Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S07 13
S07 13
Uploaded by
John WIck0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views1 page1. The document summarizes pricing and sales decisions for Madison products in the US, UK, and Japanese markets.
2. It provides information on unit costs, exchange rates, demand functions by country, and equivalent prices in US dollars.
3. The pricing decisions result in sales that fully utilize the 3000 unit capacity constraint but leave incentive for savvy customers to purchase in the UK where prices are lowest in US dollar terms.
Original Description:
asd asd asd a fg dfhdfgh fhjdgj dfgh ef grtg erg sfgsdfb bnbserge fgbsdfgbdfghdgh fgh
Original Title
S07_13
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document summarizes pricing and sales decisions for Madison products in the US, UK, and Japanese markets.
2. It provides information on unit costs, exchange rates, demand functions by country, and equivalent prices in US dollars.
3. The pricing decisions result in sales that fully utilize the 3000 unit capacity constraint but leave incentive for savvy customers to purchase in the UK where prices are lowest in US dollar terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views1 pageS07 13
S07 13
Uploaded by
John WIck1. The document summarizes pricing and sales decisions for Madison products in the US, UK, and Japanese markets.
2. It provides information on unit costs, exchange rates, demand functions by country, and equivalent prices in US dollars.
3. The pricing decisions result in sales that fully utilize the 3000 unit capacity constraint but leave incentive for savvy customers to purchase in the UK where prices are lowest in US dollar terms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
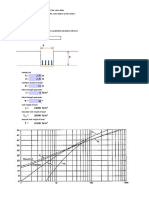
A B C D E F G H I J K
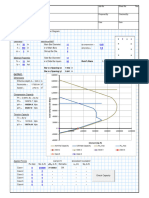
1 Madison pricing problem in U.S., UK, and Japanese markets
2
3 U.S. UK Japan
4 Unit cost 50 40.984 5181.347
5
6 ($/£) ($/¥)
7 Exchange rates 1.22 0.00965
8
9 Parameters of demand functions
10 U.S. UK Japan
11 Constant 19200000 10933620 15003380400
12 Elasticity -2 -2.2 -1.9
13
14 Pricing and sales decisions
15 U.S. UK Japan Equivalent prices in $
16 Price (in local currencies) 99.83 75.00 12317.72 99.83 91.50 118.87
17 Demand 1926.71 819.67 253.62
18 >= >= >=
19 Sales 1926.71 819.67 253.62 Partb:
Part b: All
Allof
of the
thecapacity
capacity isisused
used when
whencapacity
capacity isis
3000.However,
3000. However,ififyou
youchange
changecell
cellD22
D22to to4000
4000and
and
20 rerunSolver,
rerun Solver,you
youwill
willsee
seethat
thatnot
notall
allcapacity
capacityisis
21 Capacity constraint Total sales Capacity used.
used.
22 3000.00 <= 3000
Partc:c: The
Part Theequivalent
equivalent prices
prices inin $$ shown
shownabove
above
23 indicatethat
indicate thatthere
thereisisan
anincentive
incentiveto tobuy
buyin
inthe
theUK.
UK.
24 Monetary summary Sosavvy
So savvycustomers
customerswill
willtry
tryto
totake
takeadvantage
advantageof
of
this,regardless
this, regardlessofof where
wheretheytheylive.
live.
25 U.S. UK Japan
26 Revenues (in local currencies) 192335.24 61474.63 3124006.64
27 Revenues (in $) 192335.24 74999.05 30146.66
28
29 Profit ($) $147,481
You might also like
- Holt Algebra 1 - Chapter 01 Test PDFDocument8 pagesHolt Algebra 1 - Chapter 01 Test PDFStanleyNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle ManagementDocument26 pagesProduct Life Cycle Managementnarasimha_gudiNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument7 pagesBearing CapacityRayodcNo ratings yet
- Business Model For CCTVDocument1 pageBusiness Model For CCTVabul abbasNo ratings yet
- Pricing Swap Default RiskDocument11 pagesPricing Swap Default RiskUmlol TitaniNo ratings yet
- ICT PD ArrayDocument1 pageICT PD ArrayMKT 503No ratings yet
- ADM BES Module 6 Marketing PlanDocument32 pagesADM BES Module 6 Marketing PlanVictoria Carumba100% (1)
- The Sandwich Shop Business PlanDocument85 pagesThe Sandwich Shop Business PlanKenji Bandivas71% (7)
- J.C. Penney's "Fair and Square" Pricing StrategyDocument6 pagesJ.C. Penney's "Fair and Square" Pricing StrategySachin KandloorNo ratings yet
- D 4 Development of Beam EquationsDocument1 pageD 4 Development of Beam EquationsAHMED SHAKERNo ratings yet
- Project Tableau V3Document173 pagesProject Tableau V3Sourav KumarNo ratings yet
- S07 14Document1 pageS07 14John WIckNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Update (Live) : 1,130,114 Cases and 60,114 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Outbreak - WorldometerDocument19 pagesCoronavirus Update (Live) : 1,130,114 Cases and 60,114 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Outbreak - Worldometernilton lialungaNo ratings yet
- PembukuanUMKM Trading V.1.1Document58 pagesPembukuanUMKM Trading V.1.1Arif ParabolaaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Update (Live) : 1,080,846 Cases and 58,120 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Outbreak - WorldometerDocument20 pagesCoronavirus Update (Live) : 1,080,846 Cases and 58,120 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Outbreak - Worldometernilton lialungaNo ratings yet
- 1st-Class PPT MergedDocument38 pages1st-Class PPT MergedgregeffwffeNo ratings yet
- 1st ClassDocument15 pages1st ClassgregeffwffeNo ratings yet
- Home Page - LordsmobilecartographDocument1 pageHome Page - LordsmobilecartographDrort RerNo ratings yet
- OTC Unilab ICS With Rented and Regular JAN 2023Document5 pagesOTC Unilab ICS With Rented and Regular JAN 2023Erica CarridoNo ratings yet
- New Concrete Shearwalls (Working)Document120 pagesNew Concrete Shearwalls (Working)parkerashNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement Design ToolDocument10 pagesFlexible Pavement Design ToolEga NugrahaNo ratings yet
- FM DoubtsDocument13 pagesFM Doubtsaditi anandNo ratings yet
- Unit Costing Lecture 3Document5 pagesUnit Costing Lecture 3YashaswiNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument10 pagesFinancial Managementco.harshii.agrawalNo ratings yet
- Agn 2019Document4 pagesAgn 2019lidiNo ratings yet
- Forest Management With Linear Programming: Lecture 3 (4/3/2017)Document31 pagesForest Management With Linear Programming: Lecture 3 (4/3/2017)oNo ratings yet
- MEGA Smart Framework 0909 PlanDocument13 pagesMEGA Smart Framework 0909 PlanMega MicroNo ratings yet
- Breakeven Analysis: Fixed Cost $ Variable Cost $ Units Revenue $ Per Unit Dollars $ 1,500.00Document5 pagesBreakeven Analysis: Fixed Cost $ Variable Cost $ Units Revenue $ Per Unit Dollars $ 1,500.00dköalkNo ratings yet
- Break Even AnalysisDocument5 pagesBreak Even AnalysisNakib Jr.No ratings yet
- ACI Column PM Intax Diagram BOUNDARY ELEMENT - 2Document1 pageACI Column PM Intax Diagram BOUNDARY ELEMENT - 2dleechuyNo ratings yet
- 023Document108 pages023Angel A.S. DauriaNo ratings yet
- Amrt & DnetDocument3 pagesAmrt & DnetRaymond RaymondNo ratings yet
- Demand Curve Market Demand Worksheet 1 PDFDocument5 pagesDemand Curve Market Demand Worksheet 1 PDFSajith StephenNo ratings yet
- Project-Idi Shala-Dhadhamane & Obosha Multi Vi Llage Water Supply Project Pi Pe Di Stri Buti On Netw Ork For Aburahra KebeleDocument1 pageProject-Idi Shala-Dhadhamane & Obosha Multi Vi Llage Water Supply Project Pi Pe Di Stri Buti On Netw Ork For Aburahra KebeleMiko AbiNo ratings yet
- Aburahra PDFDocument1 pageAburahra PDFAbi DemeNo ratings yet
- Aburahra PDFDocument1 pageAburahra PDFMiko AbiNo ratings yet
- Diseño de Columnas de Concreto Basado en ACI 318-14Document1 pageDiseño de Columnas de Concreto Basado en ACI 318-14zenon mitha huarachiNo ratings yet
- SLAB DESIGN TO BS8110 WITH DEFLECTION From LotusDocument1 pageSLAB DESIGN TO BS8110 WITH DEFLECTION From LotusSumedha MayadunnaNo ratings yet
- Pivot Table 23Document8 pagesPivot Table 23Vineetha AdusumalliNo ratings yet
- Design of A SlaShortcutDDMbDocument16 pagesDesign of A SlaShortcutDDMbNaim SarkerNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Inside Mathcad - Programming - The For Loop PDFDocument13 pagesMathcad - Inside Mathcad - Programming - The For Loop PDFJéssica GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Bridge Truss Analysis ExampleDocument5 pagesBridge Truss Analysis ExampleARSLAN ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- EC63-822 Wheat People and The Plains - Supply Demand and MarkeDocument7 pagesEC63-822 Wheat People and The Plains - Supply Demand and MarkehrdksahniNo ratings yet
- Pricing Complementary ProductsDocument1 pagePricing Complementary ProductsJohn WIckNo ratings yet
- Heae The Cquivalent Cireuit Ih Fig: An R e CominedDocument1 pageHeae The Cquivalent Cireuit Ih Fig: An R e Cominedreymart cereneoNo ratings yet
- Petrofisika TM2209 W10Document25 pagesPetrofisika TM2209 W10Hafiizhoh HanafiaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Tutorial Week 6Document5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Tutorial Week 6Rajan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Talisman 4th Ed - The Cataclysm - RulebookDocument8 pagesTalisman 4th Ed - The Cataclysm - RulebookTony LeMesmerNo ratings yet
- Franklin 2018 SIP-PresentationDocument24 pagesFranklin 2018 SIP-PresentationRajat GuptaNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Order Picker (2000 KG)Document4 pagesHorizontal Order Picker (2000 KG)johnNo ratings yet
- S Eventh Semester B.E. Degree Examination, December 201 : Operations ResearchDocument7 pagesS Eventh Semester B.E. Degree Examination, December 201 : Operations ResearchBhimappa YadahalliNo ratings yet
- Rates of Man, Materials and Mark-UpsDocument104 pagesRates of Man, Materials and Mark-Upsnot aloneNo ratings yet
- 5323 Shafter Ave Oakland CA 94618 USADocument5 pages5323 Shafter Ave Oakland CA 94618 USAZain shabbirNo ratings yet
- Example Weibull Probability Plots Using The Weibull Excel ModelDocument2 pagesExample Weibull Probability Plots Using The Weibull Excel ModelAlexander Arenas JimenezNo ratings yet
- Target CostingDocument13 pagesTarget CostingEVERYTHING HERENo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Update (Live) 266,208 Cases and 11,187 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Outbreak - WorldometerDocument1 pageCoronavirus Update (Live) 266,208 Cases and 11,187 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Outbreak - WorldometerpopNo ratings yet
- Total Return (Potential)Document6 pagesTotal Return (Potential)Muhammad Fajrul IlmiNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Audiometers With SLM Type 2235 Bo0152 PDFDocument2 pagesCalibration of Audiometers With SLM Type 2235 Bo0152 PDFsinner86No ratings yet
- Recursos Vidrio Simple Arena Silice (Tonelada) 5 Carbonato de Sodio y Caliza (T) 2 Horas de Fucion 5 Costo USD 1800Document5 pagesRecursos Vidrio Simple Arena Silice (Tonelada) 5 Carbonato de Sodio y Caliza (T) 2 Horas de Fucion 5 Costo USD 1800Diego Mauricio Ospina OrtizNo ratings yet
- Caes MulticompressionDocument1 pageCaes MulticompressionhuskyjackNo ratings yet
- Universal OD Grinding - No PlanDocument1 pageUniversal OD Grinding - No PlanAzhar ImamNo ratings yet
- Копия marketing-plan-schedule-with-budget-tracker-and-dashboardDocument5 pagesКопия marketing-plan-schedule-with-budget-tracker-and-dashboardRoman8204No ratings yet
- 8 PPRA FormatDocument2 pages8 PPRA FormatEgo TaleNo ratings yet
- Ordering Decision With Quantity Discounts Inputs Quantity Discount Structure Range Names UsedDocument1 pageOrdering Decision With Quantity Discounts Inputs Quantity Discount Structure Range Names UsedCarol YouNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo Diseño A TensionDocument11 pagesEjemplo Diseño A TensionLucia MurilloNo ratings yet
- PLDI Week 02 X86liteDocument30 pagesPLDI Week 02 X86liteVictor ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Electricity Pricing Model Input Data Range Names UsedDocument3 pagesElectricity Pricing Model Input Data Range Names UsedJohn WIckNo ratings yet
- Pricing Complementary ProductsDocument1 pagePricing Complementary ProductsJohn WIckNo ratings yet
- Pricing Complementary Products: A B C D E F G H I J 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18Document3 pagesPricing Complementary Products: A B C D E F G H I J 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18John WIckNo ratings yet
- Electricity Pricing Model Range Names Used: Input DataDocument3 pagesElectricity Pricing Model Range Names Used: Input DataJohn WIckNo ratings yet
- Madison Pricing Problem in A UK Market: A B C D E F G H I 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16Document1 pageMadison Pricing Problem in A UK Market: A B C D E F G H I 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16John WIckNo ratings yet
- Rizal in USTDocument1 pageRizal in USTJohn WIckNo ratings yet
- Rizal in SpainDocument2 pagesRizal in SpainJohn WIckNo ratings yet
- CE - LiabilitiesDocument7 pagesCE - LiabilitiesJohn WIckNo ratings yet
- BLT 5a - FinalsDocument6 pagesBLT 5a - FinalsJohn WIckNo ratings yet
- Surname 1Document3 pagesSurname 1Paul NdegNo ratings yet
- Treasury ManagementDocument28 pagesTreasury ManagementmarifeNo ratings yet
- Monopoly & OligopolyDocument9 pagesMonopoly & OligopolytusharyevaleNo ratings yet
- Workshop Mod5-DerivativesDocument17 pagesWorkshop Mod5-DerivativesDave LuhrsNo ratings yet
- RETAIL Management: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesRETAIL Management: Multiple Choiceshilpashree_mbaNo ratings yet
- FF0146 01 Marketing Slides Template 16x9Document6 pagesFF0146 01 Marketing Slides Template 16x9sahaNo ratings yet
- Ans-Assignment QM 204.editedDocument9 pagesAns-Assignment QM 204.editedhamzaNo ratings yet
- CRM Unit 1 Notes Introduction To CRMDocument16 pagesCRM Unit 1 Notes Introduction To CRMKeerthi Priya100% (1)
- Bullwhip EffectDocument17 pagesBullwhip EffectSalamat AliNo ratings yet
- Cardinal Utility AnalysisDocument9 pagesCardinal Utility AnalysisVaibhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Marketing Practices in Nurjahan Edible OilDocument52 pagesMarketing Practices in Nurjahan Edible OilIstiak ThemoonNo ratings yet
- The CRM Strategy Development ProcessDocument30 pagesThe CRM Strategy Development ProcessMahmoud AffaraNo ratings yet
- Marketing Awarness Test Your KnowledgeDocument41 pagesMarketing Awarness Test Your KnowledgeThirrunavukkarasu R RNo ratings yet
- ConsumptionDocument18 pagesConsumptionRohit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Problem Formulation: A Problem Well Defined Is A Problem Half Solved!Document9 pagesProblem Formulation: A Problem Well Defined Is A Problem Half Solved!NipunNo ratings yet
- Utility, Indifference Curves Portfolio Theory - Investing in OneDocument38 pagesUtility, Indifference Curves Portfolio Theory - Investing in Oneisteaq ahamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Case Study - Not Sold OutDocument1 pageChapter 3 Case Study - Not Sold OutSagarika SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Aaker Et Al. 11th Edition PDFDocument13 pagesChapter 6 - Aaker Et Al. 11th Edition PDFCarlos Andres RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cognition, Competition, and Catallaxy in Memory of Friedrich August Von HayekDocument40 pagesCognition, Competition, and Catallaxy in Memory of Friedrich August Von HayekxiiiiNo ratings yet
- Five Forces Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesFive Forces Analysis WorksheetDanial Akbar RafsanjaniNo ratings yet
- Antero 161202180003Document15 pagesAntero 161202180003Faraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Continue Operations or Shut DownDocument2 pagesContinue Operations or Shut DownDivina Secretario0% (1)
- Porter's Five Forces of Competitive Position AnalysisDocument5 pagesPorter's Five Forces of Competitive Position AnalysisGilbert GarciaNo ratings yet