Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5-HMS PP Introduction
Uploaded by
Swapnil Ahire0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages5-HMS PP Introduction
Uploaded by
Swapnil AhireCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
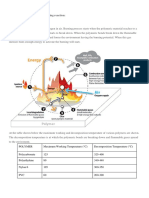
HMSPP
HIGH MELT STRENGTH POLYPROPYLENE
Elongational viscosity of polymer melts can be categorized as 'strain thinning' or 'strain
hardening', and is related to macromolecular structure and the amount of 'molecular stress'
that can be induced into a polymer melt by deformation. Linear PP melts s how 'strain
thinning' (low molecular stress), while long -chain branching leads to high molecular stress
and 'strain hardening'.
For linear PP, melt strength, as defined by maximum drawdown force in a tensile experiment,
increases with increasing zero -shear viscosity and increasing weight average molecular
weight. At lower melt temperatures, melt strength can be enhanced by flow induced
crystallization. Long -chain branched is expected to have a superior melt strength relative to
a linear PP of comparable ze ro-shear viscosity due to the 'strain -hardening' effect.
Elongational viscosity and melt strength play an important role in all processing operations
where extensional deformations occur.
In the last years, a new family of modified PP was
developed, the well -known high melt s trength
polypropylene (HMS -PP). This product is char acterize d by
a small content of long -ch ain bran ches and high
polydispersity; the presence of long -chains h as an
enormous in fluence on its melt properties.
Due to its inherent n ature, polypropylene lacks melt
strength. HMSPP contains long chain bran ches and
consequently exhibits s ignificantly high melt strength .
These HMSPP grades offer unique balan ce of process -
ability and high melt elas ticity required for f oaming,
thermoforming, and extrusion.
There are many r outes for production of HMS-PP. It is
very known th at the resistance of the melted (RF)
increases with the molecular weight. Another theoretical
possibility for the in crease of RF would be increasing the
interlacement level. As PP is a line ar polymery this
possibility was little explored.
The in crease of the molecular weight causes the
decrease of the index of fluidity. The ramification
formation of long chain doesn't alter the fluidity ind ex
and als o improves the extensibility.
HMSPP has as characteristic the high resis tan ce of th e
melted allied to great extensibility.
¤ HMS labels the product technology and process
patented developed by IPEN in partnership with BRASKEM
and EMBRARAD
¤ I t consists of a new type of irrad iated PP char acter ized
by having a ramified mole cular s tructure
¤ The market obje ctive is all the processes of PP
transformation th at deman d a large amount of elongation
of melted PP
¤ Incre ase of molecular we ight and creation of long
ramifications are the s tate of the art to solve the
problems of PP process
The main applications of H MSPP are: - extrusion,
compound foils extrusion, films, thermoforming,
coatings, foams and blow. The melted low resis tance has
limited the p articipation of PP in these segments th at
impedes or harms those processes.
HMSPP provides more elas ticity to the polypropylene in
the melted ph ase. That material, known by HMS -PP (high
melt strength polypropyle ne), it is winning market in all
Europe, for environmental reasons, where the industr y
started to apply in the production of fo ams for several
uses, mainly in d ashboard of veh icles, because they are
easier to be recycled. The pieces produced employin g the
mixture of several other plastic resins offers man y
obstacles to recycling could generate unfe asible.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- VDOT 2016 RB Specs PDFDocument1,091 pagesVDOT 2016 RB Specs PDFParamjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Organic ChemistryDocument12 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Organic ChemistryShamarie Love MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Type of Flammability - Products Need of Flame RetardenceDocument4 pagesType of Flammability - Products Need of Flame RetardenceSwapnil AhireNo ratings yet
- Analysis Spectra AbioFunctionalGrpsVollIRspectDocument17 pagesAnalysis Spectra AbioFunctionalGrpsVollIRspectKong VariNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Gate and Gate Size in Injection MoldDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Gate and Gate Size in Injection MoldSwapnil AhireNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument21 pagesPolymerIamdevilonNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument21 pagesPolymerIamdevilonNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Gate and Gate Size in Injection MoldDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Gate and Gate Size in Injection MoldSwapnil AhireNo ratings yet
- 10CDocument5 pages10CAlexis RomanNo ratings yet
- 8-What Is Bimodal PolymerDocument1 page8-What Is Bimodal PolymerSwapnil AhireNo ratings yet
- Polymer Mechanical & Other TestingDocument66 pagesPolymer Mechanical & Other TestingSwapnil AhireNo ratings yet
- Seminar 5 Tire TechnologyDocument16 pagesSeminar 5 Tire TechnologySwapnil AhireNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1 RheometerDocument11 pagesSeminar 1 RheometerSwapnil Ahire100% (1)
- Seminar-2 Rubber Compression MoldingDocument11 pagesSeminar-2 Rubber Compression MoldingSwapnil Ahire50% (2)
- Seminar-4 Blow MoldingDocument11 pagesSeminar-4 Blow MoldingSwapnil AhireNo ratings yet
- Seminar-3 Rubber Transfer MoldingDocument10 pagesSeminar-3 Rubber Transfer MoldingSwapnil AhireNo ratings yet
- Astm F 2329Document5 pagesAstm F 2329haharameshNo ratings yet
- Construction Algorithm For Zero Divisor Graphs of Comm RingDocument9 pagesConstruction Algorithm For Zero Divisor Graphs of Comm RingBBBBBNo ratings yet
- Cloruro de ViniloDocument25 pagesCloruro de ViniloJulissa MármolNo ratings yet
- Humic Substances-Formation, Nature and Properties, Theories of Humus FormationDocument31 pagesHumic Substances-Formation, Nature and Properties, Theories of Humus FormationNanthini100% (1)
- Optimization of Process Parameters in The Production of Powdered Explosives in Ps VitezitDocument12 pagesOptimization of Process Parameters in The Production of Powdered Explosives in Ps VitezitirmaNo ratings yet
- Chem31.1 ATQ8 Santos PDFDocument3 pagesChem31.1 ATQ8 Santos PDFClaire Santos100% (1)
- Gillfab 1367B LaminateDocument2 pagesGillfab 1367B LaminateLuis AbrilNo ratings yet
- Produk LMTNOVDocument24 pagesProduk LMTNOVSeagate WaiNo ratings yet
- 2023 Msce Biology IiDocument6 pages2023 Msce Biology IiaubreymphataNo ratings yet
- 1744 - HDPE - Jay Polymer Village-Dabhil Tal-SawantwadiDocument2 pages1744 - HDPE - Jay Polymer Village-Dabhil Tal-SawantwadiAtik ModgiNo ratings yet
- Bituminous Soil Stabilization AssignmentDocument5 pagesBituminous Soil Stabilization AssignmentScott MuthuriNo ratings yet
- DLL-G7 First Quarter Lesson 7bDocument3 pagesDLL-G7 First Quarter Lesson 7bKathryna Valencia RositaNo ratings yet
- WaterproofingDocument38 pagesWaterproofingpverce100% (1)
- Reaction Rates: BIG IdeaDocument34 pagesReaction Rates: BIG Ideacarleston thurgoodNo ratings yet
- Atomoxetine CapsulesDocument2 pagesAtomoxetine Capsulesehsan050628No ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On Cell Disruption Methods PDFDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study On Cell Disruption Methods PDFMarisol MancillaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen BondDocument23 pagesHydrogen BondDhyTa Ntuew ChayankWardhimant100% (1)
- 01 - Beer Stabilisation Part 1 PDFDocument2 pages01 - Beer Stabilisation Part 1 PDFNelcy LatorreNo ratings yet
- MYP 5 - E-Assessment Revision - Periodic Table (Trends, Periods, Groups) - 43 Marks Q1Document9 pagesMYP 5 - E-Assessment Revision - Periodic Table (Trends, Periods, Groups) - 43 Marks Q1Daria DyabloNo ratings yet
- Astm D7414 22Document4 pagesAstm D7414 22barcaza_13No ratings yet
- Las 2 3Document51 pagesLas 2 3qdt282r4n8No ratings yet
- Dosage Form DesignDocument7 pagesDosage Form DesignNICOLE ANGELIQUE M. DINOYNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub Deactivation and Testing of Hydrocarbon Processing Catalysts 9780841234116 9780841215832Document464 pagesDokumen - Pub Deactivation and Testing of Hydrocarbon Processing Catalysts 9780841234116 9780841215832Ngọc Cường nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Bhu - Company - Id Bhu - Firm - Name Bhu - Registration - No Bhu - CMP - C Ompany - IdDocument9 pagesBhu - Company - Id Bhu - Firm - Name Bhu - Registration - No Bhu - CMP - C Ompany - IdSoe Nam DhendupNo ratings yet
- Stitute: NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesStitute: NCERT Solution For Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and SaltsSuneethaNo ratings yet
- Loba List 2018-19Document249 pagesLoba List 2018-19Sandeep0% (1)
- 10A-B Guides 1,2,3Document11 pages10A-B Guides 1,2,3Juan EcheverryNo ratings yet
- New Chemistry For Jee Mains FarmulaDocument48 pagesNew Chemistry For Jee Mains FarmulaSatya Kam100% (1)