Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Local Maximum and Minimum Points: Chapter 12/ Example 8
Local Maximum and Minimum Points: Chapter 12/ Example 8
Uploaded by
CAPTIAN BIBEKOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Local Maximum and Minimum Points: Chapter 12/ Example 8
Local Maximum and Minimum Points: Chapter 12/ Example 8
Uploaded by
CAPTIAN BIBEKCopyright:
Available Formats
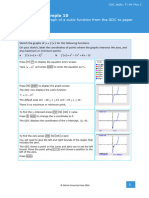
GDC skills: Casio fx-CG50
Chapter 12/ Example 8
Local maximum and minimum points
1
Consider the curve y = x+ , x ≠0.
x
dy
a Find an expression for .
dx
b Plot the curve on a GDC.
c Find the co-ordinates of any local maximum or minimum points.
d Find the gradient of two points, close to but on either side of the minimum point.
e Explain why this shows that the point found is a local minimum.
Press p 5 Y to display the equation entry screen.
1
Type x and press l to enter the equation as Y1.
x
Press u DRAW to display the graph screen
1
The GDC now displays the curve Y1 x .
x
The default axes are 6.3 x 6.3 and 3.1 y 3.1 .
1
To find the local maximum of the curve Y1 x
x
Press y G-Solv w MAX.
Press l to display the coordinates.
Press d to leave G-Solv mode and u DRAW to display the
graph screen again.
The GDC displays the local maximum point at 1, 2 .
© Oxford University Press 2019 1
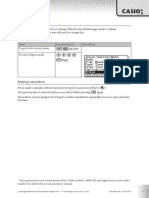
GDC skills: Casio fx-CG50
Chapter 12/ Example 8
Local maximum and minimum points
1
To find the local minimum of the curve Y1 x
x
Press y G-Solv e MIN.
Press l to display the coordinates.
Press d to leave G-Solv mode and u DRAW to display the
graph screen again.
The GDC displays the local minimum point at 1,2 .
Press d then press L p SET UP.
Scroll down to Derivative with N and use q to set this to
‘On’. Press d to return to the equation entry screen and u
DRAW to return to the graph.
To find the gradient either side of the minimum point press q
Trace.
Using $ and ! choose a point to the left of 1,2 .
dy
e.g. when x 0.9 , 0.234 .
dx
Moving to the right of 1,2 find the gradient at a second
point.
dy
e.g. when x 1.1 , 0.174 .
dx
Therefore the gradient has changed sign from negative to
positive and it must be a local minimum point.
© Oxford University Press 2019 2
You might also like
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- DesignDocument8 pagesDesignAmiya Ranjan PaniNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2: Theory of Banking - Academic Year 2016-17Document5 pagesProblem Set 2: Theory of Banking - Academic Year 2016-17thanhpham0505No ratings yet
- Business Management Paper 1 HLDocument4 pagesBusiness Management Paper 1 HLCAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Num-Up Aip (Complete)Document17 pagesNum-Up Aip (Complete)Ardy Patawaran100% (1)
- DLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalDocument13 pagesDLP g10 Math 2nd QTR Week 7 FinalCei-Cei100% (1)
- Complex Analysis For Mathematics and Engineering CompressDocument792 pagesComplex Analysis For Mathematics and Engineering CompressĐào RubyNo ratings yet
- C 5 MathsDocument6 pagesC 5 Mathsmmaaz74559100% (1)
- Graphing A Function and Its Reciprocal: Chapter 2 / Example 31Document3 pagesGraphing A Function and Its Reciprocal: Chapter 2 / Example 31lohNo ratings yet
- Using Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7Document2 pagesUsing Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Using Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7Document2 pagesUsing Solver To Find An Integral Limit: Chapter 13 / Example 7CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Domain, Range and Asymptotes: Chapter 2 / Example 7Document14 pagesDomain, Range and Asymptotes: Chapter 2 / Example 7Diandra Satria AdhitamaNo ratings yet
- Bks MaaSL 0302 gdc11 xxcg50Document1 pageBks MaaSL 0302 gdc11 xxcg50Diallo MadinaNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems With The Normal Distribution: Chapter 7 / Example 27Document3 pagesSolving Problems With The Normal Distribution: Chapter 7 / Example 27Ariane CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiSL 0903 gdc10 Xxti84Document5 pagesBks MaiSL 0903 gdc10 Xxti84W SNo ratings yet
- Finding Binomial Probabilities: Chapter 7 / Example 22Document2 pagesFinding Binomial Probabilities: Chapter 7 / Example 22Ariane CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Bks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSPDocument3 pagesBks MaiSL 1301 gdc07 XXTNSPengabd345No ratings yet
- Bks MaaHL 1003 gdc19 XXTNSPDocument2 pagesBks MaaHL 1003 gdc19 XXTNSP23493No ratings yet
- Calculus Maxima and MinimaDocument20 pagesCalculus Maxima and MinimaeliseudesafateNo ratings yet
- Basic Algebra EL-9900Document18 pagesBasic Algebra EL-9900jalejan77No ratings yet
- Graphing TechniquesDocument26 pagesGraphing TechniquesTrí VũNo ratings yet
- MANAP-Summary of Normal Distribution-Lesson 2Document6 pagesMANAP-Summary of Normal Distribution-Lesson 2PatrickNo ratings yet
- Diff. Calc. Module 2 Derivative. Slope - Rates of ChangeDocument9 pagesDiff. Calc. Module 2 Derivative. Slope - Rates of ChangeFernandez DanielNo ratings yet
- CIVL 2122 Lecture 9Document18 pagesCIVL 2122 Lecture 9Brain PuzzleNo ratings yet
- Functions and Graphs Technology (Casio)Document2 pagesFunctions and Graphs Technology (Casio)Ava PidgeonNo ratings yet
- Modelling With Power Functions: Chapter 6 / Example 11Document4 pagesModelling With Power Functions: Chapter 6 / Example 11Sophie HoltusNo ratings yet
- Hints PDFDocument10 pagesHints PDF林盈涵No ratings yet
- CFX 9850 GbplusDocument600 pagesCFX 9850 GbplusLeoNo ratings yet
- Httpsusers Math Msu eduusersbellroLB220SP12Homeworks9 PDFDocument5 pagesHttpsusers Math Msu eduusersbellroLB220SP12Homeworks9 PDFAtirut AlphabetNo ratings yet
- STEP Support Programme STEP 2 Curve Sketching Topic NotesDocument3 pagesSTEP Support Programme STEP 2 Curve Sketching Topic NotesHaoyu WangNo ratings yet
- "Just The Maths" Unit Number 13.16 Integration Applications 16 (Centres of Pressure) by A.J.HobsonDocument10 pages"Just The Maths" Unit Number 13.16 Integration Applications 16 (Centres of Pressure) by A.J.Hobsonix JanNo ratings yet
- MC TY Maxmin 2009 1Document10 pagesMC TY Maxmin 2009 1Sajida CheemaNo ratings yet
- Extension of The Mediant PropertiesDocument2 pagesExtension of The Mediant Propertiescluj24No ratings yet
- Poisson's Equation by The FEM, Continued: General Boundary Conditions and Error AnalysisDocument10 pagesPoisson's Equation by The FEM, Continued: General Boundary Conditions and Error AnalysisJaime HuarcayaNo ratings yet
- hw2 Sol PDFDocument3 pageshw2 Sol PDFMohan BistaNo ratings yet
- Homework 3: Introduction To Cryptography University of Michigan, Fall 2016 Instructor: Chris Peikert Student: SOLUTIONSDocument4 pagesHomework 3: Introduction To Cryptography University of Michigan, Fall 2016 Instructor: Chris Peikert Student: SOLUTIONSAbhijeet VermaNo ratings yet
- HW1 SolDocument2 pagesHW1 Solhenw2000No ratings yet
- Bks MaiHL 0402 gdc08 XXTNSPDocument3 pagesBks MaiHL 0402 gdc08 XXTNSPMark ChangNo ratings yet
- 08 Contour IntegrationvhdhdDocument14 pages08 Contour IntegrationvhdhdxhfakqaawuorgxbwneNo ratings yet
- Calculator Lesson 12 Slope Fields: Return To List of LessonsDocument1 pageCalculator Lesson 12 Slope Fields: Return To List of Lessonsgu_loopNo ratings yet
- 2022 1MA2 Applications of Differentiation - Notes (Students)Document21 pages2022 1MA2 Applications of Differentiation - Notes (Students)Sundaravadivel Prabhav (Njc)No ratings yet
- 15.093: Optimization MethodsDocument8 pages15.093: Optimization MethodsAnup scribdNo ratings yet
- Aero - Lect5 - 2019 GlideDocument10 pagesAero - Lect5 - 2019 GlideAftab AliNo ratings yet
- Poster Basics of Wettin The Young Laplace EquationDocument1 pagePoster Basics of Wettin The Young Laplace EquationPierre NievesNo ratings yet
- Greg Kelly, Hanford High School, Richland, WashingtonDocument7 pagesGreg Kelly, Hanford High School, Richland, WashingtonTemesgen BihonegnNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Lecture 3Document39 pagesTerm 2 Lecture 3DanielAccoUtaniNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Edge DetectionDocument32 pagesConcepts in Edge DetectionPiyush TrivediNo ratings yet
- Lec 9cDocument9 pagesLec 9cAndrea LannesNo ratings yet
- Vector True False PracticeDocument4 pagesVector True False PracticeSivakumar RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Green PDFDocument4 pagesGreen PDFadfallNo ratings yet
- ApproxDocument44 pagesApproxNaveed RiazNo ratings yet
- Calculator Skills - CasioDocument29 pagesCalculator Skills - Casio이상원No ratings yet
- Calculator Lesson 12 Slope Fields: Return To List of LessonsDocument1 pageCalculator Lesson 12 Slope Fields: Return To List of LessonsJulián KaiharaNo ratings yet
- 1 The Integral As An AntiderivativeDocument10 pages1 The Integral As An AntiderivativemrtfkhangNo ratings yet
- Curve-Sketching Using The DerivativeDocument56 pagesCurve-Sketching Using The DerivativejoeNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetics by Besavilla Vol 2Document12 pagesElectro Magnetics by Besavilla Vol 2Joshua MacaldoNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology, Gandhinagar Tools of Theoretical Physics (PH 608), 2019 Home Assignment 2Document3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Gandhinagar Tools of Theoretical Physics (PH 608), 2019 Home Assignment 2Nitin PooniaNo ratings yet
- 08 Contour IntegrationDocument13 pages08 Contour IntegrationMasud SarkerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Application of DifferentiationDocument28 pagesUnit 2 Application of Differentiationafiq hayqalNo ratings yet
- W W V V: Topic IntroductionDocument2 pagesW W V V: Topic Introductionarcee.sevenNo ratings yet
- Normal PDFDocument5 pagesNormal PDFjohngreen13No ratings yet
- PHY103AA: PHYSICS II - ElectrodynamicsDocument9 pagesPHY103AA: PHYSICS II - ElectrodynamicsRAJ MEENANo ratings yet
- Applied Linear Algebra - Boyd Slides Part 7Document6 pagesApplied Linear Algebra - Boyd Slides Part 7usmanali17No ratings yet
- Bks MaiSL 12uu ct00 XxaannDocument2 pagesBks MaiSL 12uu ct00 XxaannCAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Maths AI IBDocument7 pagesMaths AI IBCAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- 13 Approximating Irregular Spaces: Integration: 1 The Graph Shows The Velocity/time Graph in M/s ForDocument3 pages13 Approximating Irregular Spaces: Integration: 1 The Graph Shows The Velocity/time Graph in M/s ForCAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- 13.1 Finding Areas: Represents. 1.5 7 +Document3 pages13.1 Finding Areas: Represents. 1.5 7 +CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Ebook Knowledge and TechnologyDocument82 pagesCh2 Ebook Knowledge and TechnologyCAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument5 pagesResearch ProposalCAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Maths AI IB AnswerDocument19 pagesMaths AI IB AnswerCAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Planning The TOK Essay Part One. Introductory Steps: Advice On Creating Your Essay Plan. Page 2-5Document14 pagesPlanning The TOK Essay Part One. Introductory Steps: Advice On Creating Your Essay Plan. Page 2-5CAPTIAN BIBEKNo ratings yet
- Kevin Swingler - Lecture 4: Multi-Layer PerceptronsDocument20 pagesKevin Swingler - Lecture 4: Multi-Layer PerceptronsRoots999No ratings yet
- FERUMDocument195 pagesFERUMLaura ManolacheNo ratings yet
- Math 21 Lec 1.1 Limit of A Function and Limit Theorems (Handouts)Document28 pagesMath 21 Lec 1.1 Limit of A Function and Limit Theorems (Handouts)RAEE VENDNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 6th Maths Sura Sample Guide Term 1 em 218917Document56 pagesNamma Kalvi 6th Maths Sura Sample Guide Term 1 em 218917Radhanagarathinam NNo ratings yet
- P1 CIE Maths A-LevelDocument8 pagesP1 CIE Maths A-LevelMilos KrejicNo ratings yet
- Exact Differential EquationsDocument17 pagesExact Differential EquationsWASEEM_AKHTERNo ratings yet
- Math 7 - 3Document2 pagesMath 7 - 3Luz Marie CorveraNo ratings yet
- Test Grade 7Document23 pagesTest Grade 7Nguyen DuyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 PDFDocument8 pagesExercise 1 PDFLeong Yue HanNo ratings yet
- COURSE CODE::Discrete Structures and Automata Theory Course Prerequisites: Basic Mathematics and Programming Course ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCOURSE CODE::Discrete Structures and Automata Theory Course Prerequisites: Basic Mathematics and Programming Course ObjectivesSanika DivekarNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Module 3 Parent LetterDocument4 pagesGrade 5 Module 3 Parent Letterapi-285755972No ratings yet
- Chapter One: Exex Ex XXX XDocument24 pagesChapter One: Exex Ex XXX XLushila MinjNo ratings yet
- ASNHS Enhanced Mathematics 7-EderioDocument2 pagesASNHS Enhanced Mathematics 7-EderioAmelita TupazNo ratings yet
- f6 Pure Mathematics Revision Exercise 20090413 Paper 1 Long QueastionsDocument2 pagesf6 Pure Mathematics Revision Exercise 20090413 Paper 1 Long Queastions20/21-5B-(05) HoMeiYi/何美誼No ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants ProjectDocument5 pagesMatrices and Determinants ProjectkunjapNo ratings yet
- Math 10-Q1-PT-TQDocument4 pagesMath 10-Q1-PT-TQMarvin Jamon CampoNo ratings yet
- Csec Maths January 2009Document30 pagesCsec Maths January 2009Christian SNo ratings yet
- A Survey On TOA Based Wireless Localization and NLOS Mitigation TechniquesDocument18 pagesA Survey On TOA Based Wireless Localization and NLOS Mitigation TechniquesazizbahmaniNo ratings yet
- UNSWReservoirCharacterisation 2011.pdf0Document216 pagesUNSWReservoirCharacterisation 2011.pdf0raghib83No ratings yet
- Geometric ModellingDocument138 pagesGeometric ModellingSandeela NaveedNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Abdirahman Ali - U1sigfigspracticews 1Document1 pageKami Export - Abdirahman Ali - U1sigfigspracticews 1jackNo ratings yet
- Elementary ProblemsDocument5 pagesElementary ProblemsCharlie PinedoNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Quadratic EquationsDocument10 pagesGraphs of Quadratic EquationsROSLINA BINTI ABDUL RASHID MoeNo ratings yet
- Maths 041 Set 3 2022 - 23)Document9 pagesMaths 041 Set 3 2022 - 23)owenknight3456No ratings yet
- Module 1 - FunctionsDocument26 pagesModule 1 - FunctionsMonhannah Calimbol Sumapal LimbutunganNo ratings yet
- MuirheadDocument19 pagesMuirheadRitabrata RoyNo ratings yet