Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Machining (CHM) : Selective and Controlled Dissolution of
Uploaded by
Ankit OlaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Machining (CHM) : Selective and Controlled Dissolution of
Uploaded by
Ankit OlaCopyright:
Available Formats
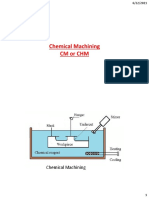
CHEMICAL MACHINING (CHM)
It is the process of material removal
using reactive chemical solutions through
selective and controlled dissolution of
workpiece material.
Common processing steps:
1. Preparing: pre-cleaning
2. Masking: Application of chemically resistive material
3. Etching: Exposure to etchant
4. Remove mask: stripping and cleaning
5. Finish: Inspection & post-processing
Etch Factor = Undercut/Depth of Cut
Processing Sequence of Step Etching
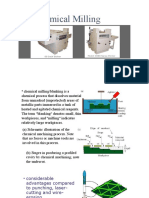
CHM Processes:
1. Chemical Milling
2. Chemical Blanking
3. Chemical Engraving
4. Chemical Polishing
Chemical Milling Chemical Blanking
CHEMICAL MACHINING (CHM)
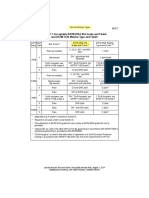
Masking Techniques
Sl Type Coating thickness (mm) Etching depth (mm) Tolerance (mm) Part size
No. (m)
1 Cut and peel 0.025-0.13 >1.5-13 ±0.13 - ±0.75 large
2 Screen printed <0.05 <=1.5 ±0.05 - ±0.18 <1.2x1.2
3 Photochemical <1.5 ±0.025- ±0.005 <0.9x1.5
Photochemical Machining (PCM)
A Clean Metal
B Photo-resist Coating
C Negative & Exposure
D Resist Developed & Partially Removed
E Partially Etched
F Fully Etched and Separated
The selection of proper maskant for a particular application is accomplished by
evaluating the job with respect to the six factors defined as follows.
The purpose of an etchant is to dissolve a metal by turning it into a metallic salt
CHEMICAL MACHINING (CHM)
Applications of CHM
1. Chemical machining using cut and peel masks usually involves very large workpieces. Like:
– Large turbine engine containment rings,
– Aluminium aircraft spars, wing skin, structural parts with numerous surface areas are
etched to be removed unnecessary metal for better strength to weight ratio.
2. Aluminium pressure vessel bulk heads are chemically milled using the cut-and-peel masking
technique.
3. Titanium alloy turbine engine and space shuttle components are chemically milled with specific
patterns designed to greatly reduce the weight of the component without compromising structural
integrity.
4. Racing can body weight is reduced by CHM. Range of high-performance car engine and
transmission components are chemically milled to reduce weight
Because chemical milling removes material from all surfaces simultaneously, the overall
processing time is only a fraction of what it would be if done by conventional milling.
5. Chemical blanking, which is most frequently performed by PCM is often a highly cost-effective
process when compared with mechanical blanking or stamping of thin sheet metal. Because die
cost is not encountered when using PCM, a saving of 10:1 can be realized. (only a one time
change for the photo master is required with PCM. Any design change can easily be incorporated
just by changing the photo master.)
6. High detailed engraving on front panel of equipment.
7. Aluminium vent screens of helicopter.
8. Integrated circuitry.
9. In one of the variations of chemically milling, the material can be tapered by controlling the rate
of withdrawal of the part from the etchant.
ADVANTAGES
• Many work-pieces can be etched simultaneously.
• All the surfaces are exposed to the chemical at the same time simultaneously.
• No distortion.
• Externally thin & delicate material can be worked without distortion.
• Low capital investment.
• Burr free.
• Tooling cost usually less.
DISADVANTAGES
• Chemical disposal is costly.
• Limited depth of cut.
• Workpiece must have homogeneous structure (metallurgical/ physical).
• Sharp radii difficult to produce.
• Skilled operators and good photographic facilities are required in PCM.
• Etchant vapors are quite corrosive.
You might also like
- Chemical MachiningDocument23 pagesChemical MachiningAbhishek Chadaga100% (6)
- Chemical MachiningDocument23 pagesChemical MachiningАбдельнасир АбдельрахманNo ratings yet
- B 36 Chemical MachiningDocument9 pagesB 36 Chemical MachiningEmmanuvel Joseph AjuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Machining (CM)Document28 pagesChemical Machining (CM)raghurockramNo ratings yet
- Chemical MachiningDocument5 pagesChemical MachiningomenNo ratings yet
- CHMDocument40 pagesCHMzeya_12345No ratings yet
- Chemicqalmachining 160807092633Document23 pagesChemicqalmachining 160807092633aalv2003No ratings yet
- Week 5 - Chemical Machining (CHM)Document39 pagesWeek 5 - Chemical Machining (CHM)Luis Gustavo PachecoNo ratings yet
- Chemical MachiningDocument39 pagesChemical MachiningAntoni tonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Machining CM or CHMDocument18 pagesChemical Machining CM or CHMSam prabhakarNo ratings yet
- Chemical MachiningDocument25 pagesChemical MachiningAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Processes: - Chemical Milling - Photochemical Milling - ElectropolishingDocument38 pagesChemical Processes: - Chemical Milling - Photochemical Milling - ElectropolishingvkrishnarajNo ratings yet
- BTL GCTDocument10 pagesBTL GCTMinh ChiếnNo ratings yet
- Chemical Machining ProcessesDocument2 pagesChemical Machining ProcessesMuhammadHamzaNo ratings yet
- PemtlogamDocument13 pagesPemtlogamAntoni tonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1:chemical Machining: Instructor: Omar Elmabrouk Engineer: Rania.A. Elrifai 2011/2012 SpringDocument29 pagesLecture 1:chemical Machining: Instructor: Omar Elmabrouk Engineer: Rania.A. Elrifai 2011/2012 SpringTAVI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Photo Chemical Machining (PCM)Document10 pagesPhoto Chemical Machining (PCM)ashishsinglaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Machining: Production TechnologyDocument6 pagesChemical Machining: Production TechnologyHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- CHM - New Edited Version-UnlockedDocument39 pagesCHM - New Edited Version-UnlockedTasdik TasinNo ratings yet
- Metallography Is Defined As The Study of Metal and Its AlloysDocument6 pagesMetallography Is Defined As The Study of Metal and Its AlloysbazilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document11 pagesChapter 13ZamhureenNo ratings yet
- Advanced Manufacturing EngineeringDocument35 pagesAdvanced Manufacturing EngineeringKrishnanunni SNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Abrasive Surface FinishingDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Abrasive Surface FinishingAnkett LahaseNo ratings yet
- Revised Chemical MachiningDocument23 pagesRevised Chemical MachiningAnkit vksNo ratings yet
- 9 - Nontraditional Machining (2hr-33 Slides)Document33 pages9 - Nontraditional Machining (2hr-33 Slides)Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Machining Iem-18-19Document7 pagesChemical Machining Iem-18-19RafiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Non-Traditional Machining ProcessesDocument40 pagesUnit 8: Non-Traditional Machining ProcessesManish Kumar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- A Report On: Abrasive Jet Machining: BY:-Akshay Gupta 10BME0345 G1 SlotDocument11 pagesA Report On: Abrasive Jet Machining: BY:-Akshay Gupta 10BME0345 G1 SlotAkshay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Machining Processes For Aircraft Parts Manufacturing (May 2019)Document105 pagesChemical Machining Processes For Aircraft Parts Manufacturing (May 2019)Luis Gustavo PachecoNo ratings yet
- Chemicalmachining 161205062610Document15 pagesChemicalmachining 161205062610Ring MasterNo ratings yet
- PYL726 2022 Lecture 29Document16 pagesPYL726 2022 Lecture 29piyushNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools and Devices For Special Technologies: Slovak University of TechnologyDocument23 pagesMachine Tools and Devices For Special Technologies: Slovak University of Technologyrajamannar322No ratings yet
- Lectut MIN-216 PDF UNIT 2 Advanced Manufacturing ProcessesDocument92 pagesLectut MIN-216 PDF UNIT 2 Advanced Manufacturing Processesvishal guptaNo ratings yet
- NTM Module 3Document12 pagesNTM Module 3RishiJpNo ratings yet
- NTM IntroductionDocument22 pagesNTM IntroductionvkrishnarajNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Metal Matrix Composite (MMC) Brake RotorDocument15 pagesAluminium Metal Matrix Composite (MMC) Brake RotorDEVANSH JAINNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Advanced Manufacturing ProcessesDocument100 pagesUNIT 2 Advanced Manufacturing ProcessesCHANDAN RAJNo ratings yet
- Chemical & Photochemical MachiningDocument16 pagesChemical & Photochemical MachiningAyush ChopraNo ratings yet
- PFM 2Document35 pagesPFM 2Mariam SherifNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentVivek Rampure KNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Machining ProcessesDocument64 pagesUnconventional Machining Processesdeepak kantipudiNo ratings yet
- 3421 Chemical and Electrochemical Separating ProcessesDocument18 pages3421 Chemical and Electrochemical Separating ProcessesupenderNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Machining Processes C. Devanathan-137-200Document64 pagesUnconventional Machining Processes C. Devanathan-137-200LokitoPaTlpvRomeroHernandezNo ratings yet
- Nontraditional Machining: Compiled By: Norliana Mohd AbbasDocument57 pagesNontraditional Machining: Compiled By: Norliana Mohd AbbasA TalkNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrications of Abrasive Jet Machine: Presented byDocument31 pagesDesign and Fabrications of Abrasive Jet Machine: Presented byAnuj TripathiNo ratings yet
- Photochem Ical Machin Ing by SK Afsar Ahmed 35000719030 Me-7Thsem Advanced Manufactur Ing Techno LogyDocument18 pagesPhotochem Ical Machin Ing by SK Afsar Ahmed 35000719030 Me-7Thsem Advanced Manufactur Ing Techno LogyAlam SkNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Jet MachiningDocument20 pagesAbrasive Jet Machiningsenthil kannan vNo ratings yet
- Non Conventional Machining MethodsDocument24 pagesNon Conventional Machining MethodsGaurav Nigam100% (1)
- ASE 02 FundamentalDocument62 pagesASE 02 FundamentalsriNo ratings yet
- AF3 Corrosion Prevention and Control - EgyptAir ReportDocument20 pagesAF3 Corrosion Prevention and Control - EgyptAir ReportmostafaNo ratings yet
- Mechaning AssignementDocument28 pagesMechaning AssignementWaseem AkramNo ratings yet
- UCMP Int 3 Scheme of EvaluationDocument9 pagesUCMP Int 3 Scheme of EvaluationananthakumarNo ratings yet
- 54 Lapping & Polishing Basics PDFDocument7 pages54 Lapping & Polishing Basics PDFNagi NayakNo ratings yet
- Machining Process 2Document10 pagesMachining Process 2hmoa2050No ratings yet
- Micro Machining-Module 3Document36 pagesMicro Machining-Module 3rejeesh_rajendranNo ratings yet
- Advance Machining ProcessDocument201 pagesAdvance Machining ProcessAnmol SharmaNo ratings yet
- Abrassive Jet Machining Main FileDocument34 pagesAbrassive Jet Machining Main FilearjunNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Mat Characterization (1) (1) - ExtractedDocument9 pagesLab Manual - Mat Characterization (1) (1) - ExtractedAdvay Singh raizadaNo ratings yet
- Design Guidelines for Surface Mount TechnologyFrom EverandDesign Guidelines for Surface Mount TechnologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Diesel Power Plant-1Document7 pagesDiesel Power Plant-1Ankit OlaNo ratings yet
- Solving A Real Life Problem: CFL/Bulb Remover Subject-Machine Design LabDocument10 pagesSolving A Real Life Problem: CFL/Bulb Remover Subject-Machine Design LabAnkit OlaNo ratings yet
- 1refrigeration and Air-ConditioningDocument39 pages1refrigeration and Air-ConditioningAnkit OlaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2Ankit OlaNo ratings yet
- ABRASIVE JET MACHINING ModellingDocument3 pagesABRASIVE JET MACHINING ModellingAnkit OlaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Machining (Usm)Document9 pagesUltrasonic Machining (Usm)Ankit OlaNo ratings yet
- Steel Defect GuideDocument15 pagesSteel Defect Guidegrd4100% (3)
- History and Govenrment 35 - 60Document26 pagesHistory and Govenrment 35 - 60scarletjane888No ratings yet
- RCSC Table 2.1 Nut and Washer TypesDocument1 pageRCSC Table 2.1 Nut and Washer TypesAdam JonesNo ratings yet
- High Tensile Steel 4140Document2 pagesHigh Tensile Steel 4140Lazzarus Az GunawanNo ratings yet
- MP 2Document8 pagesMP 2Empty DivineNo ratings yet
- High Effi Ciency Drilling in Various Types of Machining: SeriesDocument16 pagesHigh Effi Ciency Drilling in Various Types of Machining: SeriesnofearnemNo ratings yet
- Sealbond Etl-100: Epoxy Tank Lining (100% Solids) Solvent Free System Food GradeDocument2 pagesSealbond Etl-100: Epoxy Tank Lining (100% Solids) Solvent Free System Food GradegregNo ratings yet
- Machining Center'S CNC Control Programming ManualDocument182 pagesMachining Center'S CNC Control Programming ManualAndrei Broasca100% (1)
- AGC Catalogus Part 1Document8 pagesAGC Catalogus Part 1Gersom WurstenNo ratings yet
- ME6302 MFT FullDocument227 pagesME6302 MFT FullmonaNo ratings yet
- Paints ReportDocument2 pagesPaints ReportEm Israel Jr.No ratings yet
- AG FBE REPAIR S1401 REV5 Feb10Document3 pagesAG FBE REPAIR S1401 REV5 Feb10Ahmed FodaNo ratings yet
- Recent Mineral Processing PublicationsDocument12 pagesRecent Mineral Processing PublicationsDavid YuleNo ratings yet
- Wps 7018 SmawDocument1 pageWps 7018 SmawErick VazquezNo ratings yet
- GravureDocument491 pagesGravureRD Gravure Toyo InkNo ratings yet
- Norton Saint Gobian AbrasivesDocument2 pagesNorton Saint Gobian Abrasivesagniva dattaNo ratings yet
- Table Air Ean English Imperial TablesDocument2 pagesTable Air Ean English Imperial TablesKucing SayuNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resistance and Lifetime of Polyimide-B-Polyurea Novel Copolymer CoatingsDocument10 pagesCorrosion Resistance and Lifetime of Polyimide-B-Polyurea Novel Copolymer CoatingsmiguelNo ratings yet
- Pipes - Below - 405 - With - Benddies - in Detail PDFDocument1 pagePipes - Below - 405 - With - Benddies - in Detail PDFnikhiljith o uNo ratings yet
- 5 Machinability and Machining EconomicsDocument48 pages5 Machinability and Machining Economicssakali aliNo ratings yet
- 34 CR Mo 4Document2 pages34 CR Mo 4ceca nikolicNo ratings yet
- Education Articles .......Document269 pagesEducation Articles .......Bali GondalNo ratings yet
- Milling Tools and Inserts 2004 PDFDocument122 pagesMilling Tools and Inserts 2004 PDFPalade LucianNo ratings yet
- Brochure EN Ver - Thai Parkerizing Company ProfileDocument4 pagesBrochure EN Ver - Thai Parkerizing Company ProfileTAEWARAT RAKRUANGNo ratings yet
- AluminiumDocument48 pagesAluminiumGhiffariAwliyaMuhammadAshfaniaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Heat TreatmentDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Heat TreatmentAzhar AliNo ratings yet
- Trivalent Chromates FAQDocument3 pagesTrivalent Chromates FAQfastenersworldNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal OperationsDocument63 pagesSheet Metal OperationsDilip ShenoyNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationYaSsin Saad100% (1)
- RPN 181221Document2 pagesRPN 181221aleerossNo ratings yet