Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elec Comms
Uploaded by
seia deirahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elec Comms
Uploaded by
seia deirahCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
Based on the prior knowledge in semiconductor and knowing the importance of transistor
biasing and its three regions of operation; discuss between the members of the group on how
electron movement is affected based on the (Forward or Reverse) biasing applied in a PNP
transistor.
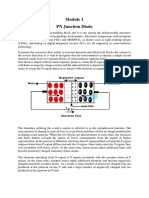
There are three types of biasing of diodes-
1. Forward biasing: In forwarding bias, the P terminal is connected to the battery's positive terminal
and the N terminal to the negative.
2. Reversed bias: In reversed bias, the P terminal is connected to the battery's negative terminal and
the N terminal to positive.
3. No bias or unbiased: when there is no biasing applied to the diode. For the PNP transistor, when
VBE is used, then PN terminals will be forward bias and the force applied at P and N terminals
by the battery to move the electrons and holes due to this force, electron holes charges can easily
penetrate the PN junction and moved across the intersection and therefore current will flow in
opposite directions of battery applied. NP will be reversed bias when we use it, and it will start
attracting the electrons and holes at the terminal due to opposite charges applied at terminals. The
junction width will increase as we increase applied voltage. A time comes when depletion width
breaks and a large amount of current will flow in this current, called reverse Saturation current.
What is the significance of the characteristic of the curve?
A curve depicted on a graph from two axes, exposure, and density, describes the qualities and
performance of sensitive emulsions. A characteristic curve is a graph that displays the relationship
between the amount of exposure used on a film and the density produced after processing. The shape of
the curve represents the film's tonal response to a wide range of vulnerabilities and a single processing
stage. As the curve's slope drops, the film's ability to record the contrast between repeated exposures
decreases, finally halting when the curve approaches horizontal. Pump performance curves are essential
indicators of pump characteristics provided by the manufacturer. These curves are fundamental in
predicting the variation in the differential head across the pump as the flow changes.
Explain the difference among the saturation, cut-off, and active regions.
Saturation is the entirely conducting condition in a semiconductor junction. In diode and bipolar
transistor applications, the term is most often used. A bipolar transistor is considered to be saturated when
the base-emitter current reaches a maximum under changing bias. While cutoff is a state of negligible
conduction that occurs when a control parameter typically a well-defined voltage or electric current, but it
could also be incident light intensity, or a magnetic field is lowered or increased beyond a value or the
conduction threshold, it is a property of several types of electronic components. The transition from
normal conduction to cutoff may be more or less sudden, depending on the type of device in issue, and
the rate of this transition also varies substantially. Finally, the active region is the region between cutoff
and saturation. The collector-base junction remains to reverse biased in the active part, but the base-
emitter hub remains forward biased. As a consequence, the transistor will continue to function normally
in this location.
You might also like
- Department of Mechatronic Engineering: Power DiodeDocument12 pagesDepartment of Mechatronic Engineering: Power DiodeEng King'e FredrickNo ratings yet
- BEEE NotesDocument23 pagesBEEE Notessonali2408100% (6)
- Jfet NotesDocument12 pagesJfet NotesKshitij GaurNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDocument128 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesraghudatheshNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument9 pagesBasic ElectronicsUnknown OneNo ratings yet
- DIode, BJT, FetDocument200 pagesDIode, BJT, FetniviNo ratings yet
- Beee-Unit 2Document86 pagesBeee-Unit 2rakshnajkNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor: Business Japanese Proficiency TestDocument24 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor: Business Japanese Proficiency TestVishal SaxenaNo ratings yet
- P 1644 Automatic Street Light ControllerDocument39 pagesP 1644 Automatic Street Light ControllerharrisrajNo ratings yet
- Ade Unit-IDocument39 pagesAde Unit-IKUMAR SNo ratings yet
- Beee-Unit 2Document79 pagesBeee-Unit 2thamizhan4341No ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDocument128 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Ckts (10es32) - NotesDilip TheLipNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document97 pagesUnit 2MOHAN RuttalaNo ratings yet
- NPN BJT With Forward-Biased E-B Junction and Reverse-Biased B-C JunctionDocument9 pagesNPN BJT With Forward-Biased E-B Junction and Reverse-Biased B-C JunctionA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Inverter - Team 7Document3 pagesInverter - Team 7Noe ParedesNo ratings yet
- 0060 JfetDocument17 pages0060 JfetKrank101No ratings yet
- Example A: Find The Resistance of 6.5 M of Wire, Diameter 0.6 MM, If TheDocument4 pagesExample A: Find The Resistance of 6.5 M of Wire, Diameter 0.6 MM, If TheTara GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Топлогия Он Боард Wang2020Document5 pagesТоплогия Он Боард Wang2020Алексей ЯмаNo ratings yet
- Forward and Reverse Bias in PN Junction DiodeDocument2 pagesForward and Reverse Bias in PN Junction DiodeRaghuramNo ratings yet
- OPEYEMI Presentation On PN Juction EtcDocument13 pagesOPEYEMI Presentation On PN Juction EtcAdebisi RichardNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiDocument56 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: Arunai Engineering College TiruvannamalaiKannan TindivanamNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysicsCrystal GamingNo ratings yet
- Topic: Transducers and Associate Electronics-Displacem Ent Transducers, Resistive Strain Gauge, Bridge Circuits, Piezoelectric TransducersDocument14 pagesTopic: Transducers and Associate Electronics-Displacem Ent Transducers, Resistive Strain Gauge, Bridge Circuits, Piezoelectric TransducersJahnvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- P-N JunctionDocument6 pagesP-N JunctionMuhamad Hanif RidhaNo ratings yet
- Design High Performance Pulse Transformers in Easy StageDocument18 pagesDesign High Performance Pulse Transformers in Easy StagefagundesbrNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor and Electronic Devices TheoryDocument10 pagesSemiconductor and Electronic Devices TheoryAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument15 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorpdekraaijNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument27 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorShanti NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Senzori Miscare EnglDocument16 pagesSenzori Miscare EnglCristian GodeanuNo ratings yet
- Forward V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeDocument7 pagesForward V-I Characteristics of P-N Junction DiodeTwinkle johnsonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE PN Junction DiodesDocument24 pagesCHAPTER THREE PN Junction DiodesAma Serwaa YeboahNo ratings yet
- L2 PN Junction DiodeDocument30 pagesL2 PN Junction DiodeMarjia KhatunNo ratings yet
- Transistor Operation: Chapter - 4Document3 pagesTransistor Operation: Chapter - 4lvsaruNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 21E001 AbishekDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 1 21E001 Abishek21E001 - ABISHEK VNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - NotesDocument170 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - NoteschaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor PDFDocument16 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor PDFVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction: See Also: andDocument11 pagesP-N Junction: See Also: andRupali SinghNo ratings yet
- الكترونيك نموذجيDocument10 pagesالكترونيك نموذجيMohammed KasimNo ratings yet
- By: Jasper B. DeromaDocument26 pagesBy: Jasper B. DeromaRaging Potato100% (1)
- IIIIII L L L LDocument9 pagesIIIIII L L L LAyman Ben AlyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Frequency-Dependent Impedance For Conductors of Rectangular Cross SectionDocument10 pagesCalculation of Frequency-Dependent Impedance For Conductors of Rectangular Cross SectionAlak MajumderNo ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions With AnswersDocument10 pagesTwo Mark Questions With AnswerssenthilNo ratings yet
- Ece Lab Questons and AnswersDocument6 pagesEce Lab Questons and AnswersAditya AryamNo ratings yet
- The Bipolar Transistor As A SwitchDocument13 pagesThe Bipolar Transistor As A Switchbarzoom007No ratings yet
- B.SC Electronics D2 P3 (2022) SolutionsDocument18 pagesB.SC Electronics D2 P3 (2022) SolutionsShubham KeshriNo ratings yet
- Experiment-01: Theory: P-N Junction DiodeDocument5 pagesExperiment-01: Theory: P-N Junction Diodevamsee007No ratings yet
- EmtlDocument40 pagesEmtlammu0100% (1)
- Notes - Special TopicsDocument12 pagesNotes - Special TopicsAnkit MeenaNo ratings yet
- Modul Praktikum Elda Satu Semester 5 FinalDocument29 pagesModul Praktikum Elda Satu Semester 5 FinalZdSentono ChannelNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document14 pagesModule 1Bhakti 2913No ratings yet
- Different Types of ResistancesDocument16 pagesDifferent Types of Resistances21131A04J2 NUTULAPATI NAGA SRIPADA VALLABHA ABHIRAMNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Vs Extrinsic: Forward BiasingDocument9 pagesIntrinsic Vs Extrinsic: Forward BiasingnuruthinNo ratings yet
- BC547 TransistorDocument14 pagesBC547 TransistorErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade EngineerNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Study of Ferroresonance and Inrush Current Phenomena and Their Related Reasons in Ground Power NetworksDocument6 pagesSynchronous Study of Ferroresonance and Inrush Current Phenomena and Their Related Reasons in Ground Power NetworksDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- VERBS1 What Is ConjugationDocument9 pagesVERBS1 What Is Conjugationseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Report-Heat ExchangerDocument3 pagesReport-Heat Exchangerseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Who Wants To Be A Millionaire - Template by SlideLizardDocument25 pagesWho Wants To Be A Millionaire - Template by SlideLizardseia deirahNo ratings yet
- MonologueDocument2 pagesMonologueseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Philippine LiteratureDocument1 pagePhilippine Literatureseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document3 pagesPractical Research 2seia deirahNo ratings yet
- Engineering WorksDocument1 pageEngineering Worksseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Elec CommsDocument1 pageElec Commsseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Song About Authentic FreedomDocument1 pageSong About Authentic Freedomseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesDifferential Equationsseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Elec CommsDocument1 pageElec Commsseia deirahNo ratings yet
- Genius IO High Speed Counter User's Manual, GFK-0415EDocument145 pagesGenius IO High Speed Counter User's Manual, GFK-0415EEduardo DiazNo ratings yet
- Operation and Supply ChainDocument34 pagesOperation and Supply ChainAqib LatifNo ratings yet
- En FM-Pro4, Pro4 3G DatasheetDocument5 pagesEn FM-Pro4, Pro4 3G DatasheetJoko PitoyoNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 - AVR IO in C (ISMAIL - FKEUTM 2018)Document93 pagesTopic 10 - AVR IO in C (ISMAIL - FKEUTM 2018)Aya AmirNo ratings yet
- Mcu Installation+Manual Db68-06903a-05 221122-d07 English+and+FrenchDocument32 pagesMcu Installation+Manual Db68-06903a-05 221122-d07 English+and+FrenchNicolae RoNo ratings yet
- Manual FLC3 70Document1 pageManual FLC3 70joNo ratings yet
- TR 220 Operational ManualDocument76 pagesTR 220 Operational ManualSabby_SXBNo ratings yet
- Tutorial For Automated Design System (ADS) : You Chung Chung Cynthia FurseDocument23 pagesTutorial For Automated Design System (ADS) : You Chung Chung Cynthia Fursehassan abousalehNo ratings yet
- Iec 62109-2Document16 pagesIec 62109-2Rohit Mittal33% (6)
- A 71 Samsung Electrical Part ListDocument12 pagesA 71 Samsung Electrical Part ListIsabel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Selection and Installation of Aircraft Electric Equipment 飞机电气设备的选择和安装MIL-STD-7080Document26 pagesSelection and Installation of Aircraft Electric Equipment 飞机电气设备的选择和安装MIL-STD-7080qingtaoNo ratings yet
- Home Automation Using Arduino and IOTDocument4 pagesHome Automation Using Arduino and IOTInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A2e816 Astro Mini PCDocument2 pagesA2e816 Astro Mini PCkiroNo ratings yet
- 03 Thyssen 1Document20 pages03 Thyssen 1Rafael BrunoNo ratings yet
- Novatek NT96650 PDFDocument35 pagesNovatek NT96650 PDFRenatoNo ratings yet
- GD20-en V1.3 PDFDocument122 pagesGD20-en V1.3 PDFjhonnyNo ratings yet
- Instrument Transformers LatestDocument12 pagesInstrument Transformers Latestcarlos vidal100% (1)
- Service Manual: Washing Machine Toploader AWT 7105Document18 pagesService Manual: Washing Machine Toploader AWT 7105Jose Real LatorreNo ratings yet
- Eletrical Diagram CATERPILLAR 6020 BDocument8 pagesEletrical Diagram CATERPILLAR 6020 BAnonymous RAXcXQfo100% (1)
- Awg Cable IntroductionDocument2 pagesAwg Cable IntroductionFrancis LeeNo ratings yet
- Smart Coverage Solution System: 1800Mhz Multi-Carrier High Power Outdoor Booster SystemDocument4 pagesSmart Coverage Solution System: 1800Mhz Multi-Carrier High Power Outdoor Booster SystemGeorge KvekvetsiaNo ratings yet
- Advt 145 Corrigendum 270720230636Document5 pagesAdvt 145 Corrigendum 270720230636Ayush SinghNo ratings yet
- Timer0 Code ATmega328pDocument3 pagesTimer0 Code ATmega328pmladen divacNo ratings yet
- Frontech User's Manual PDFDocument9 pagesFrontech User's Manual PDF06l01a0224No ratings yet
- Annunciator KeyboardDocument11 pagesAnnunciator KeyboardMiguel Angel Gómez PérezNo ratings yet
- Transformer Test: Prepared By: Nishant AcharyaDocument30 pagesTransformer Test: Prepared By: Nishant AcharyaVishal PatelNo ratings yet
- Product Overview: Data Sheet - H665GR GPON Gigabit ONT With Video ServiceDocument7 pagesProduct Overview: Data Sheet - H665GR GPON Gigabit ONT With Video ServiceTuấn minh DuongNo ratings yet
- Protocol Database For Automatic Circuit Reclosers With Advanced ControllersDocument205 pagesProtocol Database For Automatic Circuit Reclosers With Advanced ControllersCata CatalinNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Datos Diodos ZENER - 1N4728A Hasta 1N4764A - Exp4Document6 pagesHoja de Datos Diodos ZENER - 1N4728A Hasta 1N4764A - Exp4Efra IbacetaNo ratings yet