Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Articulators Itl Mod4
Uploaded by
Eve Rulona0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOriginal Title
ARTICULATORS-ITL-MOD4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesArticulators Itl Mod4
Uploaded by
Eve RulonaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
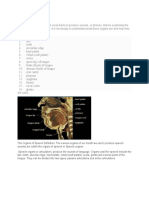
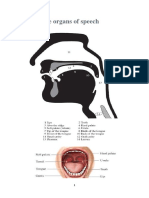
LESSON 4: PARTS OF THE VOCAL ORGAN
ARTICULATORS back of the tongue articulates at
this area to form velar sound. Its
◐ Lips – it is a visible body part at main function is to separate the
the mouth of humans and many nasal cavity from the oral cavity
animals. They serve for creating in to produce the oral speech
different sounds mainly the sounds.
labial, bilabial, and labio-dental.
◐ Uvula – it functions in tandem
◐ Teeth – it is a hard, calcified with the back of the throat, the
structure found in the jaws in palate and air coming up from the
front of the mouth. They are also lungs to create a number of
responsible for creating sounds guttural and other sounds. It is
mainly the labio-dental (which used to articulate a range of
the tongue touching the front teeth consonant sounds known as
| e.g., /f/ and /v/ and lingua-dental uvular consonants.
(e.g., /ð/ and /Ø/).
PHARYNX
◐ Tongue – it is the most
important articulator of speech. ◐ The part of the throat that is
Its wide variety of possible behind the mouth and nasal cavity
movements, it assists in forming and above the esophagus and the
the sound of speech. larynx, or the tubes going down to
the stomach and the lungs. The air
◐ Alveolar Ridge – it is a passes through here from the
structure that lies directly behind lungs into the mouth to produce a
the upper front teeth. It is the sound.
bumpy area which articulates with
the tongue for the articulation of LUNGS
alveolar sounds. It is also
considered as an important ◐ It provide the energy source for
structure in speech. the airflow. The airflow is by far the
most vital requirement for
◐ Hard Palate – is a thin producing speech sound since all
horizontal bony plate of the skull, speech sounds are made with
the concave part of the roof of the some movement of air.
mouth. The interaction between
the tongue and the hard palate LARYNX
is essential in the formation of ◐ It is an organ in the top of the
certain speech sounds. neck of tetrapods involved in
(notably /t/, /d/, and /j/). breathing, producing sound, and
◐ Velum (Soft Palate) – the lower protecting the trachea against food
part of the roof of the mouth. The aspirations. It is commonly called
LESSON 4: PARTS OF THE VOCAL ORGAN
the voice box. It houses the vocal
folds, and manipulates pitch and
volume, which is essential for
phonation.
VOCAL CORDS (VOCAL FOLDS)
◐ Are the folds of tissues in the
throat that are key in creating
sounds through vocalization. The
size of vocal cords affects pitch of
voice. It is open when breathing
and vibrating for speech or singing,
the folds are controlled via the
various nerve. Vocal cords vibrate
during the articulation of vowels
and of many consonants. It is
responsible for voice and
voicelessness of sounds. When
there is no vibration then that is
voiceless sound.
You might also like
- Organs of Speech & Their FunctionsDocument15 pagesOrgans of Speech & Their FunctionsMoljibok DanielNo ratings yet
- Master of Arts in Education Major in English The Speech OrgansDocument7 pagesMaster of Arts in Education Major in English The Speech OrgansMicka Mercado Dimaano100% (2)
- Speech Organs and Their Function:: LipsDocument2 pagesSpeech Organs and Their Function:: LipsAna MartinezNo ratings yet
- SPEECH ORGANS AND THEIR FUNCTION Class NotesDocument6 pagesSPEECH ORGANS AND THEIR FUNCTION Class Notesdark night100% (1)
- The Speech OrgannnDocument13 pagesThe Speech OrgannnMicka Mercado DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Human Speech OrgansDocument5 pagesHuman Speech OrgansLouise anasthasya altheaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Note On Speech Organ and Their Function. THR112Document18 pagesDetailed Note On Speech Organ and Their Function. THR112Samson BlessedNo ratings yet
- 4 Stages of Speech ProductionDocument17 pages4 Stages of Speech ProductionkiyomalvrNo ratings yet
- Part ADocument4 pagesPart AHassrina Hassan Basri100% (1)
- Speech Organs and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesSpeech Organs and Their Functionspuput apriani100% (3)
- Human Speech ApparatusDocument17 pagesHuman Speech ApparatusSharlin Jean PagoboNo ratings yet
- The Organs of SpeechDocument6 pagesThe Organs of SpeechAnonymous ToHeyBoEbX100% (1)
- Manner of Articulation: Speech OrganDocument7 pagesManner of Articulation: Speech OrganLipak gmailNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology PDFDocument6 pagesPhonetics and Phonology PDFanyi porfirioNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document44 pagesUnit 1Trần Lê Ngọc VyNo ratings yet
- Organs of Speech - 1Document3 pagesOrgans of Speech - 1Zhanna TerianikNo ratings yet
- Speech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageDocument7 pagesSpeech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageSherwin Ryan AvilaNo ratings yet
- Module NewDocument29 pagesModule NewIsha AmishaNo ratings yet
- Phonology and Speech Sounds ExplainedDocument24 pagesPhonology and Speech Sounds ExplainedAllene Salili HoncadaNo ratings yet
- ENG 112 NotesDocument9 pagesENG 112 Notes1972sns100% (1)
- Summary (Siti Ratna Sari - 187077 - 2018 B)Document2 pagesSummary (Siti Ratna Sari - 187077 - 2018 B)RatnaNo ratings yet
- Phonology1 1Document24 pagesPhonology1 1Mark Aldwin LopezNo ratings yet
- How The Speech Organs Work in English?Document18 pagesHow The Speech Organs Work in English?haithamNo ratings yet
- thae mechanic of speechDocument6 pagesthae mechanic of speechCyril Kaye DolorzoNo ratings yet
- SPEECH ORGAN INTRODUCTIONDocument9 pagesSPEECH ORGAN INTRODUCTIONEka MelyanaNo ratings yet
- HE Ocal Ract: The ArticulatorsDocument5 pagesHE Ocal Ract: The ArticulatorsSong Ji HyoNo ratings yet
- Mustaqim, M Shafiq Speech OrganDocument23 pagesMustaqim, M Shafiq Speech OrgankilopilasNo ratings yet
- The Organs of Speech ExplainedDocument11 pagesThe Organs of Speech ExplainedNicole Calisay VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument21 pagesOrgans of SpeechGenelyn BurgosNo ratings yet
- Ma. Martha Manette A. Madrid, EdDocument21 pagesMa. Martha Manette A. Madrid, EdFerreira AngelloNo ratings yet
- Vocal TractDocument16 pagesVocal TractniroelNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument3 pagesEnglishSaba AnatiNo ratings yet
- Part II, Lesson 3Document12 pagesPart II, Lesson 3Gomer Jay LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Phonology Full NotesDocument24 pagesPhonetics Phonology Full NotesMuralitharan Nagalingam100% (3)
- Organ SpeechDocument8 pagesOrgan SpeechRizky AnakampunNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Organs of SpeechDocument22 pagesPresentation On Organs of Speechseptiani zakariaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 PhoneticsDocument25 pagesTopic 2 PhoneticsRoger TerminatorNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Report 1-10-15Document47 pagesPhonetics Report 1-10-15Maria Victoria PadroNo ratings yet
- Essay Phonetics Question Number 2Document2 pagesEssay Phonetics Question Number 2Victor TanNo ratings yet
- Speech OrgansDocument4 pagesSpeech OrgansJoshua Basa100% (1)
- 1 - Articulatory System - Phonetics 1st YearDocument33 pages1 - Articulatory System - Phonetics 1st YearSoundes AzzedibeNo ratings yet
- Human Speech Mechanism and OrgansDocument37 pagesHuman Speech Mechanism and OrgansFahad U. SilonganNo ratings yet
- Speech OrgansDocument7 pagesSpeech OrgansFina NuratifaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsDocument15 pagesChapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsBearish PaleroNo ratings yet
- Fonetica Resumen Primer ParcialDocument11 pagesFonetica Resumen Primer Parcialemilse RodríguezNo ratings yet
- OrgansDocument15 pagesOrgansКотик КотикNo ratings yet
- Linguistics 2Document45 pagesLinguistics 2Bani AbdullaNo ratings yet
- The Organs of Speech: A Guide to Producing SoundsDocument2 pagesThe Organs of Speech: A Guide to Producing SoundsMariano SaabNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhoneticsDocument52 pagesIntroduction To PhoneticsMarco AntonioNo ratings yet
- Kel. 1Document29 pagesKel. 1Alisha Putri SetianiNo ratings yet
- Final Test PhonologyDocument10 pagesFinal Test Phonologynuha lathifahNo ratings yet
- How Speech Sounds Are Produced - Active and Passive Organs ExplainedDocument15 pagesHow Speech Sounds Are Produced - Active and Passive Organs ExplainedТаня БродаNo ratings yet
- Makalah Phonology Kelompok 2Document11 pagesMakalah Phonology Kelompok 2meldianto manugalaNo ratings yet
- Speech Organ ActivityDocument1 pageSpeech Organ ActivityJhunel Angel DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Phonetics IDocument40 pagesPhonetics Iサイ-ドさんNo ratings yet
- Resumen FinalDocument9 pagesResumen FinalmacarenaNo ratings yet
- The Spanish Phonological SystemDocument15 pagesThe Spanish Phonological SystemT of Eng100% (1)
- Report On Articulatory PhoneticsDocument4 pagesReport On Articulatory PhoneticsJobed EspantoNo ratings yet
- The physiology of language soundsDocument28 pagesThe physiology of language soundsDavina AzhaarNo ratings yet
- The Child-Voice in Singing: Treated from a physiological and a practical standpoint and especially adapted to schools and boy choirsFrom EverandThe Child-Voice in Singing: Treated from a physiological and a practical standpoint and especially adapted to schools and boy choirsNo ratings yet
- MA English Semester System 2012Document22 pagesMA English Semester System 2012Snobra Rizwan100% (1)
- Syllabi 2020 Japanese Language Courses PDFDocument58 pagesSyllabi 2020 Japanese Language Courses PDF海狸No ratings yet
- SEMANTICS: A STUDY OF MEANINGDocument4 pagesSEMANTICS: A STUDY OF MEANINGWayan Gandi100% (1)
- Expressing Your Opinion in FinnishDocument6 pagesExpressing Your Opinion in FinnishJ-m GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Shawn's Personal IDDocument3 pagesShawn's Personal IDVera CampinaNo ratings yet
- Angel Correa-Pedreros - LSA 3 Final Lesson Plan - DELTA Module 2Document11 pagesAngel Correa-Pedreros - LSA 3 Final Lesson Plan - DELTA Module 2ÁngelNo ratings yet
- hsk1 Exam h11330Document13 pageshsk1 Exam h11330Eric Hernán Cabezas Briones50% (2)
- MYP 5 Criterion C Strands For Oral ExamDocument2 pagesMYP 5 Criterion C Strands For Oral Examayaan.ahujaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense and Prepositions of PlaceDocument1 pagePresent Simple Tense and Prepositions of PlaceJHIMY PAREDESNo ratings yet
- English Tool KitDocument38 pagesEnglish Tool KitMarilou GONZALEZ100% (1)
- TensesDocument32 pagesTensesAkash AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 7a and 7b Grammar y ExcercisesDocument8 pages7a and 7b Grammar y Excercisesmariyan14No ratings yet
- QUIZ UNIT 7 & 8 - Revisión Del IntentoDocument6 pagesQUIZ UNIT 7 & 8 - Revisión Del IntentoKaren RicardoNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Writing A News ReportDocument1 pageRubric For Writing A News Reportdominic_dedNo ratings yet
- 3 Nirgianaki Et Al SETD 25Document9 pages3 Nirgianaki Et Al SETD 25Aimilia GalouniNo ratings yet
- 79 French ExpressionsDocument7 pages79 French ExpressionsTarun PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Context Clues InvestigationDocument26 pagesContext Clues InvestigationSAHARNo ratings yet
- Reading InterventionDocument20 pagesReading InterventionBryan MamucayNo ratings yet
- English5 Q2 W5 Cot1-VirgieDocument7 pagesEnglish5 Q2 W5 Cot1-VirgieVirginia Quiroz CunananNo ratings yet
- FINAL FOLA 1 COURSE SYLLABUS 1ST SEM 2021 2022 Ma Leslie Basallo 1Document10 pagesFINAL FOLA 1 COURSE SYLLABUS 1ST SEM 2021 2022 Ma Leslie Basallo 1norwyn.manloloyojrNo ratings yet
- Cheater'S Guide: Spanish Essentials For BeginnersDocument12 pagesCheater'S Guide: Spanish Essentials For BeginnersPetra Jobova100% (1)
- Presentation Peer Review FormDocument2 pagesPresentation Peer Review FormC Derick VarnNo ratings yet
- 50 Irregular Verb.sDocument2 pages50 Irregular Verb.sjavier cortes diaz0% (1)
- 2012 09 10 Simple Past Exercises - 1st EM (Web)Document3 pages2012 09 10 Simple Past Exercises - 1st EM (Web)Ednaldo RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Improving Students' Ability in Using Prepositions of Place Through Total Physical Response (TPR)Document66 pagesImproving Students' Ability in Using Prepositions of Place Through Total Physical Response (TPR)theaNo ratings yet
- English SubjectDocument11 pagesEnglish SubjectNelson IntopeNo ratings yet
- Hammink Guarani Pronominal ArgumentDocument22 pagesHammink Guarani Pronominal ArgumentmegabatNo ratings yet
- In A NutshellDocument2 pagesIn A NutshellAristotelis TzamalisNo ratings yet
- Presentperfect 2 Britishenglishstudentver 2Document3 pagesPresentperfect 2 Britishenglishstudentver 2Fray Cristhian BernalNo ratings yet