Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Description of Engine OM 607
Uploaded by
Robert GlavanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Description of Engine OM 607
Uploaded by
Robert GlavanCopyright:
Available Formats
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Engine data Unit OM 607.951
A 180 CDI
Rated output kW 80
at engine speed rpm 4000
Rated torque Nm 260
at engine speed rpm 1750-2500
Compression ratio ε 15.4:1
P01.00-3363-00
Performance graph
M Torque
OM 607.951 (80 kW)
P Power output
n Rpm
44 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
P07.16-3826-00
Top view of engine
1 High-pressure pump M16/6 Throttle valve actuator
N3/9 CDI control unit
B2/5 Hot film MAF sensor N14/3 Glow output stage
B2/5b1 Intake air temperature sensor R22/1 DPF heater booster regeneration
B6/1 Camshaft Hall sensor Y27/8 High-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
B50 Fuel temperature sensor actuator
B60 Exhaust pressure sensor Y76 Fuel injectors
G3/2 Oxygen sensor upstream of CAT Y77/1 Boost pressure positioner
Y94 Quantity control valve
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 45
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
P07.16-3827-00
View of engine from front
B40/6 Engine oil fill level sensor S43/1 Oil pressure switch
N3/9 CDI control unit Y77/1 Boost pressure positioner
N14/3 Glow output stage Y94 Quantity control valve
R22/1 DPF heater booster regeneration
46 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
P07.16-3828-00
View of engine from rear
3 Turbocharger G3/2 Oxygen sensor upstream of CAT
4 Diesel particulate filter with oxidation catalytic L5 Crankshaft position sensor
converter Y27/7 Low-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
actuator
B11/4 Coolant temperature sensor Y27/8 High-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
B19/9 Temperature sensor upstream of diesel actuator
particulate filter
B28/8 DPF differential pressure sensor
B157/2 EGR temperature sensor,
low pressure
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 47
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Belt drive Timing belt drive
The alternator and the A/C compressor (when New here is the use of a timing belt drive instead of
equipped with THERMATIC and THERMOTRONIC) a chain drive. The camshaft, coolant pump and the
are driven by a poly-V belt with six grooves. high-pressure pump are all driven by a toothed belt.
i Note
Repair instructions for changing the toothed belt
are available in the Workshop Information System
(WIS).
P13.20-2097-00 P05.10-2461-00
1 Poly-V belt 1 Crankshaft
2 Vibration damper 2 Coolant pump
3 Belt tensioner 3 High-pressure pump
4 Camshaft
A9 A/C compressor 5 Belt tensioning pulley
G2 Alternator 6 Toothed belt
48 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Turbocharging
The charging improves the degree of cylinder The compressed and thereby heated air flows over
charge. This in turn increases the engine torque and the charge air pipe to the charge air cooler. This
output. cools down the charge air and routes it over the
charge air pipe to the cylinder head.
In a supercharged engine the low pressure
compression and expansion are undertaken by an The boost pressure is regulated by the CDI control
upstream turbocharger. As a result the piston unit to match the following values and the relevant
driving mechanism can be smaller with the same components:
performance data, and this is coupled with fewer
• Charge air pressure and temperature sensor
mechanical losses. The turbocharger sucks in fresh
• Coolant temperature sensor
air through the air filter at the compressor inlet and
• Temperature sensor upstream of turbocharger
routes it by way of the compressor outlet into the
• Crankshaft position sensor for engine rpm
charge air pipe upstream of the charge air cooler.
• Injection quantity, dependent on injection
The high speed of the compressor impeller and the
period and fuel pressure
resulting high volumetric flow rate compresses the
• Exhaust back pressure sensor
air in the charge air pipe.
• Atmospheric pressure sensor
P14.20-2327-00
Charging layout
M16/6 Throttle valve actuator 1 Charge air cooler
B157/2 EGR temperature sensor, low pressure
Y27/7 Low-pressure exhaust gas recirculation A Charge air (uncooled)
actuator B Charge air (cooled)
Y27/8 High-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
actuator
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 49
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Boost pressure control
The boost pressure positioner is actuated for boost To act as protection against any thermal and
pressure control by the CDI control unit using a mechanical overloading of the turbocharger, the
pulse width modulated signal (5 to 95%). This then exhaust temperature is monitored by the CDI
continuously actuates the vacuum unit for boost control unit using the temperature sensor upstream
pressure control with vacuum to match the duty of the turbocharger and the exhaust back pressure
cycle. by the exhaust back pressure sensor. If a possible
thermal or mechanical overload is recognized, the
The adjustable guide vanes alter the flow cross-
boost pressure is reduced.
sectional area through which the exhaust flows
onto the turbine. They adapt the gas pressure
applied to the turbine to match the required boost
pressure. The speed of the turbocharger deter-
mines the volume of pre-compressed air and there-
fore the boost pressure.
i Note
A bypass bore (0.24 mm) ensures that there is a
constant opening in the ventilation (atmosphere)
to the control pressure. This is why it is not
possible to define a leak test for the boost pres-
sure positioner. The boost pressure positioner
function may be impaired by soiling of the inte-
grated filter.
P07.16-3812-00
Y77/1 Boost pressure positioner
50 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Injection system
The fuel injectors spray the fuel at high pressure
i Note
into the respective cylinder. Each injected fuel
quantity is dependent on the fuel pressure in the rail On engine 607 the fuel injectors are all coded with
and the actuation period for the corresponding the IIC code from Continental, which is located on
injection nozzle. The quantity control valve regu- the head of the injection nozzle. This coding spec-
lates the fuel quantity in the high-pressure pump. ifies the quantity characterization for each injec-
tion nozzle. If an injection nozzle is replaced, then
this coding must be notified to the CDI control unit
using Xentry Diagnostics.
P07.16-3829-00
Fuel high-pressure circuit
1 High-pressure pump B4/6 Rail pressure sensor
2 Rail B50 Fuel temperature sensor
3 High-pressure line Y76 Fuel injectors
Y94 Quantity control valve
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 51
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Post injection Heater booster DPF regeneration control
unit
Post injection is used to increase the exhaust
temperature and to support the conversion process The heater booster DPF regeneration control unit is
for the exhaust components in the oxicat and the located under the battery box and actuates the
regeneration of the diesel particulate filter (DPF). To heating elements of the heater booster DPF regen-
do so the load condition of the diesel particulate eration. It supports the thermal management as
filter is recorded with the aid of the differential pres- and when required, e.g. to enable the optimum
sure sensor (DPF). operating temperature of the diesel particulate
filter to be reached quicker so that the regeneration
New to the OM 607 are the heater booster DPF
process can be executed.
regeneration control unit and the heater booster
DPF regeneration. Increasing the engine load
through the heater booster diesel particulate filter
boosts the post injection volume far enough to
increase the exhaust temperature, and to ultimately
trigger the diesel particulate filter's regeneration
process. The soot particles in the exhaust are
subsequently burnt off.
P14.40-2474-00
N33/2 Heater booster DPF regeneration control unit
52 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Heater booster DPF regeneration Fuel preheating
The heater booster DPF regeneration is located at To ensure that the fluidity of the diesel fuel is
the front right on the engine. retained even at low outside temperatures, a
heating element is installed for fuel preheating in
The coolant flowing through is heated by four
the fuel filter housing.
heating elements and it is then routed to the
coolant pump feed line. The fuel preheating control unit is located under the
battery box.
The fuel preheating control unit actuates the
heating element for the fuel filter heater as and
when required, and it indicates the condensation
level in the fuel filter.
The fuel heater control unit is actuated when a
request is received from the CDI control unit over
the battery sensor LIN (LIN B15) by the drivetrain
control unit, and it activates the heating element for
the fuel filter heater in the fuel filter module.
i Note
The heating elements are integrated at the front of
the engine in the cooling circuit.
P14.40-2476-00
R22/1 DPF heater booster regeneration
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 53
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
The EGR reduces the nitrogen oxide (NOx) level in To do so, the CDI control unit in combination with
the exhaust. the drivetrain control unit reads in signals from the
following components:
The oxygen (O2) concentration in the combustion
chamber is reduced here. The combustion temper- • B2/5 Hot film MAF sensor
ature is lowered due to reduction in the combustion • Intake air temperature sensor
speed and through the higher heat capacity of the • Charge air pressure and temperature sensor
recirculated exhaust in comparison to the intake • Temperature sensor upstream of turbocharger
air. • Accelerator pedal sensor
• Exhaust back pressure sensor
The EGR is active from idle speed up to the upper
• Crankshaft position sensor
partial-load range. The EGR rate is determined rela-
• Exhaust flap controller actuator motor
tive to the engine load and engine rpm. The intake
• High-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
and air temperature, exhaust temperature and
actuator
exhaust back pressure are also considered.
• Low-pressure exhaust gas recirculation actuator
P14.20-2334-00
Exhaust gas recirculation system, schematic
1 Charge air cooler B2/5 Hot film MAF sensor
2 Exhaust gas recirculation cooler M16/6 Throttle valve actuator
3 Diesel particulate filter with oxidation catalytic M16/57 Exhaust flap controller
converter Y27/7 Low-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
4 Turbocharger actuator
A Intake air (fresh air) Y27/8 High-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
B Exhaust (low pressure) actuator
C Exhaust (high pressure)
54 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
P14.20-2328-00
EGR layout
1 Charge air cooler B157/2 EGR temperature sensor, low pressure
2 Low-pressure exhaust gas recirculation cooler M16/6 Throttle valve actuator
Y27/7 Low-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
actuator
Y27/8 High-pressure exhaust gas recirculation
actuator
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 55
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
High-pressure circuit exhaust gas recircu- Low-pressure circuit exhaust gas recircu-
lation lation
The CDI control unit evaluates the input signals of The exhaust gas recirculation actuator increases or
the components involved. The stored characteris- reduces the volume of recirculated exhaust gas to
tics map is then used as the basis for actuating the match the degree of actuation by the CDI control
engine high-pressure exhaust gas recirculation unit.
actuator. The different ways of actuating the
The exhaust gas cleaned by the diesel particulate
exhaust gas recirculation valves serve to regulate
filter with oxidation catalytic converter is routed
the untreated, recirculated exhaust gases.
through the drivetrain control unit into the EGR
The recirculated exhaust gases are routed into the cooler to match the actuation of the exhaust flap
charge air manifold on the cylinder head. controller. The cooled gas is routed over the
exhaust gas recirculation actuator downstream of
the hot film MAF sensor into the air intake pipe.
i Note
The exhaust gas recirculation actuators and the
exhaust flap controller are monitored through
their actual value potentiometers. P14.20-2329-00
M16/57 Exhaust flap controller
56 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
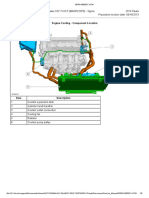
Cooling system and coolant circuit
In diesel engine OM 607 a toothed belt is used to The coolant circuit cools the engine, engine oil –
drive the coolant pump. coolant heat exchanger and exhaust heat
exchanger.
P20.00-2448-00
Coolant circuit, schematic
1 Engine radiator M13/5 Residual heat pump (with code (581) Comfort
2 Exhaust gas recirculation cooler automatic air conditioning and code (228)
3 Engine oil – Coolant heat exchanger Stationary heater)
4 Coolant expansion reservoir R22/1 DPF heater booster regeneration
5 Thermostat
6 Heater heat exchanger A Low temperature cooling circuit
7 Coolant pump B High-temperature cooling circuit
8 Restrictor C Coolant circuit ventilation
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 57
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Oil circuit
A volume-controlled oil pump supplies the oil circuit This configuration enables a lower amount of
with engine oil as and when required. energy to be used for the oil supply and it also
reduces consumption/CO2 levels.
The oil pan is made of an aluminum alloy to save
weight.
P18.20-2111-00
Oil circuit diagram
1 Oil pan A Oil filter
2 Crankcase B Engine oil – Coolant heat exchanger
3 Cylinder head C Oil pump
4 Turbocharger D Oil spray nozzle
E Plain bearing
58 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
Engine oil fill level sensor
The OM 607 engine is equipped with an engine oil The voltage applied to the connections is measured
fill level sensor in the front of the engine oil pan. It at the start of current flow (U1) and after a time
measures the current oil level in the oil pan using a period of t_1 (U2). To ensure that the current flow is
hot wire. constant the measuring points have to be adapted
accordingly, cf. dotted lines.
The measuring principle of the fill level sensor is
based on measuring the voltage U1 and U2 at the The difference in the two voltage values determines
terminals of the sensor within a specified period of how much of the hot wire is immersed in oil.
time. The sensor consists of a hot wire which is
To ensure that conditions are stable, the supply
immersed in the oil. The oil level can be calculated
voltage (Vbat) is recorded at each of the measuring
from voltage U1 and U2 and the battery voltage Vbat.
points, it will not be directly incorporated into the
Current only flows through the sensor for the dura-
calculation however.
tion of the measurement.
The measurement will be conducted once as of
For a time period of t_1=0.875 s a constant current
circuit 15 (ignition ON) and at engine OFF. If the
of I_TP=210.5 mA passes through a hot wire
engine is started before the measurement has run
thereby heating it up.
its course, the measurement will be aborted.
P18.40-2404-00
P18.40-2402-00
Fill level sensor measuring principle
B40/6 Engine oil fill level sensor 1 Higher oil level
2 Lower oil level
t Time
U Voltage
U1 Start of voltage measurement
U2 End of voltage measurement
U Voltage difference
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 59
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Description of engine OM 607
Drive
CDI control unit Drivetrain control unit
The CDI control unit and the drivetrain control unit The drivetrain control unit is located at the front left
in combination with the OM 607 engine's sensors behind the instrument panel.
and actuators forms the "CONTINENTAL SID 307"
The drivetrain control unit on the OM 607 engine
engine control system.
acts as an interface between the CDI
The CDI control unit actuates and coordinates the engine control unit and the CAN network.
input signals for the following system and functions
The following components, functions and systems
accordingly:
are controlled and coordinated:
• Fuel supply
• Alternator control
• Glue system control
• Fuel preheating
• Injection quantity control
• Radiator shutters
• Diagnosis and fault storage
• Fan motor
• Drive authorization system (DAS) and
• Manual transmission position sensor
immobilizer
• ECO start/stop function
• Thermal management
• Engine start
• Torque harmonization interface
• Exhaust gas recirculation
• Exhaust treatment
i Note
The CDI control unit is mounted to the air filter
housing and it is equipped with an internal atmo-
spheric pressure sensor.
P54.21--3317-00
P54.21-3301-00
N3/9 CDI control unit N 127 Drivetrain control unit
60 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Exhaust system
Drive
General Diesel engine OM 651
The exhaust system in all the engine variants The exhaust system of the 4-cylinder OM 651 diesel
consists of high-quality, corrosion-resistant chro- engine consists of:
mium and chromium-nickel steels which ensure a
• Decoupling element
long service life.
• Oxidation catalytic converter
On the gasoline engine the exhaust system is • Diesel particulate filter
equipped with a standard connecting point • Rear muffler
between the decoupling element and front muffler
All diesel models feature a diesel particulate filter
as well as a replacement-part connecting point
(DPF) as standard. Some national versions may
between the front and rear muffler.
deviate from this due to different emissions stan-
On the diesel engine the standard connecting point dards.
is located between the oxidation catalytic converter
and the decoupling element.
Catalytic converter system with particulate
filter
Gasoline engine M 270 DEH
The catalytic converter system includes a shared
The exhaust system of gasoline engine M 270 housing in the underfloor, which contains an oxida-
consists of: tion catalytic converter with a particulate filter
behind it. The particulate filter is made of silicone
• Catalytic converter
carbide and is able to filter solid particles out of the
• Decoupling element
exhaust gas at separation rates of over 98% relative
• Front muffler
to the particulate mass.
• Rear muffler
On the basic model, the exhaust flows out of the
rear muffler, which has a shell design, through a
tailpipe which is located in a concealed position
behind the bumper. Depending on the equipment
package involved, a twin-pipe exhaust system with
two visible exhaust tips is installed.
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 61
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Exhaust system
Drive
Diesel engine OM 607
The OM 607 engine in the new A-Class is equipped The rear end piece is formed by an invisible single-
with a newly-developed exhaust system to fulfill the pipe tailpipe (basic model) or two visible tailpipes
EU 5 emissions standard. with oval tip (depending on equipment package).
The exhaust system consists of:
• Decoupling element
• Oxidation catalytic converter
• Diesel particulate filter
• Exhaust gas recirculation cooler
• EGR line
• Exhaust flap with exhaust flap controller
• Rear muffler
P49.00-2146-00
Exhaust system for diesel engine OM 607, EU 5
version
B19/9 Temperature sensor upstream of diesel
1 Oxidation catalytic converter/diesel particulate filter particulate filter
2 Standard connecting point B28/8 Diesel particulate filter differential pressure
3 Decoupling element sensor
4 Rear muffler G3/2 Oxygen sensor upstream of CAT
5 Exhaust tip M16/57 Exhaust flap controller
62 b Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
Fuel system
Drive
The fuel tank is located in front of the rear axle The filling capacity of the fuel tank is 50 liters. This
under the rear bench seat. A blown High Density includes a reserve of roughly 6 liters. The fuel filler
Polyethylene (HDPE) fuel tank is used. The tank has flap is located at the left rear. No expansion reser-
multilayered wall structure (seven layers of plastic) voir is required because the expansion volume is in
as protection against hydrocarbon vapors. the tank itself.
P47.00-2209-00
Fuel tank for OM 607 diesel engine
1 Fuel tank B4/2 Fuel tank fill level sensor
2 Filler neck fuel level indicator, right
3 Fuel feed module M3 Fuel pump
Introduction of the New A-Class, Model Series 176 b 63
– This printout will not be recorded by the update service. Status: 06 / 2012 –
You might also like
- SSP 157 - ABF Engine ManagementDocument13 pagesSSP 157 - ABF Engine ManagementMatt DethNo ratings yet
- Map-Controlled Cooling and Camshaft Timing for 2.0L and 3.0L EnginesDocument40 pagesMap-Controlled Cooling and Camshaft Timing for 2.0L and 3.0L Enginesget_prasadns3358100% (1)
- SSP 405 14l 90kw Tsi Engine With TurbochargerDocument32 pagesSSP 405 14l 90kw Tsi Engine With TurbochargerBernard AlferlatenNo ratings yet
- VW SSPDocument46 pagesVW SSPMauri accattoliNo ratings yet
- GlkclassDocument110 pagesGlkclassnhanlam0402No ratings yet
- 1.6 66 77 2.0 105 110 135 KW TDI CR EngineDocument397 pages1.6 66 77 2.0 105 110 135 KW TDI CR EngineRSTNo ratings yet
- SSP 252 1.4 Lupo FSi EngineDocument56 pagesSSP 252 1.4 Lupo FSi EngineGoran CakoNo ratings yet
- Motor Tracker Peugeot - 8-Valve Engine DescriptionDocument23 pagesMotor Tracker Peugeot - 8-Valve Engine DescriptionJeferson WojcikiNo ratings yet
- VW-AUDI SSP 498 EngDocument64 pagesVW-AUDI SSP 498 EnggeorgescuriosNo ratings yet
- D4B802F7874-SSP 951103 Variable Automatic Transmission Multitronic 01JDocument106 pagesD4B802F7874-SSP 951103 Variable Automatic Transmission Multitronic 01JwaggcasNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Basic Diesel Engine Maintenance SecretsDocument20 pagesTop Ten Basic Diesel Engine Maintenance SecretsdonlynNo ratings yet
- SSP 992003 A6 AllroadquattroDocument56 pagesSSP 992003 A6 Allroadquattroandrei-bobNo ratings yet
- Audi A6 2005 Workshop Manual Service Repair GuideDocument89 pagesAudi A6 2005 Workshop Manual Service Repair GuideIancu GabrielNo ratings yet
- Porsche Engine Power PlusDocument4 pagesPorsche Engine Power PluswattafillingNo ratings yet
- BMW N20 Valvetronic GearDocument8 pagesBMW N20 Valvetronic GearClaudio ArakakiNo ratings yet
- The EA888 2.0L TSI Engine Gen III B: Self Study Program 820173Document21 pagesThe EA888 2.0L TSI Engine Gen III B: Self Study Program 820173MARIO100% (1)
- SSP - 212 Variable Intake Manifold in VR EnginesDocument20 pagesSSP - 212 Variable Intake Manifold in VR EnginestekNo ratings yet
- p5 5S-FE+ENGINE+REPAIR+MANUALDocument23 pagesp5 5S-FE+ENGINE+REPAIR+MANUALkavindaNo ratings yet
- SSP 508 The 1.0l 44 55 KW MPI EngineDocument36 pagesSSP 508 The 1.0l 44 55 KW MPI Enginedavorin59No ratings yet
- SSP+19+1 6L+1 8l+petrol+enginesDocument48 pagesSSP+19+1 6L+1 8l+petrol+enginesMurugan KNo ratings yet
- 1.8 5v Turbo DTC Obdii Fuel and IgnitionDocument20 pages1.8 5v Turbo DTC Obdii Fuel and IgnitionCristian CernaNo ratings yet
- 2.0-Litre Engine - SSP 233 OnlineDocument41 pages2.0-Litre Engine - SSP 233 OnlineHAMDANE HAMDANE100% (1)
- Ssp338 - The Golf Plus 2005 - Part 1Document27 pagesSsp338 - The Golf Plus 2005 - Part 1vsoltasidis7781100% (1)
- N63TU Engine PDFDocument76 pagesN63TU Engine PDFJURIJNo ratings yet
- International Engine of The Year Awards - 2012Document44 pagesInternational Engine of The Year Awards - 2012ahmtrNo ratings yet
- SSP 292Document46 pagesSSP 292Roberto VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- Byt BZB 1 8 Tsfi EngDocument51 pagesByt BZB 1 8 Tsfi EngΤασος ΑΜ100% (3)
- The New Mercedes Benz Four Cylinder Diesel Engine For Passenger CarsDocument8 pagesThe New Mercedes Benz Four Cylinder Diesel Engine For Passenger CarsBobCavNo ratings yet
- 4-Cylinder Direct Injection Engine (1 8 2 0 LTR 4-Valve - Generation II)Document397 pages4-Cylinder Direct Injection Engine (1 8 2 0 LTR 4-Valve - Generation II)AlanGaoNo ratings yet
- Service Training: Audi 2.0 Liter Chain-Driven TFSI EngineDocument58 pagesService Training: Audi 2.0 Liter Chain-Driven TFSI EngineMihaela GeorgescuNo ratings yet
- MULTI AIR ENGINE TECHNOLOGY CUTS FUEL CONSUMPTIONDocument13 pagesMULTI AIR ENGINE TECHNOLOGY CUTS FUEL CONSUMPTIONSivaji Liar100% (1)
- 2016 Ford Focus Owners Manual Version 4 - Om - EN US EN CA - 07 - 2016Document397 pages2016 Ford Focus Owners Manual Version 4 - Om - EN US EN CA - 07 - 2016Biro Gergely Noemi100% (1)
- Jaguar: Electrical Diagnostic ManualDocument176 pagesJaguar: Electrical Diagnostic Manualinfocarsservice.deNo ratings yet
- Audi A5 - SuspensionDocument56 pagesAudi A5 - SuspensionCarlos Garcia GodoyNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Brakes in Audi VehiclesDocument24 pagesCeramic Brakes in Audi VehiclesKhaled Barghouthi67% (3)
- GDIDocument7 pagesGDIlinhda561No ratings yet
- Abarth 500 2012 Misc Documents-PowertrainDocument5 pagesAbarth 500 2012 Misc Documents-PowertrainMusaHamzicNo ratings yet
- GdiDocument22 pagesGdiAnonymous ysrxggk21c100% (1)
- Twin Spark TechDocument23 pagesTwin Spark TechJainul PatelNo ratings yet
- SSP - 451 - Audi TT RS Avec Moteur TFSI R5 de 2,5 LitresDocument52 pagesSSP - 451 - Audi TT RS Avec Moteur TFSI R5 de 2,5 Litresfrancois.garcia31100% (1)
- Variable Valve TimingDocument3 pagesVariable Valve Timingsandesh ganigaNo ratings yet
- BMW 330e Plug-In Hybrid Sports SedanDocument20 pagesBMW 330e Plug-In Hybrid Sports SedanKok Hui DiongNo ratings yet
- Skoda Rapid Brake Systems EngDocument159 pagesSkoda Rapid Brake Systems EngRobert AlexandruNo ratings yet
- About GDIDocument36 pagesAbout GDInicolae_popescu_18No ratings yet
- Luk Clutch Course: Introduction To Clutch Technology For Cars and LcvsDocument60 pagesLuk Clutch Course: Introduction To Clutch Technology For Cars and LcvsKeval KamaniNo ratings yet
- SSP 327 - Audi Engines - Chain Drives - Part 2Document47 pagesSSP 327 - Audi Engines - Chain Drives - Part 2McGiver990100% (2)
- F11 DriveDocument44 pagesF11 DriveLucian GrigorieNo ratings yet
- SSP 420 2.0L TDI Engine With Common Rail Injection SystemDocument64 pagesSSP 420 2.0L TDI Engine With Common Rail Injection SystemVictor Andres BombinNo ratings yet
- Unit Injectors With Piezo Valves: Self-Study Programme 352Document24 pagesUnit Injectors With Piezo Valves: Self-Study Programme 352Truong Tran van100% (1)
- Honda Develops High-Efficiency Motor and PCU for Hybrid VehicleDocument7 pagesHonda Develops High-Efficiency Motor and PCU for Hybrid VehicleDeepak ChachraNo ratings yet
- SSP 406 VW Adaptive Chassis Control DCCDocument32 pagesSSP 406 VW Adaptive Chassis Control DCCKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Fiche Mot Diesel-DW10 FC PDFDocument2 pagesFiche Mot Diesel-DW10 FC PDFlada1119No ratings yet
- Mercedes Benz Automatic Transmission Control UnitDocument7 pagesMercedes Benz Automatic Transmission Control UnitReza VaraminiNo ratings yet
- Engine Cooling 1.6 Duratec 16V Ti VCTDocument2 pagesEngine Cooling 1.6 Duratec 16V Ti VCTIsmael Lopez100% (1)
- Engine Specifications: H.Harada K.SanadaDocument5 pagesEngine Specifications: H.Harada K.SanadaJohn GarnetNo ratings yet
- Main Engine DetailDocument9 pagesMain Engine DetailRashid Mahmood JaatNo ratings yet
- Spec Sheet Dl08 Ind 1Document8 pagesSpec Sheet Dl08 Ind 1Văn Tuấn Nguyễn100% (1)
- Spek Centriguges 5702 - E-CatalogDocument1 pageSpek Centriguges 5702 - E-Cataloghans hutajuluNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Catalog InjectoresDocument11 pagesCaterpillar Catalog Injectoresdjdahli100% (4)
- Loop Scavenging PDFDocument8 pagesLoop Scavenging PDFSandeep KulathapallilNo ratings yet
- Vol 2+3 K98ME PDFDocument865 pagesVol 2+3 K98ME PDFMarijaŽaper100% (1)
- Copy (1) My SWEP Report 2010Document30 pagesCopy (1) My SWEP Report 2010Fayemi Slim Oluwasola80% (5)
- Izuzu Motor x22 SeDocument102 pagesIzuzu Motor x22 SeGerardo FloresNo ratings yet
- Om 457 La Bluetec /om 457 La Om 460 La Bluetec /om 460 La: Operator'S ManualDocument104 pagesOm 457 La Bluetec /om 457 La Om 460 La Bluetec /om 460 La: Operator'S Manualhicham belallamNo ratings yet
- V2500 & CFM56 Difference PDFDocument5 pagesV2500 & CFM56 Difference PDFBahador100% (3)
- 307.1074.3.5 (En) Air Cooled Engine Serie 1000Document172 pages307.1074.3.5 (En) Air Cooled Engine Serie 1000Lacatusu Mircea100% (1)
- Starter LM 2500Document1 pageStarter LM 2500Aek DekaNo ratings yet
- Volvo D16-500V - 2050-Xe PDFDocument2 pagesVolvo D16-500V - 2050-Xe PDFDIONYBLINK100% (1)
- 5 Gas Exchange Processes - UpdatedDocument24 pages5 Gas Exchange Processes - UpdatedShahzaib Anwar OffNo ratings yet
- AD250-6 CompressedDocument5 pagesAD250-6 Compressedangienav5No ratings yet
- Index SBDocument46 pagesIndex SBdzakub100% (1)
- Carnot Cycle Efficiency FormulaDocument5 pagesCarnot Cycle Efficiency FormuladsathiyaNo ratings yet
- 4045DF158 POWERTECH SPECIFICATIONS For Gen Set ApplicationsDocument2 pages4045DF158 POWERTECH SPECIFICATIONS For Gen Set ApplicationsMohammed ShafekNo ratings yet
- Timing Belt - AutodataDocument6 pagesTiming Belt - AutodatacecoldclubNo ratings yet
- Hunk Oct 2007Document98 pagesHunk Oct 2007Oxen PartsNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Cat 16H NA Motor Grader (Prefix 6ZJ) Service Repair Manual (6ZJ00001 and Up)Document27 pagesCaterpillar Cat 16H NA Motor Grader (Prefix 6ZJ) Service Repair Manual (6ZJ00001 and Up)kfm8seuuduNo ratings yet
- Wartsila RTA96C Engine Technology Review PDFDocument24 pagesWartsila RTA96C Engine Technology Review PDFArgenis JimenezNo ratings yet
- DeltaHawk Brochure - 2018Document4 pagesDeltaHawk Brochure - 2018Pablo De FelipeNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Study of The Components of The EngineDocument14 pagesChapter - 3 Study of The Components of The EngineKenmoe T DonasNo ratings yet
- Torque Specs for 1KD-FTV Diesel Engine PartsDocument1 pageTorque Specs for 1KD-FTV Diesel Engine PartsTAMIRU TESFAYE100% (1)
- Operation & DataDocument506 pagesOperation & DataАндрей АндреевNo ratings yet
- 1564473186374-Question Bank SrDME DSLDocument43 pages1564473186374-Question Bank SrDME DSLVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- NSF250R PRESS INFORMATIONDocument24 pagesNSF250R PRESS INFORMATIONGuy ProcterNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions: Black/White From Original HarnessDocument2 pagesInstallation Instructions: Black/White From Original HarnessbikewireNo ratings yet
- Spec Sheet Jw6h-Ufaa-Ad c133422Document4 pagesSpec Sheet Jw6h-Ufaa-Ad c133422janter edward marpaung100% (1)
- Curtis TurbineDocument18 pagesCurtis TurbineDivya Prakash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering Code No: R1622032Document6 pagesThermal Engineering Code No: R1622032ashoku24007No ratings yet
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesFrom EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Renewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandRenewable Energy: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsFrom EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- OFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyFrom EverandOFF-GRID PROJECTS: A Comprehensive Beginner's Guide to Learn All about OffGrid Living from A-Z and Live a Life of Self-SufficiencyNo ratings yet
- The Boy Who Harnessed the Wind: Creating Currents of Electricity and HopeFrom EverandThe Boy Who Harnessed the Wind: Creating Currents of Electricity and HopeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (130)
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemFrom EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressFrom EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentFrom EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesFrom EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Implementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachFrom EverandImplementing an Integrated Management System (IMS): The strategic approachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successFrom EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresFrom EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNo ratings yet
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsFrom EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- The Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureFrom EverandThe Grid: The Fraying Wires Between Americans and Our Energy FutureRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (48)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualFrom EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridFrom EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Biogas Production: Pretreatment Methods in Anaerobic DigestionFrom EverandBiogas Production: Pretreatment Methods in Anaerobic DigestionNo ratings yet
- DIY Free Home Energy Solutions: How to Design and Build Your own Domestic Free Energy SolutionFrom EverandDIY Free Home Energy Solutions: How to Design and Build Your own Domestic Free Energy SolutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Machine Learning and Data Science in the Oil and Gas Industry: Best Practices, Tools, and Case StudiesFrom EverandMachine Learning and Data Science in the Oil and Gas Industry: Best Practices, Tools, and Case StudiesPatrick BangertRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Energy, Light and Electricity - Introduction to Physics - Physics Book for 12 Year Old | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandEnergy, Light and Electricity - Introduction to Physics - Physics Book for 12 Year Old | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Solar Electricity Basics: Powering Your Home or Office with Solar EnergyFrom EverandSolar Electricity Basics: Powering Your Home or Office with Solar EnergyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Air-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AFrom EverandAir-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&ARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)