Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xiang2020 6
Uploaded by
Stevepallmer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
xiang2020-6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageXiang2020 6
Uploaded by
StevepallmerCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Z. Xiang, et al.
Reliability Engineering and System Safety 199 (2020) 106901
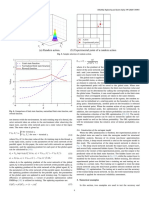
Fig. 7. Parallel model of DRL-based sampling method.
approaches (AK-MCS [35] and Latin hypercube sampling [27]) are also
employed in these two examples.
4.1. Example 1:Series system reliability problem
This example considers a widely-used benchmark problem with low
nonlinearity. It is a series system with four components, and the limit
state function is defined as [35,36]:
g1 = 3 + 0.1(x1 − x2)2 − (x1 + x2)/ 2
g2 = 3 + 0.1(x1 − x2)2 + (x1 + x2)/ 2
g3 = x1 − x2 + 7/ 2
g4 = x2 − x1 + 7/ 2
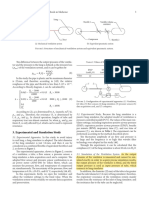
Fig. 8. The architecture of the Artificial Neural Networks of the surrogate g (x1, x2) = min{g1, g2 , g3, g4} (19)
model.
where x1 and x2 are independent standard normal random variables; g1
to g4 are the limit state functions of the components; g(x1, x2) is the
efficiency of the proposed DRL-based sampling method for structural system limit state function.
reliability assessment. The first example is a series system with two First, the direct Monte Carlo simulation is used to calculate the re-
random variables. The second example is a modified version of the first ference value of failure probability. The number of Monte Carlo po-
example with adding a nonlinear term to the limit state function. For pulations N is set to 5 × 105. Then the same Monte Carlo populations
comparison, the direct Monte Carlo simulation, a variance reduction are used to test the DRL-based sampling and Latin hypercube sampling
method (subset simulation [10]) and two surrogate modelling methods. The Monte Carlo populations and selected experimental
You might also like
- Schematic of Experimental Span of JSC "STC FGC UES" For Testing of Vibration Dampers On Wire EfficiencyDocument5 pagesSchematic of Experimental Span of JSC "STC FGC UES" For Testing of Vibration Dampers On Wire EfficiencyStevepallmerNo ratings yet
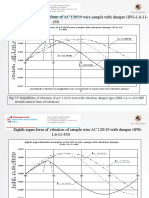
- Seventh Natural Waveform of AC 120/19 Wire Sample With Damper GPG-1,6-11-450Document5 pagesSeventh Natural Waveform of AC 120/19 Wire Sample With Damper GPG-1,6-11-450StevepallmerNo ratings yet
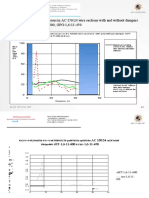
- Maximum Bending Stresses in AC 150/24 Wire Sections With and Without Dampers HVT-1,6-11-800, GPG-1,6-11-450Document5 pagesMaximum Bending Stresses in AC 150/24 Wire Sections With and Without Dampers HVT-1,6-11-800, GPG-1,6-11-450StevepallmerNo ratings yet
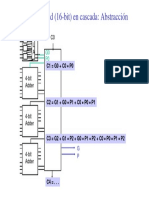
- Clase6 2014-7 PDFDocument1 pageClase6 2014-7 PDFStevepallmerNo ratings yet
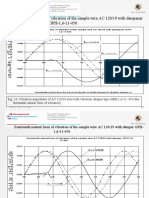
- Thirteenth Proper Form of Vibration of The Sample Wire AC 120/19 With Dampener GPH-1,6-11-450Document5 pagesThirteenth Proper Form of Vibration of The Sample Wire AC 120/19 With Dampener GPH-1,6-11-450StevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Clase6 2014-5 PDFDocument1 pageClase6 2014-5 PDFStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Fig. 5. Sample Selection of Random Action.: Z. Xiang, Et AlDocument1 pageFig. 5. Sample Selection of Random Action.: Z. Xiang, Et AlStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Mediators: The Scientific World JournalDocument1 pageMediators: The Scientific World JournalStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- 10 PDFDocument1 page10 PDFStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- BF 02129047Document14 pagesBF 02129047StevepallmerNo ratings yet
- View PDFDocument135 pagesView PDFStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- 6 PDFDocument1 page6 PDFStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Modeling of Mechanical Ventilation SystemDocument1 pageIntroduction and Modeling of Mechanical Ventilation SystemStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Tube Lung: 3. Experimental and Simulation StudyDocument1 pageTube Lung: 3. Experimental and Simulation StudyStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Section 2.2.4: 5. ConclusionsDocument1 pageSection 2.2.4: 5. ConclusionsStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- 3.4. Analysis and Discussions. The Curve and Fitted Curve ofDocument1 page3.4. Analysis and Discussions. The Curve and Fitted Curve ofStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Influence On Air Pressure Dynamic Characteristics: Figure 5: Respiratory Resistance of The SystemDocument1 pageInfluence On Air Pressure Dynamic Characteristics: Figure 5: Respiratory Resistance of The SystemStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Pressure Dynamic Characteristics of Pressure Controlled Ventilation System of A Lung SimulatorDocument1 pageResearch Article: Pressure Dynamic Characteristics of Pressure Controlled Ventilation System of A Lung SimulatorStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- 10 PDFDocument1 page10 PDFStevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 9Document1 pageComputational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 9StevepallmerNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- PC210 8M0Document8 pagesPC210 8M0Vamshidhar Reddy KundurNo ratings yet
- Ibbotson Sbbi: Stocks, Bonds, Bills, and Inflation 1926-2019Document2 pagesIbbotson Sbbi: Stocks, Bonds, Bills, and Inflation 1926-2019Bastián EnrichNo ratings yet
- Astm E53 98Document1 pageAstm E53 98park991018No ratings yet
- Daraman vs. DENRDocument2 pagesDaraman vs. DENRJeng GacalNo ratings yet
- Condition Monitoring of Steam Turbines by Performance AnalysisDocument25 pagesCondition Monitoring of Steam Turbines by Performance Analysisabuhurairaqazi100% (1)
- Dr. Eduardo M. Rivera: This Is A Riveranewsletter Which Is Sent As Part of Your Ongoing Education ServiceDocument31 pagesDr. Eduardo M. Rivera: This Is A Riveranewsletter Which Is Sent As Part of Your Ongoing Education ServiceNick FurlanoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Notation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.: T Solution:fDocument2 pagesEngineering Notation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.: T Solution:fJeannie ReguyaNo ratings yet
- QA/QC Checklist - Installation of MDB Panel BoardsDocument6 pagesQA/QC Checklist - Installation of MDB Panel Boardsehtesham100% (1)
- Labstan 1Document2 pagesLabstan 1Samuel WalshNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Fisika - Full Wave RectifierDocument11 pagesLaporan Praktikum Fisika - Full Wave RectifierLasmaenita SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Digital LiteracyDocument19 pagesDigital Literacynagasms100% (1)
- 4th Sem Electrical AliiedDocument1 page4th Sem Electrical AliiedSam ChavanNo ratings yet
- Information Security Chapter 1Document44 pagesInformation Security Chapter 1bscitsemvNo ratings yet
- TAB Procedures From An Engineering FirmDocument18 pagesTAB Procedures From An Engineering Firmtestuser180No ratings yet
- Extent of The Use of Instructional Materials in The Effective Teaching and Learning of Home Home EconomicsDocument47 pagesExtent of The Use of Instructional Materials in The Effective Teaching and Learning of Home Home Economicschukwu solomon75% (4)
- 4 Bar LinkDocument4 pages4 Bar LinkConstance Lynn'da GNo ratings yet
- M J 1 MergedDocument269 pagesM J 1 MergedsanyaNo ratings yet
- Online Learning Interactions During The Level I Covid-19 Pandemic Community Activity Restriction: What Are The Important Determinants and Complaints?Document16 pagesOnline Learning Interactions During The Level I Covid-19 Pandemic Community Activity Restriction: What Are The Important Determinants and Complaints?Maulana Adhi Setyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- 06-Apache SparkDocument75 pages06-Apache SparkTarike ZewudeNo ratings yet
- Everlube 620 CTDSDocument2 pagesEverlube 620 CTDSchristianNo ratings yet
- CV Ovais MushtaqDocument4 pagesCV Ovais MushtaqiftiniaziNo ratings yet
- Transparency Documentation EN 2019Document23 pagesTransparency Documentation EN 2019shani ChahalNo ratings yet
- Dialog Suntel MergerDocument8 pagesDialog Suntel MergerPrasad DilrukshanaNo ratings yet
- Mat Boundary Spring Generator With KX Ky KZ KMX KMy KMZDocument3 pagesMat Boundary Spring Generator With KX Ky KZ KMX KMy KMZcesar rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Convention On The Rights of Persons With Disabilities: United NationsDocument13 pagesConvention On The Rights of Persons With Disabilities: United NationssofiabloemNo ratings yet
- Social Media Marketing Advice To Get You StartedmhogmDocument2 pagesSocial Media Marketing Advice To Get You StartedmhogmSanchezCowan8No ratings yet
- 23 Things You Should Know About Excel Pivot Tables - Exceljet PDFDocument21 pages23 Things You Should Know About Excel Pivot Tables - Exceljet PDFRishavKrishna0% (1)
- Properties of Moist AirDocument11 pagesProperties of Moist AirKarthik HarithNo ratings yet
- Web Technology PDFDocument3 pagesWeb Technology PDFRahul Sachdeva100% (1)
- 450i User ManualDocument54 pages450i User ManualThượng Lê Văn0% (2)