Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NMAT Study Guide
Uploaded by
la elena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesNMAT Study Guide
Uploaded by
la elenaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
NMAT Study Guide Genetics
o Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
Part I. Mental Ability o Types of RNA
o Mendelian Mode of Inheritance
VERBAL ABILITY o Non-Mendelian Mode of Inheritance
o Pedigree Analysis
Opposites Analogies (e.g., fire and ice, tired and energetic, crying o Chromosomes
and laughing, etc.).
Plant Physiology
Object and Classification Analogies (e.g., red and color, knife
o Photosynthesis
and kitchenware, truck and vehicle, etc.).
o Parts of the Plant
Object and Related Object Analogies (e.g., dog and puppy,
o Kind of Plants
kangaroo and joey, plant and seed, etc.).
o Plant Hormones
Object and Group Analogies (e.g., wolf and pack, trees and
forest, fish and school, seagull and flock, etc.). o Reaction to Stimulus
Degree of Characteristics Analogies (e.g., cold and freezing, o Plant Bacteria Symbiosis
warm and hot, tired and exhausted, etc.). o Photoperiodism
Cause and Effect Analogies (e.g., read and learn, work and earn, Taxonomy
spin and dizzy, fire and burn, etc.). o The Five Kingdom Scheme
Effort and Result Analogies (e.g., write and letter, sculpt and o Three Domains of Life
monument, build and house, paint and painting, etc.). Ontogeny
Problem and Solution Analogies (e.g., tired and sleep, o Growth and Development
unemployment and job application, itch and scratch, etc.).
Verb Tenses Analogies (e.g., sent and send, run and ran, eat and CHEMISTRY
ate, walk and walked, etc.).
Performer and Action Analogies (doctor and heal, scientist and Inorganic Chemistry
research, soldier and fight, etc.).
Object and Part of the Whole Analogies (e.g., page and book, Matter
glass and window, brick and wall, etc.). o Properties
Object and Function Analogies (e.g., paintbrush and paint, o Intensive and Extensive Properties
keyboard and type, telephone and call, etc.). o Types of Matter
Object and Location Analogies (e.g., plane and airport, dog and Properties of Elements
doghouse, tree and forest, etc.). Properties of Compounds
Things That Go Together Analogies (e.g., salt and pepper, Properties of Mixtures
peanut butter and jelly, bread and butter, ham and cheese, spoon Atoms
and fork, etc.). o Atomic Theory of Matter
Synonym Analogies (e.g., obese and fat, slender and thin, sad and o Atomic Models
depressed, etc.). o Components of an Atom
Antonym Analogies (e.g., poverty and wealth, timid and outgoing, o Properties of an Atom
frail and strong, inflation and deflation, etc.). o Electronic Configuration
Rhyme Analogies (e.g., whey and away, glasses and mosses, deer Hund, Aufbau, and Pauli
and steer, etc.). o Quantum Mechanics
Geography Analogies (e.g., Boston and Massachusetts, Tucson Elements
and Arizona, Chicago and Illinois, Denver and Colorado, etc.). o Periodic Table of Elements
Measurement Analogies (e.g., feet and meter, pound and Classification
kilogram, quart and liter, etc.). Groups and Families
Time Analogies (e.g., September and fall, December and winter, Periodic Trends
March and spring, etc.). Compounds
o Oxidation State
INDUCTIVE REASONING o Types of Chemical Bonds
o Representation of Compounds
QUANTITATIVE APTITUDE Percent composition
o Molecular Geometry
Fundamental Operation o Intermolecular Forces
Problem Solving
o Relationships of organic compounds to:
Data Interpretation
Boiling point
Melting point
PERCEPTUAL ACUITY
Solubility
Acidity
Hidden Figure o The Mole
Mirror Image
Gases
Identical Information o Ideal Gas Law Concept
o Gas Laws
Part II. Academic Proficiency
Chemical Reactions
BIOLOGY o Types of Reactions
o Fundamental Law of Chemical Reactions
Anatomy and Physiology o Redox Reactions
o Anatomy o Stoichiometry
Circulatory System Limiting and Excess Reagents
Respiratory System o Energies, Spontaneity, Equilibrium
Nervous System Chemical Kinetics
Digestive System Chemical Equilibrium
Endocrine System o Properties of Exothermic Reaction
Urinary System o Properties of Endothermic Reactions
Reproductive System o Le Chatelier's Principles
o Physiology Dissociation of Compounds
Enzymes Acids and Bases
Cellular Transport o Definitions
Blood Clot Formation o Properties
Blood Pigments o Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
Bone Growth and Development
Computations
Accessory Organs of Digestion
Dissociation of Acids and Bases
Cellular Tonicity
Thermochemistry
Immune Response
o Thermal Properties of Matter
Cellular Biology
o The Cell Cycle o Heat and its Effects
Mitosis Radioactive Decay
Meiosis Concentrations of Solutions
o The Cell o Molality
Parts of the Cell o Molarity
o Cellular Respiration o Normality
Ecology Colligative Properties of Solutions
o Hierarchy of life
o Food Chain Organic Chemistry
o Terrestrial Biomes
Common Properties
o Aquatic Biomes
Resonance and Hybridization
o Ecological Succession
Isomers
o General Freshwater Biomes
Saturated hydrocarbons
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Nuclear Physics
Aliphatic compounds o Radioactivity
Aromatic compounds Fluid
Heterocyclic compounds o Pressure
Other organic compounds
Functional Groups SOCIAL SCIENCE
o Nomenclature
o Common Reactions Sociology
Biochemistry
Social Sciences and Research
Proteins o Definition of social sciences
Carbohydrates o Major branches
Lipids o The Scientific Method
Nucleic Acids o Types of Scientific Research
Biochemical Tests o Research Method
Sociology and Anthropology
PHYSICS o Definition of culture
o Elements of culture
Measurement o Concepts
Motion o Macro and Micro Theories about Society
o Mechanics The Role and Scope of Sociology
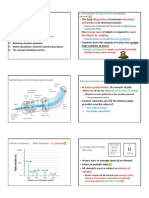
o Linear Motion/UARM o Nature of Sociology
o Free Fall Motion o The Task of Sociology as Science
o Motion Graphs o Sociology and Social Science
o Projectile Elements of Sociological Analysis
o Uniform Circular Motion o Culture
o Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation o Society and Social Structure
o Laws of Motion o Socialization
Normal force o Groups and Socialization
Friction o Social Disorganization, Deviance and Social
Tension o Control
o Kepler’s Law of Planetary Orbits o Social Inequalities
Dynamics Social Institutions
o Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation o Family
o Laws of Motion o Religion
Normal force Types
Friction Forms
Tension o Education
o Kepler’s Law of Planetary Orbits
Geography, Economy, and Work
Work o Statistics and Demography
Power o Ecology
Energy o Economics
o Potential o Factors that respond to economic systems
o Kinetic o Economy system
Momentum o Politics and Government
Impulse Forms
Fluids Social Change and Current Trends
o Density o Forms of Collective Behavior
o Specific Gravity Types of Crowd
o Pressure Theories of Crowding
o Pascal’s Law o Types of Social Movements
o Buoyant Force o Stages Leading to Eventual Acceptance by Society
o Bernoulli’s Principle Social Chance and Future Trends
o Torricelli’s Theorem o Factors of Social Change
o Venturi Effect o Theories of Social Change
Thermodynamics Important Figures in the Development of Sociology
o Laws of Thermodynamics Sociological Terms
o Change in Temperature Philippine History and Political Science
o Change in Phase o Notable figures and thinkers
o Thermal Processes o Forms of government and political systems
o Thermal Expansion
Heat Capacity Psychology
o Heat Engine
o Refrigerator Schools of Thought of Psychology
Thermal Processes Contemporary Psychological Perspectives
o Conduction o Biological
o Convection o Behavioral
o Radiation o Cognitive
Electromagnetism o Psychoanalytic
o Fundamental Law of Electrostatics o Phenomenological
o Electrostatic Force General Characteristics
o Ohm’s Law Factual Experiences
o Coulomb’s Law Nervous System
o Resistors o Parts and Functions of the Brain
o Capacitors o Central Nervous System
Electricity o Peripheral Nervous System
o Coulomb’s Law Sensation and Perception
o Ohm’s Law Consciousness
o Resistors o Sleep disorders
o Capacitors o Dreams
Light and Sound Waves Psychoactive Drugs
Magnets Memories
o Magnetic Field o Long and Short- Term
o Magnetic Force o Explicit and Implicit
Waves and Optics Motivation
o Electromagnetic Spectrum Emotions
o Properties of Waves Principles of Growth and Development
o Mirrors o Piaget’s Model of Cognitive Development
Concave o Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development
Convex Learning
o Lenses o Pavlov’s Classical Conditioning
Concave o Skinner’s Operant Conditioning
Convex Schedules of Reinforcement
o Light waves o Instrumental Conditioning
Refraction o Theories of Personality
Diffraction
Sheldon’s Body Types Theory
Jung’s Behavioral Types Theory
Body Chemistry Theory
Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory
Freud’s Psychosexual Theory
Erikson Psychosocial Stages
Theory
Jung’s Analytic Theory
o Approaches
Pavlov and Skinner’s Behavioral Approach
Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
Piaget’s Cognitive Approach
Maslow’s Humanistic Approach
Phenomenological Approach
o Psychopathologies and Therapy
Anxiety Disorders
Mood Disorders
Personality Disorders
Psychotherapy
Frustrations, Conflict, and Stress
Responses to Frustrations
Abnormal Reaction to Frustration and Stress
Neuroses
Psychoses
Psychotherapy
Social Psychology
Social Behavior
You might also like
- Nmat PartsDocument3 pagesNmat PartsmalvincayabyabNo ratings yet
- Mathematics A. Arithmetic and Number Sense F. Statistics: Science A. General ScienceDocument3 pagesMathematics A. Arithmetic and Number Sense F. Statistics: Science A. General SciencebrettNo ratings yet
- The Soul Family: A Guide to Karmic relationships, Soulmates, Soul Tribes, and Twin FlamesFrom EverandThe Soul Family: A Guide to Karmic relationships, Soulmates, Soul Tribes, and Twin FlamesNo ratings yet
- COLLEGE ENTRANCE TEST For S.Y. 2020 - 2021Document2 pagesCOLLEGE ENTRANCE TEST For S.Y. 2020 - 2021summernessNo ratings yet
- CETs TopicDocument4 pagesCETs Topicyani reyesNo ratings yet
- Topics On CetsDocument4 pagesTopics On CetsAira Joy AnyayahanNo ratings yet
- USTET Reviewers ChecklistDocument4 pagesUSTET Reviewers ChecklistAlessandria Frias CorralNo ratings yet
- UPCAT Topics ChecklistDocument2 pagesUPCAT Topics ChecklistTineesyNo ratings yet
- Math and Science Pointers For CETsDocument2 pagesMath and Science Pointers For CETsmozelleNo ratings yet
- Cet Reviewer ChecklistDocument7 pagesCet Reviewer ChecklistJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics ReviewerDocument4 pagesMathematics ReviewerJean Hershey Roasa ReyesNo ratings yet
- UPCAT Study Guide: o Biochemistry o Intermediate GeneticsDocument2 pagesUPCAT Study Guide: o Biochemistry o Intermediate Geneticsdawn bella gonzagaNo ratings yet
- UPCAT Math CoverageDocument5 pagesUPCAT Math CoverageLuisa SorianoNo ratings yet
- UPCAT Contents To ReviewDocument4 pagesUPCAT Contents To ReviewJanine SarzaNo ratings yet
- Major Online Test Series Aiims 2019Document9 pagesMajor Online Test Series Aiims 2019Snek PratikNo ratings yet
- Coverage UPCATDocument1 pageCoverage UPCATHwic Batangas SCNo ratings yet
- GEOL+1200+Final+Exam+Study+Guide+S17Document3 pagesGEOL+1200+Final+Exam+Study+Guide+S17Anonymous O9zYsK8No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabussaim mughalNo ratings yet
- Std. IX Mathematics: 1. SetsDocument9 pagesStd. IX Mathematics: 1. SetsPraful KakdeNo ratings yet
- Science Pointers-ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience Pointers-ReviewerALISON JACOB OBEDENCIONo ratings yet
- Leader Online Test Series For AipmtDocument9 pagesLeader Online Test Series For AipmtrajNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ScienceDocument9 pagesSyllabus SciencearyaarpannayakNo ratings yet
- Syllabus of The International Junior Science Olympiad - IJSODocument7 pagesSyllabus of The International Junior Science Olympiad - IJSOrunnymeadowNo ratings yet
- A. Arithmetic and Number Sense. B. Algebra. B. BiologyDocument3 pagesA. Arithmetic and Number Sense. B. Algebra. B. BiologyPatrickNo ratings yet
- Science 8th Grade Curriculum MapDocument1 pageScience 8th Grade Curriculum Mapapi-298427905No ratings yet
- From Class 9th To 10th Moving (Zenith)Document1 pageFrom Class 9th To 10th Moving (Zenith)AYUSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Grade 9 Exams: Number SystemDocument12 pagesSyllabus For Grade 9 Exams: Number SystemJiwook NohNo ratings yet
- An Overview Of: Percent Composition of Compounds Determining The Formula of A CompoundDocument17 pagesAn Overview Of: Percent Composition of Compounds Determining The Formula of A CompoundMilca Lemus LopezNo ratings yet
- Study Material Syllabus For Class Ix - 2Document1 pageStudy Material Syllabus For Class Ix - 2Avinash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Chemistry Metacognition Revision Guide CompletedDocument2 pagesYear 9 Chemistry Metacognition Revision Guide Completedsmcma99No ratings yet
- Final VVM 2023 24 Syllabus Senior GroupDocument2 pagesFinal VVM 2023 24 Syllabus Senior GroupLakshmi PranatiNo ratings yet
- 8AB CurriculumSplitup&SyllabuscoveredtillMayDocument9 pages8AB CurriculumSplitup&SyllabuscoveredtillMayRamandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1b LengthscalesDocument15 pagesChapter 1b LengthscalesMilkiNo ratings yet
- Myp Science Syllabus Scope and Sequence ExampleDocument2 pagesMyp Science Syllabus Scope and Sequence ExamplewynotpointersNo ratings yet
- DP Biology Study Guide CompleteDocument24 pagesDP Biology Study Guide CompleteShreya ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Content Outline Ideas For GR 78 Deped K 12 CurriculumDocument10 pagesContent Outline Ideas For GR 78 Deped K 12 CurriculumTeacher Gerard RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Intro To Natural ScienceDocument2 pagesIntro To Natural ScienceJerrold MangaoNo ratings yet
- Date Test Name Physics Chemistry Biology Mathema Cs Mental Ability Social ScienceDocument1 pageDate Test Name Physics Chemistry Biology Mathema Cs Mental Ability Social ScienceSachinNo ratings yet
- Progress in Multidimensional Particle Characterization: Review PaperDocument27 pagesProgress in Multidimensional Particle Characterization: Review PaperadilNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review - Topics - 201gDocument6 pagesMidterm Review - Topics - 201gapi-238589602No ratings yet
- May Exams Syllabus-Myp4Document3 pagesMay Exams Syllabus-Myp4aahil.9277No ratings yet
- Chem L1-L4Document29 pagesChem L1-L4JESSMINE SABELLANONo ratings yet
- Science Mastery Test SyllabusDocument3 pagesScience Mastery Test SyllabusShahid Imran AasiNo ratings yet
- Matm111 1st-SemesterDocument11 pagesMatm111 1st-SemesterLouise SantosNo ratings yet
- Importance of Chemistry To Daily Life Physical States of MatterDocument5 pagesImportance of Chemistry To Daily Life Physical States of Matternd555No ratings yet
- UPCAT Pointers Science A. Chemistry C. Earth Science and AstronomyDocument2 pagesUPCAT Pointers Science A. Chemistry C. Earth Science and AstronomyJulia OrdonaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work (Chemistry, Year 9)Document12 pagesScheme of Work (Chemistry, Year 9)Hon Nee ChakNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan - Science 11 Unit DDocument26 pagesUnit Plan - Science 11 Unit Dapi-453745317No ratings yet
- TimelineDocument1 pageTimelineapi-548316310No ratings yet
- MYP 2 Term-End AssessmentDocument3 pagesMYP 2 Term-End Assessmentarchit.2551srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Final VVM 2023 24 Syllabus Junior GroupDocument2 pagesFinal VVM 2023 24 Syllabus Junior GroupVIII5-39 UJAN BISWASNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Mapping Science 8Document2 pagesCurriculum Mapping Science 8John Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- P6 Science PPT 2019 PDFDocument15 pagesP6 Science PPT 2019 PDFFlaz EditsNo ratings yet
- Quasicrystals Nobel PDFDocument47 pagesQuasicrystals Nobel PDFViet NguyenHoangNo ratings yet
- Stereo ChemistryDocument48 pagesStereo Chemistrysonwalesuraj3112No ratings yet
- SBTS Schedule (Revised Syllabus) - 07-10-2023 - Jyoti Ma'mDocument16 pagesSBTS Schedule (Revised Syllabus) - 07-10-2023 - Jyoti Ma'maltmshansriNo ratings yet
- 2 Yr Foundation Schedule FinalDocument20 pages2 Yr Foundation Schedule Finalmb721507No ratings yet
- Coast Guard Navik DB SyllabusDocument1 pageCoast Guard Navik DB SyllabusDhruv SinghNo ratings yet
- NMAT Study PlanDocument5 pagesNMAT Study Planla elenaNo ratings yet
- Dani's AteDocument20 pagesDani's Atela elenaNo ratings yet
- NMAT Study PlanDocument5 pagesNMAT Study Planla elenaNo ratings yet
- Spirituality of MercyDocument43 pagesSpirituality of Mercyla elenaNo ratings yet
- NMAT Study PlanDocument5 pagesNMAT Study Planla elenaNo ratings yet
- Spirituality of CommunionDocument18 pagesSpirituality of Communionla elenaNo ratings yet
- Leaf Pack AnalysisDocument7 pagesLeaf Pack Analysisla elenaNo ratings yet
- TPJF Manuscript TemplateDocument22 pagesTPJF Manuscript Templatela elenaNo ratings yet
- 2019jahh 22 447GDocument12 pages2019jahh 22 447GTomi DwiNo ratings yet
- LV Drive Hh10 Series CatalogueDocument8 pagesLV Drive Hh10 Series CatalogueRahul MistryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 2 PDFDavid SitumorangNo ratings yet
- SBC 506Document10 pagesSBC 506Amr HassanNo ratings yet
- Engaging Students Via Discussion Boards (DB'S) : Wake Technical Community CollegeDocument31 pagesEngaging Students Via Discussion Boards (DB'S) : Wake Technical Community CollegeAntti SnellmanNo ratings yet
- Nified Rchitectural HeoryDocument30 pagesNified Rchitectural HeoryR.No ratings yet
- IB Questionbank - SL Logs WsDocument10 pagesIB Questionbank - SL Logs WsEmNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument46 pagesUntitledmaqddus butoolNo ratings yet
- REELY Chapter 7 Flashcards - QuizletDocument2 pagesREELY Chapter 7 Flashcards - QuizletCERTIFIED TROLLNo ratings yet
- Designing User-Centered Decision Support Tools For AgricultureDocument17 pagesDesigning User-Centered Decision Support Tools For AgricultureCABINo ratings yet
- Project Presentation On Rocker Bogie Suspension System: Babu Banarasi Das Northern India Institute of Technology, LucknowDocument21 pagesProject Presentation On Rocker Bogie Suspension System: Babu Banarasi Das Northern India Institute of Technology, LucknowAnoop SinghNo ratings yet
- Art in Our Life.Document2 pagesArt in Our Life.hhNo ratings yet
- Influence of Drying and Hydrothermal Treatment of Corn On The Denaturationof Salt-Soluble Proteins and Color ParametersDocument10 pagesInfluence of Drying and Hydrothermal Treatment of Corn On The Denaturationof Salt-Soluble Proteins and Color ParametersShania GintingNo ratings yet
- Math 1st CODocument6 pagesMath 1st COfloriejanedNo ratings yet
- Practice Essay For Passage TwoDocument2 pagesPractice Essay For Passage TwoVictoria KairooNo ratings yet
- Navigating The Complexities of Modern SocietyDocument2 pagesNavigating The Complexities of Modern SocietytimikoNo ratings yet
- S2 Mathematics Module 1 HandoutDocument32 pagesS2 Mathematics Module 1 HandoutAakanksha KartikNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Intention of This StudyDocument1 page1.3. Intention of This StudyJack FrostNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary AssignmentDocument5 pagesVocabulary Assignmentsimran simranNo ratings yet
- Airhead Meg CabotDocument115 pagesAirhead Meg Cabotdoggybow100% (4)
- Engineering Standards FOR Units Original Edition AUG. 1993: IPS-E-GN-100Document81 pagesEngineering Standards FOR Units Original Edition AUG. 1993: IPS-E-GN-100Pouya ZakerabbasiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document11 pagesTopic 1Mercy MissionNo ratings yet
- Discussion EssayDocument25 pagesDiscussion EssayAnkur SharmaNo ratings yet
- Grundig Cuc4511Document68 pagesGrundig Cuc4511Saulius KalasauskasNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Capitalization Values For No Load Losses and Load LossesDocument12 pagesDetermination of The Capitalization Values For No Load Losses and Load LossesSaman GamageNo ratings yet
- HDQJHJHRJQ 2Document5 pagesHDQJHJHRJQ 2hhhhhhhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- Graphs Representing Motion: Distance-Time GraphDocument26 pagesGraphs Representing Motion: Distance-Time GraphRandom GuyNo ratings yet
- Death in The Slave Pits of LorrdDocument7 pagesDeath in The Slave Pits of LorrdSpider Fan ManiacNo ratings yet
- Music Laptop Script (WhiteHat JR Customers)Document3 pagesMusic Laptop Script (WhiteHat JR Customers)Yash JainNo ratings yet
- Mat Said 2003Document10 pagesMat Said 2003sarsvathyyNo ratings yet
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionFrom EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Ingredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsFrom EverandIngredients: A Visual Exploration of 75 Additives & 25 Food ProductsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)