Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Liver Cirrhosis Drug Study
Uploaded by
Rachel Quion0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesOriginal Title
liver-cirrhosis-drug-study (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesLiver Cirrhosis Drug Study
Uploaded by
Rachel QuionCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
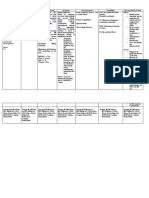
Drugs Mechanism of Indications and Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing
Action Rationale Considerations
Generic Name: Accelerates increases the Contraindicated in fever Start at lower
Heparin formation of inhibitory action of patients headache dosage
antithrombin III- antithrombin III (AT hypersensitive to hyperkalemia Monitor pt.
Brand Name: thrombin complex III) on clotting factors drug. chills for
Hep-Pak (obsolete) and deactivates (XIIa, XIa, IXa, Xa), nausea hyperkalemia
thrombin, and thrombin. vomiting during
Classifications: preventing epistaxis therapy
Therapeutic Class: conversion of Rationale: To treat bruising Check order
Anticoagulants fibrinogen to fibrin. and prevent blood osteoporosis and vial
clots. alopecia carefully.
Pharmacologic Class: Always check
Anticoagulants compatibilities
with other IV
solutions.
Dosage, Frequency Monitor VS
and Route: Do not add
low intensity heparin heparin to
infusion (UFH infusion lines
50,000units/5mL of other
infusion rate of 12 drugs, and do
units/kg/hr.) for 48 not piggyback
hours, IV other drugs
into heparin
line. If this
must be done,
ensure drug
compatibility.
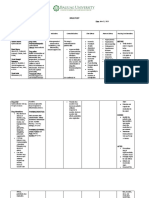
Drugs Mechanism of Indications and Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing
Action Rationale Considerations
Generic Name: Hinders bacterial to treat and prevent Contraindicated in Fever Monitor BP
Vancomycin cell-wall synthesis, various bacterial patients Headache and heart rate
damaging the infections caused by hypersensitive to Fatigue continuously
Brand Name: bacterial plasma gram-positive drug. Nausea through period
Vancocin membrane and bacteria. Abdominal of drug
making the cell pain administration.
Classifications: more vulnerable to Rationale: To Dyspnea Monitor
Therapeutic Class: osmotic pressure. prevent potentially red-man patient
Antibiotics life-threatening syndrome carefully for
infections in patient. (with rapid IV red-man
Pharmacologic infusion) syndrome
Class: nephrotoxicit which can
Glycopeptides y occur if drug is
infused too
Dosage, Frequency rapidly.
and Route: Monitor
500 mg IV every patient’s fluid
6hrs. balance and
watch for
oliguria and
cloudy urine
Carefully
monitor serum
concentrations
of vancomycin
to adjust IV
dosage
requirements.
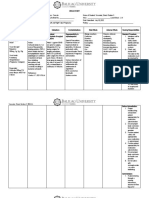
Drugs Mechanism of Indications and Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing
Action Rationale Considerations
Generic Name: Inhibits cell-wall Moderate to severe Contraindicated in headache >Before giving
Piperacillin synthesis during infections from patients insomnia drug, ask pt. about
bacterial piperacillin- hypersensitive to fever allergic reactions to
Brand Name: multiplication. resistant; producing drug and other Diarrhea/constipation penicillin,
Zosyn strains of penicillin, nausea cephalosporins, or
microorganisms in cephalosporins, or vomiting beta- lactamase
Classifications: peritonitis. beta-lactamase dyspepsia, inhibitors.
Therapeutic Class: inhibitors. pseudomembranous
Antibiotics Rationale: To treat colitis. >Monitor pt. for
and prevent pruritus diarrhea and
Pharmacologic infections. hypersensitivity initiate therapeutic
Class: reactions measures as
Extended-spectrum needed. Drug may
penicillin-beta- need to be stopped
lactamase
inhibitors >Monitor
hematologic and
Dosage, Frequency coagulation
and Route: parameters
3.375 g every 6hrs.
by IV infusion >Monitor patient’s
sodium intake and
electrolyte levels;
drug contains 65mg
of sodium
You might also like
- Pharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsFrom EverandPharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsNo ratings yet
- Piptaz DSDocument4 pagesPiptaz DSArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Student Pharmacy TechniciansFrom EverandPharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Student Pharmacy TechniciansNo ratings yet
- PiptazDocument3 pagesPiptazArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- IV Paracetamol Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pagesIV Paracetamol Nursing ResponsibilitiesLyka Sison VinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study UtiDocument4 pagesDrug Study UtiClaire MachicaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraNo ratings yet
- DS ObDocument7 pagesDS ObZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Cañete Drug StudyDocument1 pageCañete Drug StudyRena CañeteNo ratings yet
- TramadolDocument1 pageTramadolJugen Gumba Fuentes AlquizarNo ratings yet
- Nahudan-1-Drug-StudyDocument4 pagesNahudan-1-Drug-StudyYahiko PainNo ratings yet
- Patient drug chart for Abcd E. Fghi (32Document4 pagesPatient drug chart for Abcd E. Fghi (32Catherine MetraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyJjessmar Bolivar FamaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyLA GomezNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDocument5 pagesCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Classification Indication:: Hema KKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY For SrugeryDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY For SrugeryZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Acute BronchitisDocument6 pagesDrug Study Acute BronchitisCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Vitamin KDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY Vitamin KChristian Daayata50% (2)
- DiphenhydramineDocument3 pagesDiphenhydramineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument4 pagesSt. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone DSDocument3 pagesHydrocortisone DSArone Sebastian100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFerndale AlimondoNo ratings yet
- Name of The DrugsDocument1 pageName of The DrugsJake SmithNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing DiseaseDocument8 pagesDrug Study Cushing DiseaseRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic acid nursing considerations for bleeding treatmentDocument8 pagesTranexamic acid nursing considerations for bleeding treatmentsige sigeNo ratings yet
- Nursing care for hydralazine administrationDocument27 pagesNursing care for hydralazine administrationChan SorianoNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument3 pagesParacetamolTRISHA NERINo ratings yet
- Tranexamic Acid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesTranexamic Acid Drug Studyswitchlers anneNo ratings yet
- Bernadas - Ds - ErcefloraDocument3 pagesBernadas - Ds - ErcefloraBernadas, Jhon Kristopher C.No ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy ParacetamolCasilaoDocument3 pagesDrugStudy ParacetamolCasilaoArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesErtapenem Nursing ResponsibilitiesBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-FINALDocument13 pagesDRUG-STUDY-FINALLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- TB Drugs RipeDocument4 pagesTB Drugs Riperonletaba100% (1)
- Drug Study on Chlorambucil (LeukeranDocument1 pageDrug Study on Chlorambucil (LeukeranEdmarkmoises ValdezNo ratings yet
- Haemophilus Influenzae, Proteus Mirabilis, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, Enterococci, GramDocument2 pagesHaemophilus Influenzae, Proteus Mirabilis, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, Enterococci, GramLegendXNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs and AntidoteDocument114 pagesEmergency Drugs and AntidoteAlexa BelderolNo ratings yet
- ANCEFDocument2 pagesANCEFDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument25 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- MEROPENEMDocument1 pageMEROPENEMJust now0% (1)
- Chapter 3 Hospital Pharmacy Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document25 pagesChapter 3 Hospital Pharmacy Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Shamant TNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDE - CEFA (Echanique)Document1 pageDRUG STUDE - CEFA (Echanique)Echanique, James F.No ratings yet
- Supply Chain and Inventory ControlDocument11 pagesSupply Chain and Inventory Controlharshit1509dNo ratings yet
- Clinically Significant Drug Interactions - AAFPDocument19 pagesClinically Significant Drug Interactions - AAFPAbchoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKaren AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Drug Study (Vizcodne, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Document23 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Drug Study (Vizcodne, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Fluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiesDocument1 pageFluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiescen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- Ryrey A. Pacamana BSN 3C Drug StudyDocument8 pagesRyrey A. Pacamana BSN 3C Drug StudyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atracurium: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Atracurium: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Levofloxacin (Levocin)Document1 pageLevofloxacin (Levocin)Diego ︻╦̵̵͇̿̿̿̿╤─ IrisariNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!Document3 pagesDrug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!shasheeeeyNo ratings yet
- DSREVISEDDocument8 pagesDSREVISEDamvNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - CopdDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - CopdMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Severe (Updated)Document9 pagesDrug Study Severe (Updated)Rachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan Manuscript - BSITM ITTO 1B - QUION - MARKJOSEPH - RAKSO TRAVELDocument46 pagesMarketing Plan Manuscript - BSITM ITTO 1B - QUION - MARKJOSEPH - RAKSO TRAVELRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Nursing - Bone Fracture Care and ManagementDocument67 pagesOrthopedic Nursing - Bone Fracture Care and ManagementRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Riasec Test and True Colors TestDocument2 pagesRiasec Test and True Colors TestRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Employability Skills: What Employers Are Looking ForDocument8 pagesEmployability Skills: What Employers Are Looking ForRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- What Is DefibrillationDocument1 pageWhat Is DefibrillationRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Surgical ManagementDocument2 pagesSurgical ManagementRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Ruptured Appendectomy - Docx 1Document7 pagesRuptured Appendectomy - Docx 1Rachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing DiseaseDocument8 pagesDrug Study Cushing DiseaseRachel QuionNo ratings yet
- Ruptured Appendectomy - Docx 1Document7 pagesRuptured Appendectomy - Docx 1Rachel QuionNo ratings yet
- MgSO4 Uses and Nursing CareDocument11 pagesMgSO4 Uses and Nursing CareWan Ahmad FaizFaizalNo ratings yet
- Cipla LTD Internship ReportDocument49 pagesCipla LTD Internship ReportSanjay Veerabhadrakumar80% (5)
- Daftar ObatDocument18 pagesDaftar ObatFidria DiastiniNo ratings yet
- Data Collection Form RetrospectiveDocument3 pagesData Collection Form Retrospectivejamilah AlnahdiNo ratings yet
- Anabolics 2007 Dianabol ProfileDocument17 pagesAnabolics 2007 Dianabol Profilepuran123456789067% (3)
- Clinical Toxicology-4Document13 pagesClinical Toxicology-4DrAnisha PatelNo ratings yet
- Rak Syrup: Mutasi Selisih Masuk KeluarDocument35 pagesRak Syrup: Mutasi Selisih Masuk KeluarRia DewantyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Introduction BSN 1 - FIRST SEMESTERDocument9 pagesPharmacology Introduction BSN 1 - FIRST SEMESTERAisha JailaniNo ratings yet
- Funda2 PDFDocument107 pagesFunda2 PDFChin Chan100% (1)
- LeafletDocument1 pageLeafletMostafa KamalNo ratings yet
- 3819 - Ibr - November - 2020 - Written - Expression - Exam FRENKI QIRJAKODocument6 pages3819 - Ibr - November - 2020 - Written - Expression - Exam FRENKI QIRJAKOkevin hoxhaNo ratings yet
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazoleGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- 01640-Trends2003 WWW EDocument351 pages01640-Trends2003 WWW ElosangelesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Manage of Persistent Pain Older 1Document22 pagesPharmacological Manage of Persistent Pain Older 1Borja Carreño MarambioNo ratings yet
- ATI Flash Cards 05, Medications Affecting The Nervous SystemDocument110 pagesATI Flash Cards 05, Medications Affecting The Nervous SystemGiovanni MictilNo ratings yet
- Standing Orders, Life Saving Drugs for Obstetric EmergenciesDocument16 pagesStanding Orders, Life Saving Drugs for Obstetric Emergenciesvarshasharma0589% (19)
- Name of Drug Indication / Mechanism of Action Side Effect Adverse Effect Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Indication / Mechanism of Action Side Effect Adverse Effect Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- Drug EducationloloyDocument7 pagesDrug EducationloloyCHIVASNo ratings yet
- DibencozideDocument1 pageDibencozideSeno HyeonNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic DrugsDocument6 pagesAnticholinergic Drugshlouis8No ratings yet
- Company Detail UttarakhandDocument61 pagesCompany Detail UttarakhandAdtiya Devgun100% (3)
- 6 Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument4 pages6 Metronidazole Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Drug Labels: Belen G. de Los Trinos, RN, RM, USRN, MANDocument35 pagesUnderstanding Drug Labels: Belen G. de Los Trinos, RN, RM, USRN, MANNathaniel PulidoNo ratings yet
- Algesia: 37.5 MG / 325 MG Film-Coated TABLET AnalgesicDocument1 pageAlgesia: 37.5 MG / 325 MG Film-Coated TABLET AnalgesicEsel WazowskiNo ratings yet
- Drug Information HandbookDocument2 pagesDrug Information HandbookdiahNo ratings yet
- Target Product Profile Imbruvica - IbrutinibDocument1 pageTarget Product Profile Imbruvica - IbrutinibDiti ShahNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studysnowyfingers100% (1)
- Fast Dissolving Tablets: A Novel Approch To Drug Delivery - A ReviewDocument10 pagesFast Dissolving Tablets: A Novel Approch To Drug Delivery - A ReviewNova Lya SipahutarNo ratings yet
- TOS - BiopharmaceuticsDocument6 pagesTOS - BiopharmaceuticsApril Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- Reflections On Medicinal Chemistry at Merck, West Point: Chapter OneDocument9 pagesReflections On Medicinal Chemistry at Merck, West Point: Chapter OneWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet