0% found this document useful (0 votes)
257 views4 pages4.2 - Identifiable Intangible Assets
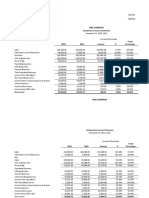
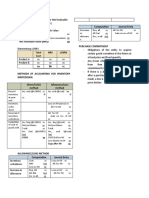
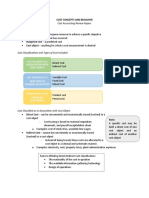
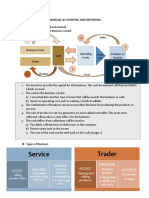
The document discusses accounting for various types of intangible assets including patents, trademarks, copyrights, franchises, leasehold improvements, website development costs, and organization costs. It provides guidance on determining the cost and amortization period for each type of intangible asset.
Uploaded by
Karyl FailmaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
257 views4 pages4.2 - Identifiable Intangible Assets
The document discusses accounting for various types of intangible assets including patents, trademarks, copyrights, franchises, leasehold improvements, website development costs, and organization costs. It provides guidance on determining the cost and amortization period for each type of intangible asset.
Uploaded by
Karyl FailmaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd