Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infographic About Articulators
Uploaded by
ANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORROOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Infographic About Articulators
Uploaded by
ANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORROCopyright:
Available Formats
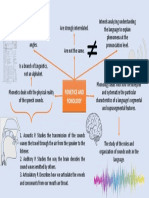
articulators and the
production
of voice
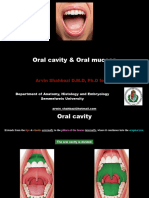
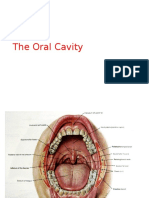
The articulators are the different parts of the mouth area that
we use when speaking, such as the lips, tongue, teeth, and jaw.
LIPS
The lips are the outermost articulator.
They are formed externally by the skin and
internally by mucous membrane. Betweeen these
TEETH two section is muscular, glandular, and fat tisue.
There are two types of teeth, deciduous The landmark's of the lip include the Vermilion,
and permanent teeth. philtrum, the columella, and the cupid's bow.
They are important for both eating and Bilabila and labiodental consonants are formed by
speech. the lips.
These teeth and their alignment play a
key role in the production of phonemes. TONGUE
The labiodental and dental consonant
are formed directly by the teeth. The tongue is considered by many
phoneticians to be the most important
articulator because of its great flexibility and
its capacity to compensate for other
structural problems.
The tongue is composed of connective tissue
covered by muscle tissue.
HARD PALATE
The hard palate is composed of the two
maxillary and two palatine bones.
The integrity of the hard palate is important for
resonance and as a point of attachment for
muscle tissue.
The front section of the hard palate is called SOFT PALATE
the alveolar ridge or process. The soft palate is locate directly behind the hard palate
Numerous consonants are formed using the and is comprised of muscle tissue with a membranous
alveolar, post alveolar, and palatal areas as a covering.
placement. The movement of the soft palate allows for
velopharyngeal closure.
The velar consonants are formed by the role of the velum
in articulation.
GLOTTIS
The glottis is the space between the vocal folds when open.
This area is important in both the production of glottal
sounds and for differentiating voiced and voiceless sounds.
MUSCLES
Numerous muscles organized into muscle
groups are important to articulation.
Facial expression, mastication, soft palate
(velar), intrinsic tongue, extrinsic tongue.
Articulation is the process of modifying the air stream by the articulators. Plosives, fricatives,
nasals, affricatives, and approximants are the result the manner of articulation.
The various vowel sounds are affected by:
lators.
- The changing shape and position of your articu
in the mout h.
- The position of your tongu
- The shape of your lips.
e
VELOPHARYNGEAL
- The size of your jaw opening. FUNCTIONING
Velopharyngeal closure is accomplished by the movement
of the velum, at the level of the superior constrictor,
backward and upward to meet the back wall of the pharynx.
This movement is used in our language for the production of
all phonemes except the nasal /m/, /n/, and /ɳ/.
TONSIL RING
The tonsil ring is a near circle of lymph tissue located near the entrance of the
nasal and oral cavity.
It serves as a protection system ridding the body of waste material.
There are three parts to the tonsillar ring: The pharyngeal tonsil, the palatine
tonsil, and the ring.
The tonsils are often enlarged in children but tend to atrophy after puberty.
You might also like
- Oral Physiology ReviewerDocument20 pagesOral Physiology ReviewerCamille Baybay100% (1)
- English Language 2Document46 pagesEnglish Language 2Mara Foresti100% (1)
- Foutsizoglou 2017 LipDocument3 pagesFoutsizoglou 2017 LippsdsportsdocNo ratings yet
- Triptico (The Tongue)Document2 pagesTriptico (The Tongue)Aldo PalominoNo ratings yet
- Pmfadj17 Ageing Lip FoutsizoglouDocument3 pagesPmfadj17 Ageing Lip FoutsizoglouIkhsan DaniNo ratings yet
- CH08 - Pass01Document46 pagesCH08 - Pass01Aini AngelaNo ratings yet
- Mels. LESSON 1 WORKBOOK para ExamenDocument3 pagesMels. LESSON 1 WORKBOOK para ExamenMaría Elena López SuárezNo ratings yet
- EssaysDocument176 pagesEssaysppdzssx7ghNo ratings yet
- Wa0017.Document38 pagesWa0017.Reem ZohairNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Introduction To Linguistics (FINAL TERM)Document7 pagesReviewer in Introduction To Linguistics (FINAL TERM)Aira MaeNo ratings yet
- Trans Savi Oto Lec 07 Anatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity and Pharynx 1st SemDocument16 pagesTrans Savi Oto Lec 07 Anatomy and Physiology of Oral Cavity and Pharynx 1st SemJoherNo ratings yet
- The Articulatory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Articulatory SystemDianne MaeNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive SystemCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- Mouth Labio Anatomy 20233 en InglesDocument7 pagesMouth Labio Anatomy 20233 en InglesraxNo ratings yet
- Mammalian System-01 (Digestive System)Document35 pagesMammalian System-01 (Digestive System)Saumya99No ratings yet
- Phonetix and LalalaDocument23 pagesPhonetix and LalalaDaniel ArnaldosNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Considerations of Speech in Complete DentureDocument4 pagesProsthodontic Considerations of Speech in Complete DentureAnurtha AnuNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument162 pagesTongueDevendra ChhonkarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of SpeechDocument13 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Speechvictor amariteiNo ratings yet
- Ent Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyDocument7 pagesEnt Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyAileen EmyNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument8 pagesPhoneticsVeronica MorarNo ratings yet
- B-M of Human Teeth - 1Document10 pagesB-M of Human Teeth - 1Magd NabilNo ratings yet
- PHONOLOGY - Organ of SpeechDocument15 pagesPHONOLOGY - Organ of SpeechAmir HakiemNo ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- Periodontium NotesDocument12 pagesPeriodontium NotesClarisse Mendoza100% (1)
- Clinical Significance of Dental Anatomy, Histology, Physiology, and Occlusion PDFDocument5 pagesClinical Significance of Dental Anatomy, Histology, Physiology, and Occlusion PDFBrenna SalomonNo ratings yet
- RT Basics Digestive SystemDocument88 pagesRT Basics Digestive Systemmaricar paracadNo ratings yet
- OrgansDocument15 pagesOrgansКотик КотикNo ratings yet
- Presentation - English MedicineDocument9 pagesPresentation - English MedicineDion MiftarajNo ratings yet
- m1 - m2 Oral OccluDocument16 pagesm1 - m2 Oral OccluJane Krystia TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Temas SelectosDocument5 pagesTemas SelectosJuan Carlos Namoc GuerraNo ratings yet
- Biology of Normal PeriodontiumDocument80 pagesBiology of Normal PeriodontiumAmmar Hussain MemonNo ratings yet
- Role of Oral Musculature in Development of OcclusionDocument61 pagesRole of Oral Musculature in Development of OcclusionLakshmi Vamadevan0% (1)
- Oral Mucous MembraneDocument227 pagesOral Mucous MembraneDR. ISHITA SINGHALNo ratings yet
- Paraoral TissuesDocument5 pagesParaoral TissuesRosette Go0% (1)
- Tongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDocument100 pagesTongue and Its Role in Pros Tho Don TicsDr Mohit Dhawan100% (18)
- Articulators Above The Larynx KEL 2Document10 pagesArticulators Above The Larynx KEL 2Della Melati SukmaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Ontent Earning CtivityDocument18 pagesThe Digestive System: Ontent Earning CtivityCamille Ann Faigao FamisanNo ratings yet
- Development and Anatomy of The Tongue2Document11 pagesDevelopment and Anatomy of The Tongue2Dr-AHmad Fasfous AL-QaisiNo ratings yet
- L7 Stomatognathic SystemDocument29 pagesL7 Stomatognathic SystemJu JuNo ratings yet
- L. 10 The Oral CavityDocument79 pagesL. 10 The Oral CavityAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- Gi BNSDocument117 pagesGi BNSBibika MallaNo ratings yet
- Gingival Epithelium: Aathira VijayakumarDocument137 pagesGingival Epithelium: Aathira VijayakumarAathira MenonNo ratings yet
- Odontogenesis NotesDocument14 pagesOdontogenesis NotesClarisse Mendoza100% (1)
- Intraoral Soft Tissue Anatomy: Morphology 115Document57 pagesIntraoral Soft Tissue Anatomy: Morphology 115Asrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Oral Cavity: Objectives For This ExerciseDocument18 pagesDigestive System: Oral Cavity: Objectives For This ExerciseRias AldilaNo ratings yet
- Oral Physiology and OcclusionDocument64 pagesOral Physiology and OcclusionFrances SyNo ratings yet
- Muscles of TongueDocument19 pagesMuscles of TongueShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedDocument57 pagesOral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedNada MohammedNo ratings yet
- Assignment Structure of Oral CavityDocument4 pagesAssignment Structure of Oral CavityNarjis BatoolNo ratings yet
- Articulators Itl Mod4Document2 pagesArticulators Itl Mod4Eve RulonaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Oral Medicine and Pathology 2010Document15 pagesClinical Oral Medicine and Pathology 2010Julio TorresNo ratings yet
- Vascular Supply and Innervation - The Cheeks Receives Its Arterial Blood SuppluDocument5 pagesVascular Supply and Innervation - The Cheeks Receives Its Arterial Blood SuppluSimina TanaseNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesDigestive SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Development of Tongue and PalateDocument79 pagesDevelopment of Tongue and PalateSanthoshi Reddy50% (2)
- Muscular Tube Lined With Mucous Membrane That Is Continuous With The External Skin at The Mouth and at The AnusDocument90 pagesMuscular Tube Lined With Mucous Membrane That Is Continuous With The External Skin at The Mouth and at The AnusRamaNo ratings yet
- Umk 2017 027Document30 pagesUmk 2017 027дашаNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnatomyDocument3 pagesDigestive System AnatomyJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Microdiseño CurricularDocument10 pagesMicrodiseño CurricularANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- 5 Week+02 - Semicolons - Writing+academic+englishDocument3 pages5 Week+02 - Semicolons - Writing+academic+englishANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- Colons: A.ppendix B P:unctuation Rules 285Document3 pagesColons: A.ppendix B P:unctuation Rules 285ANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- Writing Feedback ChartDocument2 pagesWriting Feedback ChartANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- 1 Week+01 - Commas - Writing+academic+englishDocument3 pages1 Week+01 - Commas - Writing+academic+englishANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- Listening Skills Practice: My Favorite Things - Exercises: 1. Preparation: MatchingDocument3 pagesListening Skills Practice: My Favorite Things - Exercises: 1. Preparation: MatchingANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- Live, Work or Have Lives: in CanadaDocument3 pagesLive, Work or Have Lives: in CanadaANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Saying HelloDocument4 pagesActivity 1 Saying HelloANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- There's A Pen in My Bag.: Guide Number 3 Activities Name: Angelly Daniela Martinez ChamorroDocument2 pagesThere's A Pen in My Bag.: Guide Number 3 Activities Name: Angelly Daniela Martinez ChamorroANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- P 158 Verb FormsDocument1 pageP 158 Verb FormsNancy Paulina GonzálezNo ratings yet
- PHONICSDocument48 pagesPHONICSNURUL AIN BINTI RAPIAN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- 2ndQEng10 - Performance Task With RubricsDocument2 pages2ndQEng10 - Performance Task With Rubricst3xxaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar United 10Document3 pagesEnglish Grammar United 10Christian Chuquicallata Z100% (3)
- Actividad Semana 5 Grado OctavoDocument8 pagesActividad Semana 5 Grado OctavoGabriel Garcia Esteban vianchaNo ratings yet
- Syntax - WikipediaDocument29 pagesSyntax - WikipediaHamza AfzalNo ratings yet
- The Lexical Syllabus: by Ana Marie D. CaseresDocument9 pagesThe Lexical Syllabus: by Ana Marie D. CaseresErnesto S. Caseres JrNo ratings yet
- Rule 1. Number Agreement: Billy and Jake Are Going To The MoviesDocument3 pagesRule 1. Number Agreement: Billy and Jake Are Going To The MoviesKenji CruzNo ratings yet
- 8 Plural Noun RulesDocument3 pages8 Plural Noun RulesHninn Oo WaiNo ratings yet
- Question Formation Indirect QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestion Formation Indirect QuestionsjanegrsNo ratings yet
- 2A GRAMMAR Verb Be (Plural) : We, You, They: ActivationDocument2 pages2A GRAMMAR Verb Be (Plural) : We, You, They: ActivationDanilo LiebertNo ratings yet
- CO - Q1 Oral Comm in Context SHS Module-7-FINALDocument19 pagesCO - Q1 Oral Comm in Context SHS Module-7-FINALJEANNISA NACION40% (5)
- ClosureProperties PDFDocument3 pagesClosureProperties PDFIshan JawaNo ratings yet
- Ten Lessons 1st Online Ed2Document79 pagesTen Lessons 1st Online Ed2MerajuddinNo ratings yet
- Homework Unit 10 Pag 122-125 Dennis - Paula PDFDocument5 pagesHomework Unit 10 Pag 122-125 Dennis - Paula PDFLEONCIO COSTILLANo ratings yet
- Les Verbes Réguliers enDocument3 pagesLes Verbes Réguliers enbanuNo ratings yet
- Writing A Close Analysis and Critical InterpretationDocument11 pagesWriting A Close Analysis and Critical InterpretationJALBEE MARIE ABDULRADZAKNo ratings yet
- k1 Reading GuideDocument5 pagesk1 Reading GuideJuno JavierNo ratings yet
- English Irregular NounsDocument35 pagesEnglish Irregular Nounsmay bondocNo ratings yet
- Theories in SLA (MCQS) - PDF - Second Language Acquisition - Second LanguageDocument52 pagesTheories in SLA (MCQS) - PDF - Second Language Acquisition - Second LanguageMahdNo ratings yet
- Translation Rules and ANN Based Model For English To Urdu Machine TranslationDocument12 pagesTranslation Rules and ANN Based Model For English To Urdu Machine TranslationM FNo ratings yet
- Pinyin (Mandarin) Lesson 4 - Telling Time 1Document1 pagePinyin (Mandarin) Lesson 4 - Telling Time 1Dngab01No ratings yet
- Group$ b2 g11 02 StemDocument3 pagesGroup$ b2 g11 02 StemYasmin MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH TEST UNIT #3 "Sports and Free Time Activities"Document3 pagesENGLISH TEST UNIT #3 "Sports and Free Time Activities"Ingrid E DuhaldeNo ratings yet
- English Connect 1 - Lesson 4Document9 pagesEnglish Connect 1 - Lesson 4Juliana AndradeNo ratings yet
- Lembar Kerja Peserta Didik Teks ProcedureDocument5 pagesLembar Kerja Peserta Didik Teks ProcedureNikeisha ArdhianaNo ratings yet
- The Development of Predicate According To Children's Syntactic AbilityDocument53 pagesThe Development of Predicate According To Children's Syntactic Ability이현정No ratings yet
- GBGRR10000186 Future Forms Advanced Grammar ReferenceDocument5 pagesGBGRR10000186 Future Forms Advanced Grammar ReferencelolaSteinNo ratings yet
- Should/Shouldn't: Your Friend Is Sick and You Want To Give Him/her Advice So He/she Can Feel Better?Document3 pagesShould/Shouldn't: Your Friend Is Sick and You Want To Give Him/her Advice So He/she Can Feel Better?Diego Salas SerranoNo ratings yet