Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Quick Guide: Purpose of The Test
Uploaded by
john mendozaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Quick Guide: Purpose of The Test
Uploaded by
john mendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Quick Guide
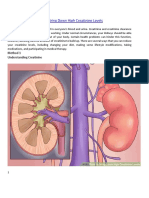
Creatinine is a byproduct of a chemical compound called creatine, which helps muscles get the
energy that they need. As a waste product, creatinine is filtered out of the blood by the kidneys
and removed from the body in urine.
A creatinine test measures the amount of this chemical in either the blood or urine. Creatinine
levels can provide an indication of how well the kidneys are working.
Creatinine may be measured alone or included in a panel of tests that include other compounds
found in the urine or blood.
About the Test
Purpose of the test
The primary use of a creatinine test is to better understand how well the kidneys are working. A
measurement of creatinine can be employed for screening, diagnosis, and/or monitoring of
kidney problems.
Screening is trying to identify health problems before there are any signs or symptoms. In
people who are at higher risk of kidney problems, a creatinine test may be used to try to detect a
problem early.
Diagnosis involves testing to determine the underlying cause after symptoms have started.
Creatinine may be measured to help diagnose symptoms that can be associated with kidney
problems such as swelling in the feet, urinary changes, loss of appetite, and fatigue. A
measurement of creatinine may also be included in a panel of tests for more general symptoms or
when evaluating a patient in the emergency room.
Monitoring is how doctors track a patient’s condition over time. For people who have kidney
disease, a creatinine test can provide information about how the disease may be progressing.
Tests of kidney function can also be used to watch for potential side effects when a patient is
prescribed medications that can affect the kidneys.
In many cases, screening, diagnosis, and monitoring of kidney problems involve more than just a
creatinine measurement. For example, creatinine may be tested in order to calculate
the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), which is an assessment of how effectively the
kidneys are filtering the blood.
What does the test measure?
A creatinine test measures the total amount of the substance creatinine in the blood or the urine.
Creatinine is a waste byproduct of the normal metabolism of creatine, a compound that is
involved in providing the muscles of the body the energy they need. In this process, some
creatine breaks down into creatinine.
In order to clear this waste product from the body, the kidneys filter creatinine out of the blood
and facilitate its removal from the body in urine.
A serum creatinine test measures the amount of creatinine in a sample of blood. A urine
creatinine test measures the total amount of creatinine in all of the urine produced during a 24-
hour period. These two values can also be compared in a creatinine clearance test.
Creatinine may be measured as part of other tests. For example, it may be included as one part of
a basic metabolic panel (BMP) or comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP). These tests help assess
the body’s energy use, electrolyte levels, and kidney function.
When should I get a creatinine test?
A creatinine test is most often prescribed when your active symptoms or overall health history
reflect an elevated risk of kidney problems.
If you have symptoms that could be caused by an underlying problem that is affecting your
kidneys, a creatinine test may be part of the diagnostic process.
If you don’t have symptoms, your doctor may suggest a creatinine test to screen for kidney
problems if you have an increased risk of kidney disease. Some risk factors for kidney disease
include:
Diabetes
A family history of kidney problems
High blood pressure
If you take a medication that has the potential to disrupt kidney function, you may receive
periodic creatinine testing to check for this side effect.
Creatinine testing can also be used to monitor your kidney health if you’ve had an abnormal
kidney function test before or if you have already been diagnosed with kidney disease.
A creatinine measurement may be taken as part of a basic or comprehensive metabolic panel
during a regular health checkup. Although there is little evidence showing the benefits of this
kind of screening in otherwise healthy people, some doctors prescribe these panels during routine
patient care.
Finding a Creatinine Test
How to get tested
Creatinine tests are normally ordered by a doctor. A blood sample taken from a vein in your arm
in a medical office or hospital is used for a creatinine blood test. For a urine creatinine test, you
use special containers to collect all of your urine over a 24-hour period.
Can I take the test at home?
Some options exist for collecting a sample for a creatinine test at home.
Urine creatinine tests are done with a 24-hour urine sample, so most doctor-prescribed urine
creatinine tests require at-home collection.
Some at-home test kits include measurements of creatinine in several samples of dried urine.
These samples are not analyzed at home but are sent to a lab where creatinine can be measured.
Some commercially available urine test strips change color based on the creatinine level.
However, test samples taken over a longer period, such as a 24-hour urine collection, are
generally considered to be more accurate than a one-time measurement for kidney function tests.
At-home blood test kits are available that include creatinine along with other measurements.
These self-collection tests require mailing a blood sample to a laboratory for analysis.
How much does the test cost?
Several different factors can change the expected cost of a creatinine test. These factors include:
Whether the test uses a sample of blood or urine
Whether the test measures creatinine alone or with other substances
Where testing is done
Whether you have health insurance coverage
The total cost may include separate charges for office visits, phlebotomy fees, or laboratory
analysis. Health insurance may cover these costs if testing is prescribed by a doctor, but you
should talk with your insurance company to find out about any out-of-pocket costs, such as a
deductible or copay, for creatinine testing.
At-home kidney tests that include creatinine are often available for around $100, but the exact
cost can depend on the manufacturer and the specific measurements included in the test.
You might also like
- The Essential Guide to Routine Blood Tests for General Health: Health, #2From EverandThe Essential Guide to Routine Blood Tests for General Health: Health, #2No ratings yet
- CreatinineDocument3 pagesCreatinineElixirNo ratings yet
- Fasting Blood Sugar LevelsDocument7 pagesFasting Blood Sugar LevelsApple RamosNo ratings yet
- CreatinineDocument4 pagesCreatinineSiamala MunusamyNo ratings yet
- Kidney FunctionDocument4 pagesKidney FunctionEinah EinahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Serum CreatinineDocument6 pagesLecture 4 Serum Creatinineايلاف ميثم مكي محمدNo ratings yet
- The Test Sample: Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)Document4 pagesThe Test Sample: Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)patel.pratimNo ratings yet
- SCR Vs CCLDocument3 pagesSCR Vs CCLKuan Siaw HuiNo ratings yet
- Urine Protein andDocument12 pagesUrine Protein andAfifah AzizNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument7 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasePradnya ParamitaNo ratings yet
- How To Bring Down High Creatinine Levels PDFDocument28 pagesHow To Bring Down High Creatinine Levels PDFAMIR100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document6 pagesChapter 12 Biochemistry and Clinical Pathology Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20prat.medbooksNo ratings yet
- Blood Test of KFTDocument3 pagesBlood Test of KFTRaghvendra RathoreNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Serum Creatinine Level Treatment - Why It Is NecessaryDocument4 pagesAyurvedic Serum Creatinine Level Treatment - Why It Is NecessaryAnonymous vfzbbCKaENo ratings yet
- How To Bring Down High Creatinine LevelsDocument30 pagesHow To Bring Down High Creatinine Levelskavitha_vk76No ratings yet
- BUN and Creatinine LevelsDocument2 pagesBUN and Creatinine LevelsRadityo Galih PermadiNo ratings yet
- Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesKidney DiseaseHariNo ratings yet
- Potassium: Test Quick GuideDocument13 pagesPotassium: Test Quick Guideprakash gusainNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 5 Renal Functions TestDocument6 pagesLab 4 5 Renal Functions TestMustafa MahdiNo ratings yet
- Lab (5) Creatinine Clearance&GFRDocument16 pagesLab (5) Creatinine Clearance&GFRAkshay Chandra Vemulapalli100% (1)
- Creatinine ClearanceDocument2 pagesCreatinine ClearancebournvilleeaterNo ratings yet
- Ren Function TestDocument10 pagesRen Function TestSankha DasNo ratings yet
- Liver Function TestDocument3 pagesLiver Function TestAngelica Joyce BarcosNo ratings yet
- AST TestDocument4 pagesAST Testmandawa786No ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests - Types, Purpose & Results InterpretationDocument12 pagesLiver Function Tests - Types, Purpose & Results InterpretationMark SudieNo ratings yet
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (Bun)Document4 pagesBlood Urea Nitrogen (Bun)Vanessa VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- I Get Asked A Lot About CreatinineDocument6 pagesI Get Asked A Lot About CreatinineZurida MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Kidney Disease Symptoms and TestingDocument3 pagesKidney Disease Symptoms and Testingmoses njengaNo ratings yet
- 3,4Biochemestry 2021 بسجDocument38 pages3,4Biochemestry 2021 بسجغالب الموسويNo ratings yet
- PIIS1548559517301738Document7 pagesPIIS1548559517301738Joseph BoatengNo ratings yet
- Basic Laboratory FormulasDocument8 pagesBasic Laboratory Formulasdr-abdullah husseinNo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument1 pageKidneySujith KuttanNo ratings yet
- India Periodic Health Check Program GSCDocument4 pagesIndia Periodic Health Check Program GSCBandhamneni VemuNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentNherriza Ingrid L. CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Kidney and Liver FunctionDocument6 pagesKidney and Liver FunctionAhmad Ripani Musyaffa AhdanLabNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function Tests: Blood TestDocument2 pagesKidney Function Tests: Blood TestMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis and Kidney Disease: What You Need To KnowDocument16 pagesUrinalysis and Kidney Disease: What You Need To KnowBayu Segara HokiNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis, Fecalysis, & Complete Blood Count: NCM 112 Rle Ward ClassDocument14 pagesUrinalysis, Fecalysis, & Complete Blood Count: NCM 112 Rle Ward ClassJabber PaudacNo ratings yet
- Procedures/Diagnostic Tests: Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) StudyDocument1 pageProcedures/Diagnostic Tests: Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) StudyKumarNo ratings yet
- 7 Ways To Lower Creatinine Level NaturallyDocument20 pages7 Ways To Lower Creatinine Level NaturallyAmjad Pathan100% (1)
- Prepared By: Carreon, Kimberley Anne D. Golez, Steffi Gabrielle Laboratory TestDocument6 pagesPrepared By: Carreon, Kimberley Anne D. Golez, Steffi Gabrielle Laboratory TeststeffiNo ratings yet
- Albumin TestDocument5 pagesAlbumin Testmandawa786No ratings yet
- Stool Guaiac TestDocument4 pagesStool Guaiac Testdeepeezee beenNo ratings yet
- 5 - Clinical 1Document21 pages5 - Clinical 1levan guluaNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin TestDocument4 pagesBilirubin Testmandawa786No ratings yet
- University of Duhok College of Science Department of Biology Second StageDocument26 pagesUniversity of Duhok College of Science Department of Biology Second StageSadeq PeeroNo ratings yet
- LFT TestDocument5 pagesLFT Testmandawa786No ratings yet
- What To Know About Uric Acid TestsDocument64 pagesWhat To Know About Uric Acid Testsmusembijosef2011No ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument8 pagesUrinalysisAruna SriNo ratings yet
- المختبر الثاني ك2Document8 pagesالمختبر الثاني ك2Hussein AlaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease Tests & Diagnosis - NIDDKDocument4 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Tests & Diagnosis - NIDDKwany.fyza54No ratings yet
- Jurnal Tugas BudianaDocument3 pagesJurnal Tugas BudianazizahNo ratings yet
- Juliet - Ikeji Seminar 1Document10 pagesJuliet - Ikeji Seminar 1joe topeNo ratings yet
- Creatinine Estimation and Creatinine Clearance TestDocument51 pagesCreatinine Estimation and Creatinine Clearance TestSasimalani SurgunnamNo ratings yet
- Aabush Getaneh Case Presentation 1Document34 pagesAabush Getaneh Case Presentation 1HABTAMU MOLLANo ratings yet
- Joanalain C. Cortez, RN Clinical InstructorDocument179 pagesJoanalain C. Cortez, RN Clinical InstructorMark CadaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Urine TestDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Urine TestRestu Yogi FahleviNo ratings yet
- Know Your Kidney Numbers - Two Simple Tests - National Kidney FoundationDocument2 pagesKnow Your Kidney Numbers - Two Simple Tests - National Kidney FoundationNaresh PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Health TalkDocument13 pagesHealth Talkwany.fyza54No ratings yet
- Urinalysis and Kidney Disease: What You Need To KnowDocument16 pagesUrinalysis and Kidney Disease: What You Need To Knowsindhuja sriramNo ratings yet
- What It IsDocument3 pagesWhat It Isjohn mendozaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: Products & ServicesDocument6 pagesSymptoms: Products & Servicesjohn mendozaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: Heart Failure Blood Clots AneurysmDocument7 pagesSymptoms: Heart Failure Blood Clots Aneurysmjohn mendozaNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: Allergic Reaction Medications Epinephrine Anaphylaxis Allergic Reaction Blood PressureDocument3 pagesSymptoms: Allergic Reaction Medications Epinephrine Anaphylaxis Allergic Reaction Blood Pressurejohn mendozaNo ratings yet
- The Epoch TimesDocument3 pagesThe Epoch Timesjohn mendozaNo ratings yet
- What Is Measles?Document4 pagesWhat Is Measles?john mendozaNo ratings yet
- Types of Diabetes Mellitus: in This ArticleDocument5 pagesTypes of Diabetes Mellitus: in This Articlejohn mendozaNo ratings yet
- What Are Ketones, and Why Are They Dangerous?Document4 pagesWhat Are Ketones, and Why Are They Dangerous?john mendozaNo ratings yet
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) TestDocument1 pageBlood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Testjohn mendozaNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR LETTER NO. 3 OF 2020 COVID-19 - RecognizedDocument2 pagesCIRCULAR LETTER NO. 3 OF 2020 COVID-19 - RecognizedSam KNo ratings yet
- Individual Development Plan FormDocument2 pagesIndividual Development Plan FormLielet MatutinoNo ratings yet
- 2 Jsss - 01 JICA STANDARDDocument165 pages2 Jsss - 01 JICA STANDARDAchmad ChusnadiNo ratings yet
- WSBB Guide For Beginners - Bench-CompressedDocument15 pagesWSBB Guide For Beginners - Bench-CompressedKatya KNo ratings yet
- PurcomDocument3 pagesPurcomJackie RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Psychology Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes PDFDocument12 pagesPsychology Class 12 Chapter 2 Notes PDFhbaki0296No ratings yet
- Master Youtube: WorkbookDocument64 pagesMaster Youtube: WorkbookLucian TrandafirNo ratings yet
- 0121 Letter Directing Employee To Undertake Fitness Work AssessmentDocument2 pages0121 Letter Directing Employee To Undertake Fitness Work AssessmentRobin james PardilloNo ratings yet
- Visual Acuity Toddler TestDocument21 pagesVisual Acuity Toddler TestDimsyafelNo ratings yet
- Ader 1985Document48 pagesAder 1985Renata MNo ratings yet
- CAS PLAN 2021 TemplateDocument4 pagesCAS PLAN 2021 TemplateTunchanok TrangansriNo ratings yet
- Hannover Polytrauma Score.4Document2 pagesHannover Polytrauma Score.4Azmi FarhadiNo ratings yet
- Final Graduation ListDocument108 pagesFinal Graduation ListJonn MashNo ratings yet
- One Page Policy Brie1introDocument2 pagesOne Page Policy Brie1introapi-539369902No ratings yet
- Committee 2020, Reporter, May Edition 2020, April 24, 2020Document32 pagesCommittee 2020, Reporter, May Edition 2020, April 24, 2020ucopresident_2130533No ratings yet
- Contract Research Report: Strategies To Promote Safe Behaviour As Part of A Health and Safety Management SystemDocument82 pagesContract Research Report: Strategies To Promote Safe Behaviour As Part of A Health and Safety Management SystemMustapha MellalNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation 4th Quarter LessonDocument4 pagesClassroom Observation 4th Quarter LessonKen AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Med HostDocument4 pagesMed HostNitika13No ratings yet
- Ncbts Domain 5Document2 pagesNcbts Domain 5Maureen Mae Estanol100% (1)
- D2 Presentation Matt Singleton Swiss Re Dementia and InsuranceDocument13 pagesD2 Presentation Matt Singleton Swiss Re Dementia and InsuranceRishi KumarNo ratings yet
- University of Southern Mindanao: Kabacan, Cotabato PhilippinesDocument7 pagesUniversity of Southern Mindanao: Kabacan, Cotabato PhilippinesAlexis banicioNo ratings yet
- VISUAL PERCEPTION DISORDER HandoutsDocument3 pagesVISUAL PERCEPTION DISORDER HandoutsJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- Chest Wall DeformitiesDocument25 pagesChest Wall DeformitiesRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Herbal Drugs For Thyroid - PDF: International Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences May 2016Document10 pagesHerbal Drugs For Thyroid - PDF: International Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences May 2016Sanju TkNo ratings yet
- Thiacloprid Draft Assessment ReportDocument109 pagesThiacloprid Draft Assessment ReportTomás Afonso CavacoNo ratings yet
- Energy Requirements For AdultsDocument3 pagesEnergy Requirements For AdultsSyifa MustikaNo ratings yet
- A Key To Occlusion: Spencer R. Atkinson, D.D.S Pasadena, CalifDocument17 pagesA Key To Occlusion: Spencer R. Atkinson, D.D.S Pasadena, CalifMazhalai SelvaNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Cognitive DistortionsDocument6 pagesPatterns of Cognitive DistortionsBushra AwanNo ratings yet
- Ways of CopingDocument5 pagesWays of Copingteena jobNo ratings yet
- MD Educ 1 Topic Learner CultureDocument1 pageMD Educ 1 Topic Learner CultureLoren DanielleNo ratings yet