Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 - 4 IT NetworkTERMS
Uploaded by
Candice ThomasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 - 4 IT NetworkTERMS
Uploaded by
Candice ThomasCopyright:
Available Formats
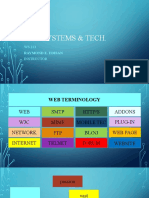
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
POOL 5:4
Topic: Computer Networks and Web Technologies
Teacher: Ms. C. Thomas
Instruction to students: Read the information below and make notes in your
notebook.
TERMS AND MEANINGS
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW) is a network of online content that gives
users access to a vast array of documents that are connected to each other by
means of hypertext or hypermedia links.
Internet
The Internet is a global wide area network that connects computer systems
across the world that allows people to share information and communicate
with each other.
Hypertext Markup Language
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is a computer language devised to
allow website creation. These websites can then be viewed by anyone else
connected to the Internet.
Hyperlinks
A hyperlink is a word, phrase, or image that you can click on to jump to a
new document or a new section within the current document. Hyperlinks are
found in nearly all Web pages, allowing users to click their way from page to
page.
Web Server
A Web server is a computer system that hosts websites. It runs Web server
software which provides access to hosted webpages over the Internet. Most
Web servers are connected to the Internet via a high-speed connection.
Web Page
A web page is a set of data or information which is designed to be viewed as
part of a website.
Protocol
A protocol is a set of technical rules that control the exchange of information
between different computers or computer networks.
File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard Internet protocol for transmitting
files between computers on the Internet over TCP/IP connections. FTP is a
client-server protocol where a client will ask for a file, and a local or remote
server will provide it.
Web Browser
A web browser, or simply "browser," is an application used to access and
view websites. Common web browsers include Microsoft Internet Explorer,
Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox.
Uniform Resource Locator
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a unique identifier used to locate
a resource on the internet. It is also referred to as a web address. For example,
www.google.com.
Download
Downloading means receiving data or a file from the Internet (or another
device) on your device.
Upload
Uploading means sending data or a file from your device to somewhere on
the Internet (or another device).
Electronic mail (email) is a digital mechanism for exchanging messages
through Internet or intranet communication platforms.
Activity
Answer all questions below.
SECTION A
1. State the difference between the internet and the world wide web.
2. State the difference between download and upload. Give an example of
each.
3. Give two examples of a URL.
4. State an example of a web browser not mentioned above.
5. Other than FTP, state and explain another protocol used on the internet.
SECTION B
1. What is a markup language?
a. Numbers that respond to a browser's request for a Web page
b. The combination of letters and numbers that make up the address
displayed on the top of your browser.
c. A computer language that describes how text should be formatted on
your browser
2. What does a Web browser do?
a. Requests, interprets and displays Web pages
b. Works as a tool to design Web pages
c. Delivers Web pages
3. What is a Web server?
a. Special code that tells a browser how to display text
b. Software that responds to a browser's request
c. A human that keeps up with Web surfers' constant demands by
manually sending Web sites back to browsers
4. When you move the cursor over a ____________, whether it is text or an
image, the arrow should change to a small pointing hand.
a. hypertext markup language
b. hyperlink
c. browser
5. What does the 'e' in e-mail stand for
a. egg
b. express
c. electronic
SECTION C
Write is meant by the following abbreviations
1. HTTP 4. FTP
2. HTML 5. URL
3. WWW
You might also like
- Web Programming with HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript, React.JS, PHP, and MySQL Fourth EditionFrom EverandWeb Programming with HTML, CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript, React.JS, PHP, and MySQL Fourth EditionNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument34 pagesCollege of Engineering and Technologydiro fufaNo ratings yet
- Network Programming in Python : The Basic: A Detailed Guide to Python 3 Network Programming and ManagementFrom EverandNetwork Programming in Python : The Basic: A Detailed Guide to Python 3 Network Programming and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Network Part Session 3Document9 pagesNetwork Part Session 3prakyathNo ratings yet
- Web Development Internet ProtocolsDocument30 pagesWeb Development Internet ProtocolsDevender YadavNo ratings yet
- FIT Class 10th SolutionDocument75 pagesFIT Class 10th SolutionAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Internet Programming All in One HandoutDocument60 pagesFundamentals of Internet Programming All in One HandoutGamal BohoutaNo ratings yet
- Web Technology - MODULE - IIDocument8 pagesWeb Technology - MODULE - IIayush sawant 5032No ratings yet
- Scroll Down To View Your Downloaded File!Document85 pagesScroll Down To View Your Downloaded File!Mohammed SabirNo ratings yet
- Text 12 A TasksDocument3 pagesText 12 A TasksСветланаNo ratings yet
- E-Notes PDF All-Units IWTDocument82 pagesE-Notes PDF All-Units IWTmysadidvd009No ratings yet
- MCAWT Unit1Document119 pagesMCAWT Unit1lepeci7607No ratings yet
- 12-IP NotesDocument3 pages12-IP NotesParasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Web TechnologiesDocument11 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Web TechnologiesadiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Computer NotesDocument38 pagesClass 10 Computer NotesShreya KatwalNo ratings yet
- 01 Basic of NetworkDocument9 pages01 Basic of NetworkHunNo ratings yet
- Web Technology Study Material GTU - 23042016 - 032646AM PDFDocument82 pagesWeb Technology Study Material GTU - 23042016 - 032646AM PDFVikalp Panseriya100% (1)
- UNIT-1 Lecture-1 A Brief Introduction To The InternetDocument78 pagesUNIT-1 Lecture-1 A Brief Introduction To The InternetRajesh GangishettyNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE: Select The Best Answer From The Choices and Write The Letter That Corresponds To Your Answer On The Answer SheetDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE: Select The Best Answer From The Choices and Write The Letter That Corresponds To Your Answer On The Answer SheetSuper MelonNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE: Select The Best Answer From The Choices and Write The Letter That Corresponds To Your Answer On The Answer SheetDocument2 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE: Select The Best Answer From The Choices and Write The Letter That Corresponds To Your Answer On The Answer SheetSuper MelonNo ratings yet
- WEB NotesDocument92 pagesWEB NotesPurushotham GowdaNo ratings yet
- Web Systems and Tech.Document61 pagesWeb Systems and Tech.Arnold ColancolanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank SolutionDocument87 pagesQuestion Bank SolutionPATEL POOJANNo ratings yet
- Concept of WWW.: J.B.Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDocument110 pagesConcept of WWW.: J.B.Institute of Engineering and TechnologyjayaraoNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument18 pagesHTMLdevendermahajanNo ratings yet
- Web TECH NOTESDocument87 pagesWeb TECH NOTESupdeshroy816No ratings yet
- Gr.10 - Networking-Set1 (Answer Key)Document8 pagesGr.10 - Networking-Set1 (Answer Key)dreadster bossNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document21 pagesUnit 1Selvam ManoNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Internet Basics NotesDocument5 pagesCH-1 Internet Basics NotesShrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Introduction To HTMLDocument20 pagesLESSON 1 Introduction To HTMLNadya Ysabelle RagoNo ratings yet
- Internet Technologies and Protocols: Abduselam A. (MCA)Document20 pagesInternet Technologies and Protocols: Abduselam A. (MCA)Obsa gabaNo ratings yet
- Networking Short NotesDocument7 pagesNetworking Short NotestonyNo ratings yet
- CS Module 1Document14 pagesCS Module 1vijayendrar219No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Internet and WebDocument34 pagesIntroduction To The Internet and WebRenzogcNo ratings yet
- CN Unit-5Document27 pagesCN Unit-5All rounder coveringNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter 1 Internet BasicDocument27 pagesClass X Chapter 1 Internet BasicMack TripathiNo ratings yet
- Sumita Arora Solved Exercise of Web Application DevelopmentDocument0 pagesSumita Arora Solved Exercise of Web Application Developmentidigiti100% (6)
- 9 How The Internet WorksDocument2 pages9 How The Internet Worksyarichek.zviagintsevNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument11 pagesUnit 3 NotesAryanNo ratings yet
- CH-9 Web Application Development PDFDocument1 pageCH-9 Web Application Development PDFJay SandukeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Web TechnologyDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Web TechnologyIkram RanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - The Internet & Its UsesDocument109 pagesChapter 5 - The Internet & Its Usesasheralt3791No ratings yet
- InternetDocument29 pagesInternetMuhammad Imran MemonNo ratings yet
- IT Unit 1 World Wide WebDocument20 pagesIT Unit 1 World Wide WebFurret MasterNo ratings yet
- What Is Internet NightDocument16 pagesWhat Is Internet NighttayituNo ratings yet
- To The Internet and WebDocument25 pagesTo The Internet and WebMegan AmethystNo ratings yet
- The Internet History1.1Document28 pagesThe Internet History1.1akki0rockeyNo ratings yet
- Web Technology UNIT-1Document20 pagesWeb Technology UNIT-1Yash TyagiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The World Wide Web PDFDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The World Wide Web PDFAmin mohammedNo ratings yet
- Web Design Notes For BCA 5th Sem 2019 PDFDocument44 pagesWeb Design Notes For BCA 5th Sem 2019 PDFArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Web EssentialsDocument6 pagesUnit-1 Web EssentialsBir MallaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument95 pagesComputer NetworksBal Kishan YadavNo ratings yet
- World Wide Web: (WWW", "Web" or "W3")Document46 pagesWorld Wide Web: (WWW", "Web" or "W3")SAI SUHAS KOTARINo ratings yet
- HTML - Unit1Document53 pagesHTML - Unit1GODDU NAVVEN BABUNo ratings yet
- The Internet - Form 2Document27 pagesThe Internet - Form 2Nirvana SuggieNo ratings yet
- Internet and Web TechnologyDocument113 pagesInternet and Web TechnologyComputer ScienceNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 WWW Q. What Is WWW?: Information and Communication TechnologyDocument8 pagesChapter-4 WWW Q. What Is WWW?: Information and Communication Technologyarbaz khanNo ratings yet
- Web IntroductionDocument7 pagesWeb Introductionpraveshcode1No ratings yet
- Internet Programming Short NoteDocument7 pagesInternet Programming Short NoteabinetblackmanNo ratings yet
- WWW Overview: WWW Stands For World Wide Web. A Technical Definition of The World Wide Web Is: AllDocument21 pagesWWW Overview: WWW Stands For World Wide Web. A Technical Definition of The World Wide Web Is: AllamarkalsyNo ratings yet
- Factorization by GroupingDocument2 pagesFactorization by GroupingCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- CAPE Information Technology Unit 2 Trial ExamDocument11 pagesCAPE Information Technology Unit 2 Trial ExamCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Notes - Mean Mode MedianDocument3 pagesNotes - Mean Mode MedianCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Factorization by GroupingDocument2 pagesFactorization by GroupingCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- CAPE IT Unit 2 May - June 2018 Paper 2Document19 pagesCAPE IT Unit 2 May - June 2018 Paper 2Candice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Number Line ActivityDocument2 pagesNumber Line ActivityCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Surface Area of Cube and CuboidDocument5 pagesSurface Area of Cube and CuboidCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Absolute and Relative ReferenceDocument2 pagesAbsolute and Relative ReferenceCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Volume of CYLINDERDocument5 pagesVolume of CYLINDERCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Volume of TRIANGULAR PRISMDocument6 pagesVolume of TRIANGULAR PRISMCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DatabaseDocument5 pagesIntroduction To DatabaseCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Volume of Cube and CuboidDocument4 pagesVolume of Cube and CuboidCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheets: Formulas and FunctionsDocument3 pagesSpreadsheets: Formulas and FunctionsCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Grade 10Document2 pagesInformation Technology Grade 10Candice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SpreadsheetDocument3 pagesIntroduction To SpreadsheetCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Information Technology POOL 5:4: Instruction To Students: Read The Information Below and Make Notes in Your NotebookDocument7 pagesInformation Technology POOL 5:4: Instruction To Students: Read The Information Below and Make Notes in Your NotebookCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Activity Equations 1Document1 pageActivity Equations 1Candice ThomasNo ratings yet
- 5 - 4 IT Network ComponentsDocument8 pages5 - 4 IT Network ComponentsCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Csec It Paper1Document4 pagesCsec It Paper1Candice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Order of OperationsDocument3 pagesOrder of OperationsCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- IT Data CommunicationDocument3 pagesIT Data CommunicationCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- Common Regular Solids ACTIVITYDocument2 pagesCommon Regular Solids ACTIVITYCandice ThomasNo ratings yet
- D103126GC10 1080544 UsDocument5 pagesD103126GC10 1080544 UsvineetNo ratings yet
- Adventages and Disadvantages of ICTDocument9 pagesAdventages and Disadvantages of ICTKatty HeeNo ratings yet
- Jboss 6.1.0 InstallDocument4 pagesJboss 6.1.0 InstallvishnuprakashNo ratings yet
- Olav Aaen Clutch Tuning Handbook PDFDocument3 pagesOlav Aaen Clutch Tuning Handbook PDFChad Robinson0% (1)
- Configuring TACACS+Document34 pagesConfiguring TACACS+Dema PermanaNo ratings yet
- Oracle12c RestoreDocument5 pagesOracle12c RestoreAnil Reddy GNo ratings yet
- AT&T Names Alex Gornbein Assistant Store Manager For Rensselaer StoreDocument3 pagesAT&T Names Alex Gornbein Assistant Store Manager For Rensselaer StoreEllen WebnerNo ratings yet
- Adapt 3701 40Document18 pagesAdapt 3701 40AlexandraAndreeaNo ratings yet
- 2515AC-3015AC-3515AC Spec SheetDocument2 pages2515AC-3015AC-3515AC Spec Sheetuniversal8888No ratings yet
- AlcatelDocument3 pagesAlcatelPaulo PeçanhaNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) : Raafat Ali Supervisor: Dr. Nizar ZarkaDocument17 pagesGaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) : Raafat Ali Supervisor: Dr. Nizar ZarkahiriNo ratings yet
- Windows Server 2003 Vs 2008Document2 pagesWindows Server 2003 Vs 2008simadrigiriNo ratings yet
- GB Batm Installationmanual v2 0Document14 pagesGB Batm Installationmanual v2 0Tee100% (1)
- OM4 Provides An Opportunity To Future-Proof Cabling Infrastructure. OM4 Is Completely Backwards-Compatible With Existing OM3 SystemsDocument2 pagesOM4 Provides An Opportunity To Future-Proof Cabling Infrastructure. OM4 Is Completely Backwards-Compatible With Existing OM3 Systemsaldebaran0473No ratings yet
- Packet Tracer 4.0 Skill Building Activity: Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT SolutionDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer 4.0 Skill Building Activity: Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT SolutionGlaiza LacsonNo ratings yet
- CSE403T Term Paper Topic11Document5 pagesCSE403T Term Paper Topic11Anish ShahNo ratings yet
- Cab Hermes Q enDocument43 pagesCab Hermes Q enDeny DenisNo ratings yet
- User Manual: Profibus DP Master To Crowcon VortexDocument15 pagesUser Manual: Profibus DP Master To Crowcon VortexNurdeny Hidayanto PribadiNo ratings yet
- Replicate and Bundle (RNB) : Kalyani Khandezod, Nitin Raut, Abdulla ShaikDocument6 pagesReplicate and Bundle (RNB) : Kalyani Khandezod, Nitin Raut, Abdulla ShaiktheijesNo ratings yet
- ADR155Document176 pagesADR155Abdou taksi lmakhfiNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies: Prepared By: Karl Kevin C BaconDocument37 pagesEmpowerment Technologies: Prepared By: Karl Kevin C BaconAngelo CenizaNo ratings yet
- NSN FlexiDocument63 pagesNSN FlexipredragnikNo ratings yet
- The 2017 Insider's Guide To AWS - Nov 30Document12 pagesThe 2017 Insider's Guide To AWS - Nov 30Prash Prak TestAcctNo ratings yet
- What Is Koha?Document26 pagesWhat Is Koha?Aslp Librarians100% (4)
- V18 BSS Parameter GuideDocument545 pagesV18 BSS Parameter GuideSarthak OhriNo ratings yet
- Epson L805Document144 pagesEpson L805olufemiNo ratings yet
- IPTV Over Next Generation Networks in ITU-TDocument18 pagesIPTV Over Next Generation Networks in ITU-TOkkar MaungNo ratings yet
- BirdDocument43 pagesBirdLeonardo AmaralNo ratings yet
- Wearable Technologies: Scott Mcgregor President & Ceo, Broadcom CorporationDocument23 pagesWearable Technologies: Scott Mcgregor President & Ceo, Broadcom CorporationRavi PilgarNo ratings yet
- Chap05gtp03kh 130222002052 Phpapp01Document26 pagesChap05gtp03kh 130222002052 Phpapp01thanhbcvt_1989No ratings yet
- The Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellFrom EverandThe Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyFrom EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (421)
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityFrom EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationFrom EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- So You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community That Will ListenFrom EverandSo You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community That Will ListenRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (24)
- The Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldFrom EverandThe Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (104)
- Python for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldFrom EverandPython for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldNo ratings yet
- More Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingFrom EverandMore Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (23)
- The Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerFrom EverandThe Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (34)
- Building Web Apps with Python and Flask: Learn to Develop and Deploy Responsive RESTful Web Applications Using Flask Framework (English Edition)From EverandBuilding Web Apps with Python and Flask: Learn to Develop and Deploy Responsive RESTful Web Applications Using Flask Framework (English Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowFrom EverandTen Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (388)
- TikTok Algorithms 2024 $15,000/Month Guide To Escape Your Job And Build an Successful Social Media Marketing Business From Home Using Your Personal Account, Branding, SEO, InfluencerFrom EverandTikTok Algorithms 2024 $15,000/Month Guide To Escape Your Job And Build an Successful Social Media Marketing Business From Home Using Your Personal Account, Branding, SEO, InfluencerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNFrom EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Designer’s Guide to Figma: Master Prototyping, Collaboration, Handoff, and WorkflowFrom EverandThe Designer’s Guide to Figma: Master Prototyping, Collaboration, Handoff, and WorkflowNo ratings yet
- Kill All Normies: Online Culture Wars From 4Chan And Tumblr To Trump And The Alt-RightFrom EverandKill All Normies: Online Culture Wars From 4Chan And Tumblr To Trump And The Alt-RightRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (240)
- How to Start a Blog with WordPress: Beginner's Guide to Make Money by Writing OnlineFrom EverandHow to Start a Blog with WordPress: Beginner's Guide to Make Money by Writing OnlineRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The $1,000,000 Web Designer Guide: A Practical Guide for Wealth and Freedom as an Online FreelancerFrom EverandThe $1,000,000 Web Designer Guide: A Practical Guide for Wealth and Freedom as an Online FreelancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- What is the Dark Web?: The truth about the hidden part of the internetFrom EverandWhat is the Dark Web?: The truth about the hidden part of the internetRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (75)
- Social Engineering: The Science of Human Hacking 2nd EditionFrom EverandSocial Engineering: The Science of Human Hacking 2nd EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (38)
- Nine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersFrom EverandNine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)