Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kahoot
Uploaded by
DCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kahoot
Uploaded by
DCopyright:
Available Formats
Kahoot 1
1. In a competitive labour market, the demand curve for labour is given by the:
Marginal revenue product
2. A monopsony type of market failure is said to occur for which one of the following?
Buyers of labour have market power.
(monopsony - employers have market power)
3. Which condition is the most likely to lead to rise in union bargaining power?
A sustained rise In GDP
4. … represents employees of MNC in the EU in discussions with management on
transnational issues
The European Works Council (Directive)
5. A state of the labour market which is often linked to a lower wage for those employed:
Monopsony
6. When the return to the factor is greater than is needed for it to supply itself:
Economic rent
7. In a/an ….. the marginal cost of labour curve lie above the average cost of labour curve:
Monopsony
8. In a perfectly competitive labour market, firms are wage takers and the marginal cost of
labour equals:
The average cost of labour
9. The addition to total revenue from employing the last person:
marginal revenue product
10. That return to the factor just sufficient to cause it to supply itself:
Transfer earnings
Kahoot 2
1. Which reason is often used to support a policy to nationalise certain industries?
Easier to consider gap between private and social cost.
2. Which reason is often used to support a policy to privatise certain industries?
Firms exposed to market forces are more efficient
3. Which one of the following comes closets to being a ‘pure’ pure good?
Electricity, health service, postal service - can be private.
Military defence - pure public good
4. When the min efficient for firms output is greater than the output of the industry?
Natural monopoly.
5. The optimum level of economic activity and associated pollution from society’s point of
use?
MSB=MSC
marginal social benefits=marginal social cost
6. Which of the following is a problem which often confronts regulators of particular
industries?
Setting a price cap
(competition is good)
7. A situation in which buyers are less able to appreciate its quality than the suppliers
Asymmetric information (to parties have different amount of information - asymmetric)
8. Marginal social costs can be defined in which one of the following ways:
MARGINAL PRIVATE COST + MARGINAL EXTERNAL COST
9. The Coase theorem suggests which of the following regarding markets with
externalities?
Efficient agreements can be reached through private trades
10. Which is a challenge to using Pigouvian taxes to counteract a negative externality?
It is difficult to set the tax to perfectly offset the ext.
(On every product we have a tax)
Kahoot 3
1. Which of the following is likely to raise the value of national output/income?
Rise in withdrawals falling short of the rise in injections
2. Which of thre following is likely to reduce the value of national output/income?
Rise in withdrawals exceeding the rise in injections
3. National output of residents located in the country, before depreciation / including taxes
+ subsidies
GDP at market prices
(gross and we look in the market prices)
4. National output of residents, located home or overseas, after depreciation /excluding
taxes subsidies
NNP at factor cost
5. Which represents the difference between GNP at market prices and GDP at market
prices?
Net property income from abroad
6. Exogenous variables
Are determined outside the model and „independent variables“
7. Which of the following is a widely used measure of the standard of living
Real output (income) per head of population
8. What increases the rate of inflation when the economy is already at full capacity
(everybody has a job)?
A reduction in rates of income tax
9. Increases in which would be likely policies trying to close a „deflationary gap“?
Consumer spendings (opposite - savings)
10. Increases in which would be likely policies trying to eliminate a „inflationary gap“
Taxes (if taxes increase, withdrawals would increase)
Kahoot 4
1. Which of the following is consistent with the idea of automatic fiscal stabilisers
Government spending fall during boom times as unemployment falls.
2. Unemployment tape if the coal industry in the UK collapses due to a switch to green
energy?
Structural unemployment
3.Which of the following situations is most likely to result in „demand pull“ inflation?
Rise in investments/government spendings (no change in productivity)
4. A fall in the Euro exchange rate against the US dollar would have the following impacts?
German exports to USA become cheaper (in dollars)
5. A rise in the dollar exchange rate agains the euro would have the following effect?
US imports romFrance become cheaper (in Dollar)
6. Which of the following government policy measures is likely to reduce frictional
unemployment?
More efficient and better informed job centres
7. Which would be most favourable (other things equal) for US exporters to Eurozone?
A strengthening of the Euro against Dollar
8. If the economy experiences inflations, then aggregate…
… demand increases faster than aggregate supply
9. Off the following sequences of price levels, which correctly represents a 5% inflation
rate?
100, 105, 110.24, 115.76 increases)
10. The Philips curve says:
The higher the inflation, the lower the unemployment.
You might also like
- The Wyckoff MethodDocument7 pagesThe Wyckoff MethodWuU234575% (4)
- RESCISSION BY VENDOR AFTER DELIVERYDocument11 pagesRESCISSION BY VENDOR AFTER DELIVERYYannah Hidalgo100% (1)
- Assignment 1 Back Bay Battery Simulation Shreya Gupta Final PDFDocument10 pagesAssignment 1 Back Bay Battery Simulation Shreya Gupta Final PDFAditya MohamadNo ratings yet
- CKMM - ERP Financials - SCN WikiDocument4 pagesCKMM - ERP Financials - SCN WikiDavid JaimesNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Personal Finance 12th Edition by KapoorDocument55 pagesTest Bank For Personal Finance 12th Edition by KapoorRobert Allgood100% (35)
- Macroeconomics Basic ConceptsDocument20 pagesMacroeconomics Basic Conceptsneo0157No ratings yet
- Economics Notes From IGCSE AIDDocument50 pagesEconomics Notes From IGCSE AIDAejaz MohamedNo ratings yet
- IMT Covid19Document9 pagesIMT Covid19Manasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of Apollo HospitalsDocument19 pagesMarketing Strategies of Apollo Hospitalssab_fthNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Green Purchases of SHS StudentsDocument103 pagesFactors Influencing Green Purchases of SHS StudentsIya Muriel100% (2)
- Eco401 Short Notes 23 To 45Document7 pagesEco401 Short Notes 23 To 45abid ali60% (10)
- Positive Normative EconomicsDocument4 pagesPositive Normative EconomicslulughoshNo ratings yet
- Economic System: (1) Factors of ProductionDocument19 pagesEconomic System: (1) Factors of ProductionEmma WongNo ratings yet
- Part 1-Suggested Answers-Edited 12-2017Document4 pagesPart 1-Suggested Answers-Edited 12-2017nguyenphuongnhung887No ratings yet
- Economics - Long Answers-1Document4 pagesEconomics - Long Answers-1Gaurab DasNo ratings yet
- Market Scenarios: Perfect Competition, Monopoly, OligopolyDocument38 pagesMarket Scenarios: Perfect Competition, Monopoly, OligopolyAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS QUIZ WITH ANSWERSDocument9 pagesECONOMICS QUIZ WITH ANSWERSROHIT PATILNo ratings yet
- Key factors impacting international trade competitivenessDocument4 pagesKey factors impacting international trade competitivenessEldar SofticNo ratings yet
- Controversies in Trade PolicyDocument7 pagesControversies in Trade PolicyCarolina MinghettiNo ratings yet
- ECO 561 Final Exam AnswersDocument10 pagesECO 561 Final Exam AnswersdavidslewisNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics, Monetary Policy, GDP, Inflation, TradeDocument31 pagesMacroeconomics, Monetary Policy, GDP, Inflation, TradeVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Session 3: International Business Environments: Country CompetitivenessDocument12 pagesSession 3: International Business Environments: Country CompetitivenessasdasdaNo ratings yet
- Economics AssignmentDocument6 pagesEconomics Assignmentsolo_sudhanNo ratings yet
- Home AssignmentDocument29 pagesHome AssignmentHmmmmmmmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Business cycle phases and trade theories explainedDocument29 pagesBusiness cycle phases and trade theories explainedHmmmmmmmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Macro Ecomomic IssueDocument11 pagesMacro Ecomomic Issueskm_1988No ratings yet
- Week4 Monopoly+&+Document40 pagesWeek4 Monopoly+&+Jack_Nguyen81No ratings yet
- Questions.: 10 MCQ (5 Marks)Document20 pagesQuestions.: 10 MCQ (5 Marks)আলম হাসিবNo ratings yet
- Economics Assignment 2Document9 pagesEconomics Assignment 2EDWINNo ratings yet
- Economics Grade 11 Lesson Note 2Document10 pagesEconomics Grade 11 Lesson Note 2Eyerusalem solomonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To International TradeDocument57 pagesIntroduction To International Tradetareq tanjimNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Group A and CDocument1 pageHomework 2 Group A and CGabriel FernandesNo ratings yet
- Ppropriate Marketing Strategy For Your Company:-: Assignment-MBA (Sem-I) ECO7748-Managerial EconomicsDocument7 pagesPpropriate Marketing Strategy For Your Company:-: Assignment-MBA (Sem-I) ECO7748-Managerial EconomicsGaurav ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics CH 10Document40 pagesMacroeconomics CH 10karim kobeissi100% (1)
- Law (2023)Document3 pagesLaw (2023)phonewaizinNo ratings yet
- A042 - Dev Shah 1Document5 pagesA042 - Dev Shah 1dev shahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1.1Document2 pagesAssignment 1.1Heina LyllanNo ratings yet
- M.Com 1st Sem National Income ConceptDocument86 pagesM.Com 1st Sem National Income ConceptViraja GuruNo ratings yet
- Unit 5me (New)Document6 pagesUnit 5me (New)Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- Questions For Competitive Markets Type I: True/False Question (Give A Brief Explanation)Document3 pagesQuestions For Competitive Markets Type I: True/False Question (Give A Brief Explanation)Hạnh Đỗ Thị ThanhNo ratings yet
- The Political Economy of Trade PolicyDocument23 pagesThe Political Economy of Trade PolicyNeha SargamNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics FinalDocument9 pagesMacro Economics FinalDeepa RaghuNo ratings yet
- Economiccs New AssiggnmmentDocument27 pagesEconomiccs New AssiggnmmentShahana BegumNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Full Economics NotesDocument36 pagesIGCSE Full Economics NotesPoonam SInghNo ratings yet
- Economic Consequences of Export InstabilityDocument16 pagesEconomic Consequences of Export InstabilityNidhi BahotNo ratings yet
- Greek Yogurt Market Merger AnalysisDocument21 pagesGreek Yogurt Market Merger Analysisgiorgos1978No ratings yet
- The Context - Political Economy of Trade - Road MapDocument41 pagesThe Context - Political Economy of Trade - Road MapRoxana BadeaNo ratings yet
- Gaborone University College Macroeconomics ExamDocument9 pagesGaborone University College Macroeconomics ExamTawanda Leonard CharumbiraNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics AssignmentDocument13 pagesMacroeconomics AssignmentAlly SallimNo ratings yet
- Economics 11th Edition Michael Parkin Solutions ManualDocument18 pagesEconomics 11th Edition Michael Parkin Solutions Manualmarthalouisaq6x100% (27)
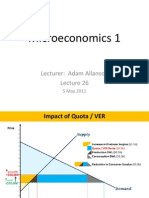
- Microeconomics 1: Lecturer: Adam AllansonDocument25 pagesMicroeconomics 1: Lecturer: Adam AllansonVicky Ke WangNo ratings yet
- Short Questions and Answers on EconomicsDocument8 pagesShort Questions and Answers on EconomicsPhương NôngNo ratings yet
- Elements of International BusinessDocument7 pagesElements of International Businesstania leonelaNo ratings yet
- 9) IndustriepolitikDocument16 pages9) IndustriepolitikMartina MazzettoNo ratings yet
- UOP E Assignments - ECO 365 & ECO 365 Final Exam Answers FreeDocument12 pagesUOP E Assignments - ECO 365 & ECO 365 Final Exam Answers FreeuopeassignmentsNo ratings yet
- Economic Policies Home AssignmentDocument7 pagesEconomic Policies Home AssignmentpalackmosokefeNo ratings yet
- Who Gains and Loses From TradeDocument4 pagesWho Gains and Loses From TradeOsmanNo ratings yet
- Ampi, Mary Jescho v. Midterm AnswersDocument5 pagesAmpi, Mary Jescho v. Midterm AnswersMary Jescho Vidal AmpilNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICSDocument8 pagesINTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICSksylviakinyanjui2No ratings yet
- Mulyiple Choice Questions On EcnomicsDocument4 pagesMulyiple Choice Questions On EcnomicssandeeproseNo ratings yet
- Effects of Subsidies on TradeDocument6 pagesEffects of Subsidies on TradeSatishSharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Microeconomics and MacroeconomicsDocument6 pagesUnit 1: Microeconomics and MacroeconomicsMạnh Đỗ ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Macroeconomics Basic Concepts and Scope of Macroeconomic Analysis What Is Macroeconomics?Document53 pagesIntroduction To Macroeconomics Basic Concepts and Scope of Macroeconomic Analysis What Is Macroeconomics?ZAKAYO NJONYNo ratings yet
- ECO111 - Written Assignment 2Document3 pagesECO111 - Written Assignment 2Thais HernandezNo ratings yet
- Poram 2 - Fob Po - PkoDocument12 pagesPoram 2 - Fob Po - PkoWaihong lamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MCQs and Analytical Qs Supply and DemandDocument8 pagesChapter 3 MCQs and Analytical Qs Supply and Demandhamna ikramNo ratings yet
- 3 2 2+activity+1Document7 pages3 2 2+activity+1Lesslie Anette Cortez SalinasNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy GameDocument9 pagesBusiness Strategy GameALI RAZANo ratings yet
- Market Forms and StructuresDocument12 pagesMarket Forms and StructuresKirankumar AriNo ratings yet
- AFM Assignment 2Document12 pagesAFM Assignment 2GetachewAwoke75% (4)
- Chapter1-2-3.2.2 IndustrialDocument40 pagesChapter1-2-3.2.2 IndustrialAlyNo ratings yet
- 13-46 Hilton AnswersDocument4 pages13-46 Hilton AnswersFernando Treviño Juarez100% (1)
- EVs Charging For Fleets - Has To Be EmobilityDocument30 pagesEVs Charging For Fleets - Has To Be EmobilitydavidalonsolorenzoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction Pricing As An Element of The Marketing MixDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Introduction Pricing As An Element of The Marketing MixYonneNo ratings yet
- Second-hand Panamax vs Newbuild Dry Bulk Carrier InvestmentDocument5 pagesSecond-hand Panamax vs Newbuild Dry Bulk Carrier InvestmentNikos NoulezasNo ratings yet
- Do Liquidity Measures Measure Liquidity by Goyenko, Holden, and Trzcinka (JFE 2009)Document29 pagesDo Liquidity Measures Measure Liquidity by Goyenko, Holden, and Trzcinka (JFE 2009)Eleanor RigbyNo ratings yet
- Marketing (MBA 7003) Assignment 2 - N02Document24 pagesMarketing (MBA 7003) Assignment 2 - N02Harsha KasunNo ratings yet
- Wassce / Waec Economics Syllabus: PreambleDocument7 pagesWassce / Waec Economics Syllabus: PreambleMichael Asante NsiahNo ratings yet
- Smart Buy LawsuitDocument26 pagesSmart Buy LawsuitjspectorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Guide to Securities MarketsDocument8 pagesChapter 03 - Guide to Securities MarketsZeinab MohamadNo ratings yet
- Costing ProblemsDocument7 pagesCosting ProblemsJoanne Pauline OcheaNo ratings yet
- Branding, PricingDocument24 pagesBranding, PricingKuldeep Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- THC 01-Module Nine &tenDocument19 pagesTHC 01-Module Nine &tenSidnnieanne BuenafeNo ratings yet
- ACS-01 (Assignment I)Document13 pagesACS-01 (Assignment I)Kovid Raj PoudelNo ratings yet
- FIFO Inventory Valuation and CostingDocument14 pagesFIFO Inventory Valuation and Costingrizwan ul hassanNo ratings yet
- MAF661 Test 2Document15 pagesMAF661 Test 2Norashikin Mohd Nor100% (1)
- Chapter 1 5 FinalDocument87 pagesChapter 1 5 FinalApollo Simon T. TancincoNo ratings yet