Professional Documents
Culture Documents
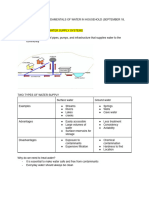
2 - Public Water Supply
Uploaded by
E&N Commission0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views18 pagesENGINEERING UTILITIES - PLUMBING CHAPTER 2
Original Title
2 - Public Water Supply (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentENGINEERING UTILITIES - PLUMBING CHAPTER 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views18 pages2 - Public Water Supply
Uploaded by
E&N CommissionENGINEERING UTILITIES - PLUMBING CHAPTER 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Public Water Supply: Sources
and Purification Process
Engr. Sean Kyle R. Mabiog, RMP, SO2
What are the General Sources of Public Water
Supply?
The 2 General Sources of Public Water Supply are:
1. Surface Waters: Streams, Rivers, and Lakes
a. Upland Surface Water
b. Lowland Surface Water
2. Groundwater
Upland Surface Waters
Water Divides and Watersheds
Major Watershed in
Oriental Mindoro
Naujan Lake and Oriental Mindoro
Watersheds (NL&OMW)
Naujan Lake and Oriental Mindoro Watersheds (NL&OMW) are situated
in Oriental Mindoro province (Region 4B, MIMAROPA) and occupy a
total area of 122,000 hectares. The Naujan Lake National Park, covering
21,655 hectares, was proclaimed a Protected Area in 1968 by virtue of
Proc. No. 335. Naujan Lake is the 5th largest lake in the Philippines. It is
recognized as a Ramsar Wetland of International Importance and part
of the East Asian-Australasian Flyway for migratory birds.
Meanwhile, the Oriental Mindoro watersheds include the Baco-
Bucayao River, Bucayao River, Mag-asawang Tubig River and Pula River.
These encompass the municipalities of Naujan, Victoria, Socorro, Pola,
Baco, San Teodoro, and Calapan City.
Groundwater
Testing in
Oriental
Mindoro
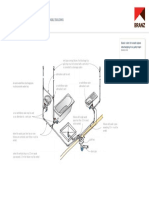
What is the Purification Process for Surface
Water Supply Source?
Surface water basic treatment process employed by commercial water
provider treats the water using the conventional method comprising of
the following:
1. Storage
2. Aeration
3. Coagulation/Flocculation
4. Sedimentation
5. Filtration
6. Disinfection/Chlorination
Storage
Runoff or surface water is first stored in a dam. Suspended matters
tend to sink to the bottom. In the course of time, disease-producing
organisms tend to die out. Thus, the storing of water improves its
quality.
Linao-Cawayan Mini Hydro Dam – San Teodoro
Inclanay Dam - Pinamalayan
Aeration
Water is sprayed into the air or cascaded in order to release trapped
gases and absorb additional oxygen for better taste. It also removes
iron compounds.
Coagulation
It is the chemical process in which the coagulant reacts with the
sediment to make it capable of combining into larger particles. Alum is
the common coagulant used.
Flocculation
It is the physical process in which the sediment particles collide with
each other and stick together.
Sedimentation
This is the process by which suspended solids are removed from the
water by gravity settling and deposition. The objective of this process is
to remove most of the suspended solids and thus reducing the loads on
the filters.
Filtration
Water is passed through a bed of fine sand in which the suspended
matters that did not settle during sedimentation are trapped and held
in place by the force of gravity or by the direction of flow.
Types of Filters
1. Slow Sand Filter – consists of large tanks with filter bed of 600mm
to 1000mm of fine sand over 300mm of gravel with suitable
drainage pipes to conduct water after passing through the filter
under its own weight.
2. Rapid Sand Filter
a. Rapid Gravity Filter
b. Rapid Pressure Filter
Disinfection/Chlorination
Chlorination is the method of introducing a controlled amount of
chlorine gas or chlorine salts to the water in order to attain a desired
degree of disinfection. Chlorine kills any disease-producing organisms
in the water.
End of discussion.
You might also like
- Clean Water Act With IntroductionDocument139 pagesClean Water Act With IntroductionChubs AllivesNo ratings yet
- Dal Lake: Issues and Management StrategiesDocument5 pagesDal Lake: Issues and Management StrategiesImtiyaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document79 pagesChemistry 1malathi_vijayan417No ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument5 pagesBiodiversityKayraine Mae Edillor CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Resources in MalaysiaDocument52 pagesWater Supply Resources in MalaysianienanienaNo ratings yet
- Water Resources EngineeringDocument2 pagesWater Resources EngineeringErald EnriquezNo ratings yet
- ENV 305 Final QuestionsDocument5 pagesENV 305 Final QuestionsAfsin RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 1ST Quarter SummaryDocument9 pagesEarth Science 1ST Quarter SummaryLeonard SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Dec Week 34Document55 pagesDec Week 34hamtum7861No ratings yet
- Module 06Document38 pagesModule 06John Keith MaderaNo ratings yet
- Marine Biodiversity of Pakistan - Current Status, Threats and Conservation NeedsDocument20 pagesMarine Biodiversity of Pakistan - Current Status, Threats and Conservation Needsshoukat aliNo ratings yet
- Sasumua Dam Case StudyDocument24 pagesSasumua Dam Case StudyElijah Kamau100% (1)
- Local Media533471763087034420Document31 pagesLocal Media533471763087034420The OrganonNo ratings yet
- 1191 Dam Eia enDocument25 pages1191 Dam Eia enFung Chye VunNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument49 pagesWater ResourcesDelta ForceNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Running WaterDocument21 pagesModule 5 Running WaterSheilla Mae SerranoNo ratings yet
- 2aquatic Science and Wetland ManagmentDocument54 pages2aquatic Science and Wetland ManagmentAbesh BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Management Action Plan of Loktak LakeDocument10 pagesManagement Action Plan of Loktak LakeChinglen KhunNo ratings yet
- Water On Earth Is Distributed Across Various ReservoirsDocument3 pagesWater On Earth Is Distributed Across Various ReservoirsDoung PichchanbosbaNo ratings yet
- Unit I. Earth & Space: Chapter 2: Water, An International ConcernDocument32 pagesUnit I. Earth & Space: Chapter 2: Water, An International ConcernRosemarie CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Environment EcologyDocument20 pagesEnvironment EcologyPriya KumariNo ratings yet
- Water Resources in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesWater Resources in The PhilippinesAllan DeGuzman Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Water Resources and Treatment, Wastewater and Water Quality ParametersDocument19 pagesWater Resources and Treatment, Wastewater and Water Quality Parametersleslie_francisco_1No ratings yet
- Reporting Earth Sci M11Document5 pagesReporting Earth Sci M11「 」No ratings yet
- Reviewer Coastal Engineering Module 8 10Document15 pagesReviewer Coastal Engineering Module 8 10pabello2020317No ratings yet
- Caroni Arena ReservoirDocument10 pagesCaroni Arena ReservoirEmmanuel RyanNo ratings yet
- DhruviPareek 21060222093 DivA ILCDocument12 pagesDhruviPareek 21060222093 DivA ILCLuNo ratings yet
- Classification of LakesDocument9 pagesClassification of LakesDeepti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nainital LakeDocument2 pagesNainital LakeajayNo ratings yet
- Water ControlDocument6 pagesWater ControlErald Enriquez100% (1)
- As CaseStudy GuideDocument28 pagesAs CaseStudy GuideAli VehbNo ratings yet
- Hydro SphereDocument33 pagesHydro SphereAlvinNo ratings yet
- Chilika Lagoon: Damages & RestorationsDocument14 pagesChilika Lagoon: Damages & RestorationseebarasatNo ratings yet
- A 2021 Vision IAS Test 8Document34 pagesA 2021 Vision IAS Test 8Archer MonarchNo ratings yet
- 08 Vision IAS CSP21 Test 8S ENVIDocument34 pages08 Vision IAS CSP21 Test 8S ENVIpuppala mokshithaNo ratings yet
- ST - John's Water ConservationDocument19 pagesST - John's Water ConservationAbhishekShubhamGabrielNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Origin of Lake and RiverDocument43 pagesLecture 2 - Origin of Lake and Riversyuhada280304No ratings yet
- FreshwaterDocument8 pagesFreshwateromar shakilNo ratings yet
- Littoral Drift Sources and Sinks Along The Indian CoastDocument7 pagesLittoral Drift Sources and Sinks Along The Indian CoastAnu SakthiNo ratings yet
- Philippines FreshwaterDocument11 pagesPhilippines FreshwaterBJ Allon Mallari100% (1)
- Coastal DataDocument133 pagesCoastal DataJegan RichardNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2 Sa Hydro Ni BryDocument4 pagesAssignment No.2 Sa Hydro Ni BryMAP BNSNo ratings yet
- Wetlands of PakistanDocument56 pagesWetlands of Pakistanlajbarkhan balochNo ratings yet
- Water Management FeaturesDocument5 pagesWater Management FeaturesSaketh VuppalapatiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Eia of Obajama DamDocument7 pagesAssignment Eia of Obajama Damawab ahmadNo ratings yet
- Assignment Eia of Obajama DamDocument7 pagesAssignment Eia of Obajama Damawab ahmadNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Freshwater OceanDocument38 pagesTopic 5 Freshwater Oceanahmad bahiyuddin21No ratings yet
- Lesson 9: Understanding The Water CycleDocument47 pagesLesson 9: Understanding The Water CycleJeremy DemateNo ratings yet
- LakesDocument14 pagesLakesmanwartejam8No ratings yet
- Buildu1 Module 1 - Fundamentals of Water in Household (September 18, 2023)Document7 pagesBuildu1 Module 1 - Fundamentals of Water in Household (September 18, 2023)giannaadrielle.benedictoNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument33 pagesWater ResourcesJolina RicoNo ratings yet
- Coastal Erosion: October 2011Document7 pagesCoastal Erosion: October 2011Diogo LamúriaNo ratings yet
- Water Is Everywhere!: Title CardDocument11 pagesWater Is Everywhere!: Title CardJervin ManabatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Report - Water PurificationDocument21 pagesChemistry Report - Water PurificationOnyxNo ratings yet
- The Earth's OceansDocument31 pagesThe Earth's Oceansglenn plazaNo ratings yet
- GEOS3009 - Mod 1 - EstuariesDocument53 pagesGEOS3009 - Mod 1 - EstuariesTrung TranNo ratings yet
- Stormwater - Retention Pond (Wet Pond) vs. Detention Pond (Dry Pond)Document2 pagesStormwater - Retention Pond (Wet Pond) vs. Detention Pond (Dry Pond)Lionel Tan100% (2)
- B.tech I Yr Environment and Ecology Unit 2 Detail NotesDocument18 pagesB.tech I Yr Environment and Ecology Unit 2 Detail Notesbhaivarun65No ratings yet
- Ecosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Fresh and Saltwater Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandEcosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Fresh and Saltwater Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- National Plumbing CodeDocument5 pagesNational Plumbing CodeE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- EU2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesEU2 ReviewerE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- 3 - Private Water Supply SourceDocument20 pages3 - Private Water Supply SourceE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- 1 - Water and The Human NeedsDocument25 pages1 - Water and The Human NeedsE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities - Plumbing SyllabusDocument1 pageEngineering Utilities - Plumbing SyllabusE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1Document2 pagesEngineering Utilities 1E&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1: Negative Charge of Electricity. Positive Charge of Electricity Not Electrically ChargedDocument3 pagesEngineering Utilities 1: Negative Charge of Electricity. Positive Charge of Electricity Not Electrically ChargedE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1: Electrical Pressure Volt (V)Document2 pagesEngineering Utilities 1: Electrical Pressure Volt (V)E&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- Measuring - Ice - Lens - Growth - and - Development - of - Soil Using GeoPIVDocument6 pagesMeasuring - Ice - Lens - Growth - and - Development - of - Soil Using GeoPIVChristian SamsonNo ratings yet
- Brochure - MBR 20 - 80 - HMIDocument2 pagesBrochure - MBR 20 - 80 - HMIkoen irawanNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Sanitation Final ExamDocument9 pagesWater Supply and Sanitation Final ExamTILAYEYIDEG50% (2)
- Abhijit Mitra, Sufia Zaman (Auth.) - Basics of Marine and Estuarine Ecology-Springer India (2016)Document490 pagesAbhijit Mitra, Sufia Zaman (Auth.) - Basics of Marine and Estuarine Ecology-Springer India (2016)Ike Elita SariNo ratings yet
- ESC Permit Closure Checklist - Sept - 2020Document2 pagesESC Permit Closure Checklist - Sept - 2020charanbagh6402No ratings yet
- Dams and BarragesDocument14 pagesDams and BarragesNaseeb AghaNo ratings yet
- Sourcebook of Alternative Technologies For Freshwater Augumentation in Some Countries in AsiaDocument5 pagesSourcebook of Alternative Technologies For Freshwater Augumentation in Some Countries in AsiaNambi HarishNo ratings yet
- Techncial Review - Practical Guidelines For Test Pumping in Water WellsDocument104 pagesTechncial Review - Practical Guidelines For Test Pumping in Water WellsKwok Ho Chung100% (1)
- Instructional Project 5 - Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesInstructional Project 5 - Lesson Planapi-290709021No ratings yet
- Env 825 (Environmental Economics Assignment)Document6 pagesEnv 825 (Environmental Economics Assignment)Olayiwola GiwaNo ratings yet
- Economy of Kanpur: Master PlanDocument1 pageEconomy of Kanpur: Master PlanPooja Aradhana PradhanNo ratings yet
- Wwe Question BankDocument45 pagesWwe Question Banknehamya100% (2)
- Notes 1 Flow in Open ChannelDocument8 pagesNotes 1 Flow in Open ChannelTing Wee KietNo ratings yet
- Gmail - Puerto Rico's Ocean Dumping Plans, 2022 Through 2032Document2 pagesGmail - Puerto Rico's Ocean Dumping Plans, 2022 Through 2032CORALationsNo ratings yet
- Greater Bridgeport Combined Sewer Overflow Guide For ResidentsDocument2 pagesGreater Bridgeport Combined Sewer Overflow Guide For ResidentsBridgeportCT100% (1)
- Kumbakonam Composite Local Planning AuthorityDocument5 pagesKumbakonam Composite Local Planning AuthoritySowmyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation by SaqibDocument39 pagesPresentation by SaqibFahad ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Scenario Analysis Using WEAP Model For A River CatchmentDocument37 pagesScenario Analysis Using WEAP Model For A River CatchmentrameshnannawareNo ratings yet
- Agriscience Fundamentals and Applications 6th Edition Burton Test Bank 1Document6 pagesAgriscience Fundamentals and Applications 6th Edition Burton Test Bank 1francisco100% (35)
- 58 Brine Persistence - Part 1 Physical PropertiesDocument7 pages58 Brine Persistence - Part 1 Physical Propertiesloai allamNo ratings yet
- The Interior Design Reference & Specification Book Everything Interior Designers Need To Know Every DayDocument1 pageThe Interior Design Reference & Specification Book Everything Interior Designers Need To Know Every DayAnonymous IGtWHoi0No ratings yet
- St. Cisondari St. Cibeureum Bulan N (Tahun) 1994 - 2005 1994 - 2005 Rata-Rata Rata-RataDocument6 pagesSt. Cisondari St. Cibeureum Bulan N (Tahun) 1994 - 2005 1994 - 2005 Rata-Rata Rata-RataAzam AufarNo ratings yet
- DENR - High Coliform Levels Render Manila Bay Unsafe For BathingDocument4 pagesDENR - High Coliform Levels Render Manila Bay Unsafe For BathingCu AgNo ratings yet
- Table PD957, BP220Document4 pagesTable PD957, BP220Ar JCNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Isometric View Ground Floor Sanitary Layout 2Nd Floor Sanitary LayoutDocument1 pageSanitary Isometric View Ground Floor Sanitary Layout 2Nd Floor Sanitary LayoutChris Gerald CruzNo ratings yet
- Basic Irrigation Engineering p1Document36 pagesBasic Irrigation Engineering p1Avonlee OrbudaNo ratings yet
- CD WorksDocument35 pagesCD WorksThulasidharan Nair Bhaskaran100% (2)
- Achievement and Drawback of Bulk Water Allocation of Irrigation Water System in Sandaresgama, Mahaweli System "H"Document37 pagesAchievement and Drawback of Bulk Water Allocation of Irrigation Water System in Sandaresgama, Mahaweli System "H"Chamin SubhawickramaNo ratings yet
- Soil & Water Assessment Tool: Introductory ManualDocument166 pagesSoil & Water Assessment Tool: Introductory ManualForrest ElvenNo ratings yet