Professional Documents
Culture Documents
16 Administering Intradermal Injections
Uploaded by
Marky RoqueCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
16 Administering Intradermal Injections
Uploaded by
Marky RoqueCopyright:
Available Formats
Administering an Intradermal Injection for Skin Tests
Purposes:
To provide a medication the client requires for allergy testing and TB
screening.
Equipment:
Client’s MAR or computer printout
Vial or ampule of the correct sterile medication
Sterile 1mL syringe calibrated into hundredths of a milliliter (tuberculin syringe
and #25 to #27 gauge safety needle that is ¼ to 5/8 inch long
Alcohol swabs
2x2 sterile gauze square (optional)
Clean gloves
Bandage (optional)
Epinephrine, in case of allergic anaphylactic reaction
No. Steps Rationale
Preparation:
1 Check the MAR.
Check the label on the medication.
Follow the 3 checks for administering
medication. Read the label (1) when it is
taken from the medication cart, (2) before
withdrawing the medication, and (3) after
withdrawing the medication
Confirm that the dose is correct.
Steps:
1 Perform hand hygiene and observe other
appropriate infection prevention procedures.
2 Prepare the medication from the ampule or vial for
medication withdrawal.
If the medication is insulin or heparin, the Double checking the dosage
dosage needs to be verified by another avoids medication errors.
nurse.
3 Prepare the client. Ensures that the right client
Introduce self and verify the client’s identity receives the right
using agency protocol. medication.
4 Explain the purpose of the medication and how it Information can facilitate
will help, using language that the client can acceptance of and
understand. Include relevant information about compliance with the therapy.
effects of the medication.
5 Provide for client privacy.
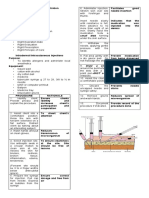
6 Select and clean the site.
Select the site (e.g., forearm about a hand’s
width above the wrist and three or four
finger widths below the antecubital space)
Apply gloves.
Cleanse the skin at the site using a firm
circular motion starting at the center and
widening the circle outward. Allow the area
to dry thoroughly.
7. Prepare the syringe for the injection.
Remove the needle cap while waiting for
the antiseptic to dry.
Expel any air bubbles from the syringe. A small amount of air will not
Small bubbles that adhere to the plunger harm the tissues.
are of no consequence.
Grasp the syringe with dominant hand, The possibility of the
close to the hub, holding it between thumb medication entering the
and forefinger. Hold the needle almost subcutaneous tissue
parallel to the skin surface, with the bevel of increases when using an
the needle up. angle greater than 15°.
8. Inject the fluid.
With the nondominant hand, pull the skin at Taut skin allows for easier
the site until it is taut. entry of the needle and less
discomfort for the client.
Insert the tip of the needle far enough to
place the bevel through the epidermis into
the dermis. The outline of the bevel should
be visible under the skin surface.
To verify that the medication
Stabilize the syringe and needle. Inject the that entered the dermis.
medication carefully and slowly to produce
a small wheal on the skin.
Withdraw the needle quickly at the same
angle at which it was inserted.
Massage can disperse the
medication into the tissue or
Do not massage the area. out through the needle
insertion site.
9. Dispose of the syringe and needle into the sharps Do not recap the needle
container. anymore prior to disposal in
the sharps container in order
to prevent needlestick
injuries.
10. Remove and discard gloves. Perform hand
hygiene.
11. Circle the injection site with ink to observe for
redness or induration (hardening), per agency
policy.
12. Document all relevant information such as: testing
material given, time, dosage, route, site and
nursing assessments.
Evaluation:
Evaluate the client’s response to the testing
substance by evaluating the condition of the
site after 30 minutes.
Document the findings and refer
appropriately.
You might also like
- Administering IntradermalDocument28 pagesAdministering IntradermalSaul Remus Q. DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Stewardship Manual of Procedures For Hospitals 2016 v2Document82 pagesAntimicrobial Stewardship Manual of Procedures For Hospitals 2016 v2kNo ratings yet
- Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering An Intramuscular Injectionapi-26570979100% (4)
- Subcutaneous InjectionDocument5 pagesSubcutaneous InjectionNovita sariNo ratings yet
- FINALMOP6 4 13WORDRADMay30 PDFDocument256 pagesFINALMOP6 4 13WORDRADMay30 PDFRyan Michael OducadoNo ratings yet
- Preparing and Administering Subcutaneous Injection PurposeDocument11 pagesPreparing and Administering Subcutaneous Injection PurposeLRBNo ratings yet
- Assess Patient Data Such As Vital Signs, Laboratory Values, and Allergies Before Preparing and Administering Medications by InjectionDocument12 pagesAssess Patient Data Such As Vital Signs, Laboratory Values, and Allergies Before Preparing and Administering Medications by InjectionLRBNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Metal Allergy and Systemic Contact Dermatitis: An OverviewDocument5 pagesReview Article: Metal Allergy and Systemic Contact Dermatitis: An OverviewsanyiNo ratings yet
- Practice Teaching Demonstration: Intramuscular InjectionDocument13 pagesPractice Teaching Demonstration: Intramuscular InjectionMegha lakra100% (1)
- Tina Jones Heent Soap Note Episodic VisitDocument5 pagesTina Jones Heent Soap Note Episodic VisitMallory ZaborNo ratings yet
- Administering A Subcutaneous InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering A Subcutaneous Injectionapi-26570979100% (5)
- Parenteral Medication ScriptDocument6 pagesParenteral Medication ScriptJoanna MontebonNo ratings yet
- Allergies and HypersensitivityDocument14 pagesAllergies and HypersensitivityBabar MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Sphere For Monitoring and EvaluationDocument50 pagesSphere For Monitoring and EvaluationMarky Roque100% (2)
- Prototype Blackboard CleanerDocument28 pagesPrototype Blackboard CleanerjennieNo ratings yet
- Administering Intradermal InjectionDocument2 pagesAdministering Intradermal InjectionMoiraMaeBeridoBalite100% (1)
- Jose Rizal Memorial State University: College of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesDocument5 pagesJose Rizal Memorial State University: College of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesJustine CagatanNo ratings yet
- Administering Intramuscular InjectionDocument7 pagesAdministering Intramuscular Injectionthanuja mathew100% (1)
- Preparing and Administering Intradermal Injection PurposeDocument10 pagesPreparing and Administering Intradermal Injection PurposeLRBNo ratings yet
- Meningococcemia: N F S LDocument45 pagesMeningococcemia: N F S LMarky Roque100% (1)
- Adminstration of Intradermal InjectionDocument2 pagesAdminstration of Intradermal InjectionMicroporeNo ratings yet
- Adminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDocument3 pagesAdminstration of Intramusclar InjectionDenise CastroNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Catheterization Enema ChecklistDocument8 pagesParenteral Catheterization Enema ChecklistJessoliver GalvezNo ratings yet
- Intramuscular Injectoin ChecklistDocument2 pagesIntramuscular Injectoin ChecklistBettina ChuaNo ratings yet
- Administering IntradermalDocument4 pagesAdministering IntradermalNezukoNo ratings yet
- 2 Intramuscular InjectionDocument5 pages2 Intramuscular InjectionKEANNA ZURRIAGANo ratings yet
- Administering An Intradermal InjectionDocument2 pagesAdministering An Intradermal InjectionKrysstal GerongaNo ratings yet
- Parenteral MedDocument3 pagesParenteral MedAya SabasNo ratings yet
- Injections ImDocument4 pagesInjections ImMariya DantisNo ratings yet
- Administering Intradermal InjectionDocument17 pagesAdministering Intradermal InjectionPattNo ratings yet
- PARENTERAL MEDICATION Manual and Checklist 1Document14 pagesPARENTERAL MEDICATION Manual and Checklist 1Hazel Shaine BaybayanNo ratings yet
- Administering An IntradermalDocument7 pagesAdministering An IntradermalCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- IM and ID Injection ChecklistsDocument2 pagesIM and ID Injection ChecklistsChesca LayosaNo ratings yet
- Administering A Subcutaneous InjectionDocument2 pagesAdministering A Subcutaneous InjectionKrysstal GerongaNo ratings yet
- Administering Parental MedicationsDocument4 pagesAdministering Parental MedicationsAmanda Joy TuizaNo ratings yet
- Administering A Subcutaneous InjectionDocument2 pagesAdministering A Subcutaneous InjectionLiana Koh VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- IntradermalDocument7 pagesIntradermalKyle Dapulag100% (1)
- IntradermalDocument2 pagesIntradermalAdrija SenNo ratings yet
- Intramuscular InjectionDocument15 pagesIntramuscular InjectionApin Pokhrel100% (1)
- INTRADERMAL Flowchart ExplanationDocument1 pageINTRADERMAL Flowchart ExplanationShenn ChavezNo ratings yet
- IV Checklist 2014Document3 pagesIV Checklist 2014İrem YaşaNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Administration of DrugsDocument3 pagesParenteral Administration of DrugspauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Parenteral PRDocument4 pagesParenteral PRGlecy CastañaresNo ratings yet
- Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument2 pagesAdministering An Intramuscular InjectionKrysstal GerongaNo ratings yet
- Med Admin ChecklistDocument9 pagesMed Admin ChecklistLoren MisticaNo ratings yet
- Intradermal Injection For Skin TestDocument3 pagesIntradermal Injection For Skin TestJuliezel IringanNo ratings yet
- RD For Id, Im, ChivDocument6 pagesRD For Id, Im, ChivPrincess Huey GreyNo ratings yet
- NCM-107-Medication Adm - SF20Document27 pagesNCM-107-Medication Adm - SF20yuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- ID-IM-SQ-E ToolDocument9 pagesID-IM-SQ-E TooltriciacamilleNo ratings yet
- Drug Preparation: (Ampule and Vial)Document25 pagesDrug Preparation: (Ampule and Vial)Ron Lucernas MayugaNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Medication: Prepared By: Level II InstructorsDocument105 pagesParenteral Medication: Prepared By: Level II InstructorsJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Tourniquet Test: Small Amount of Air Will Not Harm The TissuesDocument4 pagesTourniquet Test: Small Amount of Air Will Not Harm The TissuesjoymaeannNo ratings yet
- Injections - IdDocument3 pagesInjections - IdMariya DantisNo ratings yet
- 7-IM InjectionDocument19 pages7-IM InjectionarlixNo ratings yet
- Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesAdministering An Intramuscular InjectionPattNo ratings yet
- Checklist Administering An Intramuscular InjectionDocument3 pagesChecklist Administering An Intramuscular InjectionCAMPOSANO, JHANNA MARIENo ratings yet
- Intra MuscularDocument4 pagesIntra MuscularAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- IM ChecklistDocument3 pagesIM ChecklistMARIANNE JOY ELEAZARNo ratings yet
- RD - MedicationsDocument15 pagesRD - MedicationsJiwi YuNo ratings yet
- Administering Z-Track Intramuscular InjectionDocument5 pagesAdministering Z-Track Intramuscular InjectionRina Abigail Belleza AguedanNo ratings yet
- How To Give An Im Injection Portfolio Track ChangesDocument4 pagesHow To Give An Im Injection Portfolio Track Changesapi-582970027No ratings yet
- Performance Checklist ID and IM MedicationsDocument7 pagesPerformance Checklist ID and IM MedicationsJ-eliNo ratings yet
- Rights in Drug AdministrationDocument1 pageRights in Drug AdministrationIrish Margareth AdarloNo ratings yet
- Checklist of IM InjectionDocument5 pagesChecklist of IM InjectionSharon LawrenceNo ratings yet
- IM InjectionDocument4 pagesIM InjectionAdrija SenNo ratings yet
- Procedure Checklist Chapter 23: Administering Intramuscular InjectionsDocument3 pagesProcedure Checklist Chapter 23: Administering Intramuscular InjectionsLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument14 pagesChecklistYooleen SanchezNo ratings yet
- Survival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)From EverandSurvival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)No ratings yet
- 5B Assessing Apical Pulse-2Document4 pages5B Assessing Apical Pulse-2Marky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 6 Assessing Respiratory RateDocument2 pages6 Assessing Respiratory RateMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 14B Preparing Medications From VialsDocument4 pages14B Preparing Medications From VialsMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 13 Administering Rectal MedicationsDocument2 pages13 Administering Rectal MedicationsMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 14A Preparing Medications From AmpulesDocument3 pages14A Preparing Medications From AmpulesMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 7 Assessing Blood PressureDocument5 pages7 Assessing Blood PressureMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 5C Assessing Apical - Radial Pulse-3Document2 pages5C Assessing Apical - Radial Pulse-3Marky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 8 Assessing Oxygen SaturationDocument3 pages8 Assessing Oxygen SaturationMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Answering A Case StudyDocument1 pageGuidelines For Answering A Case StudyMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Answer in Pauline EthicsDocument3 pagesAnswer in Pauline EthicsMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 15 Mixing Medications Using One SyringeDocument2 pages15 Mixing Medications Using One SyringeMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Fall Assessment Tool: Fall Risk Factor CategoryDocument1 pageFall Assessment Tool: Fall Risk Factor CategoryMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Preboard Exam RemindersDocument2 pagesPreboard Exam RemindersMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Answer in Pauline EthicsDocument3 pagesAnswer in Pauline EthicsMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Aids Candlelight PresentationDocument23 pagesAids Candlelight PresentationMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Childbearing Client 20Document37 pagesAssessment of Childbearing Client 20Marky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Depression PowerpointDocument26 pagesDepression PowerpointMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL-PPS Forms English 2018-2Document4 pagesGLOBAL-PPS Forms English 2018-2Marky RoqueNo ratings yet
- December 1, 2017 1:00pm-5:00pm Attendance Sheet Name Signature 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20Document2 pagesDecember 1, 2017 1:00pm-5:00pm Attendance Sheet Name Signature 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20Marky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Teknik PersampelanDocument31 pagesTeknik PersampelanzackquanNo ratings yet
- CIS 2016 CalendarDocument6 pagesCIS 2016 CalendarMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- 12 Infection Control - Final 08Document38 pages12 Infection Control - Final 08sparshmeNo ratings yet
- Guidance Notes: Emergency and Disaster Preparedness For Health FacilitiesDocument56 pagesGuidance Notes: Emergency and Disaster Preparedness For Health FacilitiesMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- List of Hubs & CoordinatorsDocument3 pagesList of Hubs & CoordinatorsMarky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Childbearing Client 20Document37 pagesAssessment of Childbearing Client 20Marky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Intake Form: Raindrop Technique and Vibrational Raindrop TechniqueDocument2 pagesIntake Form: Raindrop Technique and Vibrational Raindrop TechniqueMucia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Improved Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) After 1 One Year of Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT) in Unison With Pharmacotherapy in Mild Allergic AsthmaticsDocument7 pagesImproved Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) After 1 One Year of Sublingual Immunotherapy (SLIT) in Unison With Pharmacotherapy in Mild Allergic AsthmaticsRoohi WaniNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced by Youth With Allergic Conditions: A Sociological Study in City Dera Ghazi KhanDocument12 pagesChallenges Faced by Youth With Allergic Conditions: A Sociological Study in City Dera Ghazi Khanaaaliya7777No ratings yet
- Chief Complaints: Sl. Medicine Name Dosage Freq. Duration InstructionsDocument4 pagesChief Complaints: Sl. Medicine Name Dosage Freq. Duration InstructionsGuru ReddyNo ratings yet
- Focus3 2E MiniMatura Unit6 GroupA 1kolDocument5 pagesFocus3 2E MiniMatura Unit6 GroupA 1kolOliwia StańczykNo ratings yet
- Drug Allergy: DR Sana Nisar ZaidiDocument34 pagesDrug Allergy: DR Sana Nisar ZaidisaraNo ratings yet
- Acad Dermatol Venereol - 2020 - Wollenberg - ETFAD EADV Eczema Task Force 2020 Position Paper On Diagnosis and Treatment ofDocument28 pagesAcad Dermatol Venereol - 2020 - Wollenberg - ETFAD EADV Eczema Task Force 2020 Position Paper On Diagnosis and Treatment ofmaituuyen1997No ratings yet
- RHINITISDocument2 pagesRHINITISHuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Amazing e Brochure AmendedDocument4 pagesAmazing e Brochure Amendedpartha sarathiiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-09-29 at 12.13.10 PMDocument6 pagesScreenshot 2022-09-29 at 12.13.10 PMgaalaxy ggNo ratings yet
- JaZ KyS17 - "ANG BABAENG ALLERGIC SA WIFI" Movie ReviewDocument2 pagesJaZ KyS17 - "ANG BABAENG ALLERGIC SA WIFI" Movie ReviewNathaniele Lean Castro100% (1)
- English Daily Test Label KLS 9Document5 pagesEnglish Daily Test Label KLS 9Min Ren SuNo ratings yet
- Work Environment Questionnaire 1Document2 pagesWork Environment Questionnaire 1Tr RoseNo ratings yet
- AnaphylaxisDocument15 pagesAnaphylaxisThaer ZabenNo ratings yet
- Health Condition1Document22 pagesHealth Condition1Barrack koderaNo ratings yet
- Gatau yDocument3 pagesGatau yAlfero FransNo ratings yet
- Front PageDocument11 pagesFront PageJake PaduaNo ratings yet
- Angioedem A: BY: Palak Khanna Sadhana Shukla Madiha Bano RehamaniDocument18 pagesAngioedem A: BY: Palak Khanna Sadhana Shukla Madiha Bano RehamanipalNo ratings yet
- Appropiate Allergic Testing and The Interpretation - Dr. Deshinta Putri Mulya, SP - PD (K) KAIDocument40 pagesAppropiate Allergic Testing and The Interpretation - Dr. Deshinta Putri Mulya, SP - PD (K) KAIEllenNo ratings yet
- Allergic RhinitisDocument11 pagesAllergic RhinitisCarmila Olbe ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Using Disinfectants and Gels: ATL Ultrasound P.O. Box 3003 Bothell, WA 98041-3003 USA 4700-0249-18 Rev A June 2001Document73 pagesUsing Disinfectants and Gels: ATL Ultrasound P.O. Box 3003 Bothell, WA 98041-3003 USA 4700-0249-18 Rev A June 2001Foued MbarkiNo ratings yet
- Allergy ReportDocument5 pagesAllergy ReportDílìp ÎñdúrkãrNo ratings yet
- 10 Rights in Drug AdministrationDocument25 pages10 Rights in Drug AdministrationNathaniel PulidoNo ratings yet
- Study. RSUD Soetomo Surabaya. Vol. 26. No 3. Universitas AirlanggaDocument2 pagesStudy. RSUD Soetomo Surabaya. Vol. 26. No 3. Universitas AirlanggaKhoirunnisaSPazkaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument5 pagesDiagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationKenneth SyNo ratings yet
- Instruction For Use For Surgical GlovesDocument1 pageInstruction For Use For Surgical Gloveshitham shehataNo ratings yet