoe 1Document2 pagesLtoe 1lexdei88No ratings yet
- Summary, Analysis & Review of Peter J. D’Adamo’s Eat Right 4 Your TypeFrom EverandSummary, Analysis & Review of Peter J. D’Adamo’s Eat Right 4 Your TypeNo ratings yet
- Call For Nomination-Application For Year 2023Document4 pagesCall For Nomination-Application For Year 2023Aminu Hassan100% (1)
- HSPH TDOV FlyerfinalDocument1 pageHSPH TDOV FlyerfinalAminu HassanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy UmyuDocument8 pagesAnatomy UmyuAminu HassanNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Sample Tubes Used in PhlebotomyDocument2 pagesThe Different Types of Sample Tubes Used in PhlebotomyAminu HassanNo ratings yet
- 2 Information About InsectsDocument3 pages2 Information About InsectsSaaaaaNo ratings yet
- DIVA-5 Diva 5 Id English FormDocument20 pagesDIVA-5 Diva 5 Id English FormEspíritu Ciudadano92% (26)
- Worksheet coronavirus-COVID-19-facts-and-adviceDocument4 pagesWorksheet coronavirus-COVID-19-facts-and-adviceF RengifoNo ratings yet
- Compartment Syndrome AinulDocument32 pagesCompartment Syndrome AinulShidevNo ratings yet
- Autism PaperDocument5 pagesAutism PaperMaggie NielsenNo ratings yet
- Cymbalta (Duloxetine HCL) Patient Information - Side Effects and Drug Images at RxlistDocument7 pagesCymbalta (Duloxetine HCL) Patient Information - Side Effects and Drug Images at Rxlisteiad-mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Malaria DR TariqDocument32 pagesMalaria DR Tariqdr_hammadNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea Cardiac Origin STPDocument21 pagesDyspnea Cardiac Origin STPmeiliaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJanie StubbertNo ratings yet
- EpisiotomyDocument18 pagesEpisiotomyAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Capaian Kinerja Peserta RSDocument14 pagesCapaian Kinerja Peserta RSAyu AzrinaNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Dan Lesi Rahang Pada Radiograf: Border Periosteal ReactionDocument6 pagesGambaran Dan Lesi Rahang Pada Radiograf: Border Periosteal ReactionI Dewa Ayu SavitriNo ratings yet
- Zhongfeng Liv-4: Middle SealDocument2 pagesZhongfeng Liv-4: Middle Sealray72roNo ratings yet
- COPDDocument7 pagesCOPDstudy mailNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Immunity: Shimelis Teshome (BSC MLS)Document31 pagesAdaptive Immunity: Shimelis Teshome (BSC MLS)Shimelis Teshome AyalnehNo ratings yet
- Somatic Symptom Disorders and Personality DisordersDocument15 pagesSomatic Symptom Disorders and Personality Disordersapi-287575009No ratings yet
- Anti HAVDocument3 pagesAnti HAVHassan GillNo ratings yet
- Bowel EliminationDocument5 pagesBowel EliminationDimple Castañeto CalloNo ratings yet
- Pain Management in AnimalsDocument184 pagesPain Management in Animalsssarbovan100% (1)
- Diseases of ImmunityDocument13 pagesDiseases of ImmunityRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Tn-I Plus: Warnings and PrecautionsDocument5 pagesTn-I Plus: Warnings and PrecautionsAniket DubeyNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Why Does This Sample Need Recollected? Beth Warning, MS, MLS University of Cincinnati MLS ProgramDocument8 pagesObjectives: Why Does This Sample Need Recollected? Beth Warning, MS, MLS University of Cincinnati MLS ProgramMarj MendezNo ratings yet
- Knee FlexionDocument4 pagesKnee FlexionJeg1No ratings yet
- SarkopeniaDocument8 pagesSarkopeniaRamadhanaNo ratings yet
- EPM MCQs Post Course Test 2017 v1Document2 pagesEPM MCQs Post Course Test 2017 v1Maisie RobertsNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Combined Antibiotic Ophthalmic Solution in The Treatment of Hordeolum After Incision and Curettage: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial: A Pilot StudyDocument4 pagesEffectiveness of Combined Antibiotic Ophthalmic Solution in The Treatment of Hordeolum After Incision and Curettage: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial: A Pilot StudyYuyun SaragihNo ratings yet
- Lee 1995Document5 pagesLee 1995Thasya TamaraNo ratings yet
- 1E - Group E - Anquilo-Boter-Deraco-Magno-Parame-Sitoy-WhelessDocument10 pages1E - Group E - Anquilo-Boter-Deraco-Magno-Parame-Sitoy-WhelessAdrea DeracoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labor. BBBB WWPPTXDocument53 pagesAbnormal Labor. BBBB WWPPTXHamss Ahmed100% (2)
- Raja LeeterDocument3 pagesRaja LeeterSyed's Way PoolNo ratings yet
- Report HPV, Shingles and Chicken PoxDocument4 pagesReport HPV, Shingles and Chicken PoxJarold PerezNo ratings yet