Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simple present tense forms
Uploaded by
Rizka AmaliaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple present tense forms
Uploaded by
Rizka AmaliaCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple present tense - Negative and interrogative forms
In the Simple Present the negative and interrogative sentences in English are formed using
the auxiliary do or does.
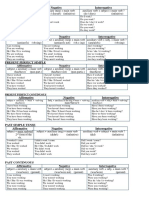
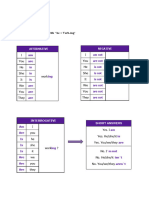
Negative form
The negative form of the Simple Present is obtained by adding do not or does not before the
base form of the verb:
Subject Auxiliary Example
I don’t I don’t work
You don’t You don’t work
He doesn’t He doesen’t work
She doesn’t She doesn’t work
It doesn’t It doesn’t work
We don’t We don’t work
You don’t You don’t work
They don’t They don’t work
As you can see, only the pronouns of the 3rd person singular (he, she, it) are followed by does
not, for all others do not use.
Interrogative form
The interrogative form of the Simple Present is obtained with the auxiliary do or does in front
of the subject.
Subject Auxiliary Example
Do I Do I work?
Do you Do you work?
Does he Does he work?
Does she Does sge work?
Does it Does it work?
Do we Do we work?
Do you Do you work?
Do they Do they work?
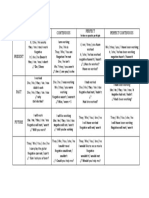
Training of the WHY-Questions
The Wh – questions (questions that use adjectives and interrogative pronouns like What,
Where, Why, When, Which, Who) are formed by putting the adjective or interrogative pronoun
Wh – at the beginning of the interrogative phrase. Here are some examples:
Affirmative Interrogative WHY QUESTIONS
They work Do they work? Why do they work?
You study Do you study? What do you study?
She drives Does she drive? Which car does she drive?
You might also like
- Simple present tense formsDocument2 pagesSimple present tense formsRizka AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Simple present tense formsDocument2 pagesSimple present tense formsRizka AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument3 pagesPresent Simplerivawo6602No ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense: Miss KimberlyDocument8 pagesPresent Simple Tense: Miss KimberlyBarbie GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Curs 1 Prezent Simple PDFDocument3 pagesCurs 1 Prezent Simple PDFELENANo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference: Unit 1 1.1 Verbs: Present SimpleDocument4 pagesGrammar Reference: Unit 1 1.1 Verbs: Present SimpleAlberto Juan BonanseaNo ratings yet
- Present simple tense regular verbsDocument1 pagePresent simple tense regular verbsAnca Diana PaleuNo ratings yet
- Frequency Adverbs in Present Simple TenseDocument3 pagesFrequency Adverbs in Present Simple Tensesuanfonson ruizNo ratings yet
- Do vs. Be: Are You Confused? Do You Need Help?: I Want To Learn EnglishDocument2 pagesDo vs. Be: Are You Confused? Do You Need Help?: I Want To Learn EnglishMartina CastilloNo ratings yet
- Present Simple WorkshopDocument6 pagesPresent Simple WorkshopVALENTINA PATIO VALENCIANo ratings yet
- Tenses Form Simplified PRESENT CONTINUOUSDocument3 pagesTenses Form Simplified PRESENT CONTINUOUSGabriella CoachNo ratings yet
- Present Simple - Prosto Sadašnje Vreme: Jednina (Singular) Množina (Plural)Document3 pagesPresent Simple - Prosto Sadašnje Vreme: Jednina (Singular) Množina (Plural)Vladan ColakovicNo ratings yet
- Tenses Form Simplified PRESENT SIMPLEDocument1 pageTenses Form Simplified PRESENT SIMPLEGabriella CoachNo ratings yet
- Chart TENSESDocument2 pagesChart TENSESMurgulet RoxanaNo ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument1 pageSimple PresentLuís MendesNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense GuideDocument6 pagesPresent Simple Tense Guidebayardo churata halanoccaNo ratings yet
- REGULAR VERB Present and PastDocument1 pageREGULAR VERB Present and Pastmacec007No ratings yet
- Engleski KolokvijumDocument1 pageEngleski KolokvijumDavudNo ratings yet
- Teoría Present Simple - Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesTeoría Present Simple - Present ContinuousMarianela MuzzuNo ratings yet
- "Year of The Fight Against Corruption and Impunity": English Activity 7 Collaborative WorkDocument4 pages"Year of The Fight Against Corruption and Impunity": English Activity 7 Collaborative WorkLucía Priscila Encalada ZapataNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense: Affirmative Form Singular PluralDocument1 pagePresent Simple Tense: Affirmative Form Singular Pluralstaza00No ratings yet
- Verbs in English LanguageDocument16 pagesVerbs in English LanguageStanilaEmilNo ratings yet
- Presente Simple InglesDocument1 pagePresente Simple InglesCrysthian EcathosNo ratings yet
- Atg Chart Presentcont PDFDocument1 pageAtg Chart Presentcont PDFAndrea Santo100% (1)
- Present ContinousDocument12 pagesPresent ContinousOchoa Rodríguez David Vicente67% (3)
- Affirmative Negative Interrogative & Short Answers Use: Does Does DoesDocument6 pagesAffirmative Negative Interrogative & Short Answers Use: Does Does DoesAlbina Flores100% (1)
- TensesDocument19 pagesTensesAlina Elena CioacaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument12 pagesPresent Simple Vs Present ContinuousTony HalimNo ratings yet
- Verb conjugations and translationsDocument3 pagesVerb conjugations and translationsDavide Ruud RossiNo ratings yet
- Presentecontinuo PDFDocument1 pagePresentecontinuo PDFdarvnNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense Negative FormDocument3 pagesSimple Present Tense Negative FormmingNo ratings yet
- Present Simple - Negative Form - Yes-No QuestionsDocument7 pagesPresent Simple - Negative Form - Yes-No QuestionsMert BayerNo ratings yet
- Inglese GrammaDocument1 pageInglese GrammaBianca DNo ratings yet
- Verb conjugation cheat sheetDocument9 pagesVerb conjugation cheat sheetPaola OteroNo ratings yet
- Handout 1Document3 pagesHandout 1edenamiriambutNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: The TensesDocument35 pagesEnglish Grammar: The TensesSzala LukeNo ratings yet
- Present Simple&ContinuousDocument6 pagesPresent Simple&ContinuousStun3ers RbNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Form Affirmative Negative InterrogativeDocument5 pagesPresent Simple Form Affirmative Negative InterrogativeAlba Benítez CruceiraNo ratings yet
- Excercices With Verb TobeDocument4 pagesExcercices With Verb TobeBárbaraRossiNo ratings yet
- Elt Oup Com - Verb Forms Interm PDFDocument1 pageElt Oup Com - Verb Forms Interm PDFMina KirovskiNo ratings yet
- Present Tense Verb ConjugationsDocument8 pagesPresent Tense Verb ConjugationsBarbara Oder100% (1)
- INPV311 E-Class File 5CDocument2 pagesINPV311 E-Class File 5CSamuelZadyFar-iNo ratings yet
- Verbs in English LanguageDocument17 pagesVerbs in English LanguageGabriel PlugaruNo ratings yet
- The Use of Verb Tenses: The Present Simple TenseDocument8 pagesThe Use of Verb Tenses: The Present Simple TenseSzabo FlorinaNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous PDFDocument3 pagesPresent Continuous PDFFardy GeldresNo ratings yet
- By Teacher Verónica Bautista: Verb To Be - AffDocument2 pagesBy Teacher Verónica Bautista: Verb To Be - AffLa Flor Bautista100% (1)
- TENSES Saliza & HaziqDocument42 pagesTENSES Saliza & HaziqSaliza HalimNo ratings yet
- Timpurile Verbale in EnglezaDocument8 pagesTimpurile Verbale in EnglezaAlin GabrielNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Afirmative Negative Interrogative Answers ExpressionsDocument4 pagesPresent Simple Afirmative Negative Interrogative Answers Expressionsingrid torresNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument3 pagesPresent Continuousrain starsNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses EB8Document4 pagesPresent Tenses EB8Michael TarabayNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Vs Present Continuous 68314Document9 pagesSimple Present Vs Present Continuous 68314AltsLeoItzNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument4 pagesPast SimpleLucas KatzNo ratings yet
- Verbal Tenses EnglishDocument15 pagesVerbal Tenses EnglishXoel Carracedo PardoNo ratings yet
- Present TenseDocument7 pagesPresent Tensedumpie archiveNo ratings yet
- Doce Tiempos Gramaticales en InglesDocument1 pageDoce Tiempos Gramaticales en InglesXimena ajilaNo ratings yet
- The Present Simple Tense (Sadašnje Prosto Vreme) : Potvrdni OblikDocument4 pagesThe Present Simple Tense (Sadašnje Prosto Vreme) : Potvrdni OblikStojan StankovicNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense Explanation With Examples PDFDocument3 pagesSimple Present Tense Explanation With Examples PDFAlessia LentoNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF TensesDocument19 pagesTYPES OF Tensesariesyue100% (2)
- Control Systems GEDocument482 pagesControl Systems GECarlos ACNo ratings yet
- Departmental Schedule, 2nd Sem 2017-2018Document70 pagesDepartmental Schedule, 2nd Sem 2017-2018Kim Kenneth Roca100% (3)
- Concept of Nation and Nationalism: Imagined Communities by Benedict AndersonDocument11 pagesConcept of Nation and Nationalism: Imagined Communities by Benedict AndersonANDREA TANNo ratings yet
- INGLES TECNICO IV (En Ambas Caras)Document45 pagesINGLES TECNICO IV (En Ambas Caras)ESGUAR INSTRUCTORESNo ratings yet
- Igcse Year 1Document3 pagesIgcse Year 1mooman109895No ratings yet
- Daily Stoic Amor Fati Excerpt From The Obstacle Is The WayDocument7 pagesDaily Stoic Amor Fati Excerpt From The Obstacle Is The WaySirLouen100% (9)
- RXF-C: Air Conditioning Technical DataDocument18 pagesRXF-C: Air Conditioning Technical DataJuan LezamaNo ratings yet
- My ResumeDocument2 pagesMy ResumeSathanandhNo ratings yet
- Espedosa Module3.5 AssignmentDocument2 pagesEspedosa Module3.5 AssignmentKhemgee EspedosaNo ratings yet
- Time Table II Sem 14-15Document5 pagesTime Table II Sem 14-15Satyam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical-Chapter 3 TheoryDocument13 pagesBasic Electrical-Chapter 3 TheorySankar RijalNo ratings yet
- Iso 1615 1976Document4 pagesIso 1615 1976Untung HariminNo ratings yet
- Measuring and managing intellectual capitalDocument6 pagesMeasuring and managing intellectual capitalAl-Farisi Ibnu EdyNo ratings yet
- University of Oxford, Financial Statements 2017-2018 PDFDocument120 pagesUniversity of Oxford, Financial Statements 2017-2018 PDFRano Digdayan MNo ratings yet
- Kermann Led: Exproof Easylight Z1Document3 pagesKermann Led: Exproof Easylight Z1Abdulaziz AlrawiNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 100 VoltDocument9 pagesMosfet 100 Voltnithinmundackal3623No ratings yet
- ABS Rules For Piping and FittingsDocument2 pagesABS Rules For Piping and Fittingsmaha100% (1)
- Apa Manual Chapter 2 SummaryDocument8 pagesApa Manual Chapter 2 SummaryAsma Masood0% (1)
- Experiment No. 2 Introduction To Combinational Circuits: Group Name: Group 7 Group Leader: JOSE DOROSAN Group MemberDocument11 pagesExperiment No. 2 Introduction To Combinational Circuits: Group Name: Group 7 Group Leader: JOSE DOROSAN Group MemberJoy PeconcilloNo ratings yet
- PROF ED 8 Assessment Learning 1Document5 pagesPROF ED 8 Assessment Learning 1Mirabel ManucducNo ratings yet
- Spring Suspension Physics FrequencyDocument2 pagesSpring Suspension Physics Frequencygkovacsds100% (1)
- Law of Insurance Eighth Semester SyllabusDocument3 pagesLaw of Insurance Eighth Semester SyllabusAastha PrakashNo ratings yet
- 11 - NRG - Cathodic Protection DesignDocument15 pages11 - NRG - Cathodic Protection DesignBalan100% (1)
- Analysis of Salem PossessedDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Salem PossessedCharity BurgessNo ratings yet
- PDF Investigating Heat - Practical ReportDocument5 pagesPDF Investigating Heat - Practical Reportapi-292599931No ratings yet
- Important NoteDocument4 pagesImportant NotemikiNo ratings yet
- StrippingDocument17 pagesStrippingGhavban David0% (1)
- Modelling of Agglomerating Systems: From Spheres To FractalsDocument13 pagesModelling of Agglomerating Systems: From Spheres To FractalsSandra BazanNo ratings yet
- 21b Text PDFDocument47 pages21b Text PDFyoeluruNo ratings yet
- NRD Idg Gy Fiyf FofkDocument7 pagesNRD Idg Gy Fiyf FofkMERA MENTALNo ratings yet