Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capitalized Expensed: Whether Taken or Not
Uploaded by
Karyl Failma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesOriginal Title
2.1_PPE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesCapitalized Expensed: Whether Taken or Not
Uploaded by
Karyl FailmaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
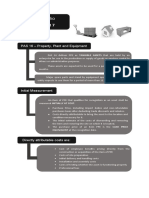
Chapter 23: Property, Plant, and Equipment (PPE) Capitalized Expensed
[PAS 16] Appraiser’s fee Removing old machine
Freight in/shipping Machine supplies
charge
ELEMENTS OF COST {PDI}
Special horn for van Storage costs
a. Purchase price, import duties, and Freight and insurance Repair charges
nonrefundable purchase taxes, less trade Trial run and other Motor vehicle
discounts and rebates testing costs registration
b. Directly attributable costs Construction of base Interest on loan
c. Initial estimate of the cost of dismantling, Noncurrent portion of Current portion of
removing the item and restoring the site on insurance premium insurance premium
which it is located, the obligation for which Irrecoverable taxes Cost of replacing
damaged part during
the entity incurs
installation
DIRECTLY ATTRIBUTABLE COSTS {ESD IPT}
ACQUISITION OF PROPERTY
1. Cost of employee benefits
2. Cost of site preparation 1. Acquisition on a cash basis
3. Initial delivery and handling costs a. Cost: Cash price equivalent (at the
4. Installation and assembly cost recognition date) = cash paid plus
5. Professional fees directly attributable costs (i.e. freight,
6. Costs of testing whether the asset is installation, etc.)
functioning properly, less the net proceeds b. “Basket price” or “lump sum price” –
from selling any items produced while apportion the single price to the assets
bringing the asset to the present location and on the basis of relative fair value
condition, such as samples produced while
testing equipment 2. Acquisition on account
a. Cost: Invoice price less discount,
whether taken or not
COSTS NOT QUALIFYING FOR RECOGNITION
3. Acquisition on installment basis
(EXPENSED OUTRIGHT) {OIC A IIR}
Case 1: Cash Price is Given
1. Costs of opening a new facility a. Cost: Cash price equivalent
2. Cost of introducing a new product or service, b. Difference: Discount on Note Payable
including costs of advertising and promotion (Dr.) – installment price minus cash
Costs of conducting business in a new price
location or with a new class or customer,
Case 2: Cash Price is Not Given
including cost of staff training
a. Cost: Present value of all payments
3. Cost of conducting business in a new location
(downpayment plus PV of note) using
or with a new class of customer, including
an implied interest rate
costs of staff training
b. Difference: Discount on Note Payable
4. Administrative and other general overhead
(Dr.) – note payable minus PV of note
costs
5. Costs incurred while an item capable of
4. Issuance of share capital
operating in the manner intended by
a. Cost: Order of Priority
management has yet to be brought into use
1. Fair value of property received
or is operated less than full capacity
2. Fair value of the share capital
6. Initial operating losses
3. Par value or stated value of the
7. Costs of relocating or reorganizing part or all
share capital
of an entity’s operations
b. Difference: Share Premium (Cr.) – fair Priority 1 Priority 2
value minus par value (FV of asset given) (TIV of asset given)
FV of asset given xxx TIV of asset given xxx
5. Issuance of bonds payable CA of asset given CA of asset given (xxx)
a. Cost: Order of priority (xxx)
1. Fair value of the bonds payable Gain/Loss from Exchange xxx Gain/Loss from Ex. xxx
2. Fair value of the asset received 8. Donation
3. Face amount of the bonds payable Case 1: Donation from Shareholder
b. a. Cost: Fair value of asset received –
c. Difference: Premium (discount) on Bonds [cr. Donated Capital]
Payable – fair value minus face amount b. Expenses incurred in connection with the
donation (registration and legal fees) –
6. Exchange [dr. Donated Capital]
Case 1: Exchange with commercial substance c. Directly attributable cost (installation and
– no cash involved testing costs)
a. Cost: Order of priority [capitalized; dr. PPE account]
1. Fair value of the asset given
Case 2: Donation from Non-shareholder
2. Fair value of the asset received
a. Cost: Fair value of asset received
3. Carrying amount of the asset given
1. Without restrictions (subsidies) –
b. Difference: Gain/loss on exchange –
[cr. Income from Donation]
fair value of asset given minus carrying
2. With restrictions (non-subsidies) –
amount of asset given
[cr. Deferred Income]
Case 2: Exchange with commercial substance
– cash is involved 9. Construction
a. Cost: Fair value of asset +/- cash a. Cost
Payor: Fair value of asset given plus 1. Direct materials
cash payment 2. Direct labor
Recipient: Fair value of asset given 3. Indirect costs and incremental
minus cash received overhead specifically identifiable or
b. Difference: Gain/loss on exchange – traceable to the construction (if not
fair value of asset given minus carrying identifiable, allocate on the basis of
amount of asset given direct labor cost or direct labor
hours)
Case 3: Exchange with no commercial
substance -------------------------------------------------------------------
a. Cost: Carrying amount of the asset Additional Tables
given
Payor: Carrying amount of asset ACQUISITION ON ACCOUNT
given plus cash payment Gross method Net method
Recipient: Carrying amount of Purchase on Equipment xxx Equipment xxx
asset given minus cash received account AP xxx AP xxx
b. No gain or loss recognized Payment within AP xxx AP xxx
discount period Cash xxx Cash xxx
7. Trade In (Form of Exchange) Equipment xxx
a. Cost: Order of Priority Payment beyond AP xxx AP xxx
discount period PD lost xxx PD lost xxx
1. Fair value of asset given plus cash
Cash xxx Cash xxx
payment
Equipment xxx
2. Trade-in value of asset given plus cash
payment (fair value of the asset
INSTALLMENT BASIS
received)
1. Cash price given
b. Difference: Gain/loss from exchange
Year Notes Fraction Interest
Payable expense
2020 500,000 5/15 40,000 Listed selling price/list price and average
2021 400,000 4/15 32,000 published retail value is ignored. It cannot
2022 300,000 3/15 24,000 be used as fair value.
2023 200,000 2/15 16,000 If fair value of asset given is not given, do
2024 100,000 1/15 8,000 not add cash paid to the fair value of the
1,500,000 120,000 asset received. It should only be added to
the fair value of asset given.
2. Cash price not given Cash price without trade-in (or cash price) is
Date Payment Interest Principal PV equal to fair value of the asset received
1.1.20 634,000 (trade in value + cash payment).
12.31.20 200,000 63,400 136,600 497,400 VAT is charged to input tax and not
12.31.21 200,000 49,740 150,260 347,140 capitalized
12.31.22 200,000 34,714 165,286 181,854 If there are cash payments not related to
12.31.23 200,000 18,146 181,854 0
trade-in (expensed), exclude from cash
paid. Only capitalizable cash paid are added
3. Term note
to fair value of asset given
Date Interest DNP PV “would have been” cash price and “would
Expense have been” capitalizable costs are all
1.1.20 - 634,000 1,366,000 capitalizable
12.31.20 136,600 497,400 1,506,600 Treasury shares are treated the same as
12.31.21 150,260 347,140 1,652,860 ordinary share capital. Thus, rules on
12.31.22 165,286 181,854 1,818,146 issuance of share capital apply
12.31.23 181,854 0 2,000,000 As to exchange transactions involving
inventories and other assets, rules on PPE
acquisition still apply
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Round off to three decimal places for PV,
Notes: unless otherwise stated.
If silent as to exchange, it is assumed to be Calculator manipulations
with commercial substance PV of Annuity Factor (for annual
If silent as to donation, assume donation installments)
from non-shareholder. Ex. 10% prevailing rate; 4 yrs.
For acquisition of PPE, purchase discount
lost account is used both in gross and net 1 + 10% = 1.10
method. For purchase, purchase discounts 1.10 ÷ ÷ M+ = = = = GT
= 3.170
lost is used only in net method.
Same entries and account used for
installment basis, both cash price given and PV Factor (for lump sum)
cash price not given. Only the tables differ. Ex. 10% ; 4 yrs.
Fair value is entirely disregarded when
1 + 10% = 1.10
exchange transaction lacks commercial
1.10 ÷ ÷ M+ = = = =
substance.
= 0.683
Assessed value for tax purposes cannot be
used as fair value figures. However, this can
be used for relative fair value allocation
purposes
For monthly installments, debit interest
expense instead of DNP
If there is no downpayment for installment
basis, the cost is the PV of note.
If no installment payment is mentioned,
assumed lump sum and use PV of 1 factor.
You might also like
- 6904 PPT Materials For UploadDocument5 pages6904 PPT Materials For UploadAljur SalamedaNo ratings yet
- NNDocument5 pagesNNMjhaye0% (1)
- PPE Cost MeasurementDocument5 pagesPPE Cost MeasurementRazel Tercino100% (1)
- PAS 16 Property, Plant & Equipment ReviewDocument21 pagesPAS 16 Property, Plant & Equipment ReviewMakoy BixenmanNo ratings yet
- IAS 16 PPE GuideDocument3 pagesIAS 16 PPE GuideRose MarieNo ratings yet
- Handout AP 2306 FDocument14 pagesHandout AP 2306 FDyosa MeNo ratings yet
- Audit 2 - Concept Map For InvestmentsDocument4 pagesAudit 2 - Concept Map For InvestmentsPrecious Recede100% (1)
- CFAS 2020 Chapter 15 and MC ProblemsDocument7 pagesCFAS 2020 Chapter 15 and MC Problems4220019No ratings yet
- FINAC1 - Accounting For Property, Plant, and Equipment 1Document3 pagesFINAC1 - Accounting For Property, Plant, and Equipment 1Jerico DungcaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Fixed Assets I. Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument45 pagesAccounting For Fixed Assets I. Property, Plant and EquipmentLayNo ratings yet
- Farap 4504Document8 pagesFarap 4504Marya NvlzNo ratings yet
- FARAP 4404 Property Plant EquipmentDocument11 pagesFARAP 4404 Property Plant EquipmentJohn Ray RonaNo ratings yet
- FAR (Final)Document27 pagesFAR (Final)CHERYL MORADANo ratings yet
- Pas 16Document5 pagesPas 16iyahvrezNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant and Equipment (Pas 16)Document1 pageProperty, Plant and Equipment (Pas 16)Jhets CalumbayNo ratings yet
- FAR: KEY ASPECTS OF PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT ACCOUNTINGDocument13 pagesFAR: KEY ASPECTS OF PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT ACCOUNTINGAl ChuaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument49 pagesNotes On Property, Plant and Equipmentcriszel4sobejanaNo ratings yet
- CFAS NotesDocument6 pagesCFAS NotesAngelNo ratings yet
- Nas 16Document33 pagesNas 16bhattag283No ratings yet
- Property, Plant, and Equipment: Probable Measured ReliablyDocument9 pagesProperty, Plant, and Equipment: Probable Measured ReliablyElle SalengaNo ratings yet
- Pas 16Document8 pagesPas 16Maxyne Dheil CastroNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio: PAS 16 - Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument3 pagesE-Portfolio: PAS 16 - Property, Plant and EquipmentKaye NaranjoNo ratings yet
- 05 Quiz 1acctDocument2 pages05 Quiz 1acctPalileo KidsNo ratings yet
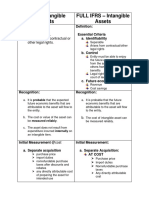
- SME vs FULL IFRS Treatment of Intangible AssetsDocument4 pagesSME vs FULL IFRS Treatment of Intangible AssetsMary Ann B. GabucanNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument5 pagesReviewercholestudyNo ratings yet
- Intangible Asset (Pas 38) : Introduction, Scope and DefinitionsDocument20 pagesIntangible Asset (Pas 38) : Introduction, Scope and Definitionskeithy joshuaNo ratings yet
- Learning Packet - Week 4Document14 pagesLearning Packet - Week 4Emmanuel ApuliNo ratings yet
- Ind As 16 Samplechapter TaxmannDocument11 pagesInd As 16 Samplechapter TaxmannsscNo ratings yet
- PPE PART 1 SummaryDocument3 pagesPPE PART 1 SummaryunknownNo ratings yet
- Initial Measurement at Cost.: Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument5 pagesInitial Measurement at Cost.: Property, Plant and EquipmentCarms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- INTACC 1 - PPE ReviewerDocument2 pagesINTACC 1 - PPE ReviewerRandom VidsNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument26 pagesProperty, Plant and EquipmentkyramaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document2 pagesChapter 03Patrick Kyle AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant and Equipment FundamentalsDocument13 pagesProperty, Plant and Equipment FundamentalsDenmark CabadduNo ratings yet
- PPE Asset Accounting GuideDocument5 pagesPPE Asset Accounting GuideWertdie stanNo ratings yet
- Ppe NotesDocument11 pagesPpe NotesHatdog KaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource WasJoy UyNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant, and Equipment With Government GrantDocument2 pagesProperty, Plant, and Equipment With Government GrantJorel DiocolanoNo ratings yet
- Ppe MemaidDocument6 pagesPpe MemaidMarshmallowNo ratings yet
- Ind AS 16 - RBM (WBS)Document7 pagesInd AS 16 - RBM (WBS)KRISHNENDU JASHNo ratings yet
- Cfas ReviewerDocument4 pagesCfas ReviewerLayla MainNo ratings yet
- 05q1 Ia1 Dela Cruz, Shiela Jane L (Bsa2a)Document3 pages05q1 Ia1 Dela Cruz, Shiela Jane L (Bsa2a)Alexandra JamesNo ratings yet
- PAS 16 Property Plant and Equipment GuideDocument4 pagesPAS 16 Property Plant and Equipment GuideKristalen ArmandoNo ratings yet
- FAR11 Intangibles - With AnsDocument18 pagesFAR11 Intangibles - With AnsAJ Cresmundo100% (1)
- FAR 006 Summary Notes - Property, Plant & EquipmentDocument9 pagesFAR 006 Summary Notes - Property, Plant & EquipmentMarynelle Labrador SevillaNo ratings yet
- University of Perpetual Help System Dalta: Calamba Campus, Brgy. Paciano RizalDocument4 pagesUniversity of Perpetual Help System Dalta: Calamba Campus, Brgy. Paciano RizalJeanette LampitocNo ratings yet
- ACCA106 Reviewer TheoriesDocument5 pagesACCA106 Reviewer TheoriesFrankie AsidoNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1_044932Document6 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1_044932AMIEL TACULAONo ratings yet
- Learn Key Concepts of Property, Plant & EquipmentDocument15 pagesLearn Key Concepts of Property, Plant & EquipmentThea Danica BrazaNo ratings yet
- Resume Akuntansi Keuangan Menengah (AKM)Document10 pagesResume Akuntansi Keuangan Menengah (AKM)Rizky AufaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Intangible AssetsDocument10 pagesReviewer Intangible AssetsMay100% (1)
- Property, Plant and Equipment Chapter 21Document15 pagesProperty, Plant and Equipment Chapter 21Dan MichaelNo ratings yet
- PPE Review For A PPE Review For A: Accounting (Far Eastern University) Accounting (Far Eastern University)Document6 pagesPPE Review For A PPE Review For A: Accounting (Far Eastern University) Accounting (Far Eastern University)JANISCHAJEAN RECTONo ratings yet
- Module 5 Property Plant EquipmentDocument16 pagesModule 5 Property Plant EquipmentTrine De LeonNo ratings yet
- Cabria CPA Review Center's Property Plant and Equipment LectureDocument9 pagesCabria CPA Review Center's Property Plant and Equipment LectureMaeNo ratings yet
- Material 3 PDF FreeDocument6 pagesMaterial 3 PDF FreeIshi Erika OrtizNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting NotesDocument2 pagesCapital Budgeting Noteszy jeiNo ratings yet
- 17 Property Plant and Equipment PART 1 PDFDocument25 pages17 Property Plant and Equipment PART 1 PDFJay Aubrey PinedaNo ratings yet
- Modes of Acquisition: Refer To The FV Hierarchy in Impairment of AssetsDocument4 pagesModes of Acquisition: Refer To The FV Hierarchy in Impairment of AssetsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 4.3 - Research and Development CostDocument3 pages4.3 - Research and Development CostKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Goodwill Is An Intangible Asset That: Normal Earnings, The ExcessDocument2 pagesGoodwill Is An Intangible Asset That: Normal Earnings, The ExcessKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Inventory Cost Flow: Computation of COGSDocument3 pagesChapter 11: Inventory Cost Flow: Computation of COGSKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28: Depletion Pfrs/Ifrs 6: Financial Reporting For The Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesDocument3 pagesChapter 28: Depletion Pfrs/Ifrs 6: Financial Reporting For The Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral ResourcesKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Inventories (PAS 2) : Included ExcludedDocument3 pagesChapter 10: Inventories (PAS 2) : Included ExcludedKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Retail Inventory Method GuideDocument3 pagesRetail Inventory Method GuideKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 - Identifiable Intangible AssetsDocument4 pages4.2 - Identifiable Intangible AssetsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Process Costing MethodsDocument7 pagesProcess Costing MethodsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 2.2A - Land and BuildingDocument3 pages2.2A - Land and BuildingKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Joint Costs and By-ProductsDocument6 pages6 - Joint Costs and By-ProductsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Joint Costs and By-ProductsDocument6 pages6 - Joint Costs and By-ProductsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 - Accounting For Production Losses (Job Order Costing)Document7 pages5.1 - Accounting For Production Losses (Job Order Costing)Karyl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Gross Profit Method: Less: LessDocument1 pageChapter 13: Gross Profit Method: Less: LessKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Computation Journal Entry: Net Realizable Value (NRV) XXDocument2 pagesComputation Journal Entry: Net Realizable Value (NRV) XXKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cost Concepts and BehaviorsDocument4 pages2 - Cost Concepts and BehaviorsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Cost Accumulation System: Defines - Cost Object - Method of Assigning Costs To ProductionDocument4 pagesCost Accumulation System: Defines - Cost Object - Method of Assigning Costs To ProductionKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Cost Concepts and BehaviorsDocument4 pages2 - Cost Concepts and BehaviorsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Process Costing MethodsDocument7 pagesProcess Costing MethodsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument2 pages1 - Introduction To Cost AccountingKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards: Loans ReceivableDocument2 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting Standards: Loans ReceivableKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 - Accounting For Production Losses (Product Costing) Increased UnitsDocument3 pages5.2 - Accounting For Production Losses (Product Costing) Increased UnitsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Cost Accumulation System: Defines - Cost Object - Method of Assigning Costs To ProductionDocument4 pagesCost Accumulation System: Defines - Cost Object - Method of Assigning Costs To ProductionKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 5.2 - Accounting For Production Losses (Product Costing) Increased UnitsDocument3 pages5.2 - Accounting For Production Losses (Product Costing) Increased UnitsKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 - Accounting For Production Losses (Job Order Costing)Document7 pages5.1 - Accounting For Production Losses (Job Order Costing)Karyl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Notes ReceivableDocument2 pagesLesson 7 - Notes ReceivableKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- A - Intro To IASBDocument4 pagesA - Intro To IASBKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- B - Conceptual Framework OverviewDocument2 pagesB - Conceptual Framework OverviewKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument2 pages1 - Introduction To Cost AccountingKaryl FailmaNo ratings yet
- Rights and Responsibilities of Partners Outlined in Partnership DeedDocument5 pagesRights and Responsibilities of Partners Outlined in Partnership DeedLegends FunanzaNo ratings yet
- ch12 SolutionsDocument49 pagesch12 Solutionsaboodyuae2000No ratings yet
- Draft Contract GLIIT-BMI GAR 5500-5300Document12 pagesDraft Contract GLIIT-BMI GAR 5500-5300Julian Nico100% (1)
- HunterDocument10 pagesHuntersuneetaNo ratings yet
- The business environment and start upDocument9 pagesThe business environment and start upPhấn LêNo ratings yet
- A Study On Nestle India - 76757220Document70 pagesA Study On Nestle India - 76757220Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Engineering and Economics Part II (Costing and Overheads)Document7 pagesEngineering and Economics Part II (Costing and Overheads)srinivas gangishettiNo ratings yet
- Case No.50 Bearneza Vs DequillaDocument1 pageCase No.50 Bearneza Vs Dequillapaul2574No ratings yet
- May 2011Document43 pagesMay 2011rgsr2008No ratings yet
- Assignment 2.1 AccountingDocument7 pagesAssignment 2.1 AccountingColine DueñasNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument32 pagesEntrepreneurshipVivek Kumar Singh100% (2)
- ConWorld - Quiz 1Document4 pagesConWorld - Quiz 1John Paul JalemNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Economic Analysis: Broad Parameters Sub Parameters Web Link YearDocument22 pagesQualitative Economic Analysis: Broad Parameters Sub Parameters Web Link YearRoshan GupthaNo ratings yet
- Management Air AsiaDocument19 pagesManagement Air AsiaPrisy ChooNo ratings yet
- Brand Architecture AssignmentDocument3 pagesBrand Architecture AssignmentNeazul Hasan75% (4)
- Notes - Unit 3Document26 pagesNotes - Unit 3ishita sabooNo ratings yet
- BEC Vantage Reading Part 1 - Teacher's Notes: 45 MinutesDocument15 pagesBEC Vantage Reading Part 1 - Teacher's Notes: 45 MinutesLy Nguyen Thi NhuNo ratings yet
- The Importance of e Service Quality in The Livestreaming Music Concert BusinessDocument18 pagesThe Importance of e Service Quality in The Livestreaming Music Concert BusinessCaptain SkyNo ratings yet
- Do It Yourself PDFDocument88 pagesDo It Yourself PDFcoutoNo ratings yet
- (VER. 3) TLE-IA6 - q0 - Mod3 - Simple Survey Using Technology - v3Document30 pages(VER. 3) TLE-IA6 - q0 - Mod3 - Simple Survey Using Technology - v3PAUL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Invoice OD116015462330009000Document1 pageInvoice OD116015462330009000Aryan Verma0% (1)
- How to Successfully Operate a Food BusinessDocument54 pagesHow to Successfully Operate a Food Businessariel paglinawanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Green Marketing On Customer Satisfaction An Empirical StudyDocument7 pagesImpact of Green Marketing On Customer Satisfaction An Empirical StudyarcherselevatorsNo ratings yet
- BL CHP 4Document11 pagesBL CHP 4Gary RaggzNo ratings yet
- The 1,500% Loophole: Better Than BitcoinDocument10 pagesThe 1,500% Loophole: Better Than BitcoinJeff Sturgeon100% (1)
- 7 Cs of Communication (Eg)Document40 pages7 Cs of Communication (Eg)Vikram KatariaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy Analysis: Biti's Hunter XDocument36 pagesMarketing Strategy Analysis: Biti's Hunter XHoàng Ngọc OanhNo ratings yet
- Driving Forces Behind Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesDriving Forces Behind Corporate Social ResponsibilitySabrina FazalNo ratings yet
- 4 & 5 Rooms: Luxurious ApartmentsDocument14 pages4 & 5 Rooms: Luxurious ApartmentsAdnanNo ratings yet