Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Uploaded by
Aakif RazaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet Breathing and Exchange of Gases
Uploaded by
Aakif RazaCopyright:
Available Formats
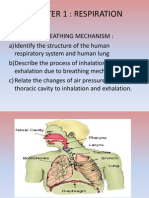
THE INDIAN SCHOOL
BIOLOGY
XI
Breathing and Exchange of gases
1. Name the pulmonary disease in which alveolar surface area involved in gas exchange is
drastically reduced due to damage in the alveolar walls :
a. Asthma
b. Pleurisy
c. Emphysema
d. Pneumonia
2. Bulk of carbon dioxide (CO2 ) released from body tissues into the blood is present as
a. Carbamino-haemoglobin in RBCs
b. Bicarbonate in blood plasma and RBCs
c. Free CO2 in blood plasma
d. 70% carbamino-haemoglobin and 30% as bicarbonate
3. The alveolar epithelium in the lung is
a. non-ciliated columnar
b. non-ciliated squamous
c. ciliated columnar
d. ciliated squamous
4. Blood analysis of a patient reveals an unusually high quantity of carboxyhaemoglobin
content. Which of the following conclusions is most likely to be correct?
a. The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of
carbon disulphide
b. The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of
chloroform
c. The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of
carbon dioxide
d. The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of
carbon monoxide
5. Name
a. the site where actual exchange of O2 and CO2 takes place between air and
blood in humans.
b. multicellular organisms in which anaerobic respiration takes place.
c. categories of people with higher vital capacity.
d. muscles that move ribs up and down
6. What is the role of oxyhaemoglobin after releasing molecular oxygen in the tissues?
7. What is principle behind diffusion of gases?
8. List the various features that facilitate the diffusion of O 2 from alveoli to the tissues
and that of CO2 from tissues to alveoli.
9. Give the average value of the following in a normal adult human
Tidal volume, Residual volume, Alveolar pO2 , Venous pO2
10. What will happen if the diaphragm of a human being is ruptured?
11. Differentiate between IRV and ERV.
12. In what form is O2 carried in the blood? What happens to it when the blood
reaches the tissues?
13. Explain how CO2 is transported from tissues to the lungs.
14. Describe the events involved in the process of breathing.
15. Explain why more O2 is released in the active tissues than in less active tissues?
16. The erythrocytes transport O2 but they respire anaerobically. Why?
17. Describe how contraction and relaxation of some muscles produce respiratory movements.
6. What is the role of molecular oxygen after releasing oxygen into the tissues
You might also like
- Respiratory Physiology MCQ'SDocument5 pagesRespiratory Physiology MCQ'SayashanpNo ratings yet
- 36 ch17 PDFDocument19 pages36 ch17 PDFShivamNo ratings yet
- Answer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)Document8 pagesAnswer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)gopeabhijit85No ratings yet
- 12 HDocument3 pages12 HManisha NishaNo ratings yet
- 11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesDocument7 pages11.17 Breathing and Exchanges of GasesMoonesh MKNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFDocument7 pagesChapter - 14 The Respiratory System PDFben martin100% (1)
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesArnav DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageSummative Test in Respiratory SystemMelvin Cabonegro100% (7)
- Respiratory - 2 - WsDocument5 pagesRespiratory - 2 - WsRatna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Respiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerDocument6 pagesRespiratory - 2 - Ws - Grade 8 Penabur - AnswerRatna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Section-I Mcqs and SeqsDocument3 pagesSection-I Mcqs and SeqsSadia NasirNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases WorksheetDocument2 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases Worksheetkaushikisrivastava95No ratings yet
- Summative Test in Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesSummative Test in Respiratory SystemJay CervantesNo ratings yet
- TERM 2 Chapter 7 Topical Revision Bio STPMDocument59 pagesTERM 2 Chapter 7 Topical Revision Bio STPMKeertana SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER Respiration and CirculationDocument5 pagesCHAPTER Respiration and CirculationlatasabarikNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesSummative Test in Respiratory SystemEden Manlosa100% (4)
- Reathing AND Xchange OF Ases: HapterDocument5 pagesReathing AND Xchange OF Ases: HapterAnannya Deshmukh100% (1)
- Test Bank For Exercise Physiology 8th Edition Scott PowersDocument17 pagesTest Bank For Exercise Physiology 8th Edition Scott PowersJamesJacksonjbpof100% (76)
- Class11 Biology Chapter 17. BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument5 pagesClass11 Biology Chapter 17. BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESrn0828027No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasessuryababaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasDocument7 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasParasNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument10 pagesNcert Solution Breathing and Exchange of GasesAyush DuttaNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch17-pdf1Document9 pages11 Biology Notes ch17-pdf1LishaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Quiz: Student Academic Learning ServicesDocument4 pagesRespiratory Quiz: Student Academic Learning ServicesFREDRICKNo ratings yet
- Breathing Exchange of GasesDocument9 pagesBreathing Exchange of Gasesravinderinst2No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Respiration Doc1Document6 pagesChapter 1 Respiration Doc1api-248021925No ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument16 pagesExercisePriyanshu PalNo ratings yet
- Self Quizzes Chapter 2-3: See This Figure Then Answer (1-2)Document3 pagesSelf Quizzes Chapter 2-3: See This Figure Then Answer (1-2)Dr DolittleNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes on Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument4 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes on Breathing and Exchange of GasesParimala deviNo ratings yet
- Physiology MCQ - RespiratoryDocument14 pagesPhysiology MCQ - RespiratoryJoseph95% (19)
- Breathing and ExchangeDocument10 pagesBreathing and ExchangeNalla Raghuram ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Notes on Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 17 Notes on Breathing and Exchange of Gasesfast-track for n2021No ratings yet
- Test Pitanja Iz Respiratornog Sistema Sa PrevodomDocument10 pagesTest Pitanja Iz Respiratornog Sistema Sa PrevodomzerohajdukNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 17 Breathing &exchange of Gases-NotesDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 17 Breathing &exchange of Gases-Notessukaina mumtazNo ratings yet
- Physiology 7 RespirationDocument6 pagesPhysiology 7 RespirationFahim Khan100% (14)
- 4 RespirationDocument6 pages4 Respirationनिरज न्यौपानेNo ratings yet
- Physiology MCQsDocument17 pagesPhysiology MCQsVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Feb2021 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17Document8 pagesNcert Solutions Feb2021 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 17TheLost GuyNo ratings yet
- Full HND Nursing Revision Questions .Document326 pagesFull HND Nursing Revision Questions .lalixs71No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument12 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gasessneh882016No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Study Notes 1Document8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Study Notes 1Raj priyam UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Breathing AnswersDocument1 pageBreathing AnswersCorry SepviaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 RespirationDocument18 pagesChapter 1 RespirationSaadiah MohammadNo ratings yet
- Test-Respiratory System Grade 8Document4 pagesTest-Respiratory System Grade 8ita yoowon50% (2)
- SPM Notes On Chapter RespirationDocument18 pagesSPM Notes On Chapter RespirationSyamila YusofNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science 1st Periodic Test ReviewDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Science 1st Periodic Test ReviewŁuci MattiasNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science, Chapter 1Document47 pagesForm 3 Science, Chapter 1qq23586% (56)
- Ch. 42 Past Test Circulation QuestionsDocument8 pagesCh. 42 Past Test Circulation QuestionsAsad YaminNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Breathing and Exchange of Gases: BIOLOGY - AssignmentDocument9 pagesChapter: Breathing and Exchange of Gases: BIOLOGY - Assignmentyogesh ahireNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ReviewerDocument8 pagesRespiratory ReviewerBLAIRY ZYNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. 2. A. B. C. D. 3.: Earth and Life Science 9 Worksheet 1 Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesA. B. C. D. 2. A. B. C. D. 3.: Earth and Life Science 9 Worksheet 1 Respiratory SystemRejNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismWindy SanNo ratings yet
- B6 Respiration and Gas Exchange.pagesDocument3 pagesB6 Respiration and Gas Exchange.pagesfakefake1025No ratings yet
- 1017MSC T6 Respiratory Revision Sheets & Answers 2011Document23 pages1017MSC T6 Respiratory Revision Sheets & Answers 2011MobarobberNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandFun Facts about Oxygen : Chemistry for Kids The Element Series | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Physick to Physiology: Tales from an Oxford Life in MedicineFrom EverandPhysick to Physiology: Tales from an Oxford Life in MedicineNo ratings yet
- Alicyclic Compounds: Monocarbocyclic Compounds C3-C5From EverandAlicyclic Compounds: Monocarbocyclic Compounds C3-C5No ratings yet
- Study Material - KEEPING QUIETDocument4 pagesStudy Material - KEEPING QUIETAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument59 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Samples Has The Largest Number of Atoms?Document2 pagesWhich of The Following Samples Has The Largest Number of Atoms?Aakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry WKDocument2 pagesClass 11 Chemistry WKAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Units and Measurement WS-1Document2 pagesUnits and Measurement WS-1Aakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 English Study Material - The Third LevelDocument5 pagesClass 12 English Study Material - The Third LevelAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Home Decor Tips for Personality and HarmonyDocument2 pagesHome Decor Tips for Personality and HarmonyAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- 11 Worksheet HydrocarbonDocument2 pages11 Worksheet HydrocarbonAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember For Note MakingDocument2 pagesPoints To Remember For Note MakingAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Happiness Lies in Simplifying LifeDocument4 pagesHappiness Lies in Simplifying LifeAakif Raza100% (1)
- English Worksheet Class Xi November 2021Document3 pagesEnglish Worksheet Class Xi November 2021Aakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesWorksheet PhotosynthesisAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Class XI English Core Worksheet 2 on Hornbill and Snapshots chaptersDocument2 pagesClass XI English Core Worksheet 2 on Hornbill and Snapshots chaptersAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Letter Writing FormatDocument10 pagesLetter Writing FormatAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Respiration in PlantsDocument1 pageWorksheet Respiration in PlantsAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ActionDocument9 pagesEnzyme ActionAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ActionDocument9 pagesEnzyme ActionAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument59 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesAakif RazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 ElectrolytesDocument115 pagesChapter 13 Electrolytessisay SolomonNo ratings yet
- Table No.1A Work Done Ground Section of Tooth (L.S, T.S) S. No. Date Title SignatureDocument38 pagesTable No.1A Work Done Ground Section of Tooth (L.S, T.S) S. No. Date Title SignatureSmila Mahajan NangiaNo ratings yet
- Penicillin G Drug StudyDocument1 pagePenicillin G Drug Studyjean therese100% (1)
- 5 Mechanisms and X-Ray Findings of AtelektasisDocument37 pages5 Mechanisms and X-Ray Findings of AtelektasisGalih Arief Harimurti WawolumajaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Trends in The Treatment Modalities andDocument4 pagesContemporary Trends in The Treatment Modalities andProsthodontics DeptNo ratings yet
- Healing Cancer The Cayce WayDocument6 pagesHealing Cancer The Cayce WayXavier Guarch100% (2)
- Congenital Ureteropelvic Junction ObstructionDocument11 pagesCongenital Ureteropelvic Junction ObstructionAimee FNo ratings yet
- Guillain Barre SyndromeDocument43 pagesGuillain Barre Syndromegabrielle magdaraogNo ratings yet
- Kegawatdaruratan Bidang Ilmu Penyakit Dalam: I.Penyakit Dalam - MIC/ICU FK - UNPAD - RS DR - Hasan Sadikin BandungDocument47 pagesKegawatdaruratan Bidang Ilmu Penyakit Dalam: I.Penyakit Dalam - MIC/ICU FK - UNPAD - RS DR - Hasan Sadikin BandungEfa FathurohmiNo ratings yet
- Hema I Chapter 11 - RBC IndicesDocument15 pagesHema I Chapter 11 - RBC IndicesKumneger DereseNo ratings yet
- 674-Article Text-5409-1-10-20210430Document6 pages674-Article Text-5409-1-10-20210430Rizca Cholidatun Ni'mahNo ratings yet
- BrastDocument4 pagesBrastSadishNo ratings yet
- Em Form NktiDocument7 pagesEm Form NktiJerico Wendell Gee RubioNo ratings yet
- Drug PowerpointDocument7 pagesDrug Powerpointanon-967218100% (9)
- Annexure 8: Medical Certificate (To Be Issued by A Registered Medical Practitioner) General ExpectationsDocument1 pageAnnexure 8: Medical Certificate (To Be Issued by A Registered Medical Practitioner) General ExpectationsRwitickNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ralph Moss Interview: Medical Writer, Author, and FilmmakerDocument27 pagesDr. Ralph Moss Interview: Medical Writer, Author, and FilmmakerRosa AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Clase 1-Fisiopatología de La Artritis ReumatoideaDocument45 pagesClase 1-Fisiopatología de La Artritis ReumatoideaPercy Williams Mendoza EscobarNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults Who Require Hospitalization - UpToDateDocument80 pagesTreatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults Who Require Hospitalization - UpToDateTran Thai Huynh NgocNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration, HomeostasisDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesis, Cell Respiration, HomeostasisTravis SatnarineNo ratings yet
- VBAC ScoreDocument3 pagesVBAC ScorepraburastraNo ratings yet
- Adventist University of The Philippines College of Dentistry Day 2 Set 6 Anesthesiology and PharmacologyDocument58 pagesAdventist University of The Philippines College of Dentistry Day 2 Set 6 Anesthesiology and PharmacologyRC DomeNo ratings yet
- Preparing For A Glucose Tolerance TestDocument3 pagesPreparing For A Glucose Tolerance Testconnect.rohit85No ratings yet
- Arul Kumar An 2013Document10 pagesArul Kumar An 2013Silvana ReyesNo ratings yet
- Identification of Salmonella Species PDFDocument23 pagesIdentification of Salmonella Species PDFMudrikaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Oral Cancer Diagnostic TechniquesDocument13 pagesEvaluation of Oral Cancer Diagnostic TechniquesSelvaArockiamNo ratings yet
- Pediatric MCQ Questions on Neuropathies, Genitalia, Heart Defects and MoreDocument17 pagesPediatric MCQ Questions on Neuropathies, Genitalia, Heart Defects and MoreAhmed Kassem100% (1)
- Gloves, gown, mask, eye protection as needed based on anticipated exposureDocument46 pagesGloves, gown, mask, eye protection as needed based on anticipated exposureJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Form 115B Student Tandem Medical Advice Form 2016Document4 pagesForm 115B Student Tandem Medical Advice Form 2016rubana555No ratings yet
- Question: 1 of 100 / Overall Score: 80%: True / FalseDocument84 pagesQuestion: 1 of 100 / Overall Score: 80%: True / FalseGalaleldin AliNo ratings yet
- Case Write Up 1-CholecystitisDocument9 pagesCase Write Up 1-CholecystitisAmbhi Gana100% (1)