Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tag: It Is A Crucial Tag. It Tells The Browser That The Content Is Located Between and - It Is Also Called The "Root" Element
Uploaded by
Yesmine MakkesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tag: It Is A Crucial Tag. It Tells The Browser That The Content Is Located Between and - It Is Also Called The "Root" Element
Uploaded by
Yesmine MakkesCopyright:
Available Formats
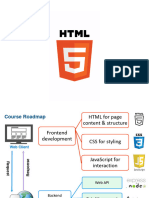
Hyper Text Markup Langauge It is used to create pages and make them functional.
• Hypertext defines the link between the web pages.
• Markup language is used to define the text document within tag which defines the
structure of web pages.
HTML elements are represented by tags <>
• Paired tag: it has to be closed, it composed from an opening tag and a closing tag with some
content inside of it.
• Unpaired tag: this one does not have to be closed it self closing tag.
< html > tag :
• It is a crucial tag. It tells the browser that the content is
located between < html > and < /html>.
• It is also called the “root” element.
The head element contains information about the web page. You can put many elements inside of it
such as:
<link rel="icon" href="favicon.ico" type="image/x-icon"/>
Title => Sets the title of the page
Link => links elements to html, such as the page icon, CSS files...Etc.
<b>: Bold Text
<i>: Italic Text
<small>: displays smaller text
<del>: defines deleted text
• Unpaired tag: (does not have a companion tag. In other words it doesn’t close)
<br>: breaks a line
HTML attributes provide additional information about a HTML element. Attributes can be
considered as properties of the element. An element may have a single attribute, many attributes, or
no attributes at all.
Attributes are placed in the opening tag, with a space after the element declaration
“alt” attribute is your plan B if your image fails to load.
<img src="path/to/image/dog.jpg" alt="A dog" >
The img tag is called unpaired
we can connect a HTML page to other web pages by creating a hyperlink using the anchor tag.
<a href="https://gomycode.tn/">Take me to GoMyCode's Website</a>
To play an audio html file, use the < audio > element:
The controls attribute is necessary. It adds audio controls, likes play, pause, and volume.
The < source > element allows you to specify alternative audio files which the browser may choose
from.
The browser will use the first recognized format.
The text between < audio >< /audio> will be displayed only if the audio file is not supported by the
browser.
<audio controls>
<source src="test.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
Please Check the audio Extension
</audio>
It is preferable to include width and height attributes in your tag, and of course to start a video
automatically we use the autoplay attribute:
<video width="320" height="240" autoplay>
<source src="test.mp4" type="video/mp4" />
Please Check the video extension.
</video>
The src attribute in the video tag replace the <source> tag
add videos from youtube and we simply use the iframe tag
<iframe
width="420"
height="315"
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/zcTFG_F0FRs">
</iframe>
there is many types of list. Let's see the most used :
• Ordered list
• Unordered list
• Description list
To create an unordered list, we use the html tag <ul> typically rendered as a bulleted list but we
can change the style of list using the type attribute. Every element of the list is wrapped with tag
<li>
<ul type="disc">
<ul type="square">
<ol> element represents an ordered list of item,
Ordered list type values can be used to change the numbering
scheme, and include the following:
• 1: Default numeric scheme
• I: Upper-case Roman numerals
• i: Lower-case Roman numerals
• A: Upper-case Alphabet
• a: Lower-case Alphabet
exp
<ol type="I">
The HTML <dl> element represents a description list. The element encloses a list of groups of
terms (specified using the <dt> element) and descriptions (provided by <dd> elements)
• <th > tags are column names
• < tr > tags are rows
• < td > tags are column values of the row
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>HTML</th>
<th>CSS</th>
<th>JS</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Paragraphs</td>
<td>Selectors</td>
<td>DOM</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Tables</td>
<td>Styles</td>
<td>Elements</td>
</tr>
</table>
semantic tags Typically focusing on using HTML to semantically structure your web content
provides several benefits, including:
• making your web content vastly more accessible to readers with disabilities
• applying styles with CSS will become more consistent and predictable
• earch engines will use the semantic information to better understand your web pages
<header >
It's typically a group of introductory or navigational aids. It may contain some elements such as a
logo, a search form, a slogan, etc.
< main >
It can contain the main section of our website, we will explain it in the next slides.
< footer >
A footer typically contains information about the author, contact information, copyright data, etc.
<nav> Element: it defines a set of navigation links
The <section> element defines a section in a document. if we want to split our home page into
sections for introduction, content, and contact information,
The <article> element defines an article in a document.
It can represent a blog entry, a news/scholarly article, and a forum post
• The <aside> element : it defines some content aside from the content it is placed in (like a
sidebar).
• <figure> and <figcaption> elements : its serves regroup images and caption in one
element.
<form>
<label>Name:</label>
<input type="text" name="first name" placeholder="Type your name here" />
<br />
<label>Number:</label>
<input type="number" name="number" value="23123456" />
<br />
<label>Birth Date:</label>
<input type="date" name="birthday" />
<br />
<label>Password:</label>
<input type="password" name="password" />
<br />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
properties of input include:
• size
• value
• maxlength
• readonly
<select>
<option value="WebTrack">Web Track</option>
<textarea name="message" cols="30" rows="5">
Welcome to GoMyCode
</textarea>
<button> elements are simple to define, and have three different type values:
• submit: submits form data to a server
• reset: resets all the data in the current form
• button: no default behavior. This type of button will be more useful when we begin our
discussion of Javascript
br hr
description list manual list ?
You might also like
- HtmlCSSJS-3Document113 pagesHtmlCSSJS-3Petre SebastianNo ratings yet
- HTML AdvanceDocument8 pagesHTML AdvanceGopalNo ratings yet
- Learn HTML and CSS In 24 Hours and Learn It Right | HTML and CSS For Beginners with Hands-on ExercisesFrom EverandLearn HTML and CSS In 24 Hours and Learn It Right | HTML and CSS For Beginners with Hands-on ExercisesNo ratings yet
- Hyper Text Markup LanguageDocument36 pagesHyper Text Markup Languageනවියා NaviyaNo ratings yet
- HTML Tags: Prepared by Shahzeb KhanDocument18 pagesHTML Tags: Prepared by Shahzeb KhanpariNo ratings yet
- INT219 1 (1)Document120 pagesINT219 1 (1)manishsingham1000No ratings yet
- HTML Fundamental Daffa Faiz AthallahDocument13 pagesHTML Fundamental Daffa Faiz AthallahDap PoyNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument58 pagesHTMLMark Lorenz BaranganNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument32 pagesHTMLAshishNo ratings yet
- Intro To HTML & Javascript: (With A Little CSS, +libraries/frameworks)Document57 pagesIntro To HTML & Javascript: (With A Little CSS, +libraries/frameworks)schmamsNo ratings yet
- 2 - HTMLDocument31 pages2 - HTMLAli HassanNo ratings yet
- Introducing HTMLDocument431 pagesIntroducing HTMLshinde_jayesh2005No ratings yet
- Introduction to HTML 1Document10 pagesIntroduction to HTML 1ahmadmuhammadbuhari313No ratings yet
- Hyper Text Markup LanguageDocument21 pagesHyper Text Markup LanguageAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- HTML and CssDocument27 pagesHTML and CssNidhihsaNo ratings yet
- HTML Training by ThiruDocument122 pagesHTML Training by ThiruKumaran RNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document76 pagesCH 2amanuel g/egziabherNo ratings yet
- HTML AttributesDocument21 pagesHTML AttributesamitNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document78 pagesCH 2Ephrem HabtamuNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument45 pagesHTMLhamA lolNo ratings yet
- Web Development Foundation Study Guide: Cygen Technology 1Document25 pagesWeb Development Foundation Study Guide: Cygen Technology 1Bruno Hlaing Wayne AungNo ratings yet
- HTML 5 SlidesDocument95 pagesHTML 5 SlidesSon NickNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 - HTML Embed MultimediaDocument54 pagesLecture 13 - HTML Embed MultimediaTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- Web Technologies: HTML BasicsDocument34 pagesWeb Technologies: HTML BasicsShoaibNo ratings yet
- Web Programming NotesDocument82 pagesWeb Programming NotesHari Krishna GangavarapuNo ratings yet
- Module2 HTMLDocument53 pagesModule2 HTMLJerrymaeNo ratings yet
- Language of Web Page - HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) The Language of The WebDocument77 pagesLanguage of Web Page - HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) The Language of The WebGajendra ShrimalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-HTMLDocument4 pagesUnit 3-HTMLNeha BhandariNo ratings yet
- IWP MQP SolpdfDocument49 pagesIWP MQP Solpdfiamsurya195No ratings yet
- HTML5 Introduction FCDocument189 pagesHTML5 Introduction FCaaronot6No ratings yet
- HTML markup language guideDocument218 pagesHTML markup language guidepavanjammulaNo ratings yet
- HTML and CSS: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument34 pagesHTML and CSS: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StylewarshanjNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument304 pagesIlovepdf MergedKaviyarasi ArunkumarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1Document44 pagesUnit - 1Kaviyarasi ArunkumarNo ratings yet
- HTML Day 1Document23 pagesHTML Day 1Un KnownNo ratings yet
- Intro HTMLDocument75 pagesIntro HTMLJoy De los SantosNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument68 pagesHTMLNushail ZiyadhNo ratings yet
- 01 HTMLDocument44 pages01 HTMLahmednooh1402No ratings yet
- HTMLDocument31 pagesHTMLmanasailla666No ratings yet
- HTMLDocument23 pagesHTMLujjawalr9027No ratings yet
- Intro HTMLDocument106 pagesIntro HTMLvikrant patilNo ratings yet
- WEB TechDocument122 pagesWEB TechR RahulNo ratings yet
- 0 - HTML Notes For BCADocument22 pages0 - HTML Notes For BCAvandv prints100% (4)
- IP Chapter2Document95 pagesIP Chapter2Abenezer TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Final Term Exam Reviewer OkDocument4 pagesFinal Term Exam Reviewer OkAquino, Maricar A.No ratings yet
- HTMLDocument35 pagesHTMLMaha IbrahimNo ratings yet
- HTML NotesDocument8 pagesHTML NotesAbhishekNo ratings yet
- HTML (BScCsit 5th Semester)Document59 pagesHTML (BScCsit 5th Semester)Rishav Malla ThakuriNo ratings yet
- Attributes, Lists, Tables, Links, and Images: CS134 Web Design & DevelopmentDocument20 pagesAttributes, Lists, Tables, Links, and Images: CS134 Web Design & DevelopmentMohsin AwanNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer ScienceDocument85 pagesDepartment of Computer Sciencesiddiqadil2No ratings yet
- HTML CHEAT SHEETDocument9 pagesHTML CHEAT SHEETsam debNo ratings yet
- HTML NotesDocument15 pagesHTML NotesTusshar GuravNo ratings yet
- HTML Guide: Introduction to HTML Elements and StructureDocument7 pagesHTML Guide: Introduction to HTML Elements and StructureJorge García GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To HTMLDocument26 pagesIntoduction To HTMLAishwariya BudhraniNo ratings yet
- WebTechnology.Unit.II.NotesDocument16 pagesWebTechnology.Unit.II.Notessivani14565220No ratings yet
- Cours2 HTMLDocument13 pagesCours2 HTMLAchraf SallemNo ratings yet
- HTML - NoteDocument8 pagesHTML - NotePrasanna Niyadagala100% (1)
- HTML IntroDocument29 pagesHTML IntrorambabudugyaniNo ratings yet
- Future of AI according to expertsDocument2 pagesFuture of AI according to expertsYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- MatlabDocument2 pagesMatlabYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Top IDS/IPS, Vulnerability Scanning and NGFW Systems ComparedDocument3 pagesTop IDS/IPS, Vulnerability Scanning and NGFW Systems ComparedYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Detect bias and ensure ethical AIDocument3 pagesDetect bias and ensure ethical AIYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- To Whom It May Concern Tunisia, 30 March 2021Document1 pageTo Whom It May Concern Tunisia, 30 March 2021Yesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document1 pagePart 1Yesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- AI Concepts Quiz GradedDocument2 pagesAI Concepts Quiz GradedYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Future of AI according to expertsDocument2 pagesFuture of AI according to expertsYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Node and MangoDBDocument1 pageNode and MangoDBYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- What Is An AlgorithmDocument9 pagesWhat Is An AlgorithmYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Detect bias and ensure ethical AIDocument3 pagesDetect bias and ensure ethical AIYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- In This Lesson, You Have LearnedDocument2 pagesIn This Lesson, You Have LearnedYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Data Manipulation LanguageDocument2 pagesData Manipulation LanguageYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Graded: AI Issues, Ethics and BiasDocument2 pagesGraded: AI Issues, Ethics and BiasYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Bootstrap CSS and JS inclusionDocument1 pageBootstrap CSS and JS inclusionYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Checking Out A File From An Earlier Commit: Initializing The Folder As A Git RepositoryDocument2 pagesChecking Out A File From An Earlier Commit: Initializing The Folder As A Git RepositoryYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Graded: What Is AI? Applications and Examples of AIDocument2 pagesGraded: What Is AI? Applications and Examples of AIYesmine Makkes100% (1)
- SQL DefnDocument7 pagesSQL DefnYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- FlexBox will make it easier to design flexible responsive layout structure without using float or positioningDocument4 pagesFlexBox will make it easier to design flexible responsive layout structure without using float or positioningYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Data StructsDocument14 pagesData StructsYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Understanding APIsDocument17 pagesUnderstanding APIsYesmine Makkes100% (1)
- Entity RelationshipDocument6 pagesEntity RelationshipYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- General Sibling Combinator Direct Child Combinator Adjacent Sibling CombinatorDocument3 pagesGeneral Sibling Combinator Direct Child Combinator Adjacent Sibling CombinatorYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Git VCS guideDocument7 pagesGit VCS guideYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Var El Document - Queryselector ('H1') Console - Log ('El:', El)Document8 pagesVar El Document - Queryselector ('H1') Console - Log ('El:', El)Yesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Dev WebDocument6 pagesDev WebYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- An Algorithm Is A Process or Set of Rules To Be Followed in Calculations or Other Problem-SolvingDocument7 pagesAn Algorithm Is A Process or Set of Rules To Be Followed in Calculations or Other Problem-SolvingYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Web App Overview and ES6 FeaturesDocument11 pagesWeb App Overview and ES6 FeaturesYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- What Is Express - Js ?: WebsiteDocument19 pagesWhat Is Express - Js ?: WebsiteYesmine MakkesNo ratings yet
- Tayabas Western Academy: Founded 1928 Candelaria, Quezon Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesTayabas Western Academy: Founded 1928 Candelaria, Quezon Republic of The PhilippinesMarDj Perez GollenaNo ratings yet
- SSL For SharingDocument4 pagesSSL For Sharingshivraj zambareNo ratings yet
- Quiz App Javascript Report Css Mini Project-1Document32 pagesQuiz App Javascript Report Css Mini Project-1Kamini SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Sap Portal Hacking and ForensicsDocument87 pagesSap Portal Hacking and Forensicsjohnburn86No ratings yet
- AWSCertified Big Data SlidesDocument415 pagesAWSCertified Big Data Slidesbhh100% (1)
- Screenshots: 1. Search EBIR Forms in Your BrowserDocument22 pagesScreenshots: 1. Search EBIR Forms in Your BrowserJohn Paul AloyNo ratings yet
- Easter Secret Code Word CardsDocument11 pagesEaster Secret Code Word CardsClaudia MacarieNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Mobile Based Transcript Request Processing System Mbts IJERTV4IS070001Document5 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Mobile Based Transcript Request Processing System Mbts IJERTV4IS070001chisom aneneNo ratings yet
- How To Install LibreNMS in Centos 8Document29 pagesHow To Install LibreNMS in Centos 8Nendar AnubiezzNo ratings yet
- GARD 8000 System Emulator InstructionsDocument20 pagesGARD 8000 System Emulator InstructionsٍJordan SportNo ratings yet
- XC User ManualDocument84 pagesXC User ManualEliana Caceres Torrico100% (1)
- ABAP On HANADocument114 pagesABAP On HANAgvrahulNo ratings yet
- PracticeInClass Word2016 W9Document4 pagesPracticeInClass Word2016 W914-Bảo NgọcNo ratings yet
- Long QuizDocument2 pagesLong QuizJoms VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- How To Collect Dynamic Values Using Data Layer Variables - Analytics HelpDocument5 pagesHow To Collect Dynamic Values Using Data Layer Variables - Analytics HelpradhikaNo ratings yet
- Yottabyte PresentationDocument2 pagesYottabyte PresentationsaiNo ratings yet
- Installation and Configuration GuideDocument16 pagesInstallation and Configuration Guideantonio carlos peixoto de miranda gomesNo ratings yet
- CIS007 - Event Driven Programming and the Role of the DispatcherDocument4 pagesCIS007 - Event Driven Programming and the Role of the DispatcherLaxman ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Upload 5 Documents To Download: Document PDFDocument1 pageUpload 5 Documents To Download: Document PDFaminjamalNo ratings yet
- Stupid Python TricksDocument101 pagesStupid Python TricksVivek ApteNo ratings yet
- HTML NotesDocument3 pagesHTML NotesirnairNo ratings yet
- Windows Run CommandsDocument7 pagesWindows Run CommandsNagaraju GanapavarapuNo ratings yet
- TeraStation User Manual SetupDocument84 pagesTeraStation User Manual SetupRalph malphNo ratings yet
- Apache JMeter Online e - Tutorial Version 0.4Document2 pagesApache JMeter Online e - Tutorial Version 0.4Performance TestingNo ratings yet
- Isilon Solve Generator: Topic SelectionsDocument18 pagesIsilon Solve Generator: Topic SelectionsDavid VoicanNo ratings yet
- Onsen UI - Course IntroductionDocument19 pagesOnsen UI - Course IntroductionMahesh VPNo ratings yet
- AppConnect 4.8.0 For iOS SDK App Developers GuideDocument270 pagesAppConnect 4.8.0 For iOS SDK App Developers GuideDumitru GorelcoNo ratings yet
- CiscoDocument92 pagesCiscoari sirwanNo ratings yet
- Web Designing Course SyllabusDocument19 pagesWeb Designing Course Syllabusreena deviNo ratings yet
- Develop Websites and Components in Adobe Experience ManagerDocument277 pagesDevelop Websites and Components in Adobe Experience ManagerDominoDevelopNo ratings yet