Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CAMARISTACM - NCP (AGE) (Activity Intolerance)
Uploaded by
Coleen Mae Camarista0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesOriginal Title
CAMARISTACM_NCP (AGE)[Activity Intolerance]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesCAMARISTACM - NCP (AGE) (Activity Intolerance)
Uploaded by
Coleen Mae CamaristaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
ILOILO DOCTOR’S COLLEGE
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING
West Avenue Timawa, Molo, Iloilo City
NCM 112 (RLE)
CARE OF CLIENTS WITH PROBLEMS IN OXYGENATION, FLUID AND ELECTROLYTES,
INFECTIOUS, INFLAMMATORY AND IMMUNOLOGIC RESPONSE, CELLULAR ABERRATIONS,
ACUTE AND CHRONIC
NURSING CARE PLAN (AGE)
A Case Study Presented to the Department of Nursing of Iloilo Doctor’s College
PRESENTED TO: MRS.
Arvi Tenderly V. Melliza, RN, M.A.N.
(NCM 112 RLE & SKILLS CLINICAL INSTRUCTOR)
PRESENTED BY:
Coleen Mae C. Camarista BSN III - G
ILOILO DOCTOR’S COLLEGE
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING
West Avenue Timawa, Molo, Iloilo City
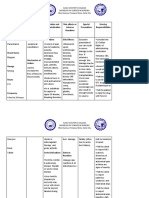
ASSESSMENT NURSING OUTCOME INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS IDENTIFICATION
SUBJECTIVE: Activity SHORT TERM INDEPENDENT: After 24 hours of
intolerance GOAL: - Monitor client’s - Fever that occurs with nursing
He came to the related to vital signs. gastroenteritis intervention,
emergency generalized After 8 hours of increases fluid loss patient will
weakness AEB nursing through perspiration maintain fluid and
room with the
weak intervention, the and increased electrolyte
chief extremities, patient will be respiration. balance, increased
complaint of distended able to identify knowledge about
vomiting abdomen, negative factors the disease and
accompanied and weak affecting activity - Provide health - To enhance patient risk of
by body overall intolerance and teaching on the ability to participate in transmission, and
appearance eliminate or client regarding activity absence of
malaise as
reduce their the organization complications AEB:
verbalized by effects. and time
the patient. Rationale: management a. Temperature is
technique to within normal
LONG TERM: prevent while on range.
OBJECTIVE: Activity
After 24 hours of activity
intolerance is
nursing b. Blood culture
Temperature: insufficient
interventions the - Assist client with - To protect patient reports are
38.5 °C physiological or
patient will activity from injury and To negative.
psychological
participate prevent over-
a) Weak overall energy poor
willingly in exhaustion c. Fluid balance is
appearance endure or necessary or achieved.
b) Distended complete desired activities
abdomen required or as evidenced by: - Monitoring and - Bacteremia. E. coli,
c) Lower desired daily managing Salmonella, and
activities.
- Coleen Mae C. Camarista (10/5/2021)
ILOILO DOCTOR’S COLLEGE
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING
West Avenue Timawa, Molo, Iloilo City
extremities a. Temperature potential Shigella are organisms
are weak is within normal complications that can enter the
range. bloodstream and
disseminate to other
b. Blood culture organs. Shock
reports are associated with
negative. diarrheal diseases
demands accurate
c. Fluid balance intake and output
is achieved. assessment and
vigorous fluid
replacement.
DEPENDENT: - Oral rehydration
Administering therapy should be
rehydration therapy delivered frequently in
small amounts. When
patients are
persistently vomiting,
they often require
frequent
administration of
fluids by full-spoons.
IV therapy is necessary
for the patient who is
severely dehydrated
or in shock.
- Coleen Mae C. Camarista (10/5/2021)
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ColorectalCancer - Case StudyDocument28 pagesColorectalCancer - Case StudyColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Exam in Analytic Geometry With AnswersDocument4 pagesExam in Analytic Geometry With Answersmvmbapple100% (6)
- Typhoid Fever Case StudyDocument27 pagesTyphoid Fever Case StudyColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Vascular Dementia (Case Study)Document22 pagesVascular Dementia (Case Study)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis Case StudyDocument29 pagesOsteoarthritis Case StudyColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Cases Torts 7-29-17 DigestDocument1 pageCases Torts 7-29-17 Digestczabina fatima delicaNo ratings yet
- Andrea Falcon - Aristotle On How Animals MoveDocument333 pagesAndrea Falcon - Aristotle On How Animals MoveLigia G. DinizNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of AbortionDocument14 pagesPros and Cons of AbortionSuman SarekukkaNo ratings yet
- The Great Psychotherapy Debate PDFDocument223 pagesThe Great Psychotherapy Debate PDFCasey Lewis100% (9)
- Chronic Renal Failure - Case Study (Group)Document35 pagesChronic Renal Failure - Case Study (Group)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Lipoproteins in Diabetes Mellitus: Alicia J. Jenkins Peter P. Toth Timothy J. Lyons EditorsDocument468 pagesLipoproteins in Diabetes Mellitus: Alicia J. Jenkins Peter P. Toth Timothy J. Lyons EditorsFELELNo ratings yet
- Hiv-Aids Case StudyDocument31 pagesHiv-Aids Case StudyColeen Mae Camarista100% (2)
- CAMARISTACM - NCP (AGE) (Deficient Fluid Volume)Document3 pagesCAMARISTACM - NCP (AGE) (Deficient Fluid Volume)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- PTB - Case-Study-Group 1Document23 pagesPTB - Case-Study-Group 1Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- CamaristaCM - ColorectalCancer (Q&A)Document4 pagesCamaristaCM - ColorectalCancer (Q&A)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- CamaristaCM - HIV and AIDS (Questions and Answers)Document5 pagesCamaristaCM - HIV and AIDS (Questions and Answers)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- PTB DrugsDocument4 pagesPTB DrugsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- CAMARISTACM - NCP (ULCERATIVE COLITIS) (Diarrhea)Document4 pagesCAMARISTACM - NCP (ULCERATIVE COLITIS) (Diarrhea)Coleen Mae Camarista0% (1)
- Drug Study - PneumoniaDocument15 pagesDrug Study - PneumoniaColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Nosedive: "A Wee Pastel Proletariat of Technology"Document2 pagesNosedive: "A Wee Pastel Proletariat of Technology"Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- CamaristaCM - Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesCamaristaCM - Nursing Care PlanColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- CamaristaCM - BreastCancer (Questions and Answers)Document4 pagesCamaristaCM - BreastCancer (Questions and Answers)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- CamaristaColeen Mae - PNEUMONIA (Case Study 1)Document31 pagesCamaristaColeen Mae - PNEUMONIA (Case Study 1)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- CamaristaColeen Mae - PNEUMONIA (Case Study 1)Document31 pagesCamaristaColeen Mae - PNEUMONIA (Case Study 1)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia AnswersDocument5 pagesPneumonia AnswersColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Document2 pagesDrugStudy - CamaristaColeenMaeC (BSN III-G) (Prednisone)Coleen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Febryruthwahyuni Lds g1718 Bilphy MRDocument11 pagesFebryruthwahyuni Lds g1718 Bilphy MRfebry sihiteNo ratings yet
- Business Communication and Behavioural StudiesDocument10 pagesBusiness Communication and Behavioural StudiesBhujangam NaiduNo ratings yet
- Enter Pre NaurDocument82 pagesEnter Pre NaurNeha singhalNo ratings yet
- Farewell Address WorksheetDocument3 pagesFarewell Address Worksheetapi-261464658No ratings yet
- Report Web AuditDocument17 pagesReport Web Auditanupprakash36No ratings yet
- Fish Immune System and Vaccines-Springer (2022) - 1Document293 pagesFish Immune System and Vaccines-Springer (2022) - 1Rodolfo Velazco100% (1)
- Drishti IasDocument36 pagesDrishti Ias23010126269No ratings yet
- Modelling The Relationship Between Hotel Perceived Value, CustomerDocument11 pagesModelling The Relationship Between Hotel Perceived Value, Customerzoe_zoeNo ratings yet
- ERF 2019 0128 H160 Noise CertificationDocument10 pagesERF 2019 0128 H160 Noise CertificationHelimanualNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Variation IDocument21 pagesHeredity and Variation Ismbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- Alamat NG BatangasDocument2 pagesAlamat NG BatangasGiennon Arth LimNo ratings yet
- Vocab Money HeistDocument62 pagesVocab Money HeistCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Parkin 8e TIF Ch27Document51 pagesParkin 8e TIF Ch27Pranta SahaNo ratings yet
- Eastwoods: College of Science and Technology, IncDocument2 pagesEastwoods: College of Science and Technology, IncMichael AustriaNo ratings yet
- Or SuperDocument2 pagesOr SuperJac BacNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Tool-Path Smoothing For 6-Axis Industrial Machining RobotsDocument10 pagesKinematic Tool-Path Smoothing For 6-Axis Industrial Machining RobotsToniolo LucaNo ratings yet
- Online Book Store System: Bachelor of Computer EngineeringDocument31 pagesOnline Book Store System: Bachelor of Computer Engineeringkalpesh mayekarNo ratings yet
- Project Documentation - Sensorflex 30G Data SheetDocument15 pagesProject Documentation - Sensorflex 30G Data SheetOmar HectorNo ratings yet
- List of Mines in IndiaDocument4 pagesList of Mines in IndiaNAMISH MAHAKULNo ratings yet
- Case DigestsDocument12 pagesCase DigestsHusni B. SaripNo ratings yet
- Rationale of Labour Welfare To Employers and EmployeesDocument20 pagesRationale of Labour Welfare To Employers and Employeesajit yadav100% (1)
- 5 Facts You Should Know About The Green MarchDocument7 pages5 Facts You Should Know About The Green MarchDriss Baouche100% (1)
- Traverse AdjustmentDocument22 pagesTraverse AdjustmenthabteNo ratings yet