Professional Documents
Culture Documents
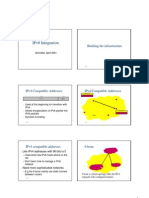
IPv6 Cheatsheet
Uploaded by
Frei Herr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesThis document provides an overview of IPv6 addressing, protocol headers, extension headers, address types, reserved ranges, multicast addresses, address assignment, autoconfiguration, DHCPv6, privacy extensions, and the neighbor discovery protocol. It summarizes IPv6 address notation, interface identifiers, and the required addresses for a node. It also outlines stateless and stateful address autoconfiguration, as well as the use of DHCPv6 and DNS servers via router advertisements.
Original Description:
Original Title
IPv6_Cheatsheet
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of IPv6 addressing, protocol headers, extension headers, address types, reserved ranges, multicast addresses, address assignment, autoconfiguration, DHCPv6, privacy extensions, and the neighbor discovery protocol. It summarizes IPv6 address notation, interface identifiers, and the required addresses for a node. It also outlines stateless and stateful address autoconfiguration, as well as the use of DHCPv6 and DNS servers via router advertisements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesIPv6 Cheatsheet
Uploaded by
Frei HerrThis document provides an overview of IPv6 addressing, protocol headers, extension headers, address types, reserved ranges, multicast addresses, address assignment, autoconfiguration, DHCPv6, privacy extensions, and the neighbor discovery protocol. It summarizes IPv6 address notation, interface identifiers, and the required addresses for a node. It also outlines stateless and stateful address autoconfiguration, as well as the use of DHCPv6 and DNS servers via router advertisements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Address Types (RFC4291)
2000::/3 Global unicast
IPv6 Cheatsheet ::/128
::1/128
Unspecified
Loopback
ff00::/8 Multicast
IPv6 Protocol header (RFC2460) fe80::/10 Link-Local unicast
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ fc00::/7 Unique Local (RFC4193)
|Version| Traffic Class | Flow Label |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Payload Length | Next Header | Hop Limit |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| |
Reserved Ranges
+ +
| | ::/0 Default Route
+ Source Address +
|
+
|
+
::ffff:0:0/96 IPv4-mapped Addresses (RFC4291)
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ 2001::/32 Teredo Tunneling (RFC4380)
| |
+ + 2001:db8::/32 Documentation (RFC3849)
| |
+
|
Destination Address +
|
2002::/16 6to4 (RFC3056)
+ +
| |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
Version(4-bit) Always set to 6 Multicast Ranges (RFC4291)
Traffic Class(8-bit) A DSCP value for QoS ff01::/16 Interface-Local scope
Flow Label(20-bit) Identifies unique flows ff02::/16 Link-Local scope
Payload Length(16-bit) Length of the payload in bytes ff04::/16 Admin-Local scope
Next Header(8-bit) Header or protocol which follows ff05::/16 Site-Local scope
Hop Limit (8-bits) Similar to IPv4's time to live field
ff08::/16 Organisation-Local scope
Source Address (128-bit) Source IP address
Destination Address(128-bit)Dest. IP addresses ff0e::/16 global scope
Extension Headers (RFC2460) Link-Local Multicast Addresses
+---------------+----------------+-----------------+-----------------
| IPv6 header | Routing header | Fragment header | fragment of TCP
ff02::1 All Nodes (RFC4291)
| | | | header + data
| Next Header = | Next Header = | Next Header = | ff02::2 All Routers (RFC4291)
| Routing | Fragment | TCP |
+---------------+----------------+-----------------+----------------- ff02::5 OSPF (RFC5340)
Hop-by-Hop Options (0) ff02::6 OSPF DR (RFC5340)
Routing (43) ff02::c SSDP (no RFC)
Fragment (44) ff02::16 MLDv2 (RFC3810)
Destination Options (60) ff02::1:2 All DHCP Agents and Servers
Authentication (51) ff02::1:3 LLMNR (RFC4795)
Encapsulating Security Payload (50) ff02::1:ffxx:xxxx Solicited-Node Address (RFC4291)
Text Representation of Addresses Interface ID
(RFC5952) Used to identify Interfaces on a link
XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX Always 64 Bits long (RFC4291)
X Hexadecimal Digit, 4 Bits (0-9, a-f) 48-Bit Ethernet MAC-Address to EUI-64 Mapping
: separates “Hextets” (4 Hex Digits)
Notation Rules
Eliminate leading zeros in all Hextets
Longest sequence of 2 or more Hextets of zeros
is replaced by :: (used only once)
Hex characters are represented in lowercase ("a", Privacy Extensions (RFC4941)
"b", "c", "d", "e", and "f") Genereate additional random Interface ID (Temporary
Examples Address) which is renewed frequently.
fe80::1 Address is used for Internet connections to hide the
ff02::1:ff52:b0eb MAC Address
2001:620:100:10a0:c87e:39ff:fe4b:8645
A Node’s required Addresses (RFC4291)
Address Assignment (RFC6177) Link-local address per interface
All configured unicast addresses
Loopback address
All nodes multicast address
Solicited node multicast address per unicast
address
Multicast address for all member groups
Stateless Address Autoconfiguration – Stateful DHCPv6 Service (RFC3315)
SLAAC (RFC4862) Used to provide DHCP Service to IPv6 nodes
DHCPv6 Server manages client addresses
Routers must set “m-Flag” in ICMPv6 RA
messages
1. Client creates own link-local unicast address
with link-local prefix and EUI-64 Interface ID
2. Clients sends ICMPv6 Router-Solicitation to
All-Routers link-local multicast Address
3. Router replies with ICMPv6 Router-
Advertisement, containing the links global
routing prefix
4. Client create own global unicast address with
1. Client sends ICMPv6 RS to all-routers address
global routing prefix and EUI-64 Interface ID
2. Upon detecting the m-flag, the client sends a
5. Client performs duplicate address detection
DHCPv6 SOLICIT to the all-dhcpv6-servers
against the newly created address
link-local multicast address
3. DHCPv6 Server relies with a DHCPv6
Duplicate Address Detection – DAD
ADVERTISE message offering a global
(RFC4862) unicast address
4. Client requests the offered address sending a
DHCPv6 REQUEST message
5. Server acknowledges address assignment
1. Client sends ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery to with DHCPv6 REPLY message
his own solicited Node link-local multicast
address, expecting no response DNS Server as an RA Option – RDNSS
2. If a host responds, the client need to create
(RFC6106)
another unicast address
Stateless DHCPv6 Service (RFC3736)
Used to provide DNS Servers to clients
No client addresses are manged
Routers must set “o-Flag” in ICMPv6 RA
messages 1. Client sends ICMPv6 RS to all-routers address
2. Router replies with ICMPv6 RA message
containing global routing prefix and DNS
information using an option field
Neighbor Discovery Protocol – NDP
(RFC4861)
Used to map IPv6 addresses and Ethernet
MAC addresses
Replaces Addess Resolution Protocol (ARP)
1. Client sends ICMPv6 RS to all-routers address
2. Upon detecting the o-flag, the client sends a
DHCPv6 REQUEST to the all-dhcpv6-servers
link-local multicast address 1. Host 1 sends ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation to
3. DHCPv6 Server relies with a DHCPv6 REPLY solicited node multicast address
message containing DNS servers and names 2. Host 2 replies with ICMPv6 Neighbor
Advertisement containing his Ethernet MAC
address
You might also like
- Ipv6 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Cheat SheetDaNnYtYpEs100% (1)
- eIP602 IPv6-AaS PDFDocument30 pageseIP602 IPv6-AaS PDFHardiyan Kesuma RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Apnic Elearning:: Ipv6 Addressing and SubnettingDocument30 pagesApnic Elearning:: Ipv6 Addressing and SubnettingChauhan WebTutsNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Cheat Sheetdecheverri100% (1)
- Ipv6 Address Types Address Type DescriptionDocument5 pagesIpv6 Address Types Address Type DescriptionroutemansNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Cheat SheetVinoth RNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Cheat SheetAndi JehanNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Subnet CheatsheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Subnet CheatsheetDEEP725No ratings yet
- Ipv6 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Cheat SheetKarlNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document25 pagesLecture 3Hạnh Hoàng ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 and Ipv6 - Binary Conversion: Ipv4 Address 192.168.50.112 /24 Address in Binary Netmask in BinaryDocument12 pagesIpv4 and Ipv6 - Binary Conversion: Ipv4 Address 192.168.50.112 /24 Address in Binary Netmask in Binaryb LiewNo ratings yet
- IPv6Document35 pagesIPv6Ngọc HuyNo ratings yet
- WG - Ipv6 Hype or RealityDocument38 pagesWG - Ipv6 Hype or RealityDavid RottmayerNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet V1.7: 0218:41Ff:Fe23:6A32Document1 pageIpv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet V1.7: 0218:41Ff:Fe23:6A32Patricio Quegles100% (1)
- Introduction To Ipv6 Ipv4 To Ipv6 Transformation: Phd. Student Nikolay Milovanov Ccie SP #20094Document60 pagesIntroduction To Ipv6 Ipv4 To Ipv6 Transformation: Phd. Student Nikolay Milovanov Ccie SP #20094xrasnaNo ratings yet
- IPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet v1.3 PDFDocument1 pageIPv6 Essentials Cheat Sheet v1.3 PDFIsaque ProfetaNo ratings yet
- Apnic Elearning:: Ipv6 Addressing and SubnettingDocument30 pagesApnic Elearning:: Ipv6 Addressing and SubnettingMohamed FayeNo ratings yet
- Eip602 Ipv6 AasDocument30 pagesEip602 Ipv6 AasChu Văn NamNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 and Ipv6 - Binary Conversion: Ipv4 Address 192.168.50.112 /24 Address in Binary Netmask in BinaryDocument12 pagesIpv4 and Ipv6 - Binary Conversion: Ipv4 Address 192.168.50.112 /24 Address in Binary Netmask in Binaryb LiewNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesIpv6 Cheat SheetnightphreakNo ratings yet
- What, Why, How: Jen Linkova Aka Furry Openwall, IncDocument61 pagesWhat, Why, How: Jen Linkova Aka Furry Openwall, IncBilal LatifNo ratings yet
- IPv6 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesIPv6 Cheat SheetKyawNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Tutorial: Address Type DescriptionDocument5 pagesIpv6 Tutorial: Address Type DescriptionSani MuhlisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 IP Version 6Document60 pagesChapter 10 IP Version 6nuhonoNo ratings yet
- IPV6 MikroTik Implementation by Mani RaissdanaDocument56 pagesIPV6 MikroTik Implementation by Mani RaissdananazloenNo ratings yet
- Computer Network - Topic 8Document14 pagesComputer Network - Topic 8Dutchman CoolNo ratings yet
- Digital Network - Lecturer3Document32 pagesDigital Network - Lecturer3sammydtechNo ratings yet
- IPv6 Cheat Sheet PDFDocument3 pagesIPv6 Cheat Sheet PDFsamiulsumanNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Tutorial: Go To CommentsDocument6 pagesIpv6 Tutorial: Go To CommentsDinkar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: IPv6 FundamentalsDocument35 pagesLesson 3: IPv6 FundamentalsMahmmoud MahdiNo ratings yet
- IPV6Document46 pagesIPV6ShubhamSetiaNo ratings yet
- IPV6Document26 pagesIPV6RmkumarsNo ratings yet
- S1 OpenLab Ver16062013Document2 pagesS1 OpenLab Ver16062013Trương Tùng Dương100% (1)
- IPv6 AddressingDocument61 pagesIPv6 AddressingmridulNo ratings yet
- Ipv 6 MainDocument48 pagesIpv 6 MainSurekha SundarrNo ratings yet
- IPv6 AaS HandoutsDocument17 pagesIPv6 AaS HandoutsHarryParadoxWayneNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Integration: Building The InfrastructureDocument9 pagesIpv6 Integration: Building The InfrastructureImamahNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Ipv6: Jaringankomputer2 Lab. Komunikasidigital Gedungd4 LT 1 Gedungd4 Lt. 1 Eepis-ItsDocument29 pagesIpv6 Ipv6: Jaringankomputer2 Lab. Komunikasidigital Gedungd4 LT 1 Gedungd4 Lt. 1 Eepis-ItsfrendianaNo ratings yet
- Florian Slaacd Bsdcan2018Document52 pagesFlorian Slaacd Bsdcan2018gfm46332No ratings yet
- Ipv6 - Addressing SchemeDocument38 pagesIpv6 - Addressing Schemepradeepagarwal62100% (1)
- IPv6 UpdateDocument48 pagesIPv6 UpdateSivagnanam ThanusiganNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Astaro2005Document19 pagesIpv6 Astaro2005ajaykumar988No ratings yet
- Đề chuẩn S1-Openlab-ver16062013Document3 pagesĐề chuẩn S1-Openlab-ver16062013Ngọc Hiếu100% (1)
- Redes de Comunicaciones de Datos Ipv6: Ing. Marco Andrés Ortiz NDocument31 pagesRedes de Comunicaciones de Datos Ipv6: Ing. Marco Andrés Ortiz NLaura Cathalina RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 12.7.4 LabDocument5 pages12.7.4 Labhiepgacute1989No ratings yet
- IPv6 LabDocument49 pagesIPv6 LabArputharaj JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Configuring and Troubleshooting Ipv6 Tcp/IpDocument40 pagesModule 5: Configuring and Troubleshooting Ipv6 Tcp/Ipalex ernyeyNo ratings yet
- IPv 6Document68 pagesIPv 6Diether SantosNo ratings yet
- Ipv6 Addressing: Yashvant Singh Centre For Excellence in Telecom Technology and ManagementDocument45 pagesIpv6 Addressing: Yashvant Singh Centre For Excellence in Telecom Technology and ManagementRitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Advanced Topics in Computer Networks: Next Generation Internet Protocol (Ipv6)Document31 pagesAdvanced Topics in Computer Networks: Next Generation Internet Protocol (Ipv6)Kamel SaifNo ratings yet
- Cisco Capitol 7Document6 pagesCisco Capitol 7diego950No ratings yet
- Mikrotik - IPv6Document45 pagesMikrotik - IPv6Musyaffak SNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol Version 4 (Ipv4) Is The Fourth Revision in The Development of TheDocument27 pagesInternet Protocol Version 4 (Ipv4) Is The Fourth Revision in The Development of TheUrvashi RoyNo ratings yet
- CIRA IPv6 Internal PolicyDocument4 pagesCIRA IPv6 Internal PolicyCanadian Internet Registration AuthorityNo ratings yet
- Implementing Ipv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity: - Ipv6, Formerly Named Ipng (Next Generation)Document71 pagesImplementing Ipv6 Addressing and Basic Connectivity: - Ipv6, Formerly Named Ipng (Next Generation)Paresh V PatelNo ratings yet
- IPv6 Addressing and Deployment in A Common WISP NetworkDocument46 pagesIPv6 Addressing and Deployment in A Common WISP NetworkcardenasccNo ratings yet
- IPv 6Document1 pageIPv 6Andrés Jonathan Enríquez JiménezNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- M.I.B Tool With D-LinkDocument6 pagesM.I.B Tool With D-LinkFrei Herr100% (1)
- Firmware Updater Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocument28 pagesFirmware Updater Guide: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineFrei HerrNo ratings yet
- Scanning Guide For Small Colour MFD'S: This Guide Covers The Following MachinesDocument29 pagesScanning Guide For Small Colour MFD'S: This Guide Covers The Following MachinesFrei HerrNo ratings yet
- Magicolor 4690mf-FieldServiceManualDocument433 pagesMagicolor 4690mf-FieldServiceManualFrei HerrNo ratings yet
- Bizhub c20-FieldServiceManualDocument495 pagesBizhub c20-FieldServiceManualFrei HerrNo ratings yet
- Magicolor 4690MF: Service ManualDocument172 pagesMagicolor 4690MF: Service ManualFrei HerrNo ratings yet
- Property Model Methodology A Landing Gear Operational Use CaseDocument17 pagesProperty Model Methodology A Landing Gear Operational Use CaseFrei HerrNo ratings yet
- HM Hs1sa Z Smart Smoke Sensor Z Wave User Manual 1.0Document4 pagesHM Hs1sa Z Smart Smoke Sensor Z Wave User Manual 1.0Frei HerrNo ratings yet
- The Speedlight Studio - Professional Portraits With Portable Flash - Michael Mowbray - by (Delu) PDFDocument178 pagesThe Speedlight Studio - Professional Portraits With Portable Flash - Michael Mowbray - by (Delu) PDFTatenda Madzingira100% (3)
- KSGER T12 Soldering Station PDFDocument3 pagesKSGER T12 Soldering Station PDFbobisa100% (2)
- Brkarc 3438Document127 pagesBrkarc 3438Max NguyenNo ratings yet
- 15.1.5 Lab - Implement GLBP - ILMDocument28 pages15.1.5 Lab - Implement GLBP - ILMAndrei Petru PârvNo ratings yet
- 3COM Product PresentationDocument142 pages3COM Product PresentationshreedeepkNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Fiber Optical Repeater Remote UnitDocument2 pagesData Sheet: Fiber Optical Repeater Remote UnitRami Abu AlhigaNo ratings yet
- Reliance CommunicationsDocument120 pagesReliance CommunicationsMadhav LavaniaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Cafe Application FormDocument4 pagesCyber Cafe Application Formkrul786100% (2)
- Computer Network LAB ManualDocument28 pagesComputer Network LAB ManualNikhil K Mishra0% (1)
- DWDM / DCI - Discovery: SP OpticalDocument21 pagesDWDM / DCI - Discovery: SP OpticalMakusNo ratings yet
- OptiX RTN 980L IP Longhaul Hardware DescriptionDocument50 pagesOptiX RTN 980L IP Longhaul Hardware DescriptionJcarlo Rodriguez67% (3)
- LTE IdentifierDocument6 pagesLTE IdentifierAnonymous zMWwN7aYNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Wireless Network Architecture Mg. Leonel HernandezDocument39 pagesCisco Unified Wireless Network Architecture Mg. Leonel HernandezJesúsPinillaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 - Lab 5.1.2.4 Teacher VersionDocument17 pagesCCNA 2 - Lab 5.1.2.4 Teacher Versionskarjosue50% (2)
- Dokumen - Tips Linx Remote Communications Interface Printeralinx Mp650388 Feb 2007Document251 pagesDokumen - Tips Linx Remote Communications Interface Printeralinx Mp650388 Feb 2007Jose LunaNo ratings yet
- HiPath 3000&5000 V9 Service Manual Issue7Document1,302 pagesHiPath 3000&5000 V9 Service Manual Issue7duyluanNo ratings yet
- KNX 100G - Setup Guide: E G H C D FDocument4 pagesKNX 100G - Setup Guide: E G H C D FSkrapNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Hardware Network Leve IIIDocument62 pagesCurriculum Hardware Network Leve IIIEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- Home Automation With ESP8266 WiFi Without Using BL 0Document16 pagesHome Automation With ESP8266 WiFi Without Using BL 0Engr Suleman MemonNo ratings yet
- Veeam Backup and RecoveryDocument42 pagesVeeam Backup and RecoveryJordan KnightNo ratings yet
- NAGIOS Inspeção Relatório de DadosDocument2 pagesNAGIOS Inspeção Relatório de DadosRuben QuintNo ratings yet
- DSTV Decoder - FREE Christian and Other ChannelsDocument1 pageDSTV Decoder - FREE Christian and Other Channelsbennieharmse0% (3)
- MulcomDocument10 pagesMulcomWalid AissaNo ratings yet
- 9500MPR - MEF8 Circuit Emulation ServicesDocument5 pages9500MPR - MEF8 Circuit Emulation ServicesedderjpNo ratings yet
- Complete Nokia SDHDocument56 pagesComplete Nokia SDHsknigam100% (2)
- Network Topologies and Technologies: Case Projects: MN405 Data and Information ManagementDocument5 pagesNetwork Topologies and Technologies: Case Projects: MN405 Data and Information ManagementSeema RaniNo ratings yet
- SPD Huawei eRAN3.0 CSFB Feature Introduction 20120529 A 1.0Document28 pagesSPD Huawei eRAN3.0 CSFB Feature Introduction 20120529 A 1.0Qusai JaberNo ratings yet
- List of Melaka CompaniesDocument3 pagesList of Melaka CompaniesNasrul SalmanNo ratings yet
- 48.4D901.021 05209-2 (DellLatitude120L)Document37 pages48.4D901.021 05209-2 (DellLatitude120L)Armando IbarraNo ratings yet
- LG-P705 Service ManualDocument221 pagesLG-P705 Service ManualSer AlBerNo ratings yet
- Fax ConfirmationDocument1 pageFax ConfirmationK'yandra GrahamNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument4 pagesComputer NetworksSavari RajNo ratings yet