Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Geothermal Energy
Uploaded by
toshali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views9 pagesOriginal Title
geothermal
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views9 pagesWhat Is Geothermal Energy
Uploaded by
toshaliCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
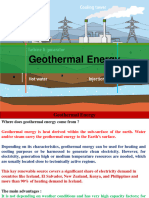
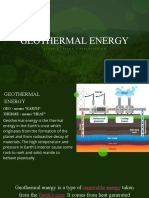
What is geothermal energy
• Geothermal energy- energy that comes from the
ground; power extracted from heat stored in the
earth
– Geo: earth
– Thermal: heat
• 70% comes from the decay of radioactive nuclei with long
half lives that are embedded within the Earth
• Some energy is from residual heat left over from Earths
formation.
• The rest of the energy comes from meteorite impacts
Different Geothermal Energy Sources
• Hot Water Reservoirs: As the name implies these are
reservoirs of hot underground water. There is a large
amount of them in the US, but they are more suited for
space heating than for electricity production.
• Natural Stem Reservoirs: In this case a hole dug into the
ground can cause steam to come to the surface. This type
of resource is rare in the US.
• Geopressured Reservoirs: In this type of reserve, brine
completely saturated with natural gas in stored under
pressure from the weight of overlying rock. This type of
resource can be used for both heat and for natural gas.
Different Geothermal Energy Sources
• Normal Geothermal Gradient: At any place on the planet, there is
a normal temperature gradient of +300C per km dug into the earth.
Therefore, if one digs 20,000 feet the temperature will be about
1900C above the surface temperature. This difference will be
enough to produce electricity. However, no useful and economical
technology has been developed to extracted this large source of
energy.
• Hot Dry Rock: This type of condition exists in 5% of the US. It is
similar to Normal Geothermal Gradient, but the gradient is
400C/km dug underground.
• Molten Magma: No technology exists to tap into the heat reserves
stored in magma. The best sources for this in the US are in Alaska
and Hawaii.
USAGE
Direct Electrical
• Heating homes • Dry steam
• Hot springs • Flash steam
• Greenhouse heating
• Binary cycle
• Food dehydration
plants
• Agriculture
– Crop drying
– Milk pasteurization
FOR ELECTRICITY
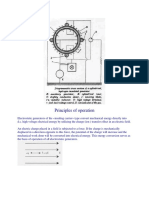
• Dry Steam Plants: These were the first type of plants
created. They use underground steam to directly turn the
turbines.
• Flash Steam Plants: These are the most common plants. These
systems pull deep, high pressured hot water that reaches
temperatures of 3600F or more to the surface. This water is
transported to low pressure chambers, and the resulting steam
drives the turbines. The remaining water and steam are then
injected back into the source from which they were taken.
• Binary Cycle Plants: This system passes moderately hot
geothermal water past a liquid, usually an organic fluid,
that has a lower boiling point. The resulting steam from
the organic liquid drives the turbines. This process does
not produce any emissions and the water temperature
needed for the water is lower than that needed in the Flash
Steam Plants (2500F – 3600F).
Environmental Effects/ Disadvantages
• Fluids drawn from the deep earth carry a mixture of gases
• Pollutants contribute to global warming and acid rain
• Construction of Plants can adversely affect land stability
• Sources may hold trace amounts of toxic
chemicals/mineral deposits
• Loud Noises
• Initial start up cost (expensive)
• Extracting large amounts of water can cause land
subsidence, and this can lead to an increase in seismic
activity. To prevented this the cooled water must be
injected back into the reserve in order to keep the water
pressure constant underground.
• Power plants that do not inject the cooled water back into
the ground can release H2S, the “rotten eggs” gas. This gas
can cause problems if large quantities escape because
inhaling too much is fatal.
Geothermal Positive Attributes
• Useful minerals, such as zinc and silica, can be extracted from
underground water.
• Geothermal energy is “homegrown.” This will create jobs, a
better global trading position and less reliance on oil producing
countries.
• US geothermal companies have signed $6 billion worth of
contracts to build plants in foreign countries in the past couple
of years.
• In large plants the cost is 4-8 cents per kilowatt hour. This cost
is almost competitive with conventional energy sources.
You might also like
- EES III 3.4 GeothermalDocument23 pagesEES III 3.4 Geothermalmbudhathoki3000No ratings yet
- Geothermal Power PlantDocument20 pagesGeothermal Power PlantCassiel CruzNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: A Renewable Source of Homegrown PowerDocument12 pagesGeothermal Energy: A Renewable Source of Homegrown PowerAxell CasimiroNo ratings yet
- IES Geothermal Energy PresentationDocument22 pagesIES Geothermal Energy PresentationPratyush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power PlantDocument38 pagesGeothermal Power PlantAvinash Jha100% (1)
- Geothermal EnergyDocument19 pagesGeothermal Energyapi-238832008No ratings yet
- Harnessing Earth's Internal HeatDocument19 pagesHarnessing Earth's Internal HeatThanujaNo ratings yet
- Non-Conventional Power GenerationDocument54 pagesNon-Conventional Power GenerationGirish Chandra MishraNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Sources of Energy: C.R M.ZaheerDocument67 pagesGeothermal Sources of Energy: C.R M.ZaheerAdeel MalikNo ratings yet
- YfytDocument19 pagesYfytNaveen Raj ENo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy PowerpointDocument19 pagesGeothermal Energy PowerpointgilangNo ratings yet
- GEOTHERMAL ENERGY PowerPointDocument25 pagesGEOTHERMAL ENERGY PowerPointRene RamiloNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power Generation ExplainedDocument74 pagesGeothermal Power Generation ExplainedMohd Arjhit AliNo ratings yet
- Geo-Thermal Power PlantDocument14 pagesGeo-Thermal Power PlantWaqas LiaquatNo ratings yet
- Energy From VolcanoesDocument16 pagesEnergy From VolcanoesJungkook567586No ratings yet
- Penugonda Keerthi. 08m61a0353. Mechanical Engineering SbitDocument30 pagesPenugonda Keerthi. 08m61a0353. Mechanical Engineering Sbitnaiduyogesh2No ratings yet
- Welcome: Viable Proposition To Harness The Fire Inside The Earth To Produce Geothermal Power in Large ScaleDocument14 pagesWelcome: Viable Proposition To Harness The Fire Inside The Earth To Produce Geothermal Power in Large Scalerashpal4No ratings yet
- Tidal & Geothermal EnergyDocument24 pagesTidal & Geothermal EnergyCIVILTEB69 AKSHATA SHINDENo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: Prepared by Aman Mishra Aarti Saini Harish Sharma Amit RajoriyaDocument12 pagesGeothermal Energy: Prepared by Aman Mishra Aarti Saini Harish Sharma Amit Rajoriyagauravkothari89No ratings yet
- NCES Unit 4Document89 pagesNCES Unit 4Kollan Manivardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Geothermal EnergyDocument31 pagesChapter 6 Geothermal EnergyMohammad Irfan AliNo ratings yet
- Guide to Geothermal Energy Sources and ApplicationsDocument21 pagesGuide to Geothermal Energy Sources and Applicationssudheer92No ratings yet
- GeothermalDocument49 pagesGeothermalYash ChorariaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Weeks 3-4Document39 pagesQuarter 3 Weeks 3-4Patricia SamsonNo ratings yet
- Labayo Geothermal-PowerDocument29 pagesLabayo Geothermal-PowerCarren MarquezNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 UNIT - 2 Geothermal Energy - Introduction.: Non-Conventional Resources and Energy System Subject Code: Tee 702Document46 pagesLecture - 2 UNIT - 2 Geothermal Energy - Introduction.: Non-Conventional Resources and Energy System Subject Code: Tee 702Ankit BaluniNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: Harnessing Heat Beneath Our FeetDocument16 pagesGeothermal Energy: Harnessing Heat Beneath Our FeetRavi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Caloocan City Geothermal ReportDocument6 pagesCaloocan City Geothermal ReportAnna Liza Lope - MotolNo ratings yet
- History and Types of Geothermal Power PlantsDocument40 pagesHistory and Types of Geothermal Power PlantsJM Garcia Bagangan0% (1)
- Geo ThermalDocument19 pagesGeo Thermalmahboob alamNo ratings yet
- Geothermal EnergyDocument19 pagesGeothermal EnergyGanesh harikantraNo ratings yet
- GeothermalDocument16 pagesGeothermalBlythe W. EmpizoNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: A Seminar Report OnDocument10 pagesGeothermal Energy: A Seminar Report OnDeepanNo ratings yet
- Geothermal EnergyDocument30 pagesGeothermal EnergySunny RajNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy NCESDocument71 pagesGeothermal Energy NCESAdarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- What Is Geothermal Energy?: Magma (Molten Rock) May Come Quite Close To The Surface Where The Crust HasDocument6 pagesWhat Is Geothermal Energy?: Magma (Molten Rock) May Come Quite Close To The Surface Where The Crust HasMichael RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Geothermal PlantDocument24 pagesGeothermal PlantVikasMantri100% (1)
- NCES Geothermal EnergyDocument33 pagesNCES Geothermal Energyv kondaNo ratings yet
- Geothermal EnergyDocument39 pagesGeothermal EnergyUsman MalikNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy PDFDocument18 pagesGeothermal Energy PDFHenri PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: Presented By: Amit Raj 09EE6406 InstrumentationDocument30 pagesGeothermal Energy: Presented By: Amit Raj 09EE6406 InstrumentationrajelecNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: Prepared By: Engr. Abigail Recacho (ME Elective 1)Document41 pagesGeothermal Energy: Prepared By: Engr. Abigail Recacho (ME Elective 1)MelbertNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Lesson 3.33.4Document22 pagesEarth Science Lesson 3.33.4Ana Marie Corales TabunarNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power PlantsDocument18 pagesGeothermal Power PlantsJustine Abanador100% (1)
- Reading GEOTHERMAL ENERGYDocument6 pagesReading GEOTHERMAL ENERGYErick ValdovinosNo ratings yet
- Geothermal PPT For Presentation)Document27 pagesGeothermal PPT For Presentation)anil patel0% (1)
- Geothermal EnergyDocument14 pagesGeothermal EnergyGelene TampariaNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy: A Sustainable SourceDocument17 pagesGeothermal Energy: A Sustainable SourceLakshmiprasad KadariNo ratings yet
- Geothermal EnergyDocument26 pagesGeothermal EnergyTolip. Tryon.No ratings yet
- Assignment Geothermal Energy .5Document6 pagesAssignment Geothermal Energy .5jawadaliNo ratings yet
- Energy?", 2018)Document10 pagesEnergy?", 2018)Laichi ArrietaNo ratings yet
- geothermal+Biofuel-2-REDocument4 pagesgeothermal+Biofuel-2-REخلدون مهند الحديثيNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy Lesson 8Document27 pagesGeothermal Energy Lesson 8heisenburg LolNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power PlantDocument31 pagesGeothermal Power PlantPao CastillonNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power PointDocument69 pagesGeothermal Power PointArielle Jean BarcenasNo ratings yet
- Energy Within Earth': Akhil Kumar 6-EE-005 EEEDocument16 pagesEnergy Within Earth': Akhil Kumar 6-EE-005 EEEAkhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Geothermal EnergyDocument10 pagesGeothermal Energyarorarudransh2010No ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources: Tidal, Geothermal & BiomassDocument33 pagesRenewable Energy Sources: Tidal, Geothermal & BiomassA0913KHUSHI RUNGTANo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power Plants 2023Document17 pagesGeothermal Power Plants 2023keiraahernandoNo ratings yet
- Highlight Read Headings Read Questions Short Notes and Summary Graphs, PhotosDocument1 pageHighlight Read Headings Read Questions Short Notes and Summary Graphs, PhotostoshaliNo ratings yet
- Kupdf Com Electric Drives by GK Dubey PDFDocument54 pagesKupdf Com Electric Drives by GK Dubey PDFtoshaliNo ratings yet
- Eee New SyllabuspdfDocument15 pagesEee New SyllabuspdftoshaliNo ratings yet
- Open Source OpportunitiesDocument7 pagesOpen Source OpportunitiestoshaliNo ratings yet
- NIT MIZORAM BTECH SYLLABUS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGDocument32 pagesNIT MIZORAM BTECH SYLLABUS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGtoshaliNo ratings yet
- Thermal P0Wer PlantDocument24 pagesThermal P0Wer PlanttoshaliNo ratings yet
- Database FundamentalsDocument32 pagesDatabase FundamentalstoshaliNo ratings yet
- Final Syllabus B Tech BOS 28 March 2016Document40 pagesFinal Syllabus B Tech BOS 28 March 2016Ruatfela PachuauNo ratings yet
- Power System Operation & ControlDocument73 pagesPower System Operation & ControlDr. Moh DoshanNo ratings yet
- Btech Course StructureDocument5 pagesBtech Course StructuretoshaliNo ratings yet
- OceanDocument5 pagesOceantoshaliNo ratings yet
- Hydr0Gen As EnergyDocument14 pagesHydr0Gen As EnergytoshaliNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase VSI Fed IM DrivesDocument4 pages3-Phase VSI Fed IM DrivestoshaliNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier Fed DC DrivesDocument3 pagesSingle Phase Full-Wave Controlled Rectifier Fed DC DrivestoshaliNo ratings yet
- Felici GeneratorDocument3 pagesFelici GeneratortoshaliNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Drive QuestionDocument2 pagesInduction Motor Drive QuestiontoshaliNo ratings yet
- Rating and Heating of Motors: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramDocument14 pagesRating and Heating of Motors: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramtoshaliNo ratings yet
- CSDocument126 pagesCSGoutam GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic of Electric Drives: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramDocument15 pagesDynamic of Electric Drives: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramtoshaliNo ratings yet
- Dynamic of Electric Drives: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramDocument21 pagesDynamic of Electric Drives: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramtoshaliNo ratings yet
- Rating and Heating of Motors: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramDocument16 pagesRating and Heating of Motors: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramtoshaliNo ratings yet
- Power System Nagrath Kothari SolutionsDocument88 pagesPower System Nagrath Kothari SolutionsChandra Sekhar Chebiyyam81% (16)
- Renewable Sources of EnergyDocument48 pagesRenewable Sources of EnergytoshaliNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electric Drives: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Electric Drives: by Dr. P.K Biswas Asst. Professor Department of Electrical Engineering NIT MizoramtoshaliNo ratings yet
- Test UploadDocument1 pageTest UploadtoshaliNo ratings yet
- Presentation 01Document28 pagesPresentation 01Rexona KhanomNo ratings yet
- Ganoderma laccase optimizationDocument9 pagesGanoderma laccase optimizationRajeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Silver Clusters in Zeolites: Structure, Stability and PhotoactivityDocument1 pageSilver Clusters in Zeolites: Structure, Stability and PhotoactivityJan HermannNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersDocument2 pagesCourse Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersbillNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, Mathematics & Physics: All India Internal Test SeriesDocument15 pagesChemistry, Mathematics & Physics: All India Internal Test Seriesmadhav aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Colorimeter Principle PDFDocument2 pagesColorimeter Principle PDFNicholasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document6 pagesExperiment 6Sobana Kanthi33% (3)
- p095 Re Struct 07 PCDocument12 pagesp095 Re Struct 07 PCmidhungbabu88No ratings yet
- Biotechnology Reviewer - Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Reviewer - Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationMaribeth VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Comenius - CodDocument13 pagesComenius - CodsridharancNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Gas Flowmeters For Permanent Installation in Hazardous AreasDocument31 pagesUltrasonic Gas Flowmeters For Permanent Installation in Hazardous AreasrudrakrNo ratings yet
- PDS-POLYKEN-1027-V1-AUG17 - AARPS-0972 PrymerDocument2 pagesPDS-POLYKEN-1027-V1-AUG17 - AARPS-0972 PrymerJoel SaucedoNo ratings yet
- Havells Wire Catalogue June 2021Document28 pagesHavells Wire Catalogue June 2021Lp BatNo ratings yet
- AJODO Eliades2006 - Orthodontic Materials Research and Applications Part 1-Current Status and Projected Future Developments in Bonding and Adhesives.Document7 pagesAJODO Eliades2006 - Orthodontic Materials Research and Applications Part 1-Current Status and Projected Future Developments in Bonding and Adhesives.drgeorgejose7818No ratings yet
- Clay Mineral Cements in SandstonesDocument3 pagesClay Mineral Cements in Sandstonesandrea.cipagautaNo ratings yet
- Cyclones ExerciseDocument4 pagesCyclones ExerciseValeria cNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument12 pagesResearch PaperKiran Niazi100% (1)
- 1967-Gupta-Outgassing From Epoxy Resins and Methods For Its ReductionDocument3 pages1967-Gupta-Outgassing From Epoxy Resins and Methods For Its ReductionroxanaNo ratings yet
- B705 Acpt1003Document3 pagesB705 Acpt1003taya1401No ratings yet
- Mesh Convergence Study Using ANSYSDocument2 pagesMesh Convergence Study Using ANSYSEric Borg SaywellNo ratings yet
- 31.PEAK Depressurization RATEDocument1 page31.PEAK Depressurization RATEDILIP MATALNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Sublimation and Melting Point DeterminationDocument4 pagesExperiment 3: Sublimation and Melting Point Determinationjane de leonNo ratings yet
- Astm A999a999mDocument12 pagesAstm A999a999mHammadNo ratings yet
- Wetland Assessment in KampalaDocument9 pagesWetland Assessment in KampalaBonny OgwalNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Protein DeterminationDocument5 pagesExp 2 Protein DeterminationNur Fadhilah100% (1)
- Heat loss and fluid temperature calculation for buried insulated and non-insulated oil pipelinesDocument34 pagesHeat loss and fluid temperature calculation for buried insulated and non-insulated oil pipelinesselisenNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Testing Method Level II QuestionsDocument14 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing Method Level II Questionskingston50% (2)
- Msds - Marpozol W-505 (GHS) Eng 130409Document5 pagesMsds - Marpozol W-505 (GHS) Eng 130409Syafarul Mohammad100% (1)
- Msds Icr 122 LSFDocument12 pagesMsds Icr 122 LSFWisnu AbaraiNo ratings yet
- PSA Oxygen Generator: Typical ApplicationsDocument2 pagesPSA Oxygen Generator: Typical ApplicationsRaghu Vir ArjampudiNo ratings yet