Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psychometric Properties of The Motivated Strategies For Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) Among Italian High School Students
Uploaded by
MarekSkorsepaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psychometric Properties of The Motivated Strategies For Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ) Among Italian High School Students
Uploaded by
MarekSkorsepaCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/281404020
PSYCHOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF THE MOTIVATED STRATEGIES FOR LEARNING
QUESTIONNAIRE (MSLQ) AMONG ITALIAN HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS
Conference Paper · July 2015
CITATIONS READS
0 215
4 authors, including:
Maria Giulia Olivari Andrea Bonanomi
Catholic University of the Sacred Heart Catholic University of the Sacred Heart
58 PUBLICATIONS 91 CITATIONS 55 PUBLICATIONS 209 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE
Emanuela Confalonieri
Catholic University of the Sacred Heart
117 PUBLICATIONS 213 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Inter-ethnic relationships in secondary education and Initial VET View project
Assessment of preterm birth on child development and on parents well being form birth to school age View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Maria Giulia Olivari on 01 September 2015.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
The 14th European Congress of Psychology
Milan, 7-10 July 2015
PSYCHOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF THE MOTIVATED STRATEGIES FOR LEARNING QUESTIONNAIRE (MSLQ)
AMONG ITALIAN HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS
Olivari M. G. 1, Bonanomi A.2, Gatti E.1, Confalonieri E. 1
1 Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Psychology Department, CRIdee, Milan, Italy
2 Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Department of Statistical Sciences, Milan, Italy
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
According to a recent review (Credé & Phillips, 2011), the
Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire (MSLQ;
Pintrich & DeGrooth, 1990) has been used to assess
student motivation and learning strategies in a variety of
settings (i.e.: online classes, street learning stations). In
the last decade, several studies have investigated the
psychometric properties of this instrument or have
assessed its validity in many different countries (i.e. Czech
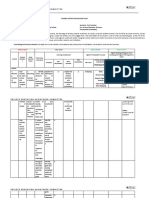
Republic, Iran, Mexico, Oman, Turkey). HIGH SCHOOL ATTENDED BY
PARTICIPANTS
In Italy, the psychometric properties of the MSLQ have 28,6% 39,3%
not been investigated yet, although the instrument has
been used to assess motivation processes among Classic
students in online contexts (Albanese et al., 2010; Bordin,
Scientific
Bastianelli & Fluperi, 2009).
32,1%
Technical
AIM
To investigate the psychometric properties of the 44-
item version of the MSLQ in an Italian high school
REGULATION
STRATEGIES
LEARNING
INTRINSIC
EFFICACY
ANXIETY
VALUE
SELF-
SELF-
TEST
students sample by:
a) exploring the factorial structure of the scale
Compared with other students in this class I think I know a great deal
b) confirming the identified factorial model about the subject
.816
c) describing reliability in term of internal consistency My study skills are excellent compared with others in this class .808
d) verifying the validity and generalizability of the factor Compared with others in this class I think I’m a good student .761
structure. I think I will receive a good grade in this class .702
Compared with other students in this class I expect to do well .695
I expect to do very well in this class .598
RESULTS
I am sure I can do an excellent job on the problems and tasks assigned
a. To explore the factorial structure of the scale we performed an EFA, for this class
.457
resulting in a 25-item 5-factor solution (Bartlett’s test of sphericity I know that I will be able to learn the material for this class .418
Chi-square=6364.6, df=300, p<.001 ; Kaiser-Mayer-Olkin=.90). I like what I am learning in this class .808
I think that what we are learning in this class is interesting .794
I think that what I am learning in this class is useful for me to know .667
b. To confirm the identified factorial model we performed a CFA, It is important for me to learn what is being taught in this class .638
providing good fit indices (Χ2=751.924, df=265, p=0.000; CFI=0.923, Understanding this subject is important to me .476
RMSEA=0.051). When I do homework, I try to remember what the teacher said in class
.704
so I can answer the questions correctly
I ask myself questions to make sure I know the material I have been
.647
c. To describe the reliability of the factors we computed Alpha studying
coefficient, showing a good internal consistency. When I study for a test I practice saying the important facts over and
.566
over to myself
SELF- INTRINSIC LEARNING TEST SELF-
Total
EFFICACY VALUE STRATEGIES ANXIETY REGULATION When I study for a test, I try to put together the information from class
.539
Cronbach’s alpha .872 .821 .760 .806 .717 .830 and from the book
When I read materials for this class, I say the words over and over to
d. To verify the validity and generalizability of the factor structure we myself to help me remember
.512
performed a multigroup CFA testing measurement invariance in two When reading I try to connect the things I am reading about with what
.481
subsamples, divided by gender. The Δχ2 between the unconstrained I already know
I have an uneasy, upset feeling when I take a test .865
and constrained models yielded no significant results. The factor
I worry a great deal about tests .724
structure is invariant by gender. I am so nervous during a test that I cannot remember facts I have
.718
Model Χ2 df RMSEA CFI Δχ2(df) p learned
Uncostrained 751.924 265 0.051 0.923 - - Even when study materials are dull and uninteresting, I keep working
.694
Invariant factor loading 1008.806 530 0.036 0.921 256.88(265) 0.628 until I finish
I work hard to get a good grade even when I don’t like a class .651
When work is hard I either give up or study only the easy parts
.481
DISCUSSION (Reversed)
The final Italian version of MSLQ is composed by 25 items and shows a 5-factor solution: Self-Efficacy References
(8 items), Intrinsic Value (5 items), Learning Strategies (6 items), Test Anxiety (3 items) and Self- Credé, M., & Phillips, L. A. (2011).A meta-analytic review of the Motivated
Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. Learning and Individual
Differences,21(4), 337-346.
Regulation (3 items). Albanese, O., Businaro, N., Cacciamani, S., De Marco, B., Farina, E., Ferrini,
T., &Vanin, L. (2010). Riflessione metacognitiva in ambienti online e
The five original factors identified by Pintrich & DeGrooth (1990) are still present in the 25 item autoregolazione nell’attività di studio nei corsi universitari. TD-
Tecnologie Didattiche, 49, 50-61.
Italian version, providing the opportunity to assess the same factors throughout a shorter and easier Bordin V., Bastianelli A., Fluperi S. (2009). Motivazione e prestazione nell’e-
learning. Atti del III Convegno Nazionale. Verso una nuova qualità
instrument. dell’insegnamento e apprendimento della Psicologia: Progettare i
corsi, progettare la formazione, pp. 352-363. URL:
Our 25-item Italian version of the MSLQ represents a useful and reliable measure to assess high http://convdidattica.psy.unipd.it/index.php? page=005
Pintrich, P. R., &DeGroot, E.V.(1990). Motivational and self-regulated
school students’ motivation, as well as, the main factors underlying the learning processes.
View publication stats
learning components of classroom academic performance.Journal of
Educational Psychology, 82(1), 33-40.
You might also like
- Learning Styles InventoryDocument5 pagesLearning Styles InventoryCarla Diana Ascensão100% (1)
- Culture and Its Role in Moral BehaviorDocument2 pagesCulture and Its Role in Moral BehaviorRoberto Velasco Mabulac100% (4)
- Pre Observation Information ANDROLYN P. RODRIGUEZDocument2 pagesPre Observation Information ANDROLYN P. RODRIGUEZKRIZZIE JOY CAILING100% (2)
- Syllabus - Basic GeographyDocument10 pagesSyllabus - Basic GeographycathyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Prelim Examination in Physical EducationDocument6 pagesReviewer For Prelim Examination in Physical EducationJasmine RiveraNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Updated MTLBDocument10 pagesSyllabus - Updated MTLBCatherine DangananNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: English 10 4Document4 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: English 10 4Marilyn Arellano67% (3)
- Syllabus in Non-Institutional Corrections (Au)Document6 pagesSyllabus in Non-Institutional Corrections (Au)Lombroso's follower100% (1)
- Module 1.1Document4 pagesModule 1.1Jen Kerly100% (2)
- Problems of Management in The 21st Century, Vol. 4, 2012Document97 pagesProblems of Management in The 21st Century, Vol. 4, 2012Scientia Socialis, Ltd.No ratings yet
- POSTEREARLIdefinitivoDocument2 pagesPOSTEREARLIdefinitivorobbyNo ratings yet
- Methods of Item Analysis in Standardized Student Assessment: An Application To An Italian Case StudyDocument17 pagesMethods of Item Analysis in Standardized Student Assessment: An Application To An Italian Case StudyNanoNo ratings yet
- Last Project (156Document45 pagesLast Project (156Angel ShabuNo ratings yet
- 2015 Measuring The Multidimensional Performance of A Museum Network 19Document23 pages2015 Measuring The Multidimensional Performance of A Museum Network 19Micaela Arratia IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Sandoval Litrev1Document29 pagesSandoval Litrev1Ceejay A. SandovalNo ratings yet
- The Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire: Internal Structure, Criterion and Incremental Validity in An Italian SampleDocument13 pagesThe Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire: Internal Structure, Criterion and Incremental Validity in An Italian SampleTiffany OikawaNo ratings yet
- IDP Template For English Majors Society 1Document10 pagesIDP Template For English Majors Society 1sordillasecond semNo ratings yet
- Metacognitive Skills Scale: Eğitim Fakü̧ltesi Dergisi January 2013Document13 pagesMetacognitive Skills Scale: Eğitim Fakü̧ltesi Dergisi January 2013Nia NaNa Try FaithfulNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Intellectual Capital and RDocument20 pagesAssessing The Intellectual Capital and Rlais.sardaNo ratings yet
- ETRD FinalversionDocument40 pagesETRD FinalversionAndreia SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Ebook PDF Consumer Behaviour 6Th Byleon Schiffman All Chapter PDF Docx KindleDocument42 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Consumer Behaviour 6Th Byleon Schiffman All Chapter PDF Docx Kindlereginald.williams416100% (25)
- Análisis de ArtículosDocument5 pagesAnálisis de ArtículosSheila Gonzalez ValverdeNo ratings yet
- FIDP TemplateDocument3 pagesFIDP TemplateJovi AbabanNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument12 pagesEmotional IntelligenceKritika PrasadNo ratings yet
- Contoh 5w1h BagusDocument8 pagesContoh 5w1h BagusPo PoNo ratings yet
- MD 0000000000022430Document10 pagesMD 0000000000022430some oneNo ratings yet
- A Meta-Synthesis On The Potential Effectiveness of A Teaching Internship ProgramDocument11 pagesA Meta-Synthesis On The Potential Effectiveness of A Teaching Internship ProgramNelvin NoolNo ratings yet
- Job Crafting and Job Satisfaction in A Sample of Italian Teachers: The Mediating Role of Perceived Organizational SupportDocument14 pagesJob Crafting and Job Satisfaction in A Sample of Italian Teachers: The Mediating Role of Perceived Organizational SupportNely SofwaNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter TOS (SOCIAL SCIENCE)Document2 pages4th Quarter TOS (SOCIAL SCIENCE)Vivan FeNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Activities of Improving The Quality of Teaching Political Theory Subjects - Research at Universities Under The Ministry of Industry and Trade of VietnamDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting The Activities of Improving The Quality of Teaching Political Theory Subjects - Research at Universities Under The Ministry of Industry and Trade of VietnamInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Exam Question EvaluationDocument16 pagesExam Question Evaluationlyndon_baker_1No ratings yet
- Social Work Course Map SPRING 2020Document3 pagesSocial Work Course Map SPRING 2020latedonthompsonNo ratings yet
- Costa PosterDocument1 pageCosta PosterBirmingham Summer School 2012No ratings yet
- The Measurement of Emotional Intelligence A Critic PDFDocument19 pagesThe Measurement of Emotional Intelligence A Critic PDFFrancisco MuñozNo ratings yet
- Psych-312 Manual 2022Document198 pagesPsych-312 Manual 2022Josiah BacaniNo ratings yet
- Review of Educational Research 2011 Yeager To 267 301Document35 pagesReview of Educational Research 2011 Yeager To 267 301Ligue91No ratings yet
- 00 IntroDocument33 pages00 Introchhavi jainNo ratings yet
- Hpe Forward Planning DocumentDocument8 pagesHpe Forward Planning Documentapi-346324074No ratings yet
- IJBES Published Paper 23Document13 pagesIJBES Published Paper 23Damianus AbunNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Luray Ii Barangay High SchoolDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Luray Ii Barangay High SchoolNat-Nat Purisima50% (2)
- The Mini Questionnaire of Personal OrganizationDocument14 pagesThe Mini Questionnaire of Personal OrganizationKayn WestNo ratings yet
- In PsychologyDocument30 pagesIn PsychologySirajudinNo ratings yet
- 2022 A Meta-Analysis of The Relationships CommitmentDocument12 pages2022 A Meta-Analysis of The Relationships CommitmentMei Li TreNo ratings yet
- ValckeJenniferW 2017 DifferencesInContentP IntegratingContentAndDocument18 pagesValckeJenniferW 2017 DifferencesInContentP IntegratingContentAnd李靖怡No ratings yet
- The Effect of Problem-Based Video Animation Instructions To Improve Students' Critical Thinking SkillsDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Problem-Based Video Animation Instructions To Improve Students' Critical Thinking SkillsSOLEH RITONGANo ratings yet
- School-Age Assessment of Attachment: An Analysis of Non-Verbal Behavior Using Dr. NotesDocument2 pagesSchool-Age Assessment of Attachment: An Analysis of Non-Verbal Behavior Using Dr. NotesFernando Hilario VillapecellínNo ratings yet
- GE-113 - Course SyllabusDocument6 pagesGE-113 - Course SyllabusRico CombinidoNo ratings yet
- BandurasTheory 1977Document24 pagesBandurasTheory 1977Cristhian AndresNo ratings yet
- AUGUST 2020 Biological Psychology: School of Liberal Arts & SciencesDocument16 pagesAUGUST 2020 Biological Psychology: School of Liberal Arts & Scienceskaine poohNo ratings yet
- 1 Where Is The Learning in Learning AnalytDocument15 pages1 Where Is The Learning in Learning AnalytCarlos terceroNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1796 012110Document10 pagesFibonacci 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1796 012110AnnisaNo ratings yet
- MeasuringForgiveness AsystematicReviewDocument17 pagesMeasuringForgiveness AsystematicReviewKristel OlilaNo ratings yet
- A Phenomenological Study of TH Passers and NonPassDocument19 pagesA Phenomenological Study of TH Passers and NonPassPhylicia RamosNo ratings yet
- Funmi Questionnaire Main2Document26 pagesFunmi Questionnaire Main2Toheeb AlarapeNo ratings yet
- Inteligência Emocional Percebida de Professores Universitários Com Base Na Natureza Da Matéria MinistradaDocument10 pagesInteligência Emocional Percebida de Professores Universitários Com Base Na Natureza Da Matéria MinistradaVinicius AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- FHUM Psychology 2019Document9 pagesFHUM Psychology 2019Rama OktNo ratings yet
- Successful Employment Outcomes For People With Disabilities: A Proposed Conceptual ModelDocument23 pagesSuccessful Employment Outcomes For People With Disabilities: A Proposed Conceptual ModellucimaramcarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Corporate Governance - Maksi Rev 4 PDFDocument5 pagesSyllabus Corporate Governance - Maksi Rev 4 PDFPriyance NababanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Effectiveness of Instructional Design Features in Simulation-Based Education: Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument32 pagesComparative Effectiveness of Instructional Design Features in Simulation-Based Education: Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisPablo Ignacio Lillo ArayaNo ratings yet
- Art BonaviaJulian2022EffectiveBehaviorsinWorkTeamsDocument9 pagesArt BonaviaJulian2022EffectiveBehaviorsinWorkTeamsElaine SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Banduras TheoryDocument24 pagesBanduras TheoryCatarina RamosNo ratings yet
- Mca Syllabus 2020 2021Document85 pagesMca Syllabus 2020 2021Aniket SharmaNo ratings yet
- Social and Emotional Learning in The Ibero-American Context: A Systematic ReviewDocument12 pagesSocial and Emotional Learning in The Ibero-American Context: A Systematic ReviewS. M.No ratings yet
- Sherpa Tenzin-QuestionnaireDocument54 pagesSherpa Tenzin-QuestionnaireKert SilvaNo ratings yet
- Designing Performance Measurement Systems: Theory and Practice of Key Performance IndicatorsFrom EverandDesigning Performance Measurement Systems: Theory and Practice of Key Performance IndicatorsNo ratings yet
- Adoption of Data Analytics in Higher Education Learning and TeachingFrom EverandAdoption of Data Analytics in Higher Education Learning and TeachingNo ratings yet
- Pananaliksik Sa Wika at Pantikan Major 20Document12 pagesPananaliksik Sa Wika at Pantikan Major 20Marc Anthony ManzanoNo ratings yet
- GB570 Course PreviewDocument10 pagesGB570 Course PreviewNatalie Conklin100% (1)
- TCALLP UNIT I Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument18 pagesTCALLP UNIT I Learner Centered Psychological PrinciplesJeanette Torralba Esposito0% (1)
- CH 8 - Performance ManagementDocument30 pagesCH 8 - Performance ManagementAg SyazrienNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Goals of Anthropology, Sociology and Political ScienceDocument12 pagesThe Nature and Goals of Anthropology, Sociology and Political ScienceAl Cheeno AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- 4 Lista Teme Disertatie 2020-2021 BSCMC EnglezaDocument3 pages4 Lista Teme Disertatie 2020-2021 BSCMC EnglezaqawsfawsfNo ratings yet
- DAISY Individual-Learning-Monitoring-Plan - Lagging-BehindDocument2 pagesDAISY Individual-Learning-Monitoring-Plan - Lagging-BehindLadyAngelIgnacioValgunaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed 1 Modules 5 To 9 - Arnulfo L. Dela CruzDocument9 pagesProf. Ed 1 Modules 5 To 9 - Arnulfo L. Dela CruzArn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CNN Student News Worksheet-AVIDDocument2 pagesCNN Student News Worksheet-AVIDScience TeacherNo ratings yet
- Elementary School Teachers Belief On Integrating TechnologyDocument16 pagesElementary School Teachers Belief On Integrating TechnologyThea ToñacaoNo ratings yet
- Art & AestheticsDocument65 pagesArt & Aestheticsshahedemon shahedemonNo ratings yet
- Nestle Case StudyDocument8 pagesNestle Case StudySufiya ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Five Day's Online Faculty Development Programme On Design, Develop and Deliver Online Courses (August 02-06, 2021)Document1 pageFive Day's Online Faculty Development Programme On Design, Develop and Deliver Online Courses (August 02-06, 2021)DrPoonam DeshwalNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 8 (Health) : For LearnerDocument25 pagesMAPEH 8 (Health) : For LearnerRichelle IldefonsoNo ratings yet
- Modul 02 MK Ars 201 Hospitall Entrepreuneurship LeadershipDocument27 pagesModul 02 MK Ars 201 Hospitall Entrepreuneurship Leadershipenik utmawatiNo ratings yet
- Carthel Science Educational Foundation, Inc. San Vicente, San Manuel, Tarlac S.Y 2020-2021Document5 pagesCarthel Science Educational Foundation, Inc. San Vicente, San Manuel, Tarlac S.Y 2020-2021Noel AquinoNo ratings yet
- My Grading PhilosophyDocument1 pageMy Grading Philosophyapi-550448225No ratings yet
- A Survey On Critical Literacy As A Pedagogical ApproachDocument7 pagesA Survey On Critical Literacy As A Pedagogical ApproachLaying Ayu MeriryNo ratings yet
- Leadership Behavior and Motivation: Learning OutcomesDocument42 pagesLeadership Behavior and Motivation: Learning Outcomesaditya anugrahNo ratings yet
- Ped3samsul, Alwasim - Final ExaminationDocument6 pagesPed3samsul, Alwasim - Final ExaminationDanizelle Kaye Cadocoy BernardoNo ratings yet
- RDR2013 05 QP8665460 ELA Common Core Textbook and Instruction WebDocument7 pagesRDR2013 05 QP8665460 ELA Common Core Textbook and Instruction WebBill LeeNo ratings yet
- Psyc 352 Final Project Paulina PiatekDocument22 pagesPsyc 352 Final Project Paulina Piatekapi-540523647No ratings yet
- Section D IgdDocument26 pagesSection D Igdbattagiri sai jyothiNo ratings yet
- Managing A Successful Business Project Talent Management of TESCO Bank, UKDocument17 pagesManaging A Successful Business Project Talent Management of TESCO Bank, UKDipayanNo ratings yet