0% found this document useful (0 votes)
214 views2 pagesUnderstanding AWS Load Balancers
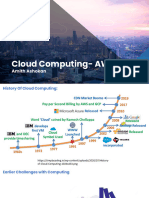
Load Balancer distributes incoming web traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource utilization and prevent any single server from being overwhelmed. An Application Load Balancer at the AWS level operates at layer 7 and routes traffic based on URL to the appropriate backend servers, such as routing requests for specific Tesla models to servers dedicated to those models. A Network Load Balancer operates at layer 4 and makes routing decisions based on TCP/SSL connections to balance traffic loads. A Classic Load Balancer operates at layer 4 and routes traffic based on IP addresses between clients and backend servers on a specified port.
Uploaded by
BharathCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
214 views2 pagesUnderstanding AWS Load Balancers
Load Balancer distributes incoming web traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource utilization and prevent any single server from being overwhelmed. An Application Load Balancer at the AWS level operates at layer 7 and routes traffic based on URL to the appropriate backend servers, such as routing requests for specific Tesla models to servers dedicated to those models. A Network Load Balancer operates at layer 4 and makes routing decisions based on TCP/SSL connections to balance traffic loads. A Classic Load Balancer operates at layer 4 and routes traffic based on IP addresses between clients and backend servers on a specified port.
Uploaded by
BharathCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd