Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 2: Evolution of Management: The Last Three Management Approaches
Uploaded by
Ngoc NguyenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2: Evolution of Management: The Last Three Management Approaches
Uploaded by
Ngoc NguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
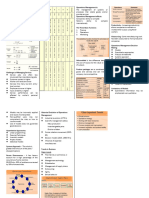
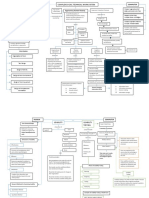
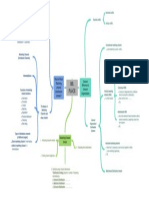
Division of Labour Adam Smith, 1776, The Wealth of
Division of labour once implemented increases the productivity Nation
Started in the 18th Century in
of the organization
Great Britain and came to
Quantitative Approach (operation approach) is The use of "Industrial Revolution" America
quantitative Techiques such as data Collection and mathematic The Industrial revolution is the term applied to the "revolution" in the
manipulation of that data to improve decision making process workplace and broader community as machinery was introduced
Quantitative Approach +Total Quality Management 2 Key Concepts into the workplace Human power was replaced by
Historical Background Machine power
Total Quality Management a management philosophy devoted Management started long time ago
to continual improvement and responding to customer needs and Factories arose and the need for
expectations. management increased
Forecast demands
Systems Approach Ensure enough materials
Open systems A system is a set of interrelated and interdependent parts Assign tasks
Interact with their environment arranged in a manner which produces a unified whole. Direct daily activities
The Last Three Management Approaches
Taylorism - Scientific Management (Efficiency) Ensure work standards were met
Closed systems Taylor published his book "Principles of Scientific Find markets for finished products
are not influenced by and do not interact with external Management" in the year 1911 1. Develop a science for each element of an individual's
environment Contigency Theory work with standardised work implements and efficient
"The bureaucracy may not always be the best structure methods for all to follow
design" Scientific Management – Taylor and Ford 2. Select right people for the right jobs and train them in the
Human Relations - a management approach that most efficient ways to accomplish the tasks
emphasizes the importance of social processes in the
organization. Dissatisfaction with the Technical 3. Compensate people for the jobs they are doing and
Approach design led to the development of the Human provide a work environment for them to reinforce their
manners
Relations school of thought Topic 2: Evolution of Management
4. Divide responsibility for managing and for working. SOme
people are more capable of managing, whereas others are
The Hawthorne studies at the Western Electric Company better at performing the tasks laid out for them.
1. Attitudes toward people are linked with productivity (Chicago) by Elton Mayo, present a positive link between
management style and productivity. Frank & Hellen they followed Taylorism and
2. The workplace is a social environment went a step further with classified hand
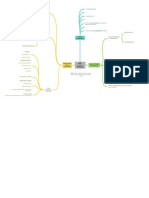
Fordism - Scientific Management (Effectiveness)
Organisational Behaviour and Human Relations motions - 17 basic motions - Therbligs
3. Psychology played an important role in productivity Ford applied the Principles of scientific
Movement management* and added assembly line technology
4. Social norms or group standards were the key that allowed for greater division of labour, as well as
determinants of individual work behavior time and motion management. Analyze basic work tasks
5. People's behavior and attitudes are closely related The ways managers design motivating jobs Use time and motion studies to eliminate time
6. Money is less factor in determining output than group Effect on Today's Business World wastes
The ways they work with employees teams
Scientific Management Today
standards Hire the best qualified workers
7. A large part of this work focused on behavioral science
methods Design incentive systems based on output
Open Communication
8. A large part of this work focused on behavioral science Henri Fayol - The Father of Strategic
methods Management
9. Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, you motivate people Management is a Universal Set of Functions
differently depend on their needs
General Administrative Theory (Planning, Organizing, Leading, Controlling)
Formal Selection
1. Division of work - Specialisation increase output
Division of Labour 14 Principles of Management
2. Authority - Managers must be able to give orders
Clearly defined Hierarchy
Max Weber - Founder of The Organization Theory 3. Discipline - Employees must obey rules
Detailed rules and regulation (Brureaucracy)
4. Unity of Command - Only one superior
Impersonal Relationship
5. Unity of Direction - Single plan of action
Career Orientation
6. Subordination if individual interests to the general interest -
Organization takes precedent
7. Remuneration - Workers must be paid a fair wage
8. Centralisation - The degree to which subordinates are
involved in decision making
9. Scalar Chain - The Line of Authority from top to bottom
10. Order - People and materials in the right place at the right
time
11. Equity - Managers should be kind and fair
12. Stability of tenure of personnel - Ensure replacements are
available to fill vacancies
13. Initiative - Employees who plan and execute will have
high effort
14. Esprit de corps - Promoting team spirit will bring Unity
and harmony
You might also like
- Scheduled Maintenance Manual: Yak-50 Aircraft With M-14P EngineDocument50 pagesScheduled Maintenance Manual: Yak-50 Aircraft With M-14P Enginebarsalona4569No ratings yet
- Maintenance Management System For Upstream Operations in Oil and Gas Industry Case Study PDFDocument7 pagesMaintenance Management System For Upstream Operations in Oil and Gas Industry Case Study PDFPearl RayNo ratings yet
- Measuring Effort in Service Organisations: July 2011Document7 pagesMeasuring Effort in Service Organisations: July 2011Sumaira BilalNo ratings yet
- Spring EditionDocument53 pagesSpring Editionkhaled azzamNo ratings yet
- Managing Innovative Strategic HRM: The Balanced Score Card Performance Management System at ITC HotelsDocument12 pagesManaging Innovative Strategic HRM: The Balanced Score Card Performance Management System at ITC HotelsAbNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi Electric Automation Book 2013 enDocument200 pagesMitsubishi Electric Automation Book 2013 enlunatiko21No ratings yet
- Digital Maturity Model (GB997A v4.0.1) : 139 Criteria To Assess Your Organization's Digital MaturityDocument1 pageDigital Maturity Model (GB997A v4.0.1) : 139 Criteria To Assess Your Organization's Digital MaturityVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Modern TheoriesDocument16 pagesModern TheoriesOsuji ChiamakaNo ratings yet
- The Automation Book: A World of SolutionsDocument136 pagesThe Automation Book: A World of Solutionsone_blanche6175No ratings yet
- New Operations Management Systems For A Digital World FinalDocument6 pagesNew Operations Management Systems For A Digital World FinalMarvellous R MakuweNo ratings yet
- MGMT2006 - Management LevelsDocument6 pagesMGMT2006 - Management LevelsJamia K GriffithNo ratings yet
- Rancang Bangun Sistem Informasi Penggajian Pada Pd. Database Computer Fernandes WiraharjoDocument6 pagesRancang Bangun Sistem Informasi Penggajian Pada Pd. Database Computer Fernandes WiraharjoImha RachmanNo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Session 3 How Should My Organization (Re) Think It Business Processes?Document20 pagesInformation Systems: Session 3 How Should My Organization (Re) Think It Business Processes?hadouiriNo ratings yet
- 20 Most Promising Utilities Technology Solution ProviderDocument2 pages20 Most Promising Utilities Technology Solution ProviderlololeoNo ratings yet
- Operation Management FormulaDocument2 pagesOperation Management FormulaBea Dela PeniaNo ratings yet
- Human Resources ManagementDocument47 pagesHuman Resources Managementreda gadNo ratings yet
- A Model Management Approach To Business Process ReengineeringDocument27 pagesA Model Management Approach To Business Process Reengineeringajayjha1972No ratings yet
- Maintenance Management System For Upstream Operations in Oil and Gas Industry Case StudyDocument7 pagesMaintenance Management System For Upstream Operations in Oil and Gas Industry Case Studylucas ronaldo coronel mendozaNo ratings yet
- MCN 111: Introduction To P&I Exposure To Industrial EngineeringDocument48 pagesMCN 111: Introduction To P&I Exposure To Industrial EngineeringRajesh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- NTPC Part2Document34 pagesNTPC Part2Deepesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Bsi Pas 99 Features and BenefitsDocument1 pageBsi Pas 99 Features and BenefitsTroy Reynolds CMP EMDNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - PMDocument17 pagesUnit 2 - PMDIVYANo ratings yet
- Development of Computer-Aided Maintenance Resources Planning (CAMRP) : A Case of Multiple CNC Machining CentersDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Computer-Aided Maintenance Resources Planning (CAMRP) : A Case of Multiple CNC Machining Centerssurekha dobaleNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chapter OneDocument35 pages1 - Chapter Onemirahaem5No ratings yet
- Advanced Model For Maintenance Management in A Continuous Improvement Cycle Integration Into The Business StrategyDocument17 pagesAdvanced Model For Maintenance Management in A Continuous Improvement Cycle Integration Into The Business StrategyHugoCabanillasNo ratings yet
- Za Deloitte Intelligent Mining InfographicDocument4 pagesZa Deloitte Intelligent Mining InfographicAgung SupriyantoNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving PresDocument121 pagesProblem Solving Presaishah farahNo ratings yet
- 03 People-Processes-Technology-Why Cant They Go AlongDocument69 pages03 People-Processes-Technology-Why Cant They Go AlongKidwvyneBeatsNo ratings yet
- Shenjun 2009Document4 pagesShenjun 2009Achintha ShashikaNo ratings yet
- R1 2004 DavenportDocument11 pagesR1 2004 DavenportDu Cong TaoNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Accounting Information Systems in Accounting: AbstractsDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Accounting Information Systems in Accounting: AbstractsRegina FlorenNo ratings yet
- Kleineer 2008-1-4Document4 pagesKleineer 2008-1-4Maria Jos� Chepillo SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Organisational Effectiveness 1ADocument178 pagesOrganisational Effectiveness 1ABandile ShobaNo ratings yet
- QMS Paper PDFDocument13 pagesQMS Paper PDFPrisman Cahya NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Performance Measurement: Methods, Tools and ApplicationsDocument4 pagesMaintenance Performance Measurement: Methods, Tools and ApplicationsŊô ĦâNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Kaizen Implementation On Employees' Affective Attitude in Textile Company in EthiopiaDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Kaizen Implementation On Employees' Affective Attitude in Textile Company in EthiopiaTravel BDNo ratings yet
- Human Resources ManagementDocument41 pagesHuman Resources Managementreda gadNo ratings yet
- Putting The Enterprise Into The Enterprise SystemDocument11 pagesPutting The Enterprise Into The Enterprise SystemBhargav MehtaNo ratings yet
- Energies 13 05766Document13 pagesEnergies 13 05766kailanaveen114No ratings yet
- Mba Om NotesDocument159 pagesMba Om Notesprabu06051984No ratings yet
- Bititci, 1997 Integrated Performance PDFDocument13 pagesBititci, 1997 Integrated Performance PDFEdson KogachiNo ratings yet
- COBIT 5 Poster 2 - What Drives IT Governance PDFDocument1 pageCOBIT 5 Poster 2 - What Drives IT Governance PDFLuis MessiasNo ratings yet
- A Multi-Time-Scale Maintenance and Production Scheduling ApproachDocument15 pagesA Multi-Time-Scale Maintenance and Production Scheduling ApproachSisawad XayyasithNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) in Enhancing The Firm ProductivityDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) in Enhancing The Firm ProductivityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A 1800058119Document7 pagesA 1800058119sheetalthomas.mbaNo ratings yet
- Time Resources Script Presenter Mauren Jorge and Esteven Heyder and Tatiana (Jorge) Industrial Engineering Is Important Because ItDocument3 pagesTime Resources Script Presenter Mauren Jorge and Esteven Heyder and Tatiana (Jorge) Industrial Engineering Is Important Because ItHJNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Introduction To Production and Operations ManagementDocument20 pagesChapter-1 Introduction To Production and Operations Managementllpud229.karrthikhNo ratings yet
- IT Isn't Just Technology: A Business Perspective On Information SystemDocument4 pagesIT Isn't Just Technology: A Business Perspective On Information SystemCharitha LakmalNo ratings yet
- 01 - 10 - Chapter 1 - BPR - An OverviewDocument23 pages01 - 10 - Chapter 1 - BPR - An OverviewRussuoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Function's Performance Evaluation Using Adapted Balanced Scorecard ModelDocument5 pagesMaintenance Function's Performance Evaluation Using Adapted Balanced Scorecard ModelDan SartoriNo ratings yet
- Ce Applied Automation Spring 2022Document53 pagesCe Applied Automation Spring 2022Renato techNo ratings yet
- Complex Social Technical Work System: Computer HumanDocument2 pagesComplex Social Technical Work System: Computer HumanCasas, Jo-an Pauline A.No ratings yet
- Strategic Use of MISDocument9 pagesStrategic Use of MISShreya DikshitNo ratings yet
- A Study of Information Systems in Human Resource Management (HRM)Document5 pagesA Study of Information Systems in Human Resource Management (HRM)Zohrak HarutyunyanNo ratings yet
- Informmation System - Hindalco MisDocument3 pagesInformmation System - Hindalco MisPurushottam WankhedeNo ratings yet
- Phylosophy of Industrial Engineering (TM1)Document30 pagesPhylosophy of Industrial Engineering (TM1)Fajar JossNo ratings yet
- Master of Computer Application DepartmentDocument3 pagesMaster of Computer Application DepartmentAshish tiwariNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Balanced Scorecard WebDocument7 pagesBeyond The Balanced Scorecard Webthomas_pachecoNo ratings yet
- Essence and Degree of Change: Delvi Olimpia (1906329202) Heti Nur Isnaini (1906329341)Document29 pagesEssence and Degree of Change: Delvi Olimpia (1906329202) Heti Nur Isnaini (1906329341)Yuni ListianiNo ratings yet
- Building Better Policies: The Nuts and Bolts of Monitoring and Evaluation SystemsFrom EverandBuilding Better Policies: The Nuts and Bolts of Monitoring and Evaluation SystemsNo ratings yet
- RMIT Student Guide - Folio by PortfoliumDocument6 pagesRMIT Student Guide - Folio by PortfoliumNgoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Semester 2 2021 Case Study: Happy CoffeeDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Management Semester 2 2021 Case Study: Happy CoffeeNgoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Rmit Student Guide - EportfolioDocument3 pagesRmit Student Guide - EportfolioNgoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Promotion - Part 1-1Document1 pageTopic 8 - Promotion - Part 1-1Ngoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 - Place-1Document1 pageTopic 6 - Place-1Ngoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Hotel Accommodation SurveyDocument2 pagesHotel Accommodation SurveyNgoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- W5. Price: New Product PricingDocument2 pagesW5. Price: New Product PricingNgoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Addisu M Research ProposalDocument16 pagesAddisu M Research ProposalAddisu MengeshaNo ratings yet
- History: Masskara FestivalDocument5 pagesHistory: Masskara FestivalNORMA SABIONo ratings yet
- Aquino vs. Heirs of Raymunda CalayagDocument7 pagesAquino vs. Heirs of Raymunda CalayagJenny ButacanNo ratings yet
- Print Server Scalability and Sizing Technical Overview WhiteDocument14 pagesPrint Server Scalability and Sizing Technical Overview Whiteapi-3734769No ratings yet
- YZF-R7 Owners Manual 2023sDocument100 pagesYZF-R7 Owners Manual 2023sSedatNo ratings yet
- 2 DX - 2 DN 1 DX - 1 DN Leaflet EN Lille 2935 0566 11Document20 pages2 DX - 2 DN 1 DX - 1 DN Leaflet EN Lille 2935 0566 11cliverNo ratings yet
- Corp CommrevDocument39 pagesCorp CommrevMary Charlene ValmonteNo ratings yet
- CivRev - Solidarios V AlampayDocument5 pagesCivRev - Solidarios V AlampayKarla Marie TumulakNo ratings yet
- HC900 Remote Termination Panel (RTP) For Analog InputsDocument8 pagesHC900 Remote Termination Panel (RTP) For Analog Inputsozzy75No ratings yet
- Case Study #3Document4 pagesCase Study #3Annie Morrison AshtonNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy Conversion Systems PDFDocument268 pagesWind Energy Conversion Systems PDFfotopredicNo ratings yet
- Resolution No. 001 S. 2023Document4 pagesResolution No. 001 S. 2023Chad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- Ashcroft ThermometerDocument2 pagesAshcroft ThermometerjlcegarraNo ratings yet
- IMM5562FDocument0 pagesIMM5562FMalek AitouazzouNo ratings yet
- Internship Report TopicsDocument1 pageInternship Report TopicsMidul Khan100% (7)
- How Entrepreneurs Craft (HBR) (Lalit Nainani)Document15 pagesHow Entrepreneurs Craft (HBR) (Lalit Nainani)virtual17No ratings yet
- List of Tables: Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and General Population in Andhra Pradesh From 1961-2001 CensusDocument5 pagesList of Tables: Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and General Population in Andhra Pradesh From 1961-2001 CensusYeshWaNthNo ratings yet
- Find Funding: Region or Country Funder (E.g. World Bank, DFID) Topic (E.g. Water & Sanitation)Document5 pagesFind Funding: Region or Country Funder (E.g. World Bank, DFID) Topic (E.g. Water & Sanitation)Bilel MarkosNo ratings yet
- New York Life Ins. Co. v. Edwards, 271 U.S. 109 (1926)Document6 pagesNew York Life Ins. Co. v. Edwards, 271 U.S. 109 (1926)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Motion For Issuance of Certificate of FinalityDocument3 pagesMotion For Issuance of Certificate of Finalitymarvilie sernaNo ratings yet
- TrainingPeaks How To Start Training With Power Ebook PDFDocument23 pagesTrainingPeaks How To Start Training With Power Ebook PDFmaorpe100% (1)
- Prosperity Game and TreatmentDocument5 pagesProsperity Game and TreatmentБојан ЈаковљевићNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Some Features of in Vitro Cultivation On Direct Germination, Callusogenesis and Morphogenesis in The Culture of Mature Barley EmbryosDocument5 pagesThe Influence of Some Features of in Vitro Cultivation On Direct Germination, Callusogenesis and Morphogenesis in The Culture of Mature Barley EmbryosInforma.azNo ratings yet
- Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid Work For South Carolina 2012Document22 pagesSocial Security, Medicare and Medicaid Work For South Carolina 2012SocialSecurityWorksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 v8.0Document102 pagesChapter 4 v8.0montaha dohanNo ratings yet
- Scheduling BODS Jobs Sequentially and ConditionDocument10 pagesScheduling BODS Jobs Sequentially and ConditionwicvalNo ratings yet
- gp30mpc 150Document27 pagesgp30mpc 150locomotoras.slpNo ratings yet
- Journal, T Accounts, Worksheet and Posting and Trial BalanceDocument31 pagesJournal, T Accounts, Worksheet and Posting and Trial Balancekenneth coronel100% (1)
- Health Promotion UnitDocument121 pagesHealth Promotion UnitsolacespunkyNo ratings yet