Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study Drug Ana
Uploaded by
Magdaraog Gabrielle A.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views7 pages JEANETTE J. ROJO
Frequency: As needed
Classification: Local anesthetic
Reference: MOSBY’S DRUG HANDBOOK 2021
Student Nurse: GABRIELLE A. MAGDARAOG Clinical Instructor: JEANETTE J. ROJO
Original Description:
Original Title
CASE STUDY DRUG ANA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document JEANETTE J. ROJO
Frequency: As needed
Classification: Local anesthetic
Reference: MOSBY’S DRUG HANDBOOK 2021
Student Nurse: GABRIELLE A. MAGDARAOG Clinical Instructor: JEANETTE J. ROJO
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views7 pagesCase Study Drug Ana
Uploaded by
Magdaraog Gabrielle A. JEANETTE J. ROJO
Frequency: As needed
Classification: Local anesthetic
Reference: MOSBY’S DRUG HANDBOOK 2021
Student Nurse: GABRIELLE A. MAGDARAOG Clinical Instructor: JEANETTE J. ROJO
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Republic of the Philippines
UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN PHILIPPINES
University Town, Northern Samar
Web: uep.edu.ph Email: ueppres06@gmail.com
COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
DRUG ANALYSIS
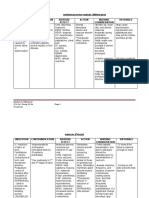
Name of Patient: NADINE LUSTRE Date Admitted: 12/05/21 Chief Complaint: MATERNAL FATIGUE Case Number: _543_
Age: _28_ Gender: FEMALE Civil Status: MARRIED Address: UNITED KINGDOM Ward: OB WARD
NAME OF SPECIFIC INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION DRUG ADVERSE SPECIFIC NURSING
DRUG ACTION INTERACTION REACTION PRECAUTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: Stimulates uterine Labour induction Hypertonic uterine Enhanced effect of Foetal distress, Women with Assess maternal blood
Oxytocin smooth muscle, contractions, mechanical prostaglandins. arrhythmias, borderline pressure periodically and
producing uterine obstruction to delivery, foetal Reduced therapeutic hypotension, cephalopelvic compare to normal values.
Brand Name: contractions similar distress; conditions wherein efficacy and myocardial disproportion, Report low blood pressure
Pitocin to those in spontaneous labour or vaginal increased risk of ischaemia, secondary uterine (hypotension), especially if
spontaneous labor. delivery is contraindicated hypotension with peripheral inertia, mild or patient experiences
Dosage: Stimulates mammary (e.g. significant cephalopelvic inhalation vasodilation, moderate degrees of dizziness, fatigue, or other
1-4 milliunits/minute gland smooth disproportion, foetal anaesthetics (e.g. tachycardia, QT pregnancy-induced symptoms.
via infusion muscle, facilitating malpresentation, placenta halothane, prolongation, uterine hypertension, CV Monitor signs of maternal
lactation. Has praevia, vasa praevia, sevoflurane, hypertonicity, disease (e.g. fluid and electrolyte
Route: vasopressor and placental abruption, cord desflurane, spasm, tetanic hypertrophic imbalances, such as low
Intravenous antidiuretic effects. presentation or prolapse, cyclopropane). contraction, cardiomyopathy, sodium levels
overdistension or impaired Enhanced effect of disseminated valvular heart (hyponatremia), low
Frequency: resistance of the uterus to vasoconstrictors and intravascular disease, ischaemic chloride levels
Once rupture, multiple pregnancy, sympathomimetics. coagulation (DIC). heart disease, (hypochloremia), or a
polyhydramnios, grand Increased risk of Potentially coronary artery relative increase in body
Classification: multiparity); presence of a arrhythmia with Fatal: Water vasospasm), long QT fluid (water intoxication).
Oxytocic uterine scar from previous drugs that may intoxication, syndrome, Signs include headache,
surgery including caesarean prolong QT interval. hypertension, haemodynamically confusion, lethargy,
Reference: section. Prolonged use in subarachnoid unstable states, irritability, decreased
MOSBY’S DRUG resistant uterine inertia, haemorrhage, history of lower- consciousness, and
HANDBOOK 2021 severe CV disease, severe rupture of the uterus. uterine-segment neuromuscular
pre-eclamptic toxaemia. caesarean section. abnormalities (muscle
Women ≥35 years. weakness and cramps).
Not intended for Report these signs to the
elective induction of physician or nursing staff.
labour. Pregnancy
and lactation.
Student Nurse: GABRIELLE A. MAGDARAOG Clinical Instructor: JEANETTE J. ROJO
Republic of the Philippines
UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN PHILIPPINES
University Town, Northern Samar
Web: uep.edu.ph Email: ueppres06@gmail.com
COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
DRUG ANALYSIS
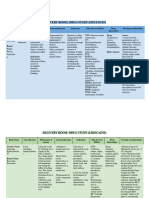
Name of Patient: NADINE LUSTRE Date Admitted: 12/05/21 Chief Complaint: MATERNAL FATIGUE Case Number: _543_
Age: _28_ Gender: FEMALE Civil Status: MARRIED Address: UNITED KINGDOM Ward: OB WARD
NAME OF SPECIFIC INDICATION CONTRAINDICATIO DRUG ADVERSE SPECIFIC NURSING
DRUG ACTION N INTERACTION REACTION PRECAUTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: Increases electrical Epidural Hypersensitivity to amides, Increase: cardiac Arrhythmia, Pregnancy, Assess:
Lidocaine stimulation threshold anaesthesia for severe heart block, depression, bradycardia, arterial breastfeeding, • ECG continuously to
of ventricle, His- obstetric caudal supraventricular toxicity: spasms, CV children, geriatric determine increased PR or
Brand Name: Purkinje system, analgesia dysrhythmias, AdamsStokes amiodarone, collapse, oedema, patients, QRS segments; if these
Xylocaine which stabilizes syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson- phenytoin, flushing, hert block, renal/hepatic develop, discontinue or
cardiac membrane, White syndrome. procainamide, hypotension, sinus disease, HF, reduce rate; watch for
Dosage: decreases propranolol, node suppression, respiratory increased ventricular
200-300 mg (as 1% automaticity. quiNIDine agitation, anxiety, depression, ectopic beats, may have to
soln Increase: coma, confusion, malignant rebolus; B/P
hypotensive effects drowsiness, hyperthermia, • Drug levels: therapeutic
Route: —MAOIs, hallucinations, myasthenia gravis, level, 1.5-5 mcg/mL • I&O
Epidural antihypertensives euphoria, headache, weight. ratio, electrolytes
Increase: hyperaesthesia, (potassium, sodium,
Frequency: neuromuscular hypoaesthesia, chlorine)
Once blockade— lightheadedness, • Toxicity: monitor for
neuromuscular lethargy, seizures, confusion,
Classification: blockers, nervousness, tremors; if these occur,
Aminoacyl amide tubocurarine; psychosis, seizure, discontinue immediately,
monitor for adverse slurred speech, notify prescriber; keep
Reference: effects unconsciousness, emergency equipment
MOSBY’S DRUG Increase: lidocaine somnolence, nausea, nearby
HANDBOOK 2021 effects, toxicity— vomiting, metallic • Malignant
cimetidine, β- taste, tinnitus, hyperthermia: tachypnea,
blockers, protease disorientation, tachycardia, changes in
inhibitors, ritonavir dizziness, B/P, increased
Increase: paraesthesia, resp temperature
hypotension— depression and
ergots; avoid convulsions. Patch: • Respiratory status: rate,
concurrent use Bruising, rhythm, lung fields for
depigmentation, crackles, watch for
Decrease: lidocaine petechiae, irritation. respiratory depression; lung
effects— Ophth: Conjunctival fields, bilateral crackles
barbiturates, hyperaemia, corneal may occur with HF;
ciprofloxacin, epithelial changes, increased respiration, pulse;
voriconazole diplopia,visual product should be
Decrease: effect of changes. discontinued
—cycloSPORINE • CNS effects: dizziness,
confusion, psychosis,
paresthesias, convulsions;
product should be
discontinued
•Pregnancy/breastfeeding:
use only if clearly needed;
use caution in
breastfeeding, excreted in
breast milk
Evaluate:
• Therapeutic response:
decreased dysrhythmias
Teach patient/family:
• About the use of
automatic lidocaine
injection device if ordered
for personal use
• To report signs of
toxicity immediately
Student Nurse: GABRIELLE A. MAGDARAOG Clinical Instructor: JEANETTE J. ROJO
Republic of the Philippines
UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN PHILIPPINES
University Town, Northern Samar
Web: uep.edu.ph Email: ueppres06@gmail.com
COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
DRUG ANALYSIS
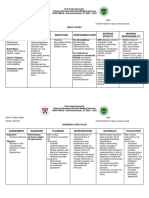
Name of Patient: KRIS AQUINO Date Admitted: 12/5/21 Chief Complaint: DIFFICULTY OF BREATHING Case Number:___234___
Age: _28_ Gender: FEMALE Civil Status: MARRIED Address: UNITED KINGDOM Ward: OB WARD
NAME OF SPECIFIC INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION DRUG ADVERSE SPECIFIC NURSING
DRUG ACTION INTERACTION REACTION PRECAUTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: β1- and β2-agonist Anaphylaxis Hypersensitivity to Do not use with CNS effects; GI Pregnancy, Assess:
EPINEPHrine causing increased sympathomimetics, sulfites, MAOIs or disturbances; breastfeeding, • Asthma: auscultate lungs,
levels of cAMP, closed-angle glaucoma, non- tricyclics; epigastric pain; CV cardiac disorders, pulse, B/P, respirations,
Brand Name: thereby producing anaphylactic shock during hypertensive crisis disorders; difficulty hyperthyroidism, sputum (color, character);
Allerjet bronchodilation, general anesthesia. may occur in micturition with diabetes mellitus, monitor pulmonary
cardiac, and CNS • Toxicity: other urinary retention; prostatic function studies before and
Dosage: stimulation; high sympathomimetics dyspnoea; hypertrophy, during treatment
0.3-0.5 mg doses cause Decrease: hyperglycaemia; hypertension, • Vasopressor: ECG
vasoconstriction via hypertensive effects sweating; organic brain during administration
Route: α-receptors; low —βadrenergic hypersalivation; syndrome, local continuously; if B/P
IM/SUBCUT doses can cause blockers, stop β- weakness, tremors; anesthesia of certain increases, decrease dose;
vasodilation via β2- blocker 3 days coldness of areas, labor, cardiac B/P, pulse q5min after
Frequency: vascular receptors. before starting extremities; dilation, coronary parenteral route; CVP,
q10-15min product hypokalaemia. insufficiency, ISVR, PCWP during
Increase: Gangrene, tissue cerebral infusion if possible;
Classification: hypotension—α- necrosis and arteriosclerosis, inadvertent high arterial
Catecholamine blockers sloughing organic heart B/P can result in angina,
Increase: cardiac (extravasation) when disease. aortic rupture, cerebral
Reference: effects— used in addition to hemorrhage
MOSBY’S DRUG antihistamines, local anaesthetics. • Inj. site: tissue sloughing;
HANDBOOK 2021 thyroid replacement Eye drops: Severe administer phentolamine
hormones Increase: smarting, blurred with NS
dysrhythmias— vision, photophobia; • Sulfite sensitivity; may
cardiac glycosides naso-lachrymal ducts be life threatening
Drug/Herb obstruction. • Cardiac status, I&O;
• Increased Oedema, hyperaemia blood glucose in diabetes
stimulation: coffee, and inflammation of • Allergic reactions,
tea, guarana, yerba the eyes with bronchospasms (swelling
maté repeated of face/lips/eyelids, rash,
administration. difficulty breathing):
withhold dose, notify
prescriber
Evaluate:
• Therapeutic response:
increased B/P with
stabilization or ease of
breathing, relief of
bronchospasm Teach
patient/family:
• About the reason for
product administration.
Student Nurse: GABRIELLE A. MAGDARAOG Clinical Instructor: JEANETTE J. ROJO
Republic of the Philippines
UNIVERSITY OF EASTERN PHILIPPINES
University Town, Northern Samar
Web: uep.edu.ph Email: ueppres06@gmail.com
COLLEGE OF NURSING AND ALLIED HEALTH SCIENCES
DRUG ANALYSIS
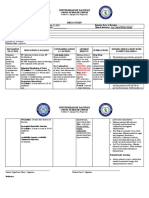
Name of Patient: KRIS AQUINO Date Admitted: 12/5/21 Chief Complaint: DIFFICULTY OF BREATHING Case Number:___234___
Age: _28_ Gender: FEMALE Civil Status: MARRIED Address: UNITED KINGDOM Ward: OB WARD
NAME OF SPECIFIC INDICATION CONTRAINDICATIO DRUG ADVERSE SPECIFIC NURSING
DRUG ACTION N INTERACTION REACTION PRECAUTION RESPONSIBILITIES
Generic Name: Prevents conversion Venous Bleeding, hypersensitivity to Increase: heparin Hypersensitivity Pregnancy, children, Assess:
Lovenox of fibrinogen to thromboembolism this product, corn, porcine action—oral reactions (e.g. chills, geriatric patients, • Bleeding, hemorrhage:
fibrin and protein (pork product). anticoagulants, fever, urticaria, alcoholism, gums, petechiae,
Brand Name: prothrombin to salicylates, dextran, asthma, rhinitis); hyperlipidemia, diabetes, ecchymosis, black tarry
Enoxaparin thrombin by NSAIDs, platelet painful, ischaemic renal disease, heparin- stools, hematuria,
enhancing inhibitory inhibitors, and cyanosed limbs; induced thrombocytopenia epistaxis, decrease in Hct,
Dosage: effects of cephalosporins, osteoporosis (in (HIT), hemophilia, B/P; HIT may occur after
15,000-20,000 U antithrombin III penicillins, long-term admin), leukemia with bleeding, product discontinuation;
ticlopidine, suppression of peptic ulcer disease, check periodically for
Route: dipyridamole, aldosterone synthesis severe thrombocytopenic sign of decreasing clots
Subcutaneous antineoplastics, leading to purpura, severe • Blood studies (Hct,
clopidogrel, SSRIs, hyperkalaemia, renal/hepatic disease, occult blood in stools)
Frequency: SNRIs, quinidine, cutaneous necrosis, blood dyscrasias, severe q3mo
12 hrly valproic acid delayed transient hypertension, subacute, • Thrombosis: monitor
Decrease: heparin alopecia, priapism, bacterial endocarditis, for increased thrombosis
Classification: action—digoxin, rebound acute nephritis; benzyl daily, in affected areas
Antigoagulant tetracyclines, hyperlipaemia; alcohol products in • Partial prothrombin time,
antihistamines, increased serum neonates/ which should be 1.5-2.5×
Reference: cardiac glycosides, concentrations of infants/pregnancy/lactatio control; for continuous IV
MOSBY’S DRUG nicotine, AST and ALT, n infusion, check aPTT
HANDBOOK 2021 nitroglycerin prolonged baseline 6 hr after initiation
Drug/Herb prothrombin time; and 6 hr after any dose
Increase: bleeding local irritation, change; use aPTT for
risk—arnica, anise, erythema, mild pain, dosing adjustments; after
chamomile, clove, haematoma or therapeutic aPTT has been
dong quai, garlic, ulceration on inj site. measured 2×, check aPTT
ginger, ginkgo, Potentially daily
feverfew, green tea, Fatal: Heparin- • Heparin-induced
horse chestnut induced thrombocytopenia (HIT):
Drug/Lab Test thrombocytopenia w/ platelet count q2-3days;
Increase: ALT, or w/out thrombosis, thrombocytopenia may
AST, INR, PT, PTT, severe haemorrhage. occur on 4th day of
potassium Decrease: treatment and resolves
platelets even during continued
treatment; HIT may
occur on the 5th-10th day
of treatment, with
platelets to 5000 mm3;
this may lead to HITT
(venous/arterial
thrombosis) even after
discontinued therapy
• Hypersensitivity: rash,
chills, fever, itching; report
to prescriber Evaluate:
•Therapeutic response:
prevention of DVT and
pulmonary emboli;
adequate anticoagulation
based on aPTT, PTT 1.5-
2.5× control
Teach patient/family:
• To avoid OTC
preparations that may cause
serious product interactions
unless directed by
prescriber; to notify all
health care providers of
heparin use • That product
may be held during active
bleeding (menstruation),
depending on condition •
About subq injection
technique if self-
administered; to rotate
sites, not to inject into
irritated or broken skin
• To use soft-bristle
toothbrush to avoid
bleeding gums; to avoid
contact sports; to use an
electric razor; to avoid IM
inj.
• To carry emergency ID
identifying product taken
• Bleeding: to report to
prescriber any signs of
bleeding: gums, under
skin, urine, stools
• To report to prescriber
any signs of
hypersensitivity: rash,
chills, fever, itching
Student Nurse: GABRIELLE A. MAGDARAOG Clinical Instructor: JEANETTE J. ROJO
You might also like
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument3 pagesDrug Study OxytocinSheena Marie M. TarleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format 1Document3 pagesDrug Study Format 1Janeenne Fe Nicole SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin Induction or Stimulation of Labor BeforeDocument4 pagesOxytocin Induction or Stimulation of Labor BeforeIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineKyla VillafrancaNo ratings yet
- LocalDocument5 pagesLocalybqbjpvtmrNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyYVETTE CLAIRE BORRESNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument3 pagesGeneric NameSittie Nashieva A. UsmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format OxytocinDocument1 pageDrug Study Format OxytocinKimberly GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AFP Abnormal MensesDocument12 pagesAFP Abnormal Mensespatrick_raj884545No ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinJuniece Marie CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho ReviseDocument10 pagesPa Tho ReviseCharl SembranoNo ratings yet
- OXYTOCIN-drug StudyDocument4 pagesOXYTOCIN-drug StudyCarissa Mae Tapec EstradaNo ratings yet
- DR Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDR Drug Studyslashmortred100% (5)
- Methylergonovine Maleate (Methergine) Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Action Nursing Consideration RationaleDocument5 pagesMethylergonovine Maleate (Methergine) Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Action Nursing Consideration RationalekeenoxkyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Oxytocin and LidocaineDocument3 pagesDrug Study Oxytocin and LidocaineHazel Grace AhitoNo ratings yet
- DR Drug Study: 401 2nd SemDocument2 pagesDR Drug Study: 401 2nd SemHazel Grace AhitoNo ratings yet
- Generic/ Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ImplicationsDocument14 pagesGeneric/ Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ImplicationsbokanegNo ratings yet
- Miole19074 Drug StudyLRDRDocument29 pagesMiole19074 Drug StudyLRDREur MioleNo ratings yet
- Case Study Preeclampsia FinDocument5 pagesCase Study Preeclampsia FinAngel Clarisse JariolNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument38 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionЕрнур КасымбаевNo ratings yet
- Prostethic Valve & PregnancyDocument11 pagesProstethic Valve & PregnancyShienna Marie SalvioNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument3 pagesOxytocinjints poterNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument3 pagesOxytocinjints poterNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug Studyjustine franchesca abonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument1 pageDrug Study OxytocinChie Hyun-AeNo ratings yet
- Caisip NCM109Document3 pagesCaisip NCM109Vannesa TarifaNo ratings yet
- AbortionDocument15 pagesAbortiondebdeepbhattacharya411No ratings yet
- Oajtmr 02 00054Document3 pagesOajtmr 02 00054MorindaNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument27 pagesDrug AnalysisCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-ncp-Abruptio Placentae (Oxytocin) - PeregrinoDocument3 pagesDrug Study-ncp-Abruptio Placentae (Oxytocin) - PeregrinoJOYCE ANN PEREGRINONo ratings yet
- Drug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingDocument6 pagesDrug Study: I Loilo Doctors' College College of NursingAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin, Dinoprostone, Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOxytocin, Dinoprostone, Cefuroxime Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-NCP-ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE (Oxytocin) - PeregrinoDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY-NCP-ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE (Oxytocin) - PeregrinoJOYCE ANN PEREGRINONo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations AssessmentDocument7 pagesDrug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations AssessmentEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Bulacan State University College of NursingDocument4 pagesBulacan State University College of NursingAmbeguia ElijahNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For OxytocinDocument2 pagesDrug Study For OxytocinAngelica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: Maisuri T. ChalidDocument44 pagesHypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: Maisuri T. ChalidinhaNo ratings yet
- OXYTOCINDocument3 pagesOXYTOCINJaye Aprile Adrianne KuizonNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Therapeutics Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument7 pagesDrug Name Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Therapeutics Effects Nursing ConsiderationsHaleNo ratings yet
- OB 2.01 - Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyDocument5 pagesOB 2.01 - Hypertensive Disorders in PregnancyvetinaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-OxytocinDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY-OxytocinCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada67% (3)
- Oxytocin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesOxytocin Drug StudyRem remNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis CuiDocument23 pagesDrug Analysis CuiMark Christian CuiNo ratings yet
- History Lab Investigation: EclampsiaDocument5 pagesHistory Lab Investigation: EclampsiaShafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- ER Drug StudyDocument4 pagesER Drug StudyNecy Tessa C. AcostaNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia and EclampsiaDocument23 pagesPreeclampsia and Eclampsiaapi-3705046100% (6)
- Hormones, Mitotic, Cancer Cell AntineoplasticDocument11 pagesHormones, Mitotic, Cancer Cell AntineoplasticFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY and CASE ANALYSISDocument6 pagesDRUG STUDY and CASE ANALYSISMa. Kaile Shyla LlacarNo ratings yet
- Generic Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)Document3 pagesGeneric Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)jennix_030883% (6)
- Drugstudy-Vd RodasDocument5 pagesDrugstudy-Vd RodasChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LP4Document5 pagesDrug Study LP4Nicxx GamingNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia: Group 3Document21 pagesEclampsia: Group 3Trisha Mae MarquezNo ratings yet
- Lp2 Drug Study FormsDocument3 pagesLp2 Drug Study FormsJed Kachel BugayongNo ratings yet
- POGI Preclampsia 2022Document52 pagesPOGI Preclampsia 2022SDM RSTINo ratings yet
- Obstetric and Gynecologic Nephrology: Women’s Health Issues in the Patient With Kidney DiseaseFrom EverandObstetric and Gynecologic Nephrology: Women’s Health Issues in the Patient With Kidney DiseaseMala SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle Related Disorders: Volume 7: Frontiers in Gynecological EndocrinologyFrom EverandMenstrual Cycle Related Disorders: Volume 7: Frontiers in Gynecological EndocrinologySarah L. BergaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Nursing NotesDocument1 pageDisaster Nursing NotesMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- CVA (Group 8)Document56 pagesCVA (Group 8)Magdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Types of PsychotherapyDocument7 pagesTypes of PsychotherapyMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations of Head InjuryDocument18 pagesPathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations of Head InjuryMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- MusculoskeletalDocument33 pagesMusculoskeletalMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Neonate Lec With RisksDocument41 pagesNeonate Lec With RisksMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Psych Case Study MAGDARAOG, GABRIELLE A.Document12 pagesPsych Case Study MAGDARAOG, GABRIELLE A.Magdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Process RecordingDocument4 pagesProcess RecordingMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Cardio NotesDocument2 pagesCardio NotesMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Group 4 - Nicu Case StudyDocument20 pagesGroup 4 - Nicu Case StudyMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Traction: Bryant Traction Buck'S ExtensionDocument3 pagesTraction: Bryant Traction Buck'S ExtensionMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Operating Room NotesDocument35 pagesOperating Room NotesMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Braces: Shantz Collar Philedelphia CollarDocument3 pagesBraces: Shantz Collar Philedelphia CollarMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: AssessmentDocument49 pagesMusculoskeletal System: AssessmentMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- POC Review NotesDocument9 pagesPOC Review NotesMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Nursing Management: SafetyDocument4 pagesNursing Management: SafetyMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Office of The Sangguniang Barangay: Page Barangay Sta. Rita Resolution No., S.2021Document2 pagesOffice of The Sangguniang Barangay: Page Barangay Sta. Rita Resolution No., S.2021Magdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- RDS PathophysioDocument2 pagesRDS PathophysioMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Case Study NCPDocument9 pagesCase Study NCPMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- University of Eastern Philippines College of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesDocument5 pagesUniversity of Eastern Philippines College of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Rds PathophysioDocument2 pagesRds PathophysioMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Anaphy and PathophyDocument6 pagesAnaphy and PathophyMagdaraog Gabrielle A.No ratings yet
- Platelet ConcentratesDocument2 pagesPlatelet ConcentratesARIF AHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Notes: Bernard-Soulier Syndrome (BSS)Document3 pagesNotes: Bernard-Soulier Syndrome (BSS)Himalaya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- DEC 2007-NPT 4-Questions and RationaleDocument21 pagesDEC 2007-NPT 4-Questions and RationaleRoy Salvador100% (2)
- An Open-Label, Randomized Prospective Study ToDocument7 pagesAn Open-Label, Randomized Prospective Study ToVhievien ChiaNo ratings yet
- Oral Path PDFDocument367 pagesOral Path PDFAashka Desai100% (2)
- Hemostasis Soalan: Edited:Dairion Gatot, Heny SyahriniDocument13 pagesHemostasis Soalan: Edited:Dairion Gatot, Heny SyahriniGiovan GaulNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Hematology A Practical Guide 2017Document297 pagesPediatric Hematology A Practical Guide 20170ishiNo ratings yet
- Adminku Journal Manager P 19 24Document6 pagesAdminku Journal Manager P 19 24RamayanaNo ratings yet
- Immuno-Serology & Blood Banking Case Study: Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument6 pagesImmuno-Serology & Blood Banking Case Study: Systemic Lupus ErythematosusRomie SolacitoNo ratings yet
- PLT Interference-Malang-231125Document6 pagesPLT Interference-Malang-231125Beatrix RosellaNo ratings yet
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin)Document1 pageLovenox (Enoxaparin)E100% (1)
- Lecture Hemophilia and Thrombocytopenic PurpuraDocument55 pagesLecture Hemophilia and Thrombocytopenic PurpuraaymenNo ratings yet
- Renal Disease and Neurology (2017)Document22 pagesRenal Disease and Neurology (2017)mysticmdNo ratings yet
- Hematology 2 Lecture Notes Platelet Quantitative DisordersDocument10 pagesHematology 2 Lecture Notes Platelet Quantitative DisorderscccomayogNo ratings yet
- PAEDS 1a - 04.10.19 ThrombocytopeniaDocument15 pagesPAEDS 1a - 04.10.19 Thrombocytopenialotp12No ratings yet
- Natural Remedies To Increase Platelet Count: Swati BurungaleDocument5 pagesNatural Remedies To Increase Platelet Count: Swati BurungaleraamNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Leukemia2Document4 pagesCase Study - Leukemia2shaiya08No ratings yet
- Neonatal EmergenciesDocument21 pagesNeonatal EmergenciesRNo ratings yet
- Coagulopathy in Liver DiseasesDocument6 pagesCoagulopathy in Liver DiseasesSergio RuizNo ratings yet
- 610PHSPDF HSIBonusReportsDocument90 pages610PHSPDF HSIBonusReportsMichael ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DisordersDocument197 pagesHematologic DisordersDanica Mae BianitoNo ratings yet
- Revolade Epar Medicine Overview - enDocument3 pagesRevolade Epar Medicine Overview - enAli KayaNo ratings yet
- Seminar - Hemorrhage 25-06-2020Document75 pagesSeminar - Hemorrhage 25-06-2020Chandra dimpleNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Adult With Unexplained Pancytopenia - UpToDateDocument28 pagesApproach To The Adult With Unexplained Pancytopenia - UpToDatesusanaNo ratings yet
- 1 Hematology Mcqs PDFDocument5 pages1 Hematology Mcqs PDFSatouri Haythem100% (1)
- HaematologyReport PDFDocument78 pagesHaematologyReport PDFhamody662002No ratings yet
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument8 pagesAcute Lymphocytic LeukemiaWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Question Text: Clear My ChoiceDocument13 pagesQuestion Text: Clear My ChoiceLylibette Anne H. CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Erythrocyte Dysplasia in Peripheral Blood Smears From 5 Thrombocytopenic Dogs Treated With Vincristine SulfateDocument7 pagesErythrocyte Dysplasia in Peripheral Blood Smears From 5 Thrombocytopenic Dogs Treated With Vincristine SulfateLaboratorio de BioquimicaNo ratings yet
- EDTA Dependent Pseudothrombocytopenia in A Patient With Scrub Typhus - A Case ReportDocument4 pagesEDTA Dependent Pseudothrombocytopenia in A Patient With Scrub Typhus - A Case ReportKatthaleeya SrinakNo ratings yet