Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revision 3 - Neurotransmitters - Ananya Achanta
Uploaded by
AnanyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision 3 - Neurotransmitters - Ananya Achanta
Uploaded by
AnanyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision 3 – Neurotransmitters – Ananya Achanta
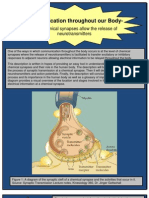
1. I) Soma/cell body
II) Dendrite
III) Axon
IV) Myelin sheath
V) Pre-synaptic axon terminal
2. When an action potential reaches the axon, the release of the neurotransmitters is
triggered.
Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into the synaptic cleft between the
sending and receiving neurons.
The neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft to bind to the receptor on the post-
synaptic neuron.
3. Excitatory neurons promote the firing of action potentials across the neuron.
Inhibitory neurons inhibit the firing of action potentials across the neuron.
4. They diffuse across the synaptic cleft.
They then bind to the receptors on the post-synaptic neuron to propagate the
transmission of action potentials across neurons.
5. They do not describe the role of cultural and cognitive functions on behavior.
It is overly reductionist and does not effectively detail complex emotions such as love.
6. This means it triggers a biological response that is similar to that of serotonin.
This is because it binds to the receptor of serotonin like serotonin does, making the
biological response also similar.
7. It is used to pinpoint the exact effect of acetylcholine as it can be administered to
participants of a study in order to form a control group.
This allows a clear IV and DV to be established, creating a clear cause-and-effect
response.
You might also like
- Technical DescriptionDocument8 pagesTechnical Descriptioncool_comic88100% (1)
- SynapseDocument12 pagesSynapseSweety DhillonNo ratings yet
- Coursematerial 150Document67 pagesCoursematerial 150Endar Wahyu SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience of Behaviors and ExperienceDocument13 pagesNeuroscience of Behaviors and ExperienceAllison MaañoNo ratings yet
- NeuronsDocument24 pagesNeuronsKen Ross ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document3 pagesLecture 3Mahreen NoorNo ratings yet
- General Physiology of SynapsesDocument30 pagesGeneral Physiology of SynapsesSanchezNo ratings yet
- Intro, PSCDocument4 pagesIntro, PSCEdgar SantosNo ratings yet
- Brains Bodies Behaviour (Psychology)Document18 pagesBrains Bodies Behaviour (Psychology)Cassia LmtNo ratings yet
- Afferent and Efferent Neurone DifferencesDocument2 pagesAfferent and Efferent Neurone DifferencesONG JUN YAO MoeNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument69 pagesCoordination and ResponseRegis WachenukaNo ratings yet
- Lecture - To Understand The Animal Behaviour We Have To Study The Different Neurone Cell CircuitsDocument2 pagesLecture - To Understand The Animal Behaviour We Have To Study The Different Neurone Cell CircuitsSauri BirriNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument7 pagesBiological Bases of BehaviorSANTHOSH KUMAR T MNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument7 pagesBiological Bases of BehaviorT M Santhosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PowerpointDocument39 pagesNervous System PowerpointManveer SidhuNo ratings yet
- Alde Annieska Learning Journal 2Document5 pagesAlde Annieska Learning Journal 2Maria AnnieskaNo ratings yet
- Neuron Structure and Function ExplainedDocument9 pagesNeuron Structure and Function Explainedvpilania2008100% (1)
- Biological basis of behaviorDocument44 pagesBiological basis of behaviorAarohi PatilNo ratings yet
- Question 3 & 4Document15 pagesQuestion 3 & 4Arslan Muhammad EjazNo ratings yet
- Nervous System QuestionnaireDocument11 pagesNervous System QuestionnaireHashley CastellyNo ratings yet
- Coordinadtion Studysheet.Document32 pagesCoordinadtion Studysheet.wafa elias100% (1)
- 5 SynapsesDocument60 pages5 Synapsesrosario gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Biological PerspectiveDocument39 pagesChapter 2 The Biological PerspectiveSULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- Week 10 BioDocument7 pagesWeek 10 BioTaze UtoroNo ratings yet
- Basic, By-The-Book Questions: (Answer: Cell Body (Or Soma), Dendrites, AxonsDocument7 pagesBasic, By-The-Book Questions: (Answer: Cell Body (Or Soma), Dendrites, AxonsDaph H.No ratings yet
- PsychologyDocument16 pagesPsychologyhasti1taaNo ratings yet
- Psy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourDocument42 pagesPsy121 - Psychobiological Determinants of BehaviourLarry UdehNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Nervous System: Lesson 1Document41 pagesStructure of The Nervous System: Lesson 1Samuel ThangarajanNo ratings yet
- Define The Following TermsDocument10 pagesDefine The Following TermsMinNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Review Answer KeyDocument18 pagesNervous System Review Answer Keydanieljohnarboleda67% (3)
- Bio Notes SynapseDocument4 pagesBio Notes SynapseLeeroy MafuruseNo ratings yet
- Synapse transmission processDocument7 pagesSynapse transmission processSinan Sa100% (1)
- C&B Chapt 2Document29 pagesC&B Chapt 2apfelbaum11122No ratings yet
- Worksheet Nervous System #2 Physiology: Neurons: Dendrites The SomaDocument2 pagesWorksheet Nervous System #2 Physiology: Neurons: Dendrites The SomaHAA-BEENo ratings yet
- PSYC 223 Lecture 3Document71 pagesPSYC 223 Lecture 3Bernard AnaneNo ratings yet
- CNS NoteDocument203 pagesCNS NoteAhmad Khair Ahmad BazliNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesCoordination and Responsedawn baniNo ratings yet
- Pocket_Companion_to_Guyton_and_Hall_Textbook_of_Medical_Physiology - ExportedDocument7 pagesPocket_Companion_to_Guyton_and_Hall_Textbook_of_Medical_Physiology - Exportedhassnfiras04No ratings yet
- 4.nervous System IDocument12 pages4.nervous System IPatricia TeyeNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument74 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourytsrajalmaharjanNo ratings yet
- Psychology 114 Biology of BehaviorDocument21 pagesPsychology 114 Biology of BehaviorruandreNo ratings yet
- 2008 Advances in Fetal Neurophysiology Jaypee JournalDocument14 pages2008 Advances in Fetal Neurophysiology Jaypee JournalDamara GardelNo ratings yet
- Unit-9 NERVOUS SYSTEMDocument37 pagesUnit-9 NERVOUS SYSTEMAmrita RanaNo ratings yet
- Biology of Nervous CoordinationDocument24 pagesBiology of Nervous CoordinationSharina GeraldNo ratings yet
- DONE BIO MOD Nervous System PDFDocument9 pagesDONE BIO MOD Nervous System PDFCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- The Bases of Human BehaviourDocument48 pagesThe Bases of Human BehaviourShrutiNo ratings yet
- Ch08 Nervous SystemDocument62 pagesCh08 Nervous SystemDanna Loize Noble LazaroNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsIrene Caballero PicazoNo ratings yet
- The 3 Main Sources of Human BehaviourDocument46 pagesThe 3 Main Sources of Human BehaviourShrutiNo ratings yet
- Biology - Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesBiology - Coordination and ResponseMiguel HallNo ratings yet
- 9.00 Exam 1 Notes: KOSSLYN CHAPTER 2 - The Biology of Mind and Behavior: The Brain in ActionDocument12 pages9.00 Exam 1 Notes: KOSSLYN CHAPTER 2 - The Biology of Mind and Behavior: The Brain in ActiondreamanujNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Hhmi Electrical Activity of NeuronsDocument2 pagesKami Export - Hhmi Electrical Activity of NeuronsKylie Wimbish0% (1)
- Neurology Notes Reviewed DAYS 1-11Document71 pagesNeurology Notes Reviewed DAYS 1-11Spark LincolnNo ratings yet
- Neuro Transm I SoresDocument5 pagesNeuro Transm I SoresPompeyo MedinaNo ratings yet
- Synapse & NeurotransmissionDocument8 pagesSynapse & NeurotransmissionAhmed OudahNo ratings yet
- Irritability Part IDocument18 pagesIrritability Part IYanique JonesNo ratings yet
- RSC Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesRSC Nervous SystemDurre shahwarNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument86 pagesGen BioPaul MagbagoNo ratings yet
- SAQ On Cultural DimensionsDocument1 pageSAQ On Cultural DimensionsAnanyaNo ratings yet
- Cultural and Behavior SAQ and ERQ OutlinesDocument2 pagesCultural and Behavior SAQ and ERQ OutlinesAnanyaNo ratings yet
- SAQ - Multi Store Memory ModelDocument1 pageSAQ - Multi Store Memory ModelAnanyaNo ratings yet
- IB - Study Plan - Psychology, Chemistry and BiologyDocument11 pagesIB - Study Plan - Psychology, Chemistry and BiologyAnanyaNo ratings yet
- English Paper 1 - November 2017Document5 pagesEnglish Paper 1 - November 2017AnanyaNo ratings yet