Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electromagnetic Theory (Theory) : Recommended Books
Uploaded by
Sonam AlviOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electromagnetic Theory (Theory) : Recommended Books
Uploaded by
Sonam AlviCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY (THEORY)
Pre-requisite: Engineering Physics and Applied Calculus.
Credit Hours 03
Contact Hours 48
RECOMMENDED BOOKS
“Engineering Electromagnetics” by William Hayt and John A. Buck , Eighth Edition,
McGraw-Hill
REFERENCE BOOKS
“Elements of Electromagnetic” Sadiku, Matthew N , Fourth Edition, Oxford University
OBJECTIVE OF COURSE
Importance of Electromagnetics study has been undoubtly enormous. Its scope penetrates into
the boundary of Electrical / Electronics / Communication / Computer Engineering especially in
the area of circuit theory, transmission line, microwave and antenna design. In this course we
will begin with electrostatics and cover the major parts of electrostatics. After it, we will focus
on detail study of magnetostatics and eventually we will able to explore important features of
electrodynamics related to electromagnet wave and its propagation. After the completion of this
course, students must be ready to understand the various phenomenon of wave propagation,
microwaves systems and antenna theory and design.
S.N DOMAIN PLO
CLO/PLOs MAPPING
O
01 Describe the fundamentals of Electrostatics and C2 01
magnetostatics.
02 Identify the characteristics of materials and relate them C1 02
to electric and magnetic fields.
03 Demonstrate the theoretical background of Maxwell’s C3 03
equations and electromagnetic wave concepts, regarding
propagation characteristics.
COURSE CONTENTS
Review of Vectors and Coordinate Systems
Cartesian, Cylindrical, Spherical System
Dot and Cross product
Differential length, area, and volume
Gradient, Divergence and Curl
Static Electric Field
Coulomb’s law and Electric Field
Gauss’ law and Divergence of Electric Flux Density
Work, Potential, Potential Gradient and Energy in Electrostatic Field
Current and Current Density, Conductor, Dielectrics, Boundary Conditions, Capacitance
Steady state magnetic Field
Steady Magnetic Field
Biot-Savart Law
Ampere’s Law
Stoke’s Theorem
Magnetic Boundary Conditions
Magnetic Material and Boundary Conditions
Magnetic Flux Density
Vector Magnetic Potential
Inductance
Time varying fields
Faraday’s Law
Displacement Current Density
Maxwell’s Equations in Differential and Integral Form
Retarded Potential
Smith chart
EM Wave Propagation
Plane Wave in Free Space
Perfect Dielectric
Lossy Dielectrics
Good Conductors
Skin Effect
Poynting Theorem
Power Density
You might also like
- An Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Theory of Microwave CircuitsK. KurokawaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsFrom EverandPrinciples of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 355 - EC6403 Electromagnetic Fields - Anna University 2013 Regulation SyllabusDocument2 pages355 - EC6403 Electromagnetic Fields - Anna University 2013 Regulation SyllabusArun GiriNo ratings yet
- B.E. EceDocument2 pagesB.E. EceJesintha CharlesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument180 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesGurusreenuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields R 22 JNTU HYD EEE Course Structure & SyllabuDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Fields R 22 JNTU HYD EEE Course Structure & Syllabupramana_gmritNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Feild Theory - EE315 - 14-07-2008Document2 pagesElectromagnetic Feild Theory - EE315 - 14-07-2008Iftikhar HussainNo ratings yet
- EmtDocument3 pagesEmtArun KumarNo ratings yet
- EMF Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEMF Course OutlineEfag FikaduNo ratings yet
- Engineering ElectromagneticDocument2 pagesEngineering ElectromagneticAnandiacrNo ratings yet
- Fallsem2022-23 Bece205l TH VL2022230102509 Reference Material 1. Syllabus Copy Bece205lDocument2 pagesFallsem2022-23 Bece205l TH VL2022230102509 Reference Material 1. Syllabus Copy Bece205lGaneshdarshan DarshanNo ratings yet
- EE302 Electromagnetics - Image.Marked PDFDocument2 pagesEE302 Electromagnetics - Image.Marked PDFvishakhhariharanNo ratings yet
- 2140909Document3 pages2140909vagoliyoNo ratings yet
- Rec402: Electromagnetic Field Theory Unit IDocument1 pageRec402: Electromagnetic Field Theory Unit IAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Electromagnetic Theory - Video CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Electromagnetic Theory - Video CourseNithya VelamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan FormatDocument8 pagesLesson Plan FormatchinmeciNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic FieldsDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic FieldsAnonymous JnvCyu85No ratings yet
- Oriented Co, For Lab Two Cois Are Normally Permitted)Document16 pagesOriented Co, For Lab Two Cois Are Normally Permitted)Phani KumarNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and TransmissionDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and TransmissionAparna LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Ece1003 Electromagnetic-field-Theory TH 2.1 47 Ece1003Document2 pagesEce1003 Electromagnetic-field-Theory TH 2.1 47 Ece1003Utkarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Emtl Ii Ii R20Document2 pagesEmtl Ii Ii R20InstagramNo ratings yet
- Ee2202 LP ADocument8 pagesEe2202 LP Aganesh4195No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Accredited by NAAC 'A'Grade, NBA Accredited & ISO 9001:2008 Certified InstitutionDocument5 pagesLecture Notes: Accredited by NAAC 'A'Grade, NBA Accredited & ISO 9001:2008 Certified InstitutionMADHINI BALAMURALI ECE0% (1)
- 18EE45Document2 pages18EE45vinod kumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction - : Ee2202 - Electromagnetic TheoryDocument2 pagesIntroduction - : Ee2202 - Electromagnetic TheoryKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plan EMT EE206Document1 pageLecture Plan EMT EE206pksvampireNo ratings yet
- Module 1 EmptyDocument90 pagesModule 1 EmptyRaghu J MandyaNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document1 pageWa0003.Jimmy MachariaNo ratings yet
- Emt PDFDocument212 pagesEmt PDFdharaniNo ratings yet
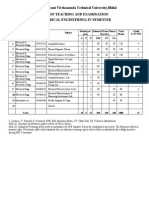
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University, Bhilai Scheme of Teaching and Examination Be (Electrical Engineering) Iv SemesterDocument12 pagesChhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University, Bhilai Scheme of Teaching and Examination Be (Electrical Engineering) Iv SemesterAnonymous l5X3VhTNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory and Transmission Lines: Unit - IDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Theory and Transmission Lines: Unit - IAkramahmedMohammad100% (1)
- EM Fields Lecture SlidesDocument89 pagesEM Fields Lecture SlidesDominic LadesmaNo ratings yet
- Eeu 202 Applied ElectromagneticsDocument2 pagesEeu 202 Applied ElectromagneticsKalnayak HumeinNo ratings yet
- EC6403 Electromagnetic FieldsDocument16 pagesEC6403 Electromagnetic FieldsmohanNo ratings yet
- Eee1004 Engineering-Electromagnetics Eth 1.1 39 Eee1004Document4 pagesEee1004 Engineering-Electromagnetics Eth 1.1 39 Eee1004Abhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Ee2202 Electromagnetic TheoryDocument2 pagesEe2202 Electromagnetic TheoryBenish CmNo ratings yet
- Emfw NotesDocument2 pagesEmfw NotesNaushad SheikNo ratings yet
- Electricity & ElectromagnetismDocument2 pagesElectricity & ElectromagnetismPrasanthNo ratings yet
- Unit1 PPTDocument107 pagesUnit1 PPTISHIKA BALSAMANTANo ratings yet
- Beee202l Electromagnetic-Theory TH 1.0 67 Beee202lDocument3 pagesBeee202l Electromagnetic-Theory TH 1.0 67 Beee202lNithish kumar RajendranNo ratings yet
- B.tech ECE Third Semester SyllabusDocument10 pagesB.tech ECE Third Semester Syllabusteranon978No ratings yet
- Bachelor of Engineering in Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesBachelor of Engineering in Electrical & Electronics EngineeringUtsav PathakNo ratings yet
- EE-241 Electromagetic Field Theory - Final VersionDocument4 pagesEE-241 Electromagetic Field Theory - Final VersionSkiwordy MediaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Engineering: ECE292 Sophomore Seminar 18 March 2008Document26 pagesElectromagnetic Engineering: ECE292 Sophomore Seminar 18 March 2008Alamgir Kabir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Department of Ece Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDepartment of Ece Lesson PlanthilselakshNo ratings yet
- Course: Core Paper III - : SyllabusDocument2 pagesCourse: Core Paper III - : SyllabusAdhara MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field and Waves: EE 221 Spring 2004Document17 pagesElectromagnetic Field and Waves: EE 221 Spring 2004Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- EMT Syllabus.....Document2 pagesEMT Syllabus.....rg_0087No ratings yet
- Emtl r15 II II Jntu A SyllabusDocument1 pageEmtl r15 II II Jntu A SyllabussubramanyamNo ratings yet
- PH2012 - Physics 2B: Credits: Semester: Number of Lectures: LecturerDocument4 pagesPH2012 - Physics 2B: Credits: Semester: Number of Lectures: LecturerHojolNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Autonomous Syllabus 10-08-19 FinalDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic Field Autonomous Syllabus 10-08-19 FinalDr. P. Rama Koteswara RaoNo ratings yet
- C V Raman College of Engineering: Importance of The SubjectDocument2 pagesC V Raman College of Engineering: Importance of The SubjectRakesh UzNo ratings yet
- Ece1003 Electromagnetic-Field-Theory TH 2.1 47 Ece1003Document2 pagesEce1003 Electromagnetic-Field-Theory TH 2.1 47 Ece1003Sheikh NoumanNo ratings yet
- Eee115 Electromagnetic-Field-Theory TH 1.20 Ac19Document2 pagesEee115 Electromagnetic-Field-Theory TH 1.20 Ac19NanduNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields For Engineers and ScientistsDocument856 pagesElectromagnetic Fields For Engineers and ScientistsMuh abid Naufal ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 EmfDocument2 pagesUnit-1 Emfrakeshkancheti100% (1)
- Field and Circuit Theory (EE-303) : Sl. No. Module Name and Topics No. ofDocument1 pageField and Circuit Theory (EE-303) : Sl. No. Module Name and Topics No. ofAshoke SutradharNo ratings yet
- Course Outline PHY-101Document3 pagesCourse Outline PHY-101Saad HamayoonNo ratings yet
- Subject Code: EE3L011 Name: Electromagnetic Field Theory L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credits: 3 Prerequisite: Mathematics - 1, Mathematics - 2Document1 pageSubject Code: EE3L011 Name: Electromagnetic Field Theory L-T-P: 3-0-0 Credits: 3 Prerequisite: Mathematics - 1, Mathematics - 2Akash PratikNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Outline of Electromagnetics, Fifth EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Electromagnetics, Fifth EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- NTC Zero Visit Form NTC ZV-001 BDocument34 pagesNTC Zero Visit Form NTC ZV-001 BSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Arduino: by Alan G. Smith September 30, 2011Document172 pagesIntroduction To Arduino: by Alan G. Smith September 30, 2011Sonam AlviNo ratings yet
- G(S) S s+1) (s+2) (s+3)Document2 pagesG(S) S s+1) (s+2) (s+3)Sonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Basic Concepts of Probability Theory: 2.1 Specifying Random ExperimentsDocument6 pagesChapter 2: Basic Concepts of Probability Theory: 2.1 Specifying Random ExperimentsSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Digital and Non-Linear Control: Frequency Domain AnalysisDocument53 pagesDigital and Non-Linear Control: Frequency Domain AnalysisSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Lecture21 HypothesisTest1Document53 pagesLecture21 HypothesisTest1Sonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Digital and Non-Linear ControlDocument32 pagesDigital and Non-Linear ControlSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Information Fusion: Muhammad Shahid Farid, Arif Mahmood, Somaya Ali Al-Maadeed TDocument17 pagesInformation Fusion: Muhammad Shahid Farid, Arif Mahmood, Somaya Ali Al-Maadeed TSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Digital Control System ModellingDocument28 pagesDigital Control System ModellingSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Derbyshire Language Scheme Detailed Test of Comprehension: Child UsesDocument1 pageDerbyshire Language Scheme Detailed Test of Comprehension: Child UsesSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Handout 1Document64 pagesHandout 1Sonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Bilal Hasnain Ali Israr Qazi Muhammad Tahir: Supervisor of The DayDocument1 pageBilal Hasnain Ali Israr Qazi Muhammad Tahir: Supervisor of The DaySonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Midterm Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesClass 5 - Midterm Computer ScienceSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Revised BSC - Final - ELECTRICAL - OBE - Based Curriculum For BOF27092017Document139 pagesRevised BSC - Final - ELECTRICAL - OBE - Based Curriculum For BOF27092017Sonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Biomedical EnggDocument225 pagesBiomedical EnggSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Till DE-39 PDFDocument173 pagesCurriculum Till DE-39 PDFSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- MTH501 Linear Algebra Handouts PDFDocument524 pagesMTH501 Linear Algebra Handouts PDFSonam Alvi75% (8)
- Computer Networks and The Internet: Raj JainDocument58 pagesComputer Networks and The Internet: Raj JainSonam AlviNo ratings yet
- COADE's Application of Welding Research Council Bulletins 107, 297 and 368Document3 pagesCOADE's Application of Welding Research Council Bulletins 107, 297 and 368shivabtowin3301100% (3)
- SPE 26647 Application of Variable Formation Compressibility For Improved Reservoir AnalysisDocument16 pagesSPE 26647 Application of Variable Formation Compressibility For Improved Reservoir AnalysisglsancorNo ratings yet
- M101 Chapter 1Document19 pagesM101 Chapter 1Alucard PetersNo ratings yet
- CleanABAPCheatSheetV1 4 1Document4 pagesCleanABAPCheatSheetV1 4 1zzgNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 Rev Summer 2011Document329 pagesAlgebra 1 Rev Summer 2011bratista0% (1)
- A Hierarchical Fused Fuzzy Deep Neural Network For Data ClassificationDocument8 pagesA Hierarchical Fused Fuzzy Deep Neural Network For Data ClassificationYosua SiregarNo ratings yet
- Special Mathematics:: Counting Problems, Discrete Probabilities, Graphs TheoryDocument137 pagesSpecial Mathematics:: Counting Problems, Discrete Probabilities, Graphs TheoryLiviaMariaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Chapter 8 WorksheetsDocument7 pagesGeometry Chapter 8 Worksheetsapi-306720213No ratings yet
- IT 06 - Object Oriented Programming OBE SyllabusDocument5 pagesIT 06 - Object Oriented Programming OBE SyllabusRamoj Bartowski100% (1)
- Analysis of ECG Signals by Dynamic Mode DecompositionDocument12 pagesAnalysis of ECG Signals by Dynamic Mode Decompositionmadhumita mishraNo ratings yet
- Past)Document9 pagesPast)Deyni LorenaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument62 pagesLaboratory Manualتبارك موسى كريم علوانNo ratings yet
- Circles For Grade 6Document6 pagesCircles For Grade 6pradeep LiyanaarachchiNo ratings yet
- DataMining ch4 PDFDocument60 pagesDataMining ch4 PDFShining ChrisNo ratings yet
- 1 - TorqueDocument9 pages1 - TorqueIvy GalamitonNo ratings yet
- Estimating Discount Rates: DCF ValuationDocument60 pagesEstimating Discount Rates: DCF Valuationyadavmihir63No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Unfolding: Keshab K. ParhiDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Unfolding: Keshab K. Parhisushant sahooNo ratings yet
- MSC BooksDocument3 pagesMSC BookssyedamiriqbalNo ratings yet
- Randomised Controlled Trials (RCTS) - Sample Size. The Magic NumberDocument4 pagesRandomised Controlled Trials (RCTS) - Sample Size. The Magic NumberrazoblancoNo ratings yet
- Magnetocaloric Effect A Review of The Thermodynamic CyclesDocument9 pagesMagnetocaloric Effect A Review of The Thermodynamic CyclesYangyangNo ratings yet
- FLAT Interest RateDocument460 pagesFLAT Interest RateCHARLES TUMWESIGYENo ratings yet
- EJ1127589Document10 pagesEJ1127589TrinhNo ratings yet
- David Farrell Dane Sprister Matthew TaylorDocument55 pagesDavid Farrell Dane Sprister Matthew TaylorQuân Trần ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Petroleum GeomechanicsDocument31 pagesPetroleum Geomechanicsginozky100% (1)
- Job Description CNC Machinist (Advanced) : Key Skills and CompetenciesDocument2 pagesJob Description CNC Machinist (Advanced) : Key Skills and CompetenciesRaya DuraiNo ratings yet
- Arima JmultiDocument11 pagesArima Jmultijota de copasNo ratings yet
- 14 SBE11e PPT Ch11Document42 pages14 SBE11e PPT Ch11Glen JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Belgian CyclingDocument20 pagesBelgian CyclingMFNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document18 pagesChapter 2FakeMe12No ratings yet
- PH537/PI515: Astrostructure and Evolution: Answer With Examples and ReferencesDocument4 pagesPH537/PI515: Astrostructure and Evolution: Answer With Examples and ReferencesSDasNo ratings yet