Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ImmunogyWorksheet MS
Uploaded by
Angeleena ANTOOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ImmunogyWorksheet MS
Uploaded by
Angeleena ANTOCopyright:
Available Formats
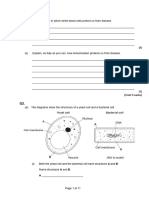
A test has been developed to determine if a person is infected with variant CJD (vCJD), the
1. human form of BSE (mad cow disease). The test detects the protein which causes vCJD in a
urine sample.
The test kit contains the following components.
(a) Complete the flow chart to describe how this test would be used.
Urine sample is added to well in test plate
↓
Plate is washed to remove unbound vCJD protein
(3)
(b) Explain why this test would detect vCJD, but not other antigens in the urine.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 5 marks)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 1 of 14
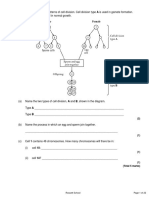
An antigen called PSA is present in the blood of men in the early stages of prostate cancer.
2.
There is a blood test for PSA. The test uses monoclonal antibodies to PSA. The stages in the
test are shown in the diagram.
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 2 of 14
(a) (i) What is an antigen?
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(ii) What is a monoclonal antibody?
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(b) (i) Explain why this test detects prostate cancer, but not any other disease.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(ii) Explain why there will not be a colour change if the blood sample does not contain
PSA.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 8 marks)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 3 of 14
Scientists have developed a new technique that can identify whether people smoke tobacco.
3. Tobacco contains nicotine, which is broken down to cotinine. Cotinine is found in fingerprints. The
new technique uses antibodies against cotinine.
(a) These scientists injected laboratory mice with cotinine. Describe how this injection
stimulates mice to produce antibodies against cotinine.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(Extra space) ________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
(b) The antibodies bind only to cotinine, and not to any other substance in the fingerprint.
Explain why.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 6 marks)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 4 of 14
(a) The graph shows the number of deaths from influenza per year in a developed country.
4.
(i) Suggest an explanation for the change in the number of deaths from influenza during
the first 10 years.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(1)
(ii) Suggest an explanation for the large increase in the number of deaths from influenza
in year 11.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 5 of 14
(b) The diagram shows some of the structures on the outside of an influenza virus.
Haemagglutinin and neuraminidase are protein molecules. Haemagglutinin binds to
receptor molecules on the surface of epithelial cells in the breathing system.
Neuraminidase is an enzyme which breaks down molecules in the surface membrane of
epithelial cells and allows the viruses to be released from the cells.
(i) Describe how T lymphocytes recognise and respond to the influenza virus.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(ii) Describe how B lymphocytes respond to the influenza virus.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 6 of 14
(c) New drugs have recently become available for treating influenza. One type is a
neuraminidase inhibitor. Explain how this type of drug would act as a treatment for
influenza.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 9 marks)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 7 of 14
The figure below shows a test that has been developed to find out if a person has antibodies to
5. the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antigen.
HIV antigens are attached to
Step 1
a test well in a dish.
A sample of blood plasma is
added to the well.
Step 2 If HIV antibodies are
present, they bind to the HIV
antigen.
The well is washed.
A second antibody with an
enzyme attached is then
Step 3
added.
This binds specifically to the
HIV antibody.
The well is washed again.
A yellow solution is added,
which changes to blue if the
Step 4
enzyme is present. A blue
colour shows that the
person has HIV antibodies.
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 8 of 14
(a) This test only detects the presence of HIV antibodies. Give two reasons why it cannot be
used to find out if a person has AIDS.
1. _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
2. _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(b) The solution will remain yellow if a person is not infected with HIV. Explain why.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(c) A mother who was infected with HIV gave birth to a baby. The baby tested positive using
this test. This does not prove the baby is infected with HIV.
Explain why.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(d) A control well is set up every time this test is used. This is treated in exactly the same way
as the test wells, except that blood plasma is replaced by a salt solution.
Use information from the figure above to suggest two purposes of the control well.
1. _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
2. _________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 8 marks)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 9 of 14
Vaccines protect people against disease. Explain how.
6.
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
(Total 5 marks)
(a) What is an antigen?
7.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(b) Describe how B-lymphocytes respond when they are stimulated by antigens.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 10 of 14
(c) The diagram shows some components of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
(i) Suggest which labelled component of the virus is most likely to act as an antigen.
Give a reason for your answer.
Component ____________________________________________________
Reason _______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(1)
(ii) A cell that HIV infects is 15 µm in diameter. Calculate how many times larger in
diameter this cell is than an HIV particle. Show your working.
Answer ____________________ times larger
(2)
(Total 9 marks)
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 11 of 14
Mark schemes
(a) add antibodies / enzyme;
1. wash to remove unbound antibodies;
add (colourless) solution;
(mark correct responses sequentially)
3
(b) antibodies specific / shape only fits one antigen;
other antigens different shape and would not bind to antibodies;
2
[5]
(a) (i) protein / glycoprotein / glycolipid / polysaccharide / molecule;
2. on surface / membrane (of cell);
causes immune response / description / triggers antibody
production;
max 2
(ii) reference to hybrid cell from tumour / cancer and
B-lymphocyte / hybridoma;
antibodies all the same / from one type of plasma cell;
specific to / complementary to / fits only one antigen;
max 2
(b) (i) antibodies specific / only binds to PSA;
PSA only associated with prostate cancer / not with other
diseases;
2
(ii) antibody with enzyme only attaches if PSA present / washed
away if no PSA;
no colour change without enzyme;
2
[8]
(a) Cotinine is an antigen;
3. Antigen/cotinine binds to (specific) T-cell/activates T-cell;
T-cell activates B-cells;
Specific B cell becomes activated;
(Specific) B cell divides/ clonal expansion;
Forms (clone of) plasma cells;
(Plasma) cell produces antibodies;
Accept macrophage presents antigen for one mark
Ignore references to memory cells and secondary
immune response
4 max
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 12 of 14
(b) Antibodies are proteins with tertiary structure/specific shape/binding sites;
Antibodies specific shape for cotinine;
Only cotinine fits;
Do not credit active site
2
[6]
(a) (i) fall in deaths due to rise in number of people with immunity / better care / targeting
4. vaccination at vulnerable;
1
(ii) mutation of virus / new strain;
mutant form not recognised by memory cells (allow antibodies);
2 max
(b) (i) T lymphocyte receptors recognise shape of haemagglutinin /
neuraminidase / viral antigen;
clone (once only);
destroy virus;
2 max
(ii) clone (once only);
produce antibodies;
effect of antibody e.g. stimulation of phagocytosis /
precipitation of toxins;
2
(c) alter shape of active site of neuraminidase / block active site;
virus unable to leave host cells;
2
[9]
(a) (To diagnose AIDS, need to look for / at)
5. 1. (AIDS-related) symptoms;
2. Number of helper T cells.
Neutral: ‘only detects HIV antibodies’ as given in the question stem
2
(b) 1. HIV antibody is not present;
Accept HIV antibodies will not bind (to antigen)
2. (So) second antibody / enzyme will not bind / is not present.
2
(c) 1. Children receive (HIV) antibodies from their mothers / maternal antibodies;
2. (So) solution will always turn blue / will always test positive (before 18 months).
Allow 1 mark for the suggestion that the child does not produce
antibodies yet so test may be negative
2
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 13 of 14
(d) (Shows that)
1. Only the enzyme / nothing else is causing a colour change;
2. Washing is effective / all unbound antibody is washed away.
2
[8]
1. Vaccines contain antigens / dead / weakened pathogens / antigens dead / weakened
6. pathogens are injected;
Ignore references to T or B cells.
2. Memory cells made;
3. On second exposure memory cells produce antibodies / become active / recognise
pathogens;
3. Idea of memory cells responding.
4. Rapidly produce antibodies / produces more antibodies;
4. Production of antibodies must be qualified for mark. Underlined
ideas essential.
5. Antibodies destroy pathogens;
5. Accept bacteria / viruses etc but not disease
[5]
(a) molecule / part of molecule / protein / glycoprotein / named molecule;
7. that stimulates an immune response / eq;
2
(b) divide by mitosis / form clones; produce plasma cells; (plasma cells)
make antibodies;
(plasma cells) produce memory cells;
4
(c) (i) glycoprotein AND
different shape to body proteins / RNA and reverse transcriptase
inside virus / phospholipids same as body’s / on the surface
of the virus;
1
(ii) 187.5;;
Accept 187 – 188
1 mark for HIV = 80nm;
2 max
[9]
Sacred Heart of Mary Girls' School Page 14 of 14
You might also like
- A Level Homework 5Document4 pagesA Level Homework 5szyzypNo ratings yet
- 3.8.2 Gene Expression - 26 MarksDocument8 pages3.8.2 Gene Expression - 26 MarksalaynasharleezNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science Set 2 Part 2 160559226Document30 pagesYear 10 Science Set 2 Part 2 160559226osasnelly2006No ratings yet
- A03 Data AnalysisDocument19 pagesA03 Data Analysisleocarlton0700No ratings yet
- InfectionandResponseHT (Copy)Document13 pagesInfectionandResponseHT (Copy)jane byersNo ratings yet
- RAMP EQsDocument11 pagesRAMP EQsalma.khaleefaNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Document17 pagesSet 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Extended Response QuestionsDocument29 pagesExtended Response QuestionsNoor MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Exam QuestionsDocument7 pagesTopic 4 Exam Questionsgul pinarNo ratings yet
- ' GenetechnologiesPart2Document49 pages' GenetechnologiesPart2dfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Cells Revision ExqsDocument15 pagesCells Revision ExqsbitbtihbyobutNo ratings yet
- Practical Skills QuestionsDocument62 pagesPractical Skills QuestionshftuuNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2Document88 pagesGenetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2kafiazabit200No ratings yet
- 2.4 The Immune System QPDocument25 pages2.4 The Immune System QPZarmina KhanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Assessment BookletDocument45 pagesTopic 2 Assessment BookletLinNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Epigenetics and RNA interference QPDocument10 pages8.2 Epigenetics and RNA interference QPthere4per410No ratings yet
- Application Questions Nx8jamDocument22 pagesApplication Questions Nx8jamdovidNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis & MeiosisamaraadomaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisHT (Copy)Document14 pagesHomeostasisHT (Copy)jane byersNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diversity and AdaptationDocument96 pagesGenetic Diversity and Adaptation/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- GeneMutationDocument35 pagesGeneMutationdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- GenetechnologiesDocument108 pagesGenetechnologiesdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Campylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaDocument5 pagesCampylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaBob yuNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentDocument15 pagesA Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- Inheritance 7 9 6Document22 pagesInheritance 7 9 6Philip VuuNo ratings yet
- Methods control microorganism growth immunity diseasesDocument2 pagesMethods control microorganism growth immunity diseasesnehru09No ratings yet
- Figure 1 Shows Part of One Strand of A DNA MoleculeDocument12 pagesFigure 1 Shows Part of One Strand of A DNA MoleculeAmal GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 4.1c Cell Biology HigherDocument64 pages4.1c Cell Biology HigherJayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Assessment BookletDocument32 pagesTopic 8 Assessment BookletjingNo ratings yet
- Comb Sci Evaluate QP MS ERDocument12 pagesComb Sci Evaluate QP MS ERlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Organisation QP 2Document31 pagesOrganisation QP 2lizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Triple HomeostasisDocument13 pagesTriple HomeostasisAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 4Document38 pagesBio Unit 4Mei NgNo ratings yet
- Inheritance QPDocument47 pagesInheritance QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- More Enzyme QuestionsDocument7 pagesMore Enzyme QuestionsAlNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- 8.4 DNA probe and Gel Electrophoresis QPDocument8 pages8.4 DNA probe and Gel Electrophoresis QPmauminamansoorNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Extra Q and MSDocument14 pagesCell Cycle Extra Q and MSKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804Document36 pagesWeek 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- B3 Infection and Response Exam BookletDocument30 pagesB3 Infection and Response Exam Bookletakio haruNo ratings yet
- Sep Only QPDocument41 pagesSep Only QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Application of Knowledge QuestionsDocument16 pagesApplication of Knowledge QuestionsElllie TattersNo ratings yet
- Extra Qs and MS Cell TransportDocument14 pagesExtra Qs and MS Cell TransportKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Membranes L4 MSDocument19 pagesMembranes L4 MSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- Biology Paper 2 Workbook - Combined HigherDocument85 pagesBiology Paper 2 Workbook - Combined Highermp2959812No ratings yet
- Exam Questions: Problem Part That Did Not Work ProperlyDocument2 pagesExam Questions: Problem Part That Did Not Work ProperlyMaria Khin YadanarNo ratings yet
- Organisation HTDocument17 pagesOrganisation HTjane byersNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Gene mutations QPDocument7 pages8.1 Gene mutations QPmauminamansoorNo ratings yet
- PopulationsinecosystemsDocument110 pagesPopulationsinecosystems/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 3.8.4.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Revision Questions - 25marksDocument8 pages3.8.4.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Revision Questions - 25marksalaynasharleezNo ratings yet
- 5.1.1 and 5.1.2Document10 pages5.1.1 and 5.1.2Aamina HussainNo ratings yet
- Joy Benemor - B1 exam questionsDocument42 pagesJoy Benemor - B1 exam questionsv2jj5qfhjpNo ratings yet
- NucleiacidsDocument89 pagesNucleiacidsdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Homework - 231012 - 184741Document15 pagesWeek 5 Homework - 231012 - 184741dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- Comparing Photosynthesis and Aerobic Respiration in Plants and AnimalsDocument8 pagesComparing Photosynthesis and Aerobic Respiration in Plants and AnimalsJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Section A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletDocument8 pagesSection A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Homeostasis QPDocument4 pages6.4 Homeostasis QPChioma UchegbuNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument13 pagesCell StructureNaimah HadiqahNo ratings yet
- OrganisationDocument28 pagesOrganisationapi-422428700No ratings yet
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyNo ratings yet
- Session 10Document2 pagesSession 10Sistine Rose Labajo100% (1)
- Advanced Laser Dental EducationDocument5 pagesAdvanced Laser Dental EducationJulia KamenovaNo ratings yet
- EYE Emergency Manual An Illustrated Guide: Second EditionDocument51 pagesEYE Emergency Manual An Illustrated Guide: Second EditionMin MawNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma ExplainedDocument28 pagesCholesteatoma ExplainedazadutNo ratings yet
- The Wellness Center in Public HospitalsDocument4 pagesThe Wellness Center in Public HospitalsMelinda IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Emergency Assistance Plan by TW 12oct21Document7 pagesEmergency Assistance Plan by TW 12oct21Than WinNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions: Musculoskeletal SystemDocument4 pagesPractice Questions: Musculoskeletal SystemSali IqraNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ChartsDocument61 pagesAntibiotic Chartspempekplg100% (1)
- Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Natural History of Thoracic Aortic AneurysmDocument5 pagesEpidemiology, Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Natural History of Thoracic Aortic AneurysmNathaliazuosNo ratings yet
- GENES ROLE IN CVD (Genomics)Document4 pagesGENES ROLE IN CVD (Genomics)bashirkinza679No ratings yet
- Kaufmann Protocol guidelines for anti-aging regimensDocument3 pagesKaufmann Protocol guidelines for anti-aging regimenszlautarevic-1No ratings yet
- (Book 4) Collins Parker, Mia - PCOS Nutrition - A Complete PCOS Diet Book With 4 Week Meal Plan and 4 Week Fitness Exercise Plan To Reduce Weight and Prevent Diabetes. PCOS Causes, Symptoms and HolDocument134 pages(Book 4) Collins Parker, Mia - PCOS Nutrition - A Complete PCOS Diet Book With 4 Week Meal Plan and 4 Week Fitness Exercise Plan To Reduce Weight and Prevent Diabetes. PCOS Causes, Symptoms and HolAndreea Daniela100% (4)
- Teenage and >35yrs preg have adverse outcomesDocument40 pagesTeenage and >35yrs preg have adverse outcomesJeyakumar MeyyappanNo ratings yet
- Rosa 2014Document6 pagesRosa 2014Michal PerkowskiNo ratings yet
- Peds Smle QsDocument56 pagesPeds Smle QsMarwa Tariq Ahmed Abdulla Ahmed Al MurbatiNo ratings yet
- x9585374 Rev1117b Pro Mag Ultra Automatic Biopsy InstrumentDocument9 pagesx9585374 Rev1117b Pro Mag Ultra Automatic Biopsy InstrumentJonathan David Castillo SanchezNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Multiple Choice Questions MCQ S 4426Document19 pagesGuidelines For Multiple Choice Questions MCQ S 4426R RatheeshNo ratings yet
- Placental AbnormalitiesDocument3 pagesPlacental AbnormalitiesThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- Kunyit Asam Efektif Mengurangi Nyeri DismenoreaDocument6 pagesKunyit Asam Efektif Mengurangi Nyeri DismenoreaSukmawatiNo ratings yet
- Summary of ECG AbnormalitiesDocument7 pagesSummary of ECG AbnormalitiesKarin AdraiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDrug Study Dexamethasoneamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Resume NdetahDocument1 pageResume Ndetahapi-484395670No ratings yet
- GE Logiq 400 500 Probe GuideDocument2 pagesGE Logiq 400 500 Probe GuideNesakkumaren SivakumaranNo ratings yet
- 10 Mcqs Canada For SampleDocument5 pages10 Mcqs Canada For SampleNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Sample Ultrasound ReportDocument3 pagesSample Ultrasound ReportPapadoveNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Practices and Physiological EffectsDocument9 pagesElectrical Safety Practices and Physiological EffectsSmr OnlyNo ratings yet
- Polyomavirus LectureDocument60 pagesPolyomavirus Lecturerggefrm75% (4)
- DSM 5 Diagnostic CategoriesDocument15 pagesDSM 5 Diagnostic Categoriesmomo connor100% (2)
- Trileptal Fda LabelDocument27 pagesTrileptal Fda Labelsameh aliNo ratings yet
- Doctors - Dermatologists Area Phone: Tuesday, 13 November 2007 13:51Document18 pagesDoctors - Dermatologists Area Phone: Tuesday, 13 November 2007 13:51pinakindpatelNo ratings yet