Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Electronics and Circuit Concepts: Questions Answers
Uploaded by
Dominic Wynes-Devlin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesKnowledge organiser for GCSE electronics
Original Title
ELECTRONICS Y9 Circuit Concepts revision booklet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKnowledge organiser for GCSE electronics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesIntroduction To Electronics and Circuit Concepts: Questions Answers
Uploaded by
Dominic Wynes-DevlinKnowledge organiser for GCSE electronics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
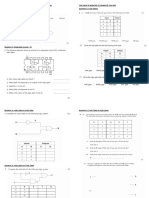
Y9 ELECTRONICS END OF TERM 1 – CIRCUIT CONCEPTS and RESISTIVE COMPONENTS REVISION
Suggested actions: read through the questions and answers and memorize. Self-quiz or peer quiz by covering
up the answers – review answers that were incorrect and repeat.
Introduction to Electronics and Circuit Concepts
Questions Answers
What are the names for the 3 parts that make an Input, Processor and Output
electronics system?
What are some examples of electronic inputs? Push-to-make, push-to-break, light sensor, temperature sensor,
motion sensor, moisture sensor, pressure sensor, pulse generator.
What are some examples of electronic processors? Latch, time delay, transducer driver, transistor, MOSFET,
comparator, counter, logic gates (AND, OR, NOT, etc.).
What are some examples of electronic outputs? Lamp (bulb), LED (light emitting diode), buzzer, siren, motor,
solenoid.
What component measures current and where should Ammeter, in series with the component
it be placed in a circuit.
What component measures a voltage drop and where Voltmeter, in parallel with the component it is measuring.
should it be placed in a circuit. E.g. Bulb, Resistor, LED, battery.
What is the rule (law) for current in a series circuit? Current is the same at all points in a series circuit.
What is the rule for current in a parallel circuit? Current is shared between the paths in a parallel circuit.
What is the rule (law) for voltage in a series circuit? The voltage across the power supply is shared across each
component in series.
What is the rule (law) for voltage in a parallel circuit? The voltage is the same across components in parallel.
What is resistance? The opposition to the flow of current?
What is the unit and unit symbol for resistance Ohms, Ω.
What is the equation for resistance? Resistance = Voltage / Current
R=V/I
What is Power? The rate of transfer of energy.
What is the unit and unit symbol for power? Watt, W.
What is the equation that relates power, energy Energy = Power x time
and time? E=Pxt
What is the equation that relates power, current Power = current x voltage
and voltage? P=IxV
What is the equation that relates power, resistance Power = current2 x resistance
and current? P = I2 x R
What is the equation that relates power, resistance Power = voltage2 / Resistance
and voltage? P = V2 / R
You should know the following prefixes when converting units:
Prefix Examples Conversion
Mega Megawatt (MW) x 1000000 (x106)
Megaohms (MΩ)
kilo kilowatt (kW) x 1000 (x103)
kilo-ohms (kΩ)
milli milliamps (mA) ÷ 1000 (x10-3)
millivolts (mV)
micro microamps (µA) ÷ 1000000 (x10-6)
microvolts (µV)
Resistive Components
Questions Answers
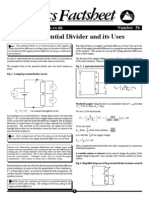
What is a potential (voltage) divider set-up? 2 or more resistors in series connected to an input voltage where
the output voltage across one of the resistors is a fraction of the
input voltage.
What are some uses of a potential divider? Audio volume controller, dimmer switches, sensor circuits
e.g. temperature sensor on a thermostat.
What is the equation for a potential divider? R2
V OUT =V ¿ ×
R1+ R 2
What effect does making the value of R2 greater VOUT increases as the voltage across R2 now takes a bigger share of
than R1 have on the output voltage VOUT? the input voltage compared to R1.
What effect does making the value of R1 greater VOUT decreases as the voltage across R1 now takes a bigger share of
than R2 have on the output voltage VOUT? the input voltage compared to R2.
What is a rheostat (variable resistor) ? Rheostat is a variable resistor that has two terminals connected, the
wiper is connected as one terminal end and varies the length.
What is a potentiometer? Potentiometer is a variable resistor that has three terminals
connected, the wiper divides the overall resistor into two.
What is the advantage of using a potentiometer over The potentiometer will provide a voltage which can be varied from
a standard variable resistor? zero up to the maximum of the supply.
State Ohm’s Law The voltage is directly proportional to the current providing the
temperature is constant.
What is an ohmic conductor and what are some Any component that obeys Ohm’s Law.
examples? e.g. Resistor, wire at constant temperature
What is a non-ohmic conductor and what are some Any component that does not obey Ohm’s Law.
examples? e.g. Filament lamp (bulb), Diode, LED.
What are the different types of switches commonly PTM (push to make), PTB (push to break), reed switch, micro switch,
used in electronics? slide switch, toggle switch, SPST, SPDT (single pole double throttle).
What does the power rating of a component mean? The highest power input allowed through a component to operate.
What are the typical ratings for a resistor? Power ratings: 0.25W, 0.5W to 50W.
What are the typical ratings for a bulb? 3.5V 0.3A, 6V 0.06A, 12V 0.2A etc.
What are the typical ratings for an LED? ~2.0 V depends on colour (2V red, 4V blue) 10 to 20 mA.
What are the typical power ratings for a motor? Small motors: 50 to 150 mA. Large industrial motors: 20 A or more.
What are the typical power ratings for a solenoid? Current rating 50 to 250 mA.
What are the typical power ratings for a buzzer Voltage rating: 12 V, Current rating: 25mA
You should be able to re-arrange the following equations:
Word equation Symbol equation Word equation Symbol equation
Calculating Resistance Calculating Power using current and resistance.
Resistance = Voltage / Current R=V/I Power = current2 x Resistance P = I2 x R
Current = Voltage / Resistance I=V/R Current = sqrt (Power/ Resistance) P
I=
√ R
distance = Work done / Force V=IR Resistance = Power/ current2 P
R=
I2
Calculating Electrical Power Calculating Power using voltage and resistance.
Power = Current x Voltage P=IxV Power = voltage2 / Resistance P = V2 / R
Current = Power / Voltage I=P/V Voltage = Sqrt (Power x Resistance) V =√P × R
Voltage = Power / Current V=P/I Resistance = Voltage2 / Power R = V2 / P
You should know the following circuit symbols:
Name Symbol Name Symbol
Cell
Resistor
Battery
Variable Resistor
Bulb
LDR
Motor
Thermistor
Buzzer
Potentiometer
LED Diode
You might also like
- ELECTRONICS Y10 Circuit Concepts and Resistive Components Revision BookletDocument4 pagesELECTRONICS Y10 Circuit Concepts and Resistive Components Revision BookletDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electric CircuitDocument81 pagesIntroduction To Electric Circuitkaushallyaa navindranNo ratings yet
- Electronics 1Document35 pagesElectronics 1api-619135742No ratings yet
- Voltage divider circuit tutorialDocument10 pagesVoltage divider circuit tutorialLi'ardi PratamaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE TERM 3 E Cape 1 - 1680Document160 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE TERM 3 E Cape 1 - 1680Shudufhadzo PrettyNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument6 pagesElectricityDarshita GolechhaNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsDocument8 pagesElectricity and Circuits Conceptual PhysicsQuinto Jaypee SeinseiNo ratings yet
- 2-Masterclass Solar - Electrical Fundamentals Batch 29Document40 pages2-Masterclass Solar - Electrical Fundamentals Batch 29Anthony PoldoNo ratings yet
- 9what Are The Elements of Power SystemDocument6 pages9what Are The Elements of Power SystemSalah Mohammed SallamNo ratings yet
- Element 3: Fundamentals of Electricity and ElectronicsDocument81 pagesElement 3: Fundamentals of Electricity and ElectronicsLeo Jade AbiertasNo ratings yet
- Electricity-summaryDocument8 pagesElectricity-summarya kamranNo ratings yet
- EET219 2023 Lecture 2Document54 pagesEET219 2023 Lecture 2j9927091No ratings yet
- Covered in This Tutorial: Ohm's LawDocument9 pagesCovered in This Tutorial: Ohm's Lawa dNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity and ElectronicsDocument80 pagesBasic Electricity and ElectronicsPidotskiNo ratings yet
- Electronics Fundamentals: Engr. Hassan Sultan Waqar Azeem Engr. Ammar HassanDocument36 pagesElectronics Fundamentals: Engr. Hassan Sultan Waqar Azeem Engr. Ammar HassanWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- OhmslawDocument17 pagesOhmslawBright OvieNo ratings yet
- Equations: Electricity Revision SummaryDocument9 pagesEquations: Electricity Revision Summaryjohn smithNo ratings yet
- Covered in This Tutorial: LearnDocument8 pagesCovered in This Tutorial: LearnRinaldyNo ratings yet
- BEEE (ELT-112) : Ac & DC CircuitsDocument21 pagesBEEE (ELT-112) : Ac & DC CircuitsRocky SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering IntroductoryDocument78 pagesElectrical Engineering Introductoryandi lisnaini ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Unit of ElectricityDocument7 pagesUnit of Electricitysana.incubationNo ratings yet
- Electronics Fast Course: With The Author's PermissionDocument20 pagesElectronics Fast Course: With The Author's PermissionAsadNo ratings yet
- UnitNo1DCCircuitspptx 2022 10 08 15 08 30pptx 2022 11 03 21 34 27Document66 pagesUnitNo1DCCircuitspptx 2022 10 08 15 08 30pptx 2022 11 03 21 34 27DUSHIMIMANA ROBIN mefgiNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Basics of Electrical CircuitsDocument80 pagesCH 3 - Basics of Electrical CircuitsnazxalafNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements: 1 ComponentsDocument15 pagesElectrical Measurements: 1 Componentsmishraanwesh7380No ratings yet
- Electricity key terms, symbols, circuitsDocument5 pagesElectricity key terms, symbols, circuitszNo ratings yet
- ASU-KALIBO IM - : Aklan State University College of Industrial Technology Kalibo, AklanDocument11 pagesASU-KALIBO IM - : Aklan State University College of Industrial Technology Kalibo, AklanAries PenalosaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Concepts and Methods - L2 - Electricity - Student - v3Document13 pagesEngineering Concepts and Methods - L2 - Electricity - Student - v3LoganP MayNo ratings yet
- CircuitsDocument22 pagesCircuitsapi-3732151100% (1)
- Electromotive ForceDocument40 pagesElectromotive ForceFebbie Ibatuan100% (1)
- Physics-Revision-1Document37 pagesPhysics-Revision-1kokobame003No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics notes-RESISTOR+INTRODocument29 pagesBasic Electronics notes-RESISTOR+INTROEphraem RobinNo ratings yet
- Current, Resistance, and Electromotive Force: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument39 pagesCurrent, Resistance, and Electromotive Force: Powerpoint Lectures ForZia Aryanti ZeeNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in TleDocument16 pagesPortfolio in TleAileen Javines50% (2)
- Unit 1 DC CircuitsDocument54 pagesUnit 1 DC CircuitssujithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Electrical CircuitDocument67 pagesChapter 1-Electrical CircuitDKM 2ANo ratings yet
- PEI Mod5@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument44 pagesPEI Mod5@AzDOCUMENTS - inBoban MathewsNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit Power CalculationsDocument3 pagesDC Circuit Power Calculationsjeremias marticioNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab 1Document13 pagesEDC Lab 1Xrein MarkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document26 pagesLesson 1Hari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law: University of The Immaculate Conception Bonifacio ST., Davao CityDocument5 pagesOhm'S Law: University of The Immaculate Conception Bonifacio ST., Davao CityRoselle TuraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Resistance: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in Physics 2-4Document21 pagesElectrical Resistance: Edexcel Igcse / Certificate in Physics 2-4Sam JordanNo ratings yet
- Potential Divider Voltage CalculatorDocument3 pagesPotential Divider Voltage CalculatorMustafa ChaarNo ratings yet
- YAYDocument4 pagesYAYshresth.gupta.ug22No ratings yet
- Electronic Engineering 2: Resistors, Elementary Resistor Circuits and The Resistor ParadoxDocument19 pagesElectronic Engineering 2: Resistors, Elementary Resistor Circuits and The Resistor ParadoxChuy G. DelallaveNo ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument19 pagesResistancexjaykaeNo ratings yet
- Electronic Engineering 2: Resistors, Elementary Resistor Circuits and The Resistor ParadoxDocument19 pagesElectronic Engineering 2: Resistors, Elementary Resistor Circuits and The Resistor ParadoxAli FaShNo ratings yet
- Basic PhysicsDocument54 pagesBasic PhysicsKarttikeya Mangalam NemaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Units of MeasureDocument36 pagesElectrical Units of MeasureHyung BaeNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit Analysis ChapterDocument41 pagesDC Circuit Analysis ChapterNUR ASYIQIN BINTI AZAHARNo ratings yet
- ECA Unit 1Document48 pagesECA Unit 1Komalaselvan VNo ratings yet
- Electrical Drives and ControlDocument224 pagesElectrical Drives and ControlvanthiyadevnNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 24 ElectricalResistanceDocument21 pagesIGCSE 24 ElectricalResistanceHAMAD NoorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Current, Resistance and Ohm'S LawDocument9 pagesLesson 1 Current, Resistance and Ohm'S LawPamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Basics: For Review and RefreshmentDocument18 pagesElectrical Basics: For Review and RefreshmentCold WaterNo ratings yet
- KS3 Energy ResourcesDocument61 pagesKS3 Energy ResourcesDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- KS3 Forces 2Document88 pagesKS3 Forces 2Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- KS3 Light 2Document46 pagesKS3 Light 2Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- KS3 Light 1Document91 pagesKS3 Light 1Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- KS3 MagnetismDocument50 pagesKS3 MagnetismDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Computing 1 Python Tutorial - LeedsDocument55 pagesComputing 1 Python Tutorial - LeedsDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- KS3 Forces 1Document94 pagesKS3 Forces 1Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- KS3 Forces 3Document36 pagesKS3 Forces 3Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- KS3 Electricity 2Document50 pagesKS3 Electricity 2Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - Sheet 3Document1 pageCalculus II - Sheet 3Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra Problem Sheet 5Document2 pagesLinear Algebra Problem Sheet 5Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- LAG ProblemSheet4Document2 pagesLAG ProblemSheet4Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- LAG ProblemSheet3Document2 pagesLAG ProblemSheet3Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- LAG ProblemSheet2Document2 pagesLAG ProblemSheet2Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - Sheet 3Document1 pageCalculus II - Sheet 3Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- LAG ProblemSheet4Document2 pagesLAG ProblemSheet4Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - Sheet 3Document1 pageCalculus II - Sheet 3Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Current and Charge: QuestionsDocument4 pagesCurrent and Charge: QuestionsDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - Sheet2Document1 pageCalculus II - Sheet2Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Electronics - ETT - Logic GatesDocument4 pagesYear 10 Electronics - ETT - Logic GatesDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Booklet - DifferentiatedDocument18 pagesMagnetism Booklet - DifferentiatedDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Calculus II - Sheet1Document1 pageCalculus II - Sheet1Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Series & Parallel Circuits ExplainedDocument24 pagesSeries & Parallel Circuits ExplainedDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Electronics Coursework Final - TemplateDocument4 pagesElectronics Coursework Final - TemplateDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Template RequisitionDocument2 pagesTemplate RequisitionDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law WS 2 - Extension SheetDocument1 pageHooke's Law WS 2 - Extension SheetDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- PRINT Y9 Electronics - Power Vsquareoverr and Isquaredr WorksheetDocument1 pagePRINT Y9 Electronics - Power Vsquareoverr and Isquaredr WorksheetDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Recomended TES ResourcesDocument1 pageRecomended TES ResourcesDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 3Document7 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 3Okiror GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Generator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualDocument3 pagesGenerator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation ManualLuciano PereiraNo ratings yet
- Sensor de Bateria PDFDocument4 pagesSensor de Bateria PDFingsespinosaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Electrical Circuits ECE Board Exam PracticeDocument180 pagesMCQ Electrical Circuits ECE Board Exam Practiceian rafael japsayNo ratings yet
- PEKA 1 Ohms Law FM5Document5 pagesPEKA 1 Ohms Law FM5Nur Syafiqah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- CAN Diagnosis Flow Chart Guide for 2005-2013 Nissan VehiclesDocument7 pagesCAN Diagnosis Flow Chart Guide for 2005-2013 Nissan VehiclesKey ChipNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Measurement of ResistanceDocument13 pagesExperiment No. 2 Measurement of ResistanceLynndon VillamorNo ratings yet
- Applications of Laplace Transforms in Modeling Dynamical SystemsDocument7 pagesApplications of Laplace Transforms in Modeling Dynamical SystemsMahlatse Morongwa MalakaNo ratings yet
- SI Units and Measuring WorksheetDocument2 pagesSI Units and Measuring WorksheetreemobeidaNo ratings yet
- II - PowerPoint Slides To Chapter 01 IntroductionDocument17 pagesII - PowerPoint Slides To Chapter 01 IntroductionVishesh Dhillon100% (2)
- Power Interface UnitDocument2 pagesPower Interface UnitPushkar MishraNo ratings yet
- Survey Meter: Model HI-3604Document45 pagesSurvey Meter: Model HI-3604Romualdy WidiyantoNo ratings yet
- EN Parameter Config.h Guide TSDZ2 Mb.20beta1.aDocument15 pagesEN Parameter Config.h Guide TSDZ2 Mb.20beta1.aAlex GarridoNo ratings yet
- TATA Fault Code PDF GuideDocument11 pagesTATA Fault Code PDF Guideshinaskhan08867% (6)
- Lorentz Lc20 12mDocument2 pagesLorentz Lc20 12mLeeLiNo ratings yet
- Test Single-Phase CompressorsDocument6 pagesTest Single-Phase CompressorsAndres CarmonaNo ratings yet
- 520 L 0804Document48 pages520 L 0804Minh CanhNo ratings yet
- 1477640352901-GE Governor ALCODocument19 pages1477640352901-GE Governor ALCOManikanta ReddyNo ratings yet
- Jy472m Y5v Ac400 PDFDocument2 pagesJy472m Y5v Ac400 PDFRithy KissNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet of Current ElectricityDocument18 pagesWork Sheet of Current ElectricityRam PandeyNo ratings yet
- LIC Chapter 1Document33 pagesLIC Chapter 1Kurma KannuruNo ratings yet
- Aces Objectives 12 EEDocument6 pagesAces Objectives 12 EEJay TabagoNo ratings yet
- Manual - IR Nirvana Troubleshooting GuideDocument63 pagesManual - IR Nirvana Troubleshooting GuideKurserg92% (51)
- IGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticeDocument27 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticealfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- Travelling Mobile Charger by C.jeyarajDocument13 pagesTravelling Mobile Charger by C.jeyarajMeghan BrownNo ratings yet
- Substation and LV General Designs For New WorkDocument4 pagesSubstation and LV General Designs For New WorkNima MahmoudpourNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice (Electric Shop)Document13 pagesWorkshop Practice (Electric Shop)muhammad omer100% (1)
- Manual de Partes Sección Motor e Implementos Ggo-01Document96 pagesManual de Partes Sección Motor e Implementos Ggo-01Eduardo SainzNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet Damper Actuator TMC24A-SRDocument4 pagesTechnical Data Sheet Damper Actuator TMC24A-SRdbricchiNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Ni Multisim 14.2 - Engineering OrientationDocument64 pagesGroup 1 - Ni Multisim 14.2 - Engineering OrientationĐặng Minh HoàngNo ratings yet