Professional Documents
Culture Documents
More Enzyme Questions
Uploaded by
AlOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
More Enzyme Questions
Uploaded by
AlCopyright:
Available Formats
(a) What is an enzyme?
1
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
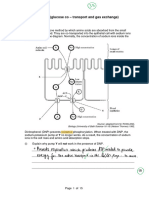
The diagram shows stages during an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
Mark Rutherford School Page 1 of 7
(b) Using the letters in the diagram, describe what is happening in this reaction.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(Extra space) ________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
(Total 5 marks)
Gelatine is a protein. When a warm gelatine solution cools, it sets to form a jelly.
2 Fresh pineapple juice contains an enzyme that digests protein.
A student investigated the effect of pineapple juice on the setting of jelly.
He set up three different tubes of warm gelatine solution and recorded which had set after three
hours. The contents of each tube and his results are shown in the table.
Tube Contents of tube Jelly formed
A 6 cm3 gelatine + 2 cm3 pineapple juice + 2 cm3 water No
B 6 cm3 gelatine + 2 cm3 pineapple juice + 2 cm3 hydrochloric acid Yes
C 6 cm3 gelatine + 2 cm3 boiled pineapple juice + 2 cm3 water Yes
(a) Explain why 2 cm3 of water was added to tubes A and C.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
Mark Rutherford School Page 2 of 7
(b) Explain the results of
tube A _____________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
tube B _____________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(4)
(c) What was the purpose of tube C?
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(Extra space) ________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
(Total 9 marks)
(a) Explain how the shape of an enzyme molecule is related to its function.
3
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
Mark Rutherford School Page 3 of 7
(b) Bacteria produce enzymes which cause food to decay. Explain how vinegar, which is
acidic, can prevent the action of bacterial enzymes in some preserved foods.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
(Total 6 marks)
In an investigation into carbohydrase activity, the contents from part of the gut of a small animal
4 were collected. The contents were added to starch solution at pH 7 and kept in a water bath at
25°C. At one-minute intervals, samples were removed and added to different test tubes
containing dilute iodine solution. The colour intensity of each sample was determined. The graph
shows the results.
(a) Explain the change in colour intensity.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
Mark Rutherford School Page 4 of 7
(b) Draw clearly labelled curves on the graph to show the expected result if the experiment
was repeated
(i) at 35 °C;
(ii) at pH 2.
(2)
(c) Explain how
(i) raising the temperature to 35 °C affects carbohydrase activity;
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(ii) decreasing the pH affects carbohydrase activity.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(7)
(Total 11 marks)
Mark Rutherford School Page 5 of 7
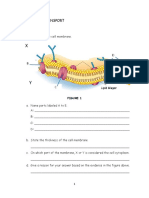
The diagram represents an enzyme molecule and three other molecules that could combine with
5 it.
(a) Which molecule is the substrate for the enzyme? Give a reason for your answer.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(b) Use the diagram to explain how a non-competitive inhibitor would decrease the rate of the
reaction catalysed by this enzyme.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(3)
(c) Lysozyme is an enzyme. A molecule of lysozyme is made up of 129 amino acid molecules
joined together. In the formation of its active site, the two amino acids that are at positions
35 and 52 in the amino acid sequence need to be close together.
(i) Name the bonds that join amino acids in the primary structure.
______________________________________________________________
(1)
Mark Rutherford School Page 6 of 7
(ii) Suggest how the amino acids at positions 35 and 52 are held close together to form
the active site.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
Mark Rutherford School Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- Respiration I QuestionsDocument79 pagesRespiration I QuestionsAayma MunirNo ratings yet
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument28 pagesScience: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsSanJoseHS100% (2)
- Week 5 Homework - 231012 - 184741Document15 pagesWeek 5 Homework - 231012 - 184741dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentDocument15 pagesA Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- Triple HomeostasisDocument13 pagesTriple HomeostasisAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument99 pagesRespirationdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Lipids ALevelDocument55 pagesLipids ALeveldfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- 5.1.1 and 5.1.2Document10 pages5.1.1 and 5.1.2Aamina HussainNo ratings yet
- A Level Paper 1 Exams 2022 77izmgDocument69 pagesA Level Paper 1 Exams 2022 77izmgMal ChenNo ratings yet
- Membranes L4 MSDocument19 pagesMembranes L4 MSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument69 pagesDigestion and Absorption/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Science Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesScience Exam QuestionscheetoNo ratings yet
- 4.1c Cell Biology HigherDocument64 pages4.1c Cell Biology HigherJayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisPart2Document31 pagesPhotosynthesisPart2dfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Biology Mock Paper 02 - CorrectedDocument13 pagesBiology Mock Paper 02 - CorrectedNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Biology Sixth Form TestDocument3 pagesBiology Sixth Form TestGeorge AshcroftNo ratings yet
- Mon Omers and Polymers a LevelDocument57 pagesMon Omers and Polymers a Leveldfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument16 pagesWaterdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Organisation QP 2Document31 pagesOrganisation QP 2lizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Biomols Extra Qs and MS Incl Some EnzymesDocument19 pagesBiomols Extra Qs and MS Incl Some EnzymesKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- B 4 Revision PackDocument64 pagesB 4 Revision PackKrish SharmaNo ratings yet
- A-Level Biology Protein Exam QuestionsDocument27 pagesA-Level Biology Protein Exam Questionsfreyamartin90676No ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument14 pagesRESPIRATIONoghieghie jattoNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Assessment Booklet: Marks 1'9 Time Allowed 165 MinutesDocument39 pagesTopic 5 Assessment Booklet: Marks 1'9 Time Allowed 165 MinutesHayley Camenzuli100% (1)
- 6.4 Homeostasis QPDocument4 pages6.4 Homeostasis QPChioma UchegbuNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 4Document38 pagesBio Unit 4Mei NgNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology WORKSHEETDocument7 pagesCSEC Biology WORKSHEETAnderson Michelle100% (1)
- Lipids PpqsDocument29 pagesLipids PpqsTerreshaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of CellsDocument29 pagesStructure and Functions of CellsKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Proteins and EnzymesDocument94 pagesProteins and Enzymesdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- F5S Chemistry Revision Worksheet (6) - Double DecompositionDocument8 pagesF5S Chemistry Revision Worksheet (6) - Double DecompositionRaymond ChanNo ratings yet
- Practical Skills QuestionsDocument62 pagesPractical Skills QuestionshftuuNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Photosynthesis QPDocument35 pages4.1 Photosynthesis QPZaynab Ameenah KhanNo ratings yet
- Energy and Ecosystems Part 2Document16 pagesEnergy and Ecosystems Part 2dfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Carbohydrates EQDocument24 pages3.1.2 Carbohydrates EQteeb1826No ratings yet
- CollisiontheoryPhysicalchemistryDocument36 pagesCollisiontheoryPhysicalchemistry/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Set 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Document17 pagesSet 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Digestion and Absorption QPDocument12 pages3.3 Digestion and Absorption QPHoyam ANo ratings yet
- Set 2 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9Document20 pagesSet 2 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9tnishtalaNo ratings yet
- A02 Practical TechniquesDocument15 pagesA02 Practical Techniquesleocarlton0700No ratings yet
- Organisation Foundation HigherDocument135 pagesOrganisation Foundation HigherSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- 1.5 KineticsDocument6 pages1.5 KineticsDonald McDonaldNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument103 pagesPhotosynthesisdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- PopulationsinecosystemsPart3Document20 pagesPopulationsinecosystemsPart3/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 2.3 Transport Across Cell Membrane QPDocument17 pages2.3 Transport Across Cell Membrane QPZarmina KhanNo ratings yet
- DNAandProteinSynthesisDocument98 pagesDNAandProteinSynthesisdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Document17 pagesSet 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Campylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaDocument5 pagesCampylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaBob yuNo ratings yet
- INSTRUCTIONDocument8 pagesINSTRUCTIONkelvinkaykatoyaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Enzymes ExtendedDocument6 pages4 - Enzymes ExtendedYashodhaNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Questions GcseDocument50 pagesBioenergetics Questions GcseDharm GajjarNo ratings yet
- A03 Data AnalysisDocument19 pagesA03 Data Analysisleocarlton0700No ratings yet
- Nutrient CyclesDocument95 pagesNutrient Cyclesdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Surface Are a to Volume Ratio Part 2Document10 pagesSurface Are a to Volume Ratio Part 2kafiazabit200No ratings yet
- Examination Pack For Paper 2 (H)Document27 pagesExamination Pack For Paper 2 (H)Beth HampsonNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 - Cell TransportDocument7 pagesTOPIC 3 - Cell TransportSiti Nurqistina Balqis Syahrul EffendyNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- PopulationsinecosystemsPart2Document94 pagesPopulationsinecosystemsPart2/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Genetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2Document88 pagesGenetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2kafiazabit200No ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- The Stress-Free Guide to Parenting a Child With ADHD: Effective and Proven Strategies for Alleviating Anxiety and Forming Strong Bonds Without the HassleFrom EverandThe Stress-Free Guide to Parenting a Child With ADHD: Effective and Proven Strategies for Alleviating Anxiety and Forming Strong Bonds Without the HassleNo ratings yet
- Geometric Proof: Level 2 Further MathsDocument19 pagesGeometric Proof: Level 2 Further MathsAlNo ratings yet
- Character Table Jekyll and HydeDocument4 pagesCharacter Table Jekyll and HydeAlNo ratings yet
- Language Paper 1 Sample Questions Qu1Document6 pagesLanguage Paper 1 Sample Questions Qu1AlNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Bio - As - 8 - 2 - Nir - Dna - HistoryDocument5 pagesLesson 3 Bio - As - 8 - 2 - Nir - Dna - HistoryAlNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets AS 1018 (Bond Polarity)Document2 pagesChemsheets AS 1018 (Bond Polarity)AlNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument26 pagesLipidsZanie CruzNo ratings yet
- Expand HIgh FidelityDocument4 pagesExpand HIgh FidelityLeonardo BeccariNo ratings yet
- Abetalipoproteinemia FinalDocument57 pagesAbetalipoproteinemia FinalKristian Cada100% (1)
- Franklin, Watson, Crick and WilkinsDocument3 pagesFranklin, Watson, Crick and WilkinsRussell MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Free Radicals and Antioxidants: A Concise GuideDocument40 pagesFree Radicals and Antioxidants: A Concise GuideAl Shella Ramayani AYNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 2nd Edition Wessner Test BankDocument18 pagesMicrobiology 2nd Edition Wessner Test Bankeugenephedrayy2bfk100% (26)
- Q1. The Diagrams Show Four Types of Linkage, A To D, Which Occur in Biological MoleculesDocument19 pagesQ1. The Diagrams Show Four Types of Linkage, A To D, Which Occur in Biological MoleculesiNo ratings yet
- LipoproteinsDocument30 pagesLipoproteinsApurba PradhanNo ratings yet
- DLP Gen - BiologyDocument4 pagesDLP Gen - BiologyGina Ano IsidroNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument2 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAmonishaNo ratings yet
- PRICE LIST 2022Document2 pagesPRICE LIST 2022hermanto soesilo100% (1)
- Lesson 6 InhibitorsDocument12 pagesLesson 6 Inhibitorstbrook2017No ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Biomolecules, Polymers, Chemistry in Everyday Life & Env. ChemistryDocument16 pagesBiomolecules: Biomolecules, Polymers, Chemistry in Everyday Life & Env. ChemistryIshanNo ratings yet
- Gene - Site-Directed MutagenesisDocument2 pagesGene - Site-Directed Mutagenesisapi-252004782No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Aka Saccharides NumberDocument2 pagesCarbohydrates Aka Saccharides NumberAngelica Llamas0% (1)
- Proximate Composition and Mineral Content of Two Edible Species of (Tree Spinach)Document10 pagesProximate Composition and Mineral Content of Two Edible Species of (Tree Spinach)Eswari PerisamyNo ratings yet
- Genetics - For NEET, Medical & B - Sanjay KhareDocument139 pagesGenetics - For NEET, Medical & B - Sanjay Khareteamindian gamersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 B Inhibition of Enzyme Activity 3rd Year Chemistry Dep'tDocument21 pagesChapter 4 B Inhibition of Enzyme Activity 3rd Year Chemistry Dep'telsaNo ratings yet
- DAMODARAN Food Proteins and Their ApplicationsDocument143 pagesDAMODARAN Food Proteins and Their ApplicationsItzel AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Palm Oil On Cardiovascular RiskDocument10 pagesEffects of Palm Oil On Cardiovascular RiskbudakgemukNo ratings yet
- Bot 20 Ex 6Document30 pagesBot 20 Ex 6Kath Valad-onNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 12 Term 1 Week 1 - 2021Document4 pagesLife Sciences Grade 12 Term 1 Week 1 - 2021Lucky Jr MonobeNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021Document11 pagesLab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021thesoccerprince.10No ratings yet
- Referência 9Document112 pagesReferência 9BobbyGunarsoNo ratings yet
- Forming Peptide Bonds & Enzyme CatalysisDocument26 pagesForming Peptide Bonds & Enzyme CatalysisBihandu PigeraNo ratings yet
- TMOL Ch01 Qas EvensDocument3 pagesTMOL Ch01 Qas Evensray800201No ratings yet
- 2 Cell Organelles and Other Specialized Cell StructuresDocument36 pages2 Cell Organelles and Other Specialized Cell StructuresNoob MeNo ratings yet
- Lipids BiochemistryDocument7 pagesLipids BiochemistryPojangNo ratings yet
- UK Bone FortifyDocument1 pageUK Bone FortifyDagoberto Rincon TorresNo ratings yet