Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 2.3: LIPIDS: Triglycerides Functions of Lipids
Uploaded by
Kuba DziatoszOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2.3: LIPIDS: Triglycerides Functions of Lipids
Uploaded by
Kuba DziatoszCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2.
3: LIPIDS
Functions of Lipids Triglycerides
Lipids are a class of non-polar organic molecules Triglycerides are lipids used for long-term energy storage
• Include triglyceride (adipose tissue), phospholipid (bilayer),
They are composed of a glycerol molecule covalently linked
cholesterol (animal cell membrane), steroids (hormones)
to three fatty acid chains (via condensation reactions)
Lipids may serve a variety of cellular functions, including: H O
FATTY ACIDS
• Storage of energy (triglycerides) H C O
GLYCEROL
O
• Hormonal roles (steroids)
H C O O
• Insulation (thermal)
• Protection of organs H C O
• Structural roles (cholesterol) ×3
H
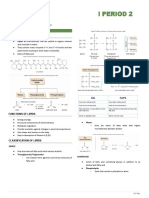
Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are long hydrocarbon chains found in certain lipids Unsaturated fatty acids occur in two distinct configurations
• Principally found in triglycerides and phospholipids
Cis Isomer Trans Isomer
Saturated Fatty Acids
• Possess no double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain
• Are generally solid at room temperatures (e.g. animal fat)
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
• Possess double bonds (mono = one ; poly = many) H atoms on the same side H atoms on different sides
• Are generally liquid at room temperature (e.g. plant oils) Double bond creates Double bond does not
kink in fatty acid chain create kink (linear chain)
O Are loosely packed and Are tightly packed and
Carboxylic
Hydrocarbon H3C (CH2 )n C usually liquid usually solid
group
OH
Occur commonly in nature Occurs in processed food
General Structure of a Saturated Fatty Acid Generally good for health Generally bad for health
Lipid Health Risks
Fats and cholesterol cannot dissolve in the blood and so are
Saturated and
packaged with proteins (as lipoproteins) for transport “BAD” trans fats raise
• Low density lipoproteins (LDLs) transport cholesterol cholesterol
from the liver to the rest of the body (bad for health) Cholesterol ✗
LDL
• High density lipoproteins (HDLs) scavenge excess
cholesterol and return it to the liver for disposal (good) deposits
Fatty acids can influence the levels of lipoproteins:
• Cis fats raise levels of HDL (➡ blood cholesterol) removes
Liver
• Saturated fats raise levels of LDL ( ︎︎ blood cholesterol) Artery
• Trans fats raise levels of LDL and lower levels of HDL
✓
Cholesterol HDL
High levels of blood cholesterol can cause atherosclerosis Cis fats lower
Breakdown
and lead to health issues like coronary heart disease (CHD) “GOOD” cholesterol
You might also like
- The Ideal Tlc Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Cut Down Cholesterol, Lose Weight And Improve Heart Health With Nutritious Tlc RecipesFrom EverandThe Ideal Tlc Diet Cookbook; The Superb Diet Guide To Cut Down Cholesterol, Lose Weight And Improve Heart Health With Nutritious Tlc RecipesNo ratings yet
- How to Have Naturally Healthy Cholesterol Levels: the best book on essentials on how to lower bad LDL & boost good HDL via foods/diet, medications, exercise & knowing cholesterol myths for clarityFrom EverandHow to Have Naturally Healthy Cholesterol Levels: the best book on essentials on how to lower bad LDL & boost good HDL via foods/diet, medications, exercise & knowing cholesterol myths for clarityNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.3: LIPIDS: Triglycerides Functions of LipidsDocument1 pageTopic 2.3: LIPIDS: Triglycerides Functions of LipidsKaleab GebreegizabiherNo ratings yet
- Lipids (Fats and Oils) : Laboratory Medicine Program Second YearDocument31 pagesLipids (Fats and Oils) : Laboratory Medicine Program Second Yeartalidah binselimNo ratings yet
- Part2 Lipids ConceptDocument69 pagesPart2 Lipids ConceptNora GamiNo ratings yet
- Fats and Minerals Reviewer 2Document8 pagesFats and Minerals Reviewer 2janmishelle208No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pathology - 028) Lipid Disorders (Notes)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Pathology - 028) Lipid Disorders (Notes)Geraldine Hernandez100% (1)
- Lipids and Lipoprotein PDFDocument13 pagesLipids and Lipoprotein PDFJezzah Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- 8 LipoproteinsDocument12 pages8 LipoproteinsSubhi Mishra100% (1)
- LipidsDocument41 pagesLipidsM Aimal KhanNo ratings yet
- Biochem LipidsDocument2 pagesBiochem Lipids813 cafeNo ratings yet
- 4 LipidsDocument8 pages4 LipidsKeizel Anne MananguNo ratings yet
- FATSDocument8 pagesFATSGeorgina Rose JalagatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument123 pagesChemistry of LipidsLyra Get100% (1)
- Are Unhe Althy, E.: "The Hidd Enk Iller"Document63 pagesAre Unhe Althy, E.: "The Hidd Enk Iller"Math YehualaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Biology of FoodDocument48 pagesChemistry and Biology of FoodjaedenNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Lipoprotiens and Urinary System PhysiologyDocument62 pagesPathology of The Lipoprotiens and Urinary System PhysiologyCarlo MaxiaNo ratings yet
- FT748 Lesson 7 - 8 - 9Document14 pagesFT748 Lesson 7 - 8 - 9ANDREA NICOLE TANNo ratings yet
- HyperlipidemiasDocument47 pagesHyperlipidemiasPushpa Paul 2021665649No ratings yet
- Lec 3 Fats in Health and DiseaseDocument21 pagesLec 3 Fats in Health and DiseaseSherif AliNo ratings yet
- HyperlipidemiasDocument62 pagesHyperlipidemiasIsrat Jahan Surovy 2225400672No ratings yet
- L4 LipidDocument57 pagesL4 LipidLe Thanh HaiNo ratings yet
- LIPIDIDocument14 pagesLIPIDIRileShampionNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Cholesterol Estimation 1Document58 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Cholesterol Estimation 1Dawlat SlamaNo ratings yet
- 2.5.2 LipidsDocument10 pages2.5.2 Lipidscamille chuaNo ratings yet
- L4 LipidDocument23 pagesL4 Lipidsampsonsoo17No ratings yet
- 1319 Lipids Vi1Document66 pages1319 Lipids Vi1Sravan DheekshaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Chemistry of LipidsDocument42 pagesBiochemistry - Chemistry of LipidsSyifaAnandaNo ratings yet
- Lipids Chemistry Revision NursingDocument40 pagesLipids Chemistry Revision NursingJohn Matthew100% (1)
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument92 pagesChemistry of LipidsSumit Tated100% (2)
- Screenshot 2022-09-14 at 9.35.22 AMDocument33 pagesScreenshot 2022-09-14 at 9.35.22 AMarihant gargNo ratings yet
- 3 Lipid MetabolismDocument54 pages3 Lipid MetabolismRahadatul Aisy100% (1)
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument57 pagesChemistry of Lipidszikri manggala putra100% (1)
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument88 pagesChemistry of LipidsDanielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- 3 LipidsDocument42 pages3 LipidsSyifaAnandaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Structure and Function Lecture Dorothy FinalDocument39 pagesLipid Structure and Function Lecture Dorothy FinalMarvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Presentation-Lipids and LipoproteinsDocument43 pagesInstructor's Presentation-Lipids and Lipoproteinsjomel rondinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidDocument49 pagesChemistry of LipidPayoja RajNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument6 pagesLipidsespiritumikhailehayah28No ratings yet
- 1.02 - Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionsDocument7 pages1.02 - Hemostasis, Surgical Bleeding and TransfusionsPhilip Patrick LeeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument70 pagesChemistry of LipidsArpit JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Lipids Fats and Oils PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 4 - Lipids Fats and Oils PDFChandan SinghNo ratings yet
- 3) LipidsDocument32 pages3) LipidsRRONNo ratings yet
- Lipids Part 1Document30 pagesLipids Part 1qwerty masterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument88 pagesChemistry of LipidsNovia EkaNo ratings yet
- Biochem - LipidsDocument21 pagesBiochem - Lipids813 cafeNo ratings yet
- CholesterolDocument9 pagesCholesterolNajmedin AziziNo ratings yet
- Biochem 1Document40 pagesBiochem 1LinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Lipid Disorders & CholesterolDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Lipid Disorders & CholesterolBratatiNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolisam2Document9 pagesLipid Metabolisam2dhruviksuthar1407No ratings yet
- Corps GrasDocument12 pagesCorps GrasNozha HammamiNo ratings yet
- Reducing Your Blood CholesterolDocument43 pagesReducing Your Blood CholesterolDuncan T100% (1)
- LipoproteinDocument42 pagesLipoproteinRone Jacob JacobNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I (SGS 236)Document25 pagesBiochemistry I (SGS 236)Mustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument26 pagesLipidseugieniogienioNo ratings yet
- 11 05 Lipids PDFDocument5 pages11 05 Lipids PDFSweta SumanNo ratings yet
- Halal Food Analysis: InstructorsDocument39 pagesHalal Food Analysis: Instructors20b0509No ratings yet
- Lipids: Ghina Assaf Chedid, MSCDocument45 pagesLipids: Ghina Assaf Chedid, MSCYouness Abou SalehNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument23 pagesChemistry of Lipidsbrian mgabiNo ratings yet
- Lipids (Mcmurry Ch. 27)Document15 pagesLipids (Mcmurry Ch. 27)Meisy RadhistaNo ratings yet
- Hypolipidemic Drugs PharmdDocument38 pagesHypolipidemic Drugs Pharmddarlington D. y ayimNo ratings yet
- Practical Cardiology An Approach To The Management of Problems in Cardiology (PDFDrive)Document405 pagesPractical Cardiology An Approach To The Management of Problems in Cardiology (PDFDrive)hendratj90No ratings yet
- 7 - Nutrition 1Document24 pages7 - Nutrition 1tamani elkhairNo ratings yet
- The Potential of Hull-Less Barley: ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Potential of Hull-Less Barley: ReviewobadiNo ratings yet
- The Preanalytical PhaseDocument24 pagesThe Preanalytical PhaseArturo Eduardo Huarcaya OntiverosNo ratings yet
- Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Trials of Morus AlbaDocument14 pagesPhytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Trials of Morus AlbaArief WibisonoNo ratings yet
- Hyprlipdemia 2020 4th EditionDocument24 pagesHyprlipdemia 2020 4th EditionLillian KrazemNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Composition of Plant Milk (Soybean)Document29 pagesNutritional Composition of Plant Milk (Soybean)Ekoh Endurance60% (5)
- 7 FatBurning Foods For All Day Energy 1116Document40 pages7 FatBurning Foods For All Day Energy 1116Angelo MarottaNo ratings yet
- Exams MedsurgDocument29 pagesExams MedsurgUy Jezrielle MicahNo ratings yet
- Lipid Profile L - DeterminatinDocument33 pagesLipid Profile L - DeterminatinaliNo ratings yet
- Akshay Kumar Healthians ReportDocument30 pagesAkshay Kumar Healthians ReportakshakumNo ratings yet
- Fenugreek Health Benefits and Medicinal UsesDocument15 pagesFenugreek Health Benefits and Medicinal UsesSanjay PatilNo ratings yet
- உடல் கூறுDocument86 pagesஉடல் கூறுshopping vNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Lipid Metabolism LectureDocument55 pagesDisorders of Lipid Metabolism LectureRichard SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document8 pagesPaper 1Julio BenitesNo ratings yet
- Pathology MCQDocument42 pagesPathology MCQJim Jose Antony100% (17)
- Lab Report: National Aluminium Company LimitedDocument3 pagesLab Report: National Aluminium Company LimitedSanjay GuptaNo ratings yet
- InTech-Soybean Nutrition and HealthDocument22 pagesInTech-Soybean Nutrition and HealthkidanemariamNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of CVSDocument311 pagesBiochemistry of CVSAsne ManNo ratings yet
- HDL Cholesterol (Direct) BXC0421 A25 A15Document2 pagesHDL Cholesterol (Direct) BXC0421 A25 A15jef1234321No ratings yet
- Quiz Lipids and LipoproteinsDocument9 pagesQuiz Lipids and LipoproteinsAllyah Ross DuqueNo ratings yet
- Smart 2015 by Dave PalumboDocument116 pagesSmart 2015 by Dave PalumboВиктор Цонев-Каброне100% (17)
- Williams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 14th Edition Nix Test BankDocument10 pagesWilliams Basic Nutrition and Diet Therapy 14th Edition Nix Test Bankjonathanmelendezscpjzgfikb100% (12)
- Biochem Lec Reviewer CompleteDocument32 pagesBiochem Lec Reviewer CompleteLexa CyNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument18 pagesCoronary Heart DiseasesamjaisheelNo ratings yet
- Factores para FNRDocument10 pagesFactores para FNRPOMYNo ratings yet
- HDL RandoxDocument4 pagesHDL RandoxJesus Guillermo Caceres FernandezNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Essay BiochemistryDocument3 pagesComprehensive Essay BiochemistryFloreleneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 47 - Lipid-Lowering AgentsDocument13 pagesChapter 47 - Lipid-Lowering AgentsJonathonNo ratings yet