Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Etoricoxib - Martindale 39th
Uploaded by
Cachimbo PrintCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Etoricoxib - Martindale 39th
Uploaded by
Cachimbo PrintCopyright:
Available Formats
58
Profile Effects on the gastrointestinal trad. Etodolac is reported mobet; Flogojet; Valorel; China: Rheumon ({ii'Jll); Cz.: Trau-
to be a preferential inhibitor of cydo-oxygenase-2 (COX- mont; Ger.: Rheumon; Gr.: Celanatt; Cimalt; Etofenol; Eto-
Ethylmorphine hydrochloride is an opioid analgesic 2) and consequently it may produce less gastric toxicity gelt; Fenamt; Ferepatt; Herponil; Irifone; Kovotherm;
(p. 109.1) and has properties similar to those of codeine than the non-selective NSAIDs such as naproxen. 1 - 3 Melferut; Pazergicelt; Radermin; Reuminat; Roiplon; Vellodry-
(p. 41. l). It is used mainly as a cough suppressant. It has also l.Taha AS, et al. Effect of repeated therapeutic doses of naproxen and
ingt; Hong Kong: Flogoprofen; Hung.: Activon; Rheumon; Irl.:
been used for its analgesic and antidiarrhoeal properties. It etodolac on gastric and duodenal mucosa! prostaglandins (PGs) in Etoflam; Ital.: Gemadol; Mex.: Bayro; Metotrop; Poi.: Rheu-
was formerly given in eye drops as a lymphagogue. rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Cut 1989; 30: A751. mon; Traumon; Port.: Inalgex; Reumon; Spica; Rus.: Revmonn
Ethylmorphine free base and the camphorate and 2. Bianchi Porro G, et al. A double-blind gastroscopk evaluation of the (PeBMOHH); Spain: Aspitopic; Flogoprofen; Zenavan; Switz.:
camsilate have also been used. cffects of etodolac and naproxen un the gastroinLestinal mucosa of Rheumon; Traumalix; Turk.: Doline; Efamat; Etofast; Fleximat;
rheumatic patients. J Intern Med 1991; 229: 5-8. Flexo; Painex; Restafen; Rheumon; Thenno Etox; Thermo-Efe-
References. 3. Weideman RA, et al. Risks of clinically signilicant upper gastrointestinal
mat; Venez.: Traflan.
l. Aasmundstad TA, et al. Biotransformation and pharmacokinetics of events with etodolac and naproxen: a historical cohort analysis.
ethylmorphine aíter a single oral dose. BrJClin Phannacol 1995; 39: 611- Gastroenterology 2004; 127: 1322-8.
20.
Multi-ingredient Preparotions. Arg.: Bayagel; Austria: Thermo-
2. Jonasson B. et al. Fatal poisonings where ethylmorphine from Rheumon; Gr.: Thermo-Roiplont; Mex.: Bayro Tennot; Poi.:
antitussive medications contributed to death. Int J Legal Med 1999; lnteractions Thenno-Rheumon; Turk.: Restafen Plus; Thermo-Doline; Ther-
112: 299-302.
For interactions associated with NSAIDs, see p. 108.3. mo-Rheumon; Thermoflex; Thermove; Venez.: Reugel.
3. Helland A, et al. Death of a 10-month-old boy after exposure to
ethylmorphine. J Forensic Sd 2010; 55: 551-3.
Pharmacokinetics
Preparations
........................... Etodolac is a chiral compound given as the racemate. Peak
Etoricoxib IBAN, USAN. r/NN)
Proprietary Preparations (details are given in Volume B) plasma concentrations of the active S-enantiomer and of the ttoricoxib; Etoricoxibum; Etoríkoksib; Etorikoksibi; Etorikoxib;
inactive R-enantiomer usually occur within about 2 hours L-791456; MK-0663; MK-663; 3top~KOKCl16,
Single-ingredient Preparations. Arg.: Dionina; Belg.: Codethy-
of an oral dose but plasma concentrations of the R- 5-Chloro-6' -methyJ-3-[p-(methylsu lfonyl)phenylJ-2,3' -bipyri-
line; Tussethyl; Fin.: CocilJana; Fr.: Clarix Toux Seche
Codethyline; Pectosan Toux Sechet; Peter's Sirop; India: Dio- enantiomer have been reported to greatly exceed those of dine.
nindon; UK: Collins Elixir. the S-enantiomer. Both enantiomers are highly bound to C1gl-1 15CIN¡02S=358.8
plasma proteins. Both are also distributed to the synovial CAS - 202409-33-4.
Multi-ingredient Preparations. Belg.: Baume Pulmonaire; Saint- fluid, although the difference in their concentrations may
bois; Chile: Codelasa; Fin.: Indalgin; Fr.: Tussipax; Tussipax; not be as large as the difference in plasma concentrations. ATC MOIAHQ5.
Vegetoserum; Hung.: Tabletta antidolorica; Norw.: Cosylan; The plasma half-life of total etodolac has been reported to be ATC Vet - QM01AH05.
Solvipect comp; Spain: Demusint; Swed.: Cocillana-Etyfin; about 7 hours; excretion is mainly in the urine as UNll - WRX4NFY03R.
Lepheton; Switz.: Phol-Tux; Sano Tusst; Turk.: Fenokodin; hydroxylated metabolites and glucuronide conjugares;
Neocodint; Venez.: Novacodin. sorne may be excreted in the bile.
Uses and Administration
References.
l. Brocks DR, et al. Stereoselective disposition of etodolac enantiomers in Etoricoxib is an NSAID (p. 103.2) reported to be a selective
Etodolac IBAN, USAN, r/NNJ synovial fluid. JC!in Pharmacol 1991; 31: 741-6.
2. Brocks DR, et al. The stereoselective pharmacokinetics of etodolac in
inhibitor of cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2). lt is used in the
symptomatic relief of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis,
AY-24236; i:todolaakki; ttodolac; Etodolaco; Etodolacum; young and elderly subjects, and after cholecystectomy. J Clin Pharmacol
ankylosing spondylitis, and acute gouty arthritis. Etoricoxib
1992; 32: 982-9.
Etodolak; Etodolák; Etodolákas; Etodollc Acld: 3Ti5tlOJ1aK. 3. Brocks DR, Jamali F. Etodolac dinical pharmacokinetics. Clin is also used for the short-term treatment of moderate
t!lcDíethyl-1,3,4,9-tetrahydropyrano[3,4-b]indol-1-ylacetic Pharmacokinet 1994; 26: 259-74. postoperative dental pain.
acid. · 4. Boni J, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aclion of etodolac In osteoarthritis, it is given in a usual dose of 30 mg once
in patients after oral surgery. J Clin Pharmacol 1999; 39: 729-37.
C11l-l21N03=287.4 5. Boni JP, et al. Pharmacokinetics of etodolac in patients with stable
daily, increased to 60mg once daily if necessary. The
0\5 - 41340-25"4. juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther 1999; 21: 1715-24. recommended dose in rheumatoid arthritis and in
ATC-'-"MOTA808. ankylosing spondylitis is 90 mg once daily; higher doses of
120 mg once daily are used in gouty arthritis although such
ATC Vet - QM01A808.
UNJI~ 2M36281008.
P.r~P.~.r~.ti?.n.~ .. doses should only be used far the acute symptomatic period
Proprietary Preparations (details are given in Volume B) and for a maximum of 8 days. For postoperative dental pain,
Phormocopoeios. In Eur. (see p. vii), Jpn, and US. Single-ingredient Preparations. Braz.: Flancox; China: Etolac (ti<
the reconunended dose of etoricoxib is 90 mg once daily for
Ph. Eur. 9; (Etodolac). A white or almost white crystalline 'W/); Lodine ('.l)'T); Na Zhi (~~ll:); Shu Ya Ke (ílf'l!UiiJ); Yi Fen
a maximum of 3 days.
powder. Practically insoluble in water; freely soluble in ('Í&3t=); Denm.: Todolac; Fin.: Lodine; Fr.: Lodine; Gr.: Ecridox-
For dosage recommendations in patients with hepatic
alcohol and in acetone. ant; Etolact; Impovitusst; Loninet; Lubetylt; Ofniskelt; Silgo- impairment, see below.
USP 39: (Etodolac). Store in airtight containers. nitrant; India: Etofact; Etolor; Etomax; Etova; Israel: Etopan; References.
Jpn: Hypen; Ospain; Osteluc; Paipelac; Raipeckt; Philipp.: Eto- l. Patrignani P, et al. Clinical pharmacology of etoricoxib: a novel selective
flamt; Port.: Dualgan; Exodolan; Sodolac; Rus.: Nobedolac COX2 inhibitor. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2003; 4: 265-84.
Uses and Administration (Ho6e.[{onax); Switz.: Lodine; Thai.:. Etonox; Turk.: Barca; 2. Dallob A, et al. Characterization of etoricoxib, a novel, selective COX-2
Dolarit; Edolar; Esodax; Etodin; Etol; Etopan; Etotac; Etoteva; fohibitor. J Clín Pharmacol 2003 43: 573-85.
Etodolac, a pyrano'indoleacetic acid derivative, is an NSAID 3. Martina SD, et al. Etoricoxib: a highly selective COX-2 inhibitor. Ann
(p. 103.2) reported to be a preferential inhibitor of cyclo- Etoxa; Lodine; Maxdol; Tadolak; Tilac; UK: Ecco~olac; Etopan; Pharmacother 2005; 39: 854-62.
oxygenase-2 (COX-2). It is used for rheumatoid arthritis, Lodine; Ukr.: Etol (3Ton).
including juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and osteoarthritis Multi-ingredient Preparations. India: Etolex-P; Etolor-P; Eto- Administration in hepotic impoirment. The maximum
and far the treatment of acute pain. max-P; Etova-P; Turk.: Etofam; Etolio. oral dose of etoricoxib in patients with mild hepatic
For the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarth- impairment (Child-Pugh score of 5 to 6), regardless of
ritis, the recommended oral dose is initially 0.6 to l g daily in Pharmacopoeial Preparotions
BP 2016: Etodolac Capsules; Etodolac Tablets; indication, is 60 mg once daily; those with moderate
divided doses adjusted according to response to a usual dose impairment (Child-Pugh 7 to 9) should be given a maxi-
of 300 to 600 mg daily. Modified-release preparations are USP 39: Etodolac Capsules; Etodolac Extended-Release Tablets;
Etodolac Tablets. mum of 60 mg every other day or 30 mg once daily. Etori-
available far once-daily use in these conditions. For doses in coxib should not be given to patients with severe hepatic
children, see below. impairment (Child-Pugh 10 or more).
For the treatment of acute pain, the recommended dose
is 200 to 400 mg every 6 to 8 hours to a maximum of 1 g Etofenamate IBAN, USAN. r/NN)
daily. Musculoskeletal and joint disorders, The selective cydo-
8;577;. Bay-d-1107; Etofenamaattí; Etofenamat; Etofenamát; oxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor etoricoxib is used in the
Reviews. Etofenamatas; Étofénamate; Etofenamato; Etofenamatüm; ireatment of ankylosing spondylitis (see Spondyloarthro-
l. Tirunagari SK, et al. Single dose oral etodolac for acute postoperative
pain in adults. Available in The Cochrane Database of Systematic
TV-485; "TVX-485; WHR-5020; 3ro<j>eHaMaT.. pathies, p. 14.3), osteoarthritis (p. 12.3), and rheumatoid
Reviews; Issue 3. Chichester: John Wiley; 2009 (accessed 09/09/09). 2'(2-Hydroxyethoxy)ethyl N-(aaa-triftuoro-m-tolyl)anthrani- arthritis (p. 13. l ); it is also used in gouty arthritis
late. (p. 608.1). However, in the UK, it is recommended that
Administration in children. In the USA modified-release C,.H 18 F 3 N0 4~369.3 the use of selective COX-2 inhibitors is limited to patients
preparations of etodolac may be given for the oral treat- C45 - 30544-47-9. with good cardiovascular health and at high risk o! devel-
ment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children aged 6 to oping serious gastrointestinal problems if given a
ATC .~ M02M06,
16 years. Doses are given once daily according to body- non-selective NSAID (see p. 106.3).
AT(Vet--:-- QM02AA06.
weight as follows; References.
UN// - KZFOXM66JC.
• 20 to 30 kg; 400 mg l. Cochrane DJ, et al. Etoricoxib. Drugs 2002; 62: 2637-51.
• 31 to 45 kg; 600 mg Phormocopoeios. In Eur. (see p. vii). 2. Schumacher HR, et al. Randomised double blind trial of etoricoxib and
• 46 to 60 kg: 800 mg indometadn in treatment of acute gomy arthritis. BMJ 2002; 324: 1488-
Ph. Eur. 9: (Etofenamate). A yellowish viscous liquid. 92.
• over 60kg: l g Practically insoluble in water; miscible with alcohol and 3. Gottesdiener K. et al. Results of a randomized. dose-ranging tria! of
with ethyl acetate. etoricoxib in patients with osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002; 41:
Adverse Effects, Treatment, and Precautions 1052-61.
4. Wiesenhutter CW, et al. Evaluation of the comparative efficacy of
As for NSAIDs in general, p. 105.2. Profile etoricoxib and ibuprofen for treatment of patients with osteoarthritis: a
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Mayo Clin Proc 2005;
The presence of phenolic metabolites of etodolac in the Etofenamate is an NSAID (p. 103.2) that has been applied 80: 470-9.
urine may give rise to a false-positive reaction for bilirubin. topically in a concentration of 5 or 10% for the relief of pain 5. van der Heijde D, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of etoricoxib in
and inflammation associated with musculoskeletal, joint, ankylosing spondylitis: results of a fifty-two-week, randomized,
Effects on the blood. Agranulocytosis has been reported in and soft-tissue disorders. lt has also been given by deep controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 1205-15.
a patient receiving etodolac. 1 Coombs-positive haemolytic 6. Curtis SP, et al. Etoricoxib in the treatment of osteoarthritis over 52-
intramuscular injection in single doses of 1 g. weeks: a double-blind, active-comparator controlled trial
anaemia due to sensitivity to etodolac metabolites has also [NCT00242489]. BMC Muscu/oske!et Disord 2005; 6: 58. Available at:
be en reporte d. 2 http://www.biomedcen tra l. com 1content/pdf/14 71- 24 7 4-6- 5 8. pdf
l. Cramer RL, et al. Agranulocytosis associated with etodolac. Ann (accessed 01/ l l /07)
Pharmacother 1994; 28: 458-60. Praprietary Preparations (details are given in Volume B) 7. Bingham CO, et al. Efficacy and safety of etoricoxib 30 mg and celecoxib
2. Cunha PO, et al. Immune hemolytic anemia caused by sensitivity to a 200 mg in the treatment of osteoarthritis in two identically designed,
metabolite of etodolac. a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Single-ingredient Preparations. Arg.: Flogol; Austria: Rheumon; randomized, placebo-controlled, non-inferiority studies. Rheumatology
Transfusion 2000; 40: 663-8. Traumon; Belg.: Flexium; Braz.: Aspisport; Bayro; Chile: Cal- (Oxford) 2007; 46: 496-507.
Ali cross-references refer to entries in Volume A
59
8. Croom KF, Siddiqui MAA. Etoricoxib: a review of its use in the 3. EMEA. EMEA recommends strengthening warnings and contra- derivative, the major metabolite. Both are inactive or only
symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, anky- indications for etoricoxib-containing medicines used in the treatment of weak cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. Excretion is
losing spondylitis and acute gouty arthritis. Drugs 2009; 69: 1513-32. rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis (issued 26th June,
2008). Available at: http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfslhuman/press/pr/ mainly via the urine (70%) with only 20% ol a dose
33363608en.pdf (accessed 16/07/08) appearing in the faeces. Studies in animals suggest that
Pain. A systematic review 1 found that a single 120-mg etoricoxib may cross the placenta and that sorne is
dose ol etoricoxib, given orally, provided effective pain Effects on the gastrointestinal trad. It is generally distributed into breast milk.
relief alter surgery. When compared indirectly, etoricoxib accepted that the inhibition ol cyclo-oxygenase-1 (COX-1) References.
was considered to be at least as effective as other com- plays a role in the adverse gastrointestinal effects al the l. Agrawal NGB, et al. Single- and multiple-dose phannacokinetics of
monly used analgesics. NSA!Ds, and that the selective inhibition o! the other iso- etoricoxib, a selective inhibitor of cydooxygenase-2, in man. J Clin
1. Clarke R, et al. Single dose oral etoricoxib for acute postoperative pain in form, COX-2, by NSA!Ds such as etoricoxib may cause less Pharmacol 2003; 43: 268-76.
adults. Available in The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews; Issue 2. Agrawal NGB, et al. Pharmacokinetics of etoricoxib in patients with
gastrotoxicity than that seen with the non-selective inhibi- hepatic impairment. J Clin Pharmacol 2003; 43: l 136-48.
5. Chichester: John Wiley; 2014 (accessed 25/05/16).
tion ol the traditional NSA!Ds. However, licensed product 3. Agrawal NGB, et al. Pharmacokinetics of etoricoxib in patients with renal
information states that upper gastrointestinal perforation, impairment. J Clin Pharmacol 2004; 44: 48-58.
Adverse Effects, Treatment, and Precautions ulceration, and bleeds, in sorne cases fatal, have occurred 4. Takemoto JK, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic
profile of etoricoxib. Clin Pharmacokinet 2008; 47: 703-20.
with etoricoxib treatment; consequently, it should be used
As far NSA!Ds in general, p. 105.2. with caution in patients with a history of, or at risk of
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and developing, such events. In addition, etoricoxib should not Preparations
angioedema have occurred in patients receiving etoricoxib; be used in patients with active gastrointestinal ulceration
it should be stopped at the first signs ol hypersensitivity. Proprietary Preparations (details are given in Volume B)
or bleeding.
Etoricoxib should not be used in patients with ischaemic Results from controlled studies have suggested that Single-ingredient Preparations. Arg.: Arcoxia; Austral.: Arcoxia;
heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, or cerebrovascular NSA!Ds selective far COX-2 were associated with a lower Austria: Arcoxia; Belg.: Arcoxia; Ranacoxt; Braz.: Arcoxia;
disease. It should be used with caution in patients with incidence of serious gastrointestinal effects. In a study 1 of Chile: Arcoxia; China: Arcoxia (~j¡_ffi); Cz.: Arcoxia; Denm.:
significant risk factors for cardiovascular disease such as the pooled data from 3 randomised clinical studies, Arcoxia; Fin.: Arcoxia; Fr.: Arcoxia; Ger.: Arcoxia; Exinef; Gr.:
hypertension, hyperlipidaemia, and diabetes mellitus. etoricoxib (in doses of 60 or 90 mg daily) was associated Arcoxia; Turoxt; Hong Kong: Arcoxia; Hung.: Arcoxia; India:
Etoricoxib, particularly at high doses, may be associated with significantly less frequent upper gastrointestinal Alcoxib; Coxet; Coxifact; Doricox; E-Trom; Ebov; Eleton; Erofi·
with more frequent and severe hypertension compared clinical events than diclolenac (!50mg daily). The result ca; Eteron; Eticox; Etobus; Etocos; Etody; Etofan; Etolex; Etom;
with other NSA!Ds and selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX- was attributed to the lower rate of uncomplicated ulcers Etori; Etorica; Etosaid; Etoshine; Etosym; Etoxib; Etozox; Etrik;
2) inhibitors; blood pressure monitoring during etoricoxib with etoricoxib compared with diclofenac; there was no Etro; Etrobax; Ezact; Hicox; Hireto; lfydrox; Intacoxia; Ixidol;
treatment is recommended. Etoricoxib should not be used difference in the rate of complicated gastrointestinal events Kingcox; Kretos; L-Kon; M-Kon; Nucoxia; O·Cox; Indon.:
in patients with hypertension whose blood pressure is not between the 2 drugs. The lower rate ol uncomplicated Arcoxia; Irl.: Acoxxelt; Arcoxia; Israel: Arcoxia; Ital.: Algix;
controlled (see also Effects on the Cardiovascular System, events with etoricoxib compared with diclofenac was not Arcoxia; Exinef; Tauxib; Malaysia: Arcoxia; Mex.: Arcoxia;
below). Neth.: Arcoxia; Auxibt; Norw.: Arcoxia; NZ: Arcoxia; Philipp.:
affected by treatment with low-dose aspirin or proton pump
Etoricoxib is also contra-indicated in patients with Arcoxia; Arcoxib; Xibra; Poi.: Arcoxia; Port.: Arcoxia; Exxiv;
inhibitors. An analysis2 by the manufacturer, o! pooled data
inflammatory bowel disease, moderate to severe heart Turox; Rus.: Arcoxia (ApKOKCHa); S.Afr.: Arcoxia; Singapore:
from 1O randomised clinical studies, found that etoricoxib
failure (NYHA class 11 to IV), and renal impairment Arcoxia; Spain: Acoxxel; Arcoxia; Exxiv; Swed.: Arcoxia;
(in daily doses ol 60, 90, or 120 mg) was associated with a Turox; Switz.: Arcoxia; Thai.: Arcoxia; UK: Arcoxia; Ukr.:
associated with a creatinine clearance of less than lower combined risk of upper gastrointestinal perforations
30 mL/minute. It should be avoided in patients with severe Arcoxia (ApKoKcux); Venez.: Arcoxia.
and bleeding, and symptomatic gastroduodenal ulcers when
hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score o! 10 or more). compared with non-selective NSAIDs (diclolenac 150mg Mul~·ingredient Prepara~ons. India: Etro-P; Nucoxia-MR;
Therapy should be stopped il persistently abnormal liver daily, ibuprofen 2.4 g daily, or naproxen 1 g daily) as a Nucoxia-P; Nucoxia-SP.
enzyme values are seen. Caution is recommended when group. This reduced risk was seen even in patients with
using etoricoxib in dehydrated patients; it may be advisable known risk factors for such complications such as the
to rehydrate patients befare giving etoricoxib. elderly and those with a history ol gastrointestinal reactions. Etorphine Hydrochloride (BANM, r/NNM)
l.Laine L, et al. Assessment of upper gastrointestinal safety of etoricoxib
Effects on the cardiovascular syslem. There have been and didofenac in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in Etorfina, hidrocloruro de; ttorphine, Chlorhydrate d';
concerns about the adverse cardiovascular effects of selec- the Multinational Etoricoxib and Diclofenac Arthritis Long-term Etorphini Hydrochloridum; Hidrocloruro de etorflna; M-99;
(MEDAL) programme: a randomised comparison. Lancet 2007; 369: 19-Propylorvinol Hydrochloride; 3róp<j>~Ha f1<Apoxnopiil,t¡.
tive cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors alter the world- 465-73.
wide withdrawal al rolecoxib (see p. 129.3). The cardio- 2. Ramey DR, et al. The incidence of upper gastrointestinal adverse events (6R,7R,14R)-7,8-Dihydro-7-[(1 R)-1-hydroxy-1-methylbutyl]~
vascular safety of etoricoxib has been assessed in the in dinical trials of etoricoxib vs. non-selective NSAIDs: an updated O-methyl-6, 14a-ethenomorphine hydrochloride; (2Rl·HH-
MEDAL programme, 1 which pooled data lrom 3 studies combined analysis. Curr Med Res Opin 2005; 21: 715-22. (5R,6R,7 R, 14/l)-4,5-Epoxy-3-hyd roxy-6-methoxy-9a-methyl-
involving over 30 000 patients with either osteoarthritis or 6, 14-ethenomorphinan: 7-yl]pentan-2-ol hydrochloride.
rheumatoid arthritis. Patients with osteoarthritis were Effects on the kidneys. Limited evidence o! the renal toxi-
city ol the selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors C2sH 33NO,,,HCl=448.0
given etoricoxib 60 or 90 mg daily; those with rheumatoid CAS - 14521-%-1 (etorphine); 13764-49-3 (etorphine
arthritis received 90 mg daily. In ali studies, diclolenac such as etoricoxib suggests that such NSA!Ds appear to
have effects on renal function similar to those of the hydrochloride).
150 mg daily was given as the comparator; low-dose
aspirin ( 100 mg daily or less) was also allowed where indi- non-selective NSA!Ds (see p. 107.1 ). UN// - 8CBEOIN748.
cated. After an average treatment duration of 18 months, Pharmacopoeias. In BP(Vet).
the rates of thrombotic events such as myocardial infarc- Porphyria. The Drug Database far Acule Porphyria, com-
piled by the Norwegian Porphyria Centre (NAPOS) and BP(Vet) 2016; (Etorphine Hydrochloride). A white or
tion, stroke, and sudden or unexplained death with etori-
the Porphyria Centre Sweden, classifies etoricoxib as possi- almos! white microcrystalline powder. Sparingly soluble in
coxib were similar to those far diclolenac. (It has been
bly porphyrinogenic; it sbould be used only when no safer water and in alcohol; very slightly soluble in chlorofarm;
suggested that diclofenac itself may increase the risk o!
alternative is available and precautions should be consid- practically insoluble in ether. A 2% solution in water has a
sorne thrombotic events; far further details, see p. 105.3.)
ered in vulnerable patients. 1 pH ol 4.0 to 5.5. Protect from light.
The programme also found that the rate of sorne other
non-thrombotic cardiovascular events was increased with l. The Drug Database for Acute Porphyria. Available at: http://www.
etoricoxib: one ol the 3 studies showed that there was a
drugs-porphyria.org {accessed 23/ 10/ l l} Uses and Administration
non-significan! increase in the rate of heart failure with Etorphine hydrochloride is a highly poten! opioid analgesic
etoricoxib 90 mg daily compared with diclolenac; withdra- lnteractions (p. 109 .1) used far reversible neuroleptanalgesia (see
wals due to oedema were also more frequent with high- The metabolism ol etoricoxib is mediated by the cytochrome Anaesthetic Techniques, p. 1932.3) in veterinary medicine.
dose etoricoxib than with diclofenac or etoricoxib 60 mg P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4. Use with other drugs that inhibit It is given with acepromazine maleate or levomepromazine
daily. In addition, the number ol patients stopping treat- or induce this isoenzyme may result in changes in plasma (Immobilon) to restrain animals and befare minar veterinary
ment because ol hypertension was higher with both doses concentration of etoricoxib. In addition, in vitro studies surgery. The duration of action of etorphine is up to about
of etoricoxib than with diclofenac. Similar results were suggest that severa] other isoenzymes may also media te the 45 to 90 minutes depending on the species but it may be
seen in the other 2 studies. main metabolic pathway ol etoricoxib. Rifampicin, a poten! longer in man, especially if the large animal preparation is
In another study2 that pooled pre-licensing data, the risk inducer of CYP isoenzymes, has produced decreased plasma involved.
of thrombotic events with etoricoxib, given at a dose of at concentrations of etoricoxib.
least 60 mg daily, was also faund to be similar to that for
f?.~Pf!.~.~~'!~f!..~'!1...~!!.~.~~~~?.!. . . . ,........... ,.............. .
Etoricoxib is an inhibitor of human sulfotransferase
placebo treatment, ibuprolen (2.4 g daily), diclolenac activity and has been shown to increase the plasma
( 150 mg daily), and naproxen ( 1 g daily), although there concentration of ethinylestradiol. Interactions wjth other As far Opioid Analgesics, p. 110.1.
was a trend towards more events with etoricoxib than with drugs, such as oral salbutamol and minoxidil, also
naproxen. For details on the relative risk of thrombotic
events associated with non-selective NSA!Ds, see p. 105.3.
metabolised by this enzyme may be a possibility and Adverse Effects and Treatment
licensed product information advises care with such
After a recommendation from the EMEA's Committee combinations. As far Opioid Analgesics in general, p. 111.1. Etorphine is
far Medicinal Products far Human Use (CHMP), 3 licensed Por interactions associated with NSAIDs in general, see not used therapeutically in humans.
product information for etoricoxib states that it must not be p. 108.3. Etorphine hydrochloride is highly potent and rapid
given to patients whose blood pressure is persistently above acting; minute amounts can exert serious effects leading to
140/90mmHg and inadequately controlled; in addition, coma. It may be absorbed through skin and mucous
high blood pressure should be controlled befare starting
Pharmacokinetics
........................ ........................ . membranes. It is thus advisable to inject an antagonist
treatment and monitored for 2 weeks afterwards then Etoricoxib is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract immediately after contamination of skin or mucous
regularly therealter. after oral doses. Peak plasma concentrations occur in about membranes with preparations containing etorphine hydro-
Por discussion and advice on the use of selective COX-2 1 hour in !asted adults; faod delays absorption by about 2 chloride and to wash the affected areas copiously.
inhibitors in patients with cardiovascular or cerebrovascular hours, although it has no effect on the extent o! absorption. Accidental injection or needle scratch injuries should also
disease, see under Celecoxib, p. 38.2. Plasma protein binding is about 92 % . Al steady state the be treated immediately by injecting an antagonist. Naloxone
l. Cannon CP, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with etoricoxib and half-lile ol etoricoxib is about 22 hours. Etoricoxib is is preferred as the antagonist in medical treatment.
didofenac in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in the extensively metabolised with less than 2 % ol a dose However, veterinary preparations of etorphine are supplied
Multinational Etoricoxib and Diclofenac Arthritis Long-term (MEDAL) recovered in the urine as the parent drug. The majar route
programme: a randomised comparison. Lancet 2006; 368: 1771-81.
with a preparation (Revivan) containing diprenorphine
2. Curtis SP, et al. Pooled analysis of thrombotic cardiovascular events in of metabolism is via cytochrome P450 isoenzymes including hydrochloride (p. 1582.2) and this should be used far
clinical trials of the COX-2 selective inhibitor etoricoxib. Curr Med Res CYP3A4 to form the 6' -hydroxymethyl derivative ol immediate first·aid antagonism if naloxone is not available.
Opin 2006; 22: 2365-74. etoricoxib, which is then oxidised to the 6' -carboxylic acid
The symbol t denotes a preparation no longer actively marketed
You might also like
- Tingenone, A Pentacyclic Triterpene, Induces Peripheral Antinociception Due To Cannabinoid Receptors Activation in Mice - InflammopharmacologyDocument9 pagesTingenone, A Pentacyclic Triterpene, Induces Peripheral Antinociception Due To Cannabinoid Receptors Activation in Mice - InflammopharmacologyRenata MendesNo ratings yet
- ErythropoietinDocument24 pagesErythropoietinactivnetNo ratings yet
- Topical Anaesthesia in Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: GlandularDocument1 pageTopical Anaesthesia in Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: GlandularHala HaylaNo ratings yet
- Neurohormonal Activation in Severe Scorpion Envenomation: Correlation With Hemodynamics and Circulating ToxinDocument6 pagesNeurohormonal Activation in Severe Scorpion Envenomation: Correlation With Hemodynamics and Circulating ToxinDaniela SalamancaNo ratings yet
- Crespo2011 PDFDocument6 pagesCrespo2011 PDFDANIELA MALAGÓN MONTAÑONo ratings yet
- Translation TerminationDocument15 pagesTranslation TerminationDavid MoralesNo ratings yet
- EROD Activity in Fish as a Biomarker of Chemical ExposureDocument5 pagesEROD Activity in Fish as a Biomarker of Chemical Exposurekheireddine fekrouneNo ratings yet
- 5 Water Contamination by NitratesDocument15 pages5 Water Contamination by NitratesBioq. GallegosNo ratings yet
- Another Flame Retardant, Tris - (1,3-Dichloro-2-Propyl) - Phosphate, and Its Expected Metabolites Are MutagensDocument3 pagesAnother Flame Retardant, Tris - (1,3-Dichloro-2-Propyl) - Phosphate, and Its Expected Metabolites Are Mutagensánh nguyễnNo ratings yet
- LoperamidaDocument19 pagesLoperamidaGlo RyndaNo ratings yet
- Peroxidative Metabolism of - Agonists Salbutamol and Fenoterol and Their AnaloguesDocument14 pagesPeroxidative Metabolism of - Agonists Salbutamol and Fenoterol and Their AnaloguesDesNo ratings yet
- Alur Hormonal Udang 2013Document50 pagesAlur Hormonal Udang 2013brian jusuf adhitamaNo ratings yet
- Ejm 93585 Original Article Gullu ArslanDocument6 pagesEjm 93585 Original Article Gullu ArslanJordan NGOUNENo ratings yet
- Exacerbation of Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity by The Anthelmentic Drug FenbendazoleDocument6 pagesExacerbation of Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity by The Anthelmentic Drug FenbendazoleSkyalesNo ratings yet
- Camparison Monovalente AntivenomsDocument1 pageCamparison Monovalente AntivenomsAndrea BaracaldoNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Enolase Activity in Cell LysatesDocument10 pagesMeasurement of Enolase Activity in Cell LysatesClinton LunaNo ratings yet
- Differential Expression Profiling of The Hepatic Proteome in A Rat Model of Dioxin ResistanceDocument13 pagesDifferential Expression Profiling of The Hepatic Proteome in A Rat Model of Dioxin Resistancegiasco78No ratings yet
- Num 04 587 PDFDocument2 pagesNum 04 587 PDFRany NugeshaNo ratings yet
- Demaegdt Et Al., 2016 (Endocrine Activity of Myctoxins and Mixtures)Document10 pagesDemaegdt Et Al., 2016 (Endocrine Activity of Myctoxins and Mixtures)Guilherme SilvaNo ratings yet
- Cabaton I In. 2009Document10 pagesCabaton I In. 2009Ola ZygmuntowiczNo ratings yet
- 2016.Zheng-Hai - Activating Nuclear Xenobiotic Receptors and Triggering ER Stress and Hepatic Cytochromes P450 Systems in Quails (Coturnix C-Coturnix) During Atrazine ExposureDocument10 pages2016.Zheng-Hai - Activating Nuclear Xenobiotic Receptors and Triggering ER Stress and Hepatic Cytochromes P450 Systems in Quails (Coturnix C-Coturnix) During Atrazine ExposureIasmin ResendeNo ratings yet
- Cacciatore in VivoDocument11 pagesCacciatore in VivoClauToreNo ratings yet
- 356 PDFDocument5 pages356 PDFraysellaNo ratings yet
- The Rodenticidal Effect of Indomethacin: Pathogenesis and PathologyDocument12 pagesThe Rodenticidal Effect of Indomethacin: Pathogenesis and PathologyNana Tabi GyekyeNo ratings yet
- Yang 2003Document12 pagesYang 2003พรี้ขิง อะครับNo ratings yet
- Inhibition of Prostaglandin Synthesis During Polystyrenemicrosphere-Induced Pulmonary Embolism in The RatDocument10 pagesInhibition of Prostaglandin Synthesis During Polystyrenemicrosphere-Induced Pulmonary Embolism in The RatshintaNo ratings yet
- Petroianu 2005Document5 pagesPetroianu 2005Bilel ChefiratNo ratings yet
- Influence of antidepressants on salivary gland ecto-enzymesDocument7 pagesInfluence of antidepressants on salivary gland ecto-enzymesconstanceNo ratings yet
- Toxin Production of SalmonellaDocument13 pagesToxin Production of Salmonellaistine capulongNo ratings yet
- Ivermectin Is A Nonselective Inhibitor of Mammalian P-Type AtpasesDocument6 pagesIvermectin Is A Nonselective Inhibitor of Mammalian P-Type AtpasesnadjanairaNo ratings yet
- TMP 84 BDocument12 pagesTMP 84 BFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Varayoud Et Al., 2008 Endosulfan ModulatesDocument8 pagesVarayoud Et Al., 2008 Endosulfan Modulateslucasmonje1978No ratings yet
- Endo 4252Document12 pagesEndo 4252nepretipNo ratings yet
- Minireview Glycopyrrolate: Et Al., Cardiovascular EffectsDocument5 pagesMinireview Glycopyrrolate: Et Al., Cardiovascular EffectsGeotamNo ratings yet
- Organophosphates LiteratureDocument13 pagesOrganophosphates LiteratureSenkatuuka LukeNo ratings yet
- M.SC - Animalbiotechnology - 2012 PDFDocument12 pagesM.SC - Animalbiotechnology - 2012 PDFSudeeksha RavikotiNo ratings yet
- Jurell 1981Document4 pagesJurell 1981Sam CastilloNo ratings yet
- Fenoterol HydrobromideDocument2 pagesFenoterol HydrobromideAnonymous XgX8kTNo ratings yet
- Muñoz-Pérez2016 Article CharacterizationOfMelatoninSynDocument14 pagesMuñoz-Pérez2016 Article CharacterizationOfMelatoninSynMinaNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences influence of propylene glycolDocument7 pagesEuropean Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences influence of propylene glycolgalangpramadhan pcNo ratings yet
- Rodriguez Pez Cebra 3BP-2015Document5 pagesRodriguez Pez Cebra 3BP-2015Gabriela RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Antiinflamatory Coral CoelenterataDocument10 pagesAntiinflamatory Coral CoelenterataEviNo ratings yet
- Rhythms in The Endocrine System of Fish: A Review: ArticleDocument34 pagesRhythms in The Endocrine System of Fish: A Review: ArticleBagas Lantip PrakasaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Trifluoromethylated Dihydrocoumarins, Indanones, and Arylpropanoic Acids by Tandem Superacidic Activation of 2 - (Trifluoromethyl) Acrylic Acid With ArenesDocument8 pagesPreparation of Trifluoromethylated Dihydrocoumarins, Indanones, and Arylpropanoic Acids by Tandem Superacidic Activation of 2 - (Trifluoromethyl) Acrylic Acid With ArenesDiogo DiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 AdrenocorticoidsDocument36 pagesChapter 28 AdrenocorticoidsCapuNo ratings yet
- Echinochrome A and Cytokine Storm SyndromeDocument11 pagesEchinochrome A and Cytokine Storm SyndromeNicolas Fernandez RubilarNo ratings yet
- Opioid and Non-Opioid Analgesics 7: Stephan A. SchugDocument20 pagesOpioid and Non-Opioid Analgesics 7: Stephan A. Schugnuri khonsa auliartiNo ratings yet
- Bala 2000Document8 pagesBala 2000Lydia CasasniNo ratings yet
- 05 Perrin, V. L. (1985) - Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Ergotamine in Migraine and Cluster Headache. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 10 (4), 334-352Document19 pages05 Perrin, V. L. (1985) - Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Ergotamine in Migraine and Cluster Headache. Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 10 (4), 334-352Emmanuel López BarjauNo ratings yet
- A Single Dose of Metyrapone Caused Londg Term Dysregulation of The Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis in The RatDocument8 pagesA Single Dose of Metyrapone Caused Londg Term Dysregulation of The Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis in The RatNatalia Butron GranadosNo ratings yet
- 2020 - A.nigrum&A.subhirsutum - JFood BiochemDocument14 pages2020 - A.nigrum&A.subhirsutum - JFood BiochemcerenacirNo ratings yet
- Heo 2010Document7 pagesHeo 2010Maryyy BatistaNo ratings yet
- Human Cytochrome p450 EnzymesDocument154 pagesHuman Cytochrome p450 EnzymesasaNo ratings yet
- GaulDocument11 pagesGaulEdwin Pasha Jr.No ratings yet
- Antiinflamatoire SouzaDocument5 pagesAntiinflamatoire SouzaKa RimaNo ratings yet
- Antiallergic Activity of TylogeninDocument10 pagesAntiallergic Activity of TylogeninRahul RanaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Assessing Endoplasmic Reticulum HomeostasisDocument16 pagesA Guide To Assessing Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasisfernando dominguezNo ratings yet
- Environmental Occurrence, Analysis, and Toxicology of Toxaphene CompoundsDocument30 pagesEnvironmental Occurrence, Analysis, and Toxicology of Toxaphene CompoundsZhola Varyan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- JNR 22553Document11 pagesJNR 22553Chaitali ParalikarNo ratings yet
- Foot Calcaneal Fracture - Rehabilitation ProtocolDocument7 pagesFoot Calcaneal Fracture - Rehabilitation ProtocolAdmirNo ratings yet
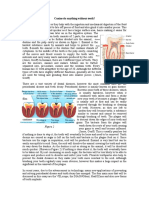
- Teeth EssayDocument3 pagesTeeth EssayKazeNo ratings yet
- NURS 6521N Final Exam Question and Answers Feb 2020 (100/100)Document19 pagesNURS 6521N Final Exam Question and Answers Feb 2020 (100/100)Judy Durkin0% (1)
- The Child With A Fluid and Electrolyte Alteration: Body Water Is Located in Two Major CompartmentsDocument19 pagesThe Child With A Fluid and Electrolyte Alteration: Body Water Is Located in Two Major CompartmentsAyeza DuaNo ratings yet
- EBMT 2021 ProgramDocument288 pagesEBMT 2021 Programtirillas101No ratings yet
- JC 18Document8 pagesJC 18emiliaclyde39No ratings yet
- AlbuminDocument16 pagesAlbuminMaroofAliNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examinations Crib Sheet v7Document36 pagesClinical Examinations Crib Sheet v7aparish10100% (1)
- ME210 Gastrointestinal TimetableDocument6 pagesME210 Gastrointestinal TimetableEka Irina Akma KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- Data PersonilDocument74 pagesData Personilpanji_208No ratings yet
- Program Book11Document1,124 pagesProgram Book11heocon857351No ratings yet
- NURS FPX 5003 Assessment 3 Intervention and Health Promotion Plan for Diverse PopulationDocument6 pagesNURS FPX 5003 Assessment 3 Intervention and Health Promotion Plan for Diverse PopulationCarolyn HarkerNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure NarrativeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure NarrativeAlfred BucabucaNo ratings yet
- Consideraciones Practicas en La Administracion y Dosis de Cannabis MedicinalDocument8 pagesConsideraciones Practicas en La Administracion y Dosis de Cannabis MedicinalGerardo QGNo ratings yet
- Segaletal 2019GeriatricAnxietyScaleDocument8 pagesSegaletal 2019GeriatricAnxietyScaleMapodettNo ratings yet
- Ncma219 Lec MidtermDocument51 pagesNcma219 Lec MidtermMacababbad Joshua MiguelNo ratings yet
- Bovi-Shield Gold FP 5 VL5Document2 pagesBovi-Shield Gold FP 5 VL5טורו קוראזוןNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice IVDocument11 pagesNursing Practice IVJohn wewNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Prostate CancerDocument16 pagesCase Study On Prostate Cancerferdz02100% (5)
- Poisoning in ChildrenDocument11 pagesPoisoning in ChildrenAndriana HalfienNo ratings yet
- Desired Dose Xquantity Onhand 160 MG 125 MG: FormulaDocument7 pagesDesired Dose Xquantity Onhand 160 MG 125 MG: FormulaSHEENA AL MAAGAD TIMBALNo ratings yet
- Cocaine's Journey from Medicine to Deadly AddictionDocument6 pagesCocaine's Journey from Medicine to Deadly AddictionDoniele DalorNo ratings yet
- Head Nursing ToolDocument26 pagesHead Nursing ToolJeneva L. LauzonNo ratings yet
- Jordanian Surgical Society - PPT LastDocument166 pagesJordanian Surgical Society - PPT LastNessreen Jamal100% (1)
- OBA Medical QuestionsDocument9 pagesOBA Medical QuestionsishafaraNo ratings yet
- Ent Mcqs For Part I Exam: Prepared By: Dr. Fouad ShamsanDocument86 pagesEnt Mcqs For Part I Exam: Prepared By: Dr. Fouad ShamsanAli QuwarahNo ratings yet
- Sanofi Just Got Its First Cancer Drug Approved in A Decade.Document7 pagesSanofi Just Got Its First Cancer Drug Approved in A Decade.Antonietta BlacconeriNo ratings yet
- EndometriosisDocument45 pagesEndometriosisIngrid MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document41 pagesGroup 1SELEMAYE ZENEBENo ratings yet
- Injectable Bone Graft and Allograft Bone Chips in The Treatment of Benign Bone LesionDocument8 pagesInjectable Bone Graft and Allograft Bone Chips in The Treatment of Benign Bone LesionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet