Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BSN 1
BSN 1
Uploaded by
ino zuii javier0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesOriginal Title
bsn 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views3 pagesBSN 1
BSN 1
Uploaded by
ino zuii javierCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
integumentary system skin, hair, glands and nails
major functions protection, sensation, vitamin d production, temp regulation, aexcretion
2 layers of skin epidermis and dermis
epidermis stratified squamous; most superficial layer
dermis dense connective tissue
2 layers dernis papillary layer and reticular layer
papillary projections called derman papillae; pain receptors
reticular layer blood vessels, glands, nerve receptor
layer of epidermis strata and stratum basale
strata layers
melanin pigment produced by melanocytes
stratum basale deepest epidermal layer; attached to basal lamina
normal skin color determinants melanin, carotene, hemoglobin
melanin yellow, brown or black pigment
cartone orange-yellow pigment
hemoglobin red coloring from blood
appendages of skin sebaceous glands
acne active infection of sebaceous gland
sweat glands widely distributed in the skin
2 types of SG eccrine and apocrine
eccrine open via duct to pore on skin surface
apocrine ducts empty into hair follicles
appendages of skin hair and nail
hair produced by hair bulb; hard keratinized epithelial cells
melanocytes provide pigment of hair
hair anatomy central medulla, cortex arround medulla, cuticle on outside cortex
associated hair structure hair follicle, arrector pilli, sebaceous gland, sweat gland
hair follicle dermal and epidermal sheat surround hair rot
arrector pilli smooth muscle
nails scale like modifications of epidermis
nail structure free edge, body, root of nail, heavily keratinized
skeletal system bones (skeleton), joints, cartilages, ligaments (bone to bone) (tendon=bone to mus
divided into 2 division axial and appendicular
axial skeleton skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
appendicular skeleton limbs, pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle
functions of bones support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation
skeleton has how many bones? 206
2 basic types of bone tissue compact and spongy bone
homogenous compact bone
many open sacs spongy bone
classification of bones long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones
gross anatomy of long bone diaphysis, epiphysis, articular cartilage, medullary cavity
shaft and composed of compact diaphysis
ends of the bone; spongy epiphysis
covers the external surface of eparticular cartilage
cavity of the shaft medullary cavity
contains yellow marrow
ation, aexcretion
bone) (tendon=bone to muscle)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Laurente's Theory of Nursing PracticeDocument20 pagesLaurente's Theory of Nursing Practiceino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Harinam Diksha Reference Material For Written Test PDFDocument80 pagesHarinam Diksha Reference Material For Written Test PDFV Sai Prashaanth83% (6)
- Prepared By: Javier, Ino Zuii Along With: Cambi, Canales and SacayDocument2 pagesPrepared By: Javier, Ino Zuii Along With: Cambi, Canales and Sacayino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines:: Theoretical Foundations of NursingDocument2 pagesGeneral Guidelines:: Theoretical Foundations of Nursingino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Biochem Prelim Outline ReviewerDocument8 pagesBiochem Prelim Outline Reviewerino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Midterm - MovementDocument2 pagesMidterm - Movementino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Exile in DapitanDocument46 pagesChapter 22 Exile in Dapitanino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Cecilia Laurente Theory of Nursing Practice and CareerDocument3 pagesCecilia Laurente Theory of Nursing Practice and Careerino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Cecilia LaurenteDocument3 pagesCecilia Laurenteino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Rizal As Our Foremost HeroDocument12 pagesRizal As Our Foremost Heroino zuii javierNo ratings yet
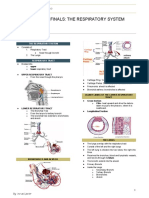
- Semifinals Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesSemifinals Respiratory Systemino zuii javierNo ratings yet
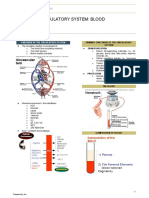
- Circulatory System: BloodDocument8 pagesCirculatory System: Bloodino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Topic Outline:: Lesson 9: Carbohydrates MetabolismDocument17 pagesTopic Outline:: Lesson 9: Carbohydrates Metabolismino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Semifinals-Lesson 7-Enzymes and VitaminsDocument4 pagesSemifinals-Lesson 7-Enzymes and Vitaminsino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Semifinals-Lesson 8-Nucleic AcidDocument4 pagesSemifinals-Lesson 8-Nucleic Acidino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Midterm - Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMidterm - Muscular Systemino zuii javierNo ratings yet
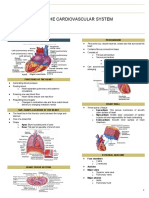
- Midterm - Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesMidterm - Cardiovascular Systemino zuii javierNo ratings yet
- Prompt MidjourneyDocument2 pagesPrompt MidjourneyAndrea MinopoliNo ratings yet
- Airbus Aircraft Data For Visual Aids Calibration v5.0Document2 pagesAirbus Aircraft Data For Visual Aids Calibration v5.0Yuzwan AfzanNo ratings yet
- DWG - BKM NH 365 BGP V Sic STR MNB 143+113Document12 pagesDWG - BKM NH 365 BGP V Sic STR MNB 143+113BEKEM InfraNo ratings yet
- Referencia Gramatical PEARSONDocument147 pagesReferencia Gramatical PEARSONGuille AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Honey Bees StatisticalSummaryDocument2 pages2019 Honey Bees StatisticalSummaryrob burrNo ratings yet
- Sylvania 1986 Large Lamp Ordering GuideDocument88 pagesSylvania 1986 Large Lamp Ordering GuideAlan Masters100% (2)
- Truss 6 V - Plate Connection DesignDocument9 pagesTruss 6 V - Plate Connection DesignSiddharth Tiwari100% (1)
- The Solution Design Optimization of Breaker Plate in Extrusion MachinesDocument3 pagesThe Solution Design Optimization of Breaker Plate in Extrusion MachinesMehul PatelNo ratings yet
- Saac Newton: Early Life and EducationDocument9 pagesSaac Newton: Early Life and EducationGabriel André AlvesNo ratings yet
- What Is Pool (Billiard) Game?: History of Billiards (Or Pool)Document7 pagesWhat Is Pool (Billiard) Game?: History of Billiards (Or Pool)Dekzie Flores MimayNo ratings yet
- Linde LNG Material Safety DatasheetDocument11 pagesLinde LNG Material Safety DatasheetSANo ratings yet
- Tormax United Kingdom - Imotion 2202 - Operations - Instructions For UseDocument20 pagesTormax United Kingdom - Imotion 2202 - Operations - Instructions For UseRico AndrianNo ratings yet
- Kenneth Graves and Kenneth Davis v. Anschutz Oil Co., Inc., A Corporation, 280 F.2d 364, 10th Cir. (1960)Document8 pagesKenneth Graves and Kenneth Davis v. Anschutz Oil Co., Inc., A Corporation, 280 F.2d 364, 10th Cir. (1960)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- B2 Listening 11Document1 pageB2 Listening 11Juan MiguelNo ratings yet
- Plastics Material Selection Criteria: BY N.Mohan Kumar Cipet ChennaiDocument16 pagesPlastics Material Selection Criteria: BY N.Mohan Kumar Cipet ChennaisouravNo ratings yet
- Crime Scene Search BDocument41 pagesCrime Scene Search BJoshua ReyesNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Fine Art's Notes Unit 1 Rajasthani School of Miniature RaingtingDocument14 pagesClass Xii Fine Art's Notes Unit 1 Rajasthani School of Miniature RaingtingZyRoxNo ratings yet
- Senses BrochureDocument7 pagesSenses Brochuresandip samantaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Aptitude, Maths, Data Interpretation (DI), Speed MathsDocument17 pagesQuantitative Aptitude, Maths, Data Interpretation (DI), Speed MathsSanjeev ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Megamat 10: The New Powerful Generation of MEGAMAT Single DrivesDocument2 pagesMegamat 10: The New Powerful Generation of MEGAMAT Single DrivesAndresMarcanoNo ratings yet
- Price Offer L T Consutruction CSPDCL RDSSDocument2 pagesPrice Offer L T Consutruction CSPDCL RDSSAshish bhattNo ratings yet
- Hardest Past Paper Questions Between 2009-2015 2. Hardest Mixed Exercise Questions From The Text Book 3. Hardest Solomon Paper QuestionsDocument83 pagesHardest Past Paper Questions Between 2009-2015 2. Hardest Mixed Exercise Questions From The Text Book 3. Hardest Solomon Paper QuestionsAli EhabNo ratings yet
- Anat 51 To 92qDocument48 pagesAnat 51 To 92qMuhieddin GhosnNo ratings yet
- Mohr Stress Circle Exercise-KrDocument8 pagesMohr Stress Circle Exercise-KrFelipe Camacho HurtadoNo ratings yet
- A Literature Survey of Benchmark Functions For Global Optimisation Problems PDFDocument45 pagesA Literature Survey of Benchmark Functions For Global Optimisation Problems PDFAmreen KhanNo ratings yet
- Howden XRV Users ManualDocument162 pagesHowden XRV Users ManualAliNo ratings yet
- RAMA 54294 05101381924087 0025066601 01 Front RefDocument30 pagesRAMA 54294 05101381924087 0025066601 01 Front RefrezabatariNo ratings yet
- Model Yuea36Fs-Uer-K V/PH/HZ 230/1/60: Exploded View and Spare Part ListDocument4 pagesModel Yuea36Fs-Uer-K V/PH/HZ 230/1/60: Exploded View and Spare Part ListJose Enrique Sanchez ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Manual XORO en HRS8664 HRS8660 HRS8659 HRS8658 HRS8566v2 HRS8556v2 HRS2610Document40 pagesManual XORO en HRS8664 HRS8660 HRS8659 HRS8658 HRS8566v2 HRS8556v2 HRS2610Aaa AaNo ratings yet