Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brandches of Economics: Opportunity Cost (Whatever Must Be Given Up To Obtain Some Items)
Brandches of Economics: Opportunity Cost (Whatever Must Be Given Up To Obtain Some Items)
Uploaded by
Lam PhúcOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brandches of Economics: Opportunity Cost (Whatever Must Be Given Up To Obtain Some Items)
Brandches of Economics: Opportunity Cost (Whatever Must Be Given Up To Obtain Some Items)
Uploaded by
Lam PhúcCopyright:
Available Formats
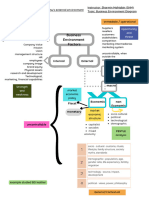
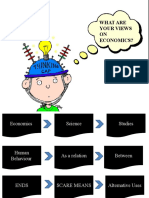
Economics is the study of how society manages its scare resources Definition
Using limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants MacroEeconomics The study of economy - wide phenomena (inflation, unemployment, economic growth)
Two branches of Economics
Government MicroEconomics The study of how buyers and sellers make decisions and how they interact in market
Firm Economic agents Factual analysis
Household/Individual Positive analysis No personal judgement involved
Choose which of wants to satisfy Can be tested, can be proven or disproven
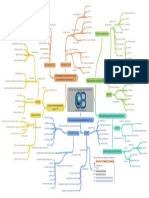
Opportunity cost
The limited nature of society's resources What is Scarcity? Approach in Economics
(whatever must be given up to obtain some items)
Trade - offs Economic problem Opinion - based analysis
Brandches of Economics
Nature resources Normative analysis Involves personal judgement or ideals
RENT Land
Raw materials Cannot be proven or disproven
Human services Qualitative method
WAGE/ SALARY Labor
Physical or intellectual Quantitative method
Equipments Economic resources Model A simplified version of reality that allow us to observe, understand, make predictions about economic behavior
INTEREST Machines Capital What is Economics? Includes: theory, assumption, equation, data
Factories Different assumptions
Economic models
Economists disagree
Combine all resources into the production of GAS Different opinions, value judgements, normative views about what policy should try to accomplish
PROFIT Entrepreneurial ability
Revenue - Cost Scientists trying to explain the world
Economists play roles
Policy advisors trying to help improve the world
Markets for goods and services
Markets for factors of production Types of markets
People face trade - offs
Financial markets
Decisions of threee agents
The cost of sth is what you give up to get it
What to produce? How people make decisions?
Rational people think at the margin
How to produce? Basic questions of Economics
People respond to incentives
For whom to produce?
Trade can make everyone better off
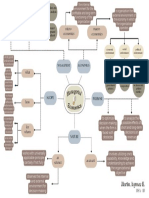
Ten principles of Economics How people interact? Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity
The Government or central authority Command economy
Direct Economics activities through the price system: Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes
Businesses and consumers
- The interaction of buyers and sellers determines prices
- Each price reflects the good's value and the cost of producing
Adam Smith's Invisible Hand Market economy
A country's standard of living depends on its ability to produce GAS
- Maximize society's economic well-being Law of supply and demand Economic systems
How the economy as a whole works? Prices rise when the government prints too much money
Combine
Society faces a short - run trade - off between inflation and unemployment
Government takes care of people's needs Mixed economy
Marketplace take care of people's want
You might also like
- VALLEJOS ACCTG 301 Biological Assets Answer KeyDocument4 pagesVALLEJOS ACCTG 301 Biological Assets Answer KeyEllah Rah78% (9)
- Entity-Level Controls Fraud QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesEntity-Level Controls Fraud QuestionnaireKirby C. LoberizaNo ratings yet
- Capsule On Business Economics Student Journal NovemberDocument10 pagesCapsule On Business Economics Student Journal NovemberNitesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Business EconomicsDocument10 pagesBusiness Economicsanjanirai1991No ratings yet
- Managerial Economics in A Global Economy - ch1 The Nature and Scope of Managerial Economics..Document10 pagesManagerial Economics in A Global Economy - ch1 The Nature and Scope of Managerial Economics..tutorisaac20No ratings yet
- Business Economics Ca Foundation - Paper 4 (Part 1) - Business EconomicsDocument5 pagesBusiness Economics Ca Foundation - Paper 4 (Part 1) - Business EconomicsbnanduriNo ratings yet
- I G Economics SampleDocument12 pagesI G Economics SampleNietharshan Eapen100% (1)
- 4.eco BCK Charts Demandr by ICAIDocument14 pages4.eco BCK Charts Demandr by ICAIHimanshu SoniNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics NotesDocument5 pagesApplied Economics NotesKhixel Jane PabroNo ratings yet
- Class 1 - Introduction - ManagerialEconDocument17 pagesClass 1 - Introduction - ManagerialEconria maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document10 pagesModule 1thelmaNo ratings yet
- Bos 50520Document18 pagesBos 50520Shaji SNo ratings yet
- Asim Sir Notes Unit 1&2Document44 pagesAsim Sir Notes Unit 1&2Vishal kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Economics CH - 1 NotesDocument6 pagesEconomics CH - 1 NotesRaghav KhetanNo ratings yet
- 8.eco Notes by Shristi AgarwalDocument6 pages8.eco Notes by Shristi AgarwalEduGrow TutorialsNo ratings yet
- MGT401 - Enviornmental Scanning - SHM - Section 3Document4 pagesMGT401 - Enviornmental Scanning - SHM - Section 3Labib RahmanNo ratings yet
- My Top Ten Takeaways From COMM329: Centralization/ DecentralizationDocument1 pageMy Top Ten Takeaways From COMM329: Centralization/ Decentralizationsiddharth royNo ratings yet
- Applied Econ NotesDocument14 pagesApplied Econ NotesCZARINA AUDREY SILVANONo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument1 pageManagerial EconomicsVan Amiel HerreraNo ratings yet
- Christian Homburg, Sina Böhler, Sebastian Hohenberg: Full Length ArticleDocument18 pagesChristian Homburg, Sina Böhler, Sebastian Hohenberg: Full Length ArticleelianaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economis Joshi SirDocument13 pagesManagerial Economis Joshi SirVarun KattiNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi DiriDocument27 pagesEvaluasi Diriiain-suNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics ReviewerDocument26 pagesManagerial Economics ReviewerAlyssa Faith NiangarNo ratings yet
- Caie As Economics 9708 TheoryDocument15 pagesCaie As Economics 9708 TheoryMasimba MafukidzeNo ratings yet
- Com501-Concept 2-4Document4 pagesCom501-Concept 2-4Russel PerezNo ratings yet
- MANECONDocument13 pagesMANECONMae AsprecNo ratings yet
- Admas University: Faculty of EconomicsDocument10 pagesAdmas University: Faculty of EconomicsHuyil ShufferNo ratings yet
- Economics Referencer For Quick RevisionDocument15 pagesEconomics Referencer For Quick RevisionNeeraj BhattNo ratings yet
- Mefa Unit 1 1 PDFDocument22 pagesMefa Unit 1 1 PDFbhuvana vuyyuruNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rokiah AlaviDocument10 pagesDr. Rokiah Alaviasma munifatussaidahNo ratings yet
- Referencer For Quick Revision: Foundation Course Paper-4: Business Economics & Business and Commercial KnowledgeDocument19 pagesReferencer For Quick Revision: Foundation Course Paper-4: Business Economics & Business and Commercial KnowledgeRashi thiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics and DefinitionsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Economics and Definitionslakshmi.vennelaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Scope: Mario Rosario Wisnu Aji Email: Mario - Aji@dsn - Dinus.ac - IdDocument21 pagesManagerial Economics Scope: Mario Rosario Wisnu Aji Email: Mario - Aji@dsn - Dinus.ac - IdLia CollineNo ratings yet
- Basic Consept in EconomicsDocument32 pagesBasic Consept in EconomicsSri HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Action Plan-Applied EconomicsDocument21 pagesAction Plan-Applied EconomicsJhereza Angel R. MocorroNo ratings yet
- P20010041 Agil Darudriyo MSDM MAPPING THEORY K1a201Document4 pagesP20010041 Agil Darudriyo MSDM MAPPING THEORY K1a201rianimeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics by Dr. K. Arun VikramDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Economics by Dr. K. Arun Vikramnaga sNo ratings yet
- Bos 50520Document15 pagesBos 50520Mithilesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Micro 1to3 English ColourDocument13 pagesMicro 1to3 English Colourhanoonaa786No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Basic Microeconomics - Pcbet 22 302aDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Basic Microeconomics - Pcbet 22 302aAGONCILLO SOPIA NICOLENo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics Introduction To EconomicsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Economics Introduction To EconomicsRajKumarNo ratings yet
- Individuals Firms Resource OwnersDocument2 pagesIndividuals Firms Resource OwnersDenise CastroNo ratings yet
- Unit - One MEDocument13 pagesUnit - One MEsnreddy85No ratings yet
- What Are Your Views ON Economics?Document10 pagesWhat Are Your Views ON Economics?bahetipriyanka1No ratings yet
- Decision Making - Analysis and IntuitionDocument11 pagesDecision Making - Analysis and IntuitionAnne MargaretteNo ratings yet
- AP Chapter 1 Less 1Document4 pagesAP Chapter 1 Less 1Hannah Denise BatallangNo ratings yet
- What Is Economy?Document13 pagesWhat Is Economy?Kartikey AasalNo ratings yet
- Using Financial Accounting Information For Evaluation and ControlDocument5 pagesUsing Financial Accounting Information For Evaluation and ControlMihaela SburleaNo ratings yet
- Silvio Napoli at Schindler India: Conclusion Session - 5Document6 pagesSilvio Napoli at Schindler India: Conclusion Session - 5Payal Priya Chand100% (1)
- 805 Individual AssignmentDocument8 pages805 Individual AssignmentTory LeyeNo ratings yet
- ManEcon Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesManEcon Cheat SheetClarisse Danielle Macasieb RomualdoNo ratings yet
- Economics For Business Decisions: Introduction To Managerial Economics Module - 1Document75 pagesEconomics For Business Decisions: Introduction To Managerial Economics Module - 1Tushar SahuNo ratings yet
- Workshop-SE Batch IIIDocument28 pagesWorkshop-SE Batch IIIBerkah Fajar Tamtomo KionoNo ratings yet
- Applied Economics Reviewer ST 1Document2 pagesApplied Economics Reviewer ST 1anastacio.althea.nievaNo ratings yet
- Nasirin, Sherilyn D. BS Accountancy 1A: Economic TheoryDocument4 pagesNasirin, Sherilyn D. BS Accountancy 1A: Economic TheoryANNooonynmousNo ratings yet
- Part I: Nature and Scope of Managerial Economics DescriptionDocument8 pagesPart I: Nature and Scope of Managerial Economics DescriptionGamers PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument104 pagesManagerial Economicskibebew shenkuteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Nature Scope and Practice of Managerial EconomicsDocument6 pagesChapter 1 The Nature Scope and Practice of Managerial EconomicsJoyce LagaoNo ratings yet
- Economic Systems - 2021103 - 121042Document1 pageEconomic Systems - 2021103 - 121042ShaviniNo ratings yet
- The Political Economy of Participatory EconomicsFrom EverandThe Political Economy of Participatory EconomicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Factors Affecting Policyholders' Satisfaction Towards Life Insurance: An Empirical Study On Life Insurance Policyholders in BangladeshDocument8 pagesFactors Affecting Policyholders' Satisfaction Towards Life Insurance: An Empirical Study On Life Insurance Policyholders in BangladeshIjaems JournalNo ratings yet
- Time-Cost Trade-OffDocument15 pagesTime-Cost Trade-OffRONNEL MALONGNo ratings yet
- Final Exam (Project Management)Document4 pagesFinal Exam (Project Management)Vusal GahramanovNo ratings yet
- Ukpaye-2017-2018 - 18500Document2 pagesUkpaye-2017-2018 - 18500Anonymous jEmTt5o6No ratings yet
- Development BanksDocument17 pagesDevelopment BanksAsim jawedNo ratings yet
- Keseluruhan Jurnal: Ud Buana (Diana Puspitasari)Document3 pagesKeseluruhan Jurnal: Ud Buana (Diana Puspitasari)diana puspitasariNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Cotton Textile Supply Chain Programme and Potential For Scale-Up in Hyderabad, IndiaDocument87 pagesEvaluation of Cotton Textile Supply Chain Programme and Potential For Scale-Up in Hyderabad, IndiaOxfamNo ratings yet
- Brand Building Unit 1Document12 pagesBrand Building Unit 1Viraj VeeraNo ratings yet
- 71 3e2c9505Document110 pages71 3e2c9505JohnNo ratings yet
- Chemical IndustryDocument33 pagesChemical Industryjuan carlos100% (1)
- Sales Force Compensation and MotivationDocument33 pagesSales Force Compensation and MotivationThenappan GanesenNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Books Invoice No 4048Document1 pageDynamic Books Invoice No 4048Pioneer Book ZoneNo ratings yet
- Notes On The OFW HandbookDocument2 pagesNotes On The OFW HandbookmntzkalexNo ratings yet
- Call Centres Transforming IndiaDocument44 pagesCall Centres Transforming Indiaarun1974No ratings yet
- 0561-Marketing Theory & PracticeDocument11 pages0561-Marketing Theory & PracticeMuhammad NazirNo ratings yet
- British Council IELTS Online ApplicationDocument3 pagesBritish Council IELTS Online ApplicationNasrullah AliNo ratings yet
- ECET518 Midterm Engineering ManagementDocument39 pagesECET518 Midterm Engineering ManagementJeninaNo ratings yet
- BUS - MATH 11 Q1 Module 9 PDFDocument21 pagesBUS - MATH 11 Q1 Module 9 PDFKrisha FernandezNo ratings yet
- StatementOfAccount 7245571180 18092022 070918Document3 pagesStatementOfAccount 7245571180 18092022 070918somesh chandraNo ratings yet
- IFRS-8 Operating Segments: 1. Core PrincipleDocument11 pagesIFRS-8 Operating Segments: 1. Core PrincipleNATIONAL SAVINGSNo ratings yet
- A Study On Digital Rupee of RBI 1Document95 pagesA Study On Digital Rupee of RBI 1Prema J MNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Finance - Sri Lanka - Annual Report - 2017Document412 pagesMinistry of Finance - Sri Lanka - Annual Report - 2017lkwriterNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Structure of A Business PlanDocument16 pagesUnit 9 Structure of A Business Plansrisuryanii714No ratings yet
- A Financial Stability Analysis of The Irish Commercial Property Market by Maria WoodsDocument16 pagesA Financial Stability Analysis of The Irish Commercial Property Market by Maria WoodsirubyistNo ratings yet
- Week 3 HomeworkDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Homeworkapi-331018879No ratings yet
- ECONOMICS-3-Production and CostDocument18 pagesECONOMICS-3-Production and CostTonny NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Challenge of DemocracyDocument21 pagesThe Challenge of DemocracyAndros MafraNo ratings yet
- Project Feasibility Writing GuideDocument24 pagesProject Feasibility Writing Guideمحمداویس کیانیNo ratings yet
- Target Costing, Kaizen Costing and Life Cycle Costing: Advanced Cost AccountingDocument20 pagesTarget Costing, Kaizen Costing and Life Cycle Costing: Advanced Cost AccountingFatemaNo ratings yet