Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 2 Understand CO1: Mobile Computing Security - (Wireless Network + Cellular Network)
Uploaded by
wexidaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 2 Understand CO1: Mobile Computing Security - (Wireless Network + Cellular Network)
Uploaded by
wexidaCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Show the benefits of using mobile computing with 2 Understand CO1
examples.
Mobile Computing - Computing environment over physical mobility.
The user of mobile computing environment will be able to access data, information or logical objet from
any device in any network while on a move.
-------------------------------- Mobile Computing benefits - Advantage and Disadvantage
---------------------------1) Availability - System and its services are available at any time.
2) Location Flexibility - Use of portable device allowed many employees to continue their work,
regardless of the lo cation.
3) Increased Productivity - As MC allows to be available all time, there are higher rates of engagement
and productivity. (Fr eg - Application developed in Android) - Connectivity using Phone.
4) Cost Effective - As employee can work from their home, --> Overhead cost is low. For E.g. -> No need
of an equipment for an employee- (computer, desk etc.)
2 Relate the security concerns of mobile users with needs of 2 Analyze CO2
mobile user
Mobile Computing Security - (Wireless Network + Cellular Network)
1) User Authentication - It is a process which confirms user's identity, to ensure that user really is who
he claims to be. Authentication Factors
– 1.1) Knowledge Factors - (Something user knows) - Password, Passphrase, Personal Identification
number (PIN), Secruity Question.
1.2) Ownership Factors - (Something user has) - ID Card, Security Token, Implanted Device.
1.3) Inherence Factors - (Something user is or does) - DNA sequence, Fingerprint, Voice, Face, Signature,
Retinal Pattern.
*1.4) Something you do - typing speed, locational information, Captchas,
Types of Authentication –
1) Single Factor Authentication- User provide only username and password to get authenticate to use
any website.
2) Two factor Authentication - Combination of login credentials + something (Could be a PIN), later use
to authenticate yourself.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
3) Multi Factor Authentication - Take more than one factor to authenticate ---> Username + password
with PIN and with biometric factor.
4) One Time Password (OTP) - automatic generated alphanumeric character, active for few minutes to
use, to authenticate yourself. Once that OTP is used it is going to be expire and never work.
5) API Authentication - API key Authentication - Google Webmaster - API Key
6) Open Authentication (Login with facebook). -> "Home work"
Security Attacks –
1) BruteForce Attack.
2) Dictionary Attack.
3) Password Sniffing (Wireshark, BRO, NMAP)
4) Man in the Middle Attack (DNS, ARP, Session Hijacking).
2) User Access Control (Authorization) - allows only those user to connect to network, who are
authenticated or per mitted access via network admin.
3) Data Privacy - Ensure the data transmitted over network is completely encrypted and not eavesdrop
by unauthorised person. HTTPS, SSH, RSA(Anonymous Network) --> Fingerprinting -> Grabbing
information from the activity doing over the internet. Cookie, Session, Social Engineering(trick your
mind), man in the middle attack, User String (Browser Version, Operating System, Encoding Styles) -->
"Enumeration Techniques".
4) Data Integrity - Check the message /data from sender to receiver in between it is not
altered/modified by the intruder.
5) key Management - Creation, protection and distribution of keys used for encrypting data.
3 Compare different propagation modes and enlist which 2 Analyze CO2
one is better in what scenario.
Different Propogation Modes-
*Guided Media - Wired -- > We will not cover ->
*Unguided Media - Wireless --> We will cover -> Medium - AIR
-> Transport electromagnetic waves without any physical conductor - "Wireless
Communication".
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
In electromagnetic spectrum - ranging from 3Khz - 900Thz is for wireless connection.
3 Propogation mode
1) Ground Wave (Below 2Mhz)- Radio wave travel through the lowest portion of the
atmosphere.
- Low Frequency signal emnate in all direction from the transmitting antenna and follow the
curvature of the planet.
—
- Distance depends upon the power of the signal (higher the power, larger the signal).
2) Skywave Propogation (2-30Mhz) — Higher frequencies radiates upwards into the ionosphere.
(DTH - Direct to Home).
3) Line of Sight (Above 30Mhz) - Very high frequencies , transmit in straight line, directly from
antenna to antenna
Antenna must be directional, facing each other, or either tall enough to not to be affected by the
curvature of the earth
4 Analyze different strategies for channel assignment 2 Understand CO1
Channel Assignment Strategies-
------------------------------
1) Fixed Channel assignment
2) dynamic channel assignment
3) handoff assignment
1) Fixed channel assignment -
channels are pre-allocated to different cell.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
cell1 - 50Khz, cell2 - 40Khz, cell3 - 60Khz.
Following aspects -
-Any new call attempts in a cell, after all the channels of that cell become occupied. ---> New user is
going to be blocked.
- very simple and requires least of processing.
- Problem - New user can't handle
Resolve using -"Borrowing process"
- Cell in this channel is allowed to borrow channel from adjacent cell, if their channels are fully occupied,
while adjacent cell have free channels.
---> Borrowing Process --> can be handle by --> MSC -> Mobile Switching Centre. Big office (main office
of BSNL).
MSC -->
a) monitor the process and give permission to borrowing cells, to borrow channel on following aspects -
1) donating cells is not affected by the borrowing process.
2) No interference will occur by moving the channel from one cell to another.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
----------------------------------------------
Dynamic Channel Assignment Strategy
------------------------------------
- Channels are not pre allocated to any cells.
- Any channel can be allocated to any desired cell during the operation of the system, or if any cell is
asking for the channel.
Following aspects -
1) Each MSC monitors all cells and all channels.
2) Each time a cell request made, a MSC assings a channels to Base station(BS).
3) MSC has some processing algorithms -
Possibility of future blocking in cells.
frequency being used in the cell.
Reuse Distance of the channel.
4) MSC assigns a channel only if it is not used, and if it will not cause co-channel interference with any
cell.
5) MSC processing algorithm provides higher capacity --> less blocking.
6)But it requires high computational power.
7) MSC collects real time data of channel occupancy, traffic distribution, RSSI(Radio signal strength
indicator).
--------------------------------------------------------
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
3)Handoff/Handover strategy
---------------
process of transferring and active call from one cell to another cell as the mobile unit moves from first
cell to other cell, without disconnecting the call.
The amount of received power by mobile phone or the amount of received power by tower(acces
point), or both are usually need to determine, whether a handoff is necessary or not.
---------------------------- ***-------------------------------
5 Derive the equation for distance to frequency reuse ratio 2 Understand CO1
Let T = total number of duplex channels K cells = size of cell cluster (typically 4, 7,12, 21)N = T/K =
number of channels per cell
For a specific geographic area, if clusters are replicated M times, then total number of channels
– system capacity = M xT
– Choice of K determines distance between cells using the same frequencies – termed co-channel cells
– K depends on how much interference can be tolerated by mobile stations and path loss
Example: cell cluster size K = 7, frequency reuse
factor = 1/7, assume T = 490 total channels,
N = T/K = 70 channels per cell
Assume T = 490 total channels,K = 7,
N = 70 channels/cellClusters are replicated M=3 times System capacity = 3x490 = 1470 total channels
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
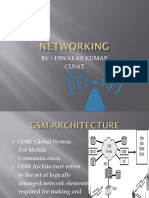
6 Discuss GSM Architecture in detail with its 5 Understan CO1
suitable Diagram. d
GSM Architecture
----------------
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
There are three section of GSM Architecture
a) Radio Subsystem (RSS)
b) Network and Switching System (NSS)
c) Operating Subsystem OSS)
1) Radio Subsystem - MS + BSC
-----------------------------
- It mainly consist of MS (Mobile Station) - this MS consist of Mobile equipment (ME)(your device)
and SIM (Subscriber Identity Module).
ME --> IMEI
SIM --> IMSI
Base Transceiver System (BTS)
-----------------------------
- It is a radio transceiver system (transmit + receive), within the coverage area of cell.
- It allows MS to commmunicate with the network, through a radio link.
- Transmission and Reception at the BTS with the MS is done via - omnidirectional and directional
antenna.
- Major function is to transmit the signal of desired function with a proper format.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
---------------------------------------------------------
Base Station Controller (BSC)
- More than one BTS are connected and controlled by one BSC.
- Handles the switchover of a mobile user from one BTS to another BTS during roaming and handoff.
- It also controls the transmitted power.
- It uses Time division multiplexing (TDM) to communicate with BTS.
--------------------------------------------------
Transcoding and Rate Adaptation Unit (TRAU)
---------------------------------------------
It is a logical part of BSC, but resides very close to MSC, to reduce the significant transmission cost.
The most important role of TRAU is to convert the speech from 16Kbps to 64 Kbps over the PSTN or
ISDN network.
================================================================
b) Network Switching Subsytem (NSS)
Consist of MSC (Mobile Switching Centre) - has many database HLR(home location register) VLR (visiting
location register),
Mobile Switching Center (MSC)
-Many BSC is going to be handle by one MSC.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
- It plays a major role in supporting mobility of a user.
- It controls both switching and management together by controlling the number of BSC to it.
- it also does the registration and authentication of a user and its equipment
- When a request comes, MSC sends the request to the authentication center for the user information
and performs authentication.
- Once authentication done, only then the MSC registers the MS with its associated VLR.
- This information is updated with the HLR, that may reside in the same network.
- It also routes the call from one MSC to other MSC.
- It does the formatiing, if one end is using PSTN and the other end is using ISDN.
Home Location Register(HLR)
- It maintained all the information related to the mobile subscriber in its database.
- The database in HLR remains intact and unchanged until the termination of the subscription.
- HLR is a huge database, located with this home network, which stores the administrative information
of the mobile subscriber - Subscriber current location (give by VLR), type of subscription, IMSI.
Visiting Location Register (VLR)
- This gives the current location of mobile station.
- the database is temporary. , to which the subscriber currently registers.
- it is dynamic in nature, and interacts with HLR when recording the data of particular mobile subscriber.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
- If a user under VLR makes a call then VLR precisely knows the position of the user in a single cell.
============================================================
c) Operation Subsystem (OSS)
Consist of AuC (Authentication Center) + EIR (Equipment Identity Register) + OMC (Operating and
Management Center)
Authentication Center (AuC) -
- It is a database that stores a copy of secret key that user's SIM card to enable the authentication and
encryption over the radio link.
Operating and Management Centre (OMC) -
Centrally monitors and contrls the network element, for smooth running of the network and guarantee
the best possible "QoS" in the network.
Perform
a) Network Monitoring
b) Network Measurement
c) Fault Management
d) Network Development.
Equipment Identity Register (EIR) - IMEI
It stores the IMEI of all valid mobile on the network.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
This number checks by the network during a call.
7 Explain Call Routing of GSM with MTC and MOC 2 Analyze CO2
Call routing:
- Human voice is analog in nature, so we need to convert to digital signal for convienent transferring of
information.
* Mobile Originating Call (MOC).
* Mobile Terminating Call (MTC)
1) User(Friend) dials the phone number of GSM subscriber.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
2)The phone gets to PSTN Network(with the help of destination number) gets to know the number
belongs to hte GSM network and forward that call to GMSC(Gateway MSC).
3) GMSC identifies the HLR of the subscriber(included in the phone number itself) and signals the
particular HLR, The HLR now checks whether the number exist and whether the user has subscribed the
requested service.
4) It will request and MSRN from current VLR.
5,6) VLR will feedback the HLR after getting the MSRN, here HLR will get to know (determine) the MSC
responsible for the MSC and forwars this information to the GMSC.
7) The GMS can now forwrds the call setup request to the MSC indicated by HLR.
8) It request the current status of the MS from VLR again.
9) VLR will send the current status(location) of the MS, and it the MS is available the MSC intiaites and
forward that call to all BSC+BTS.
10 - end step.) After BSS sends probe to that particular MS, the MS is going to respond to the BSS, and
from BSS to MSC.
8 Define all GSM Addresses and identifiers and write 2 Understand CO1
significance of each.
GSM Address and Idenitifiers.
----------------------------
GSM distinguishes explicitly between users and equipments, it also distinguishes between subscriber
identity and telephone. To deal with these many address GSM had created their own set of address
rules.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
a) International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI)
--Every mobile device in the world had a unique identity - IMEI.
-- Allocated by equipment manufacturer and registered by network operator in a secure database
known as - EIR (Equipment Identity Register).
-- *#06# --> To check the IMEI.
b) International Mobile Subscriber Indentity (IMSI)
- when you register with GSM network, each subscriber get a unique identity.
- IMSI stored in the SIM, and secured by the network operator.
- Mobile station can only be operated , if you have valid IMSI.
3 decimal digit - Mobile Country Code (MCC) - India - 404.
2 decimal digit - Mobile Network Code (MNC) - Airtel, Delhi - 10.
Maximum 10 decimal digit - Mobile Subscriber Identification Number (MSIN) -
c) Mobile Subscriber ISDN Number (MSISDN)
- Number is the real telephone number - known to external world.
- This number is the public information, whereas the IMSI number is the private to the world.
Country Code (CC) - 1-3 decimal digit- India +91
National Destination Code (NDC) - 2-3 decimal digit - BSNL- 94 and other 98.
Subscriber Number - Maximum 10 decimal digit.
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
d) Location Area Identity (LAI)
3 digit country code 404
2 digit mobile network code 94
5 digit location area code. 0011
e) Mobile station roaming number (MSRN)
When a user is roaming to another network, a temporary ISDN number is assigned to the user, it is
assigned by the VLR of the mobile station.
f) Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI)
This is a temporary identifier assigned by the VLR.
Used in the place of IMSI for identification and addressing of MS.
TMSI is never gonna store in HLR, it is temporary store in VLR.
g) Location Mobile Subscriber Identity (LMSI)
Assigned by the VLR, stored also in HLR.
Used in searching and faster access to grab the user.
h) Cell Identifier
Within the Location Area, cell has a unique identity - know as Cell Identifier. (LAI+ CI)
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
9 What is Handover/Handoff? Explain its types in brief 1 Remember CO1
Handoff/Handover strategy
---------------
process of transferring and active call from one cell to another cell as the mobile unit moves from first
cell to other cell, without disconnecting the call.
The amount of received power by mobile phone or the amount of received power by tower (acces
point), or both are usually need to determine, whether a handoff is necessary or not.
---------------------------- ***-------------------------------
Department CE Academic Year 2021 Page 1 of 2
You might also like
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1 2 Understand CO1: Mobile Computing Security - (Wireless Network + Cellular Network)Document16 pages1 2 Understand CO1: Mobile Computing Security - (Wireless Network + Cellular Network)wexidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Wise Question List For The Final Examinations: 1 Mobile Computing Definition - Advantage and DisadvantageDocument45 pagesChapter Wise Question List For The Final Examinations: 1 Mobile Computing Definition - Advantage and DisadvantagewexidaNo ratings yet
- 1-Mobile Computing Definition - Advantage and Disadvantage: Chapter Wise Question List For The Final ExaminationsDocument34 pages1-Mobile Computing Definition - Advantage and Disadvantage: Chapter Wise Question List For The Final ExaminationswexidaNo ratings yet
- Lecture IntroductionDocument34 pagesLecture IntroductionTesfaye MentreNo ratings yet
- An Introductory Presentation On GSM System: Presented ByDocument43 pagesAn Introductory Presentation On GSM System: Presented ByLet's Go TlmNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 2021Document26 pagesLec 2 2021Al7asanAmmarNo ratings yet
- Drive Test Nemo 2Document74 pagesDrive Test Nemo 2Tarek GARANo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Project On Honeywell Tdc3000 Dcs PRDocument77 pagesToaz - Info Project On Honeywell Tdc3000 Dcs PRMorad MouradNo ratings yet
- Cs8601 Unit 2 Notes Mobile Computing Unit 2 Anna University Regulation2017Document50 pagesCs8601 Unit 2 Notes Mobile Computing Unit 2 Anna University Regulation2017mymovies1241No ratings yet
- UMTS AircomDocument20 pagesUMTS AircomDũng PhạmNo ratings yet
- DCCN Unit 1Document13 pagesDCCN Unit 1Dinesh PalavalasaNo ratings yet
- Eee G627-4Document4 pagesEee G627-4Anmol DubeyNo ratings yet
- Simulation & Performance Study of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Using MATLABDocument8 pagesSimulation & Performance Study of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Using MATLABescanusNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document34 pagesCH 3emuye bawokeNo ratings yet
- ITM Unit - 4Document18 pagesITM Unit - 4Naimisha 102No ratings yet
- Data Communication Computer Networks Notes BCA PDFDocument20 pagesData Communication Computer Networks Notes BCA PDFHemalatha S Chinnu100% (2)
- Project On Honeywell TDC3000 DcsDocument77 pagesProject On Honeywell TDC3000 DcsAbv Sai75% (4)
- Performance Evaluation of Control Networks: Ethernet, Controlnet, and DevicenetDocument33 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Control Networks: Ethernet, Controlnet, and DevicenetSudheerNo ratings yet
- 5 GTU Computer Network Mid Sem Exam PaperDocument14 pages5 GTU Computer Network Mid Sem Exam PaperNickHenryNo ratings yet
- By - Diwakar Kumar CusatDocument43 pagesBy - Diwakar Kumar CusatDIWAKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- UNIT II-Media Acess and InternetworkingDocument34 pagesUNIT II-Media Acess and InternetworkingSenthilkumar SNo ratings yet
- Network For Class 8 IcseDocument6 pagesNetwork For Class 8 IcseGAMING WITH MaDMAN100% (1)
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01irtaza mughal officialNo ratings yet
- Cellular Wireless NetworksDocument70 pagesCellular Wireless NetworkskrithideepNo ratings yet
- DCL Lecture Module Compilation PDFDocument54 pagesDCL Lecture Module Compilation PDFAga TresvallesNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Call Admission Control Scheme For Handling Handoffs in Wireless Mobile NetworksDocument18 pagesAn Efficient Call Admission Control Scheme For Handling Handoffs in Wireless Mobile NetworksijansjournalNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument27 pagesChapter TwoSalih AkadarNo ratings yet
- Ijesat 2012 02 Si 01 24Document5 pagesIjesat 2012 02 Si 01 24Ijesat JournalNo ratings yet
- Lectures-1: Nodes) Connected by Communication LinksDocument30 pagesLectures-1: Nodes) Connected by Communication LinksRam krishna shuklaNo ratings yet
- Internship at EricssonDocument19 pagesInternship at EricssonPamela WilsonNo ratings yet
- International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)Document8 pagesInternational Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)www.irjes.comNo ratings yet
- GSM OptimizationDocument176 pagesGSM OptimizationAhmed YousryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cellular Mobile Systems: Dr. K K SharmaDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Cellular Mobile Systems: Dr. K K SharmaK K SHARMANo ratings yet
- Module 4 PDFDocument18 pagesModule 4 PDFSud UiNo ratings yet
- Data Communication FaqDocument4 pagesData Communication Faqdolon10No ratings yet
- Vikash: REG. No.-11410993Document46 pagesVikash: REG. No.-11410993ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- hwk2 SolDocument3 pageshwk2 SolabhilkoNo ratings yet
- Sns College of Technology: Computer NetworksDocument27 pagesSns College of Technology: Computer NetworksgmsamyNo ratings yet
- Computer Application Chapter 5Document5 pagesComputer Application Chapter 5Mebrahtom Gebeyaw berheNo ratings yet
- Can ProtocolDocument4 pagesCan ProtocolratheeshbrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, 2 3 NetDocument5 pagesChapter 1, 2 3 NetLena MohameedNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS 18EC71 (Prof. Nadeem Pasha)Document21 pagesMODULE 1 COMPUTER NETWORKS 18EC71 (Prof. Nadeem Pasha)Nadeem Pasha100% (1)
- Networking DocumentationDocument26 pagesNetworking DocumentationAdwitiya Saigar100% (4)
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) System in Multipath EnvironmentDocument6 pagesCode Division Multiple Access (CDMA) System in Multipath EnvironmentLữ TrungNo ratings yet
- 2data Communication New 2016Document4 pages2data Communication New 2016dehemi deekshaNo ratings yet
- CS6551 Computer Networks Two Mark With AnswerDocument35 pagesCS6551 Computer Networks Two Mark With AnswerPRIYA RAJI100% (7)
- 1.1 Introduction To NetworksDocument5 pages1.1 Introduction To NetworkspraveennallavellyNo ratings yet
- 2G Overview - Training For StarLinkDocument27 pages2G Overview - Training For StarLinksrsujon470No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions With Answers On Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument44 pagesMultiple Choice Questions With Answers On Wireless Sensor NetworksEKTHATIGER63359081% (52)
- Approximate Analytical Models For Dual-Band GSM Networks Design and PlanningDocument10 pagesApproximate Analytical Models For Dual-Band GSM Networks Design and Planningmashu45No ratings yet
- Architecture of OCB-283: Venkata Videhi Balusupati, Pavani Velaga, A.Rama KrishnaDocument4 pagesArchitecture of OCB-283: Venkata Videhi Balusupati, Pavani Velaga, A.Rama Krishnaabouibacarbrahim0101No ratings yet
- Midterm F2021 SolutionDocument8 pagesMidterm F2021 SolutionSkylar WillNo ratings yet
- CMC Unit 1 NotesDocument19 pagesCMC Unit 1 Notesdharani kodatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument109 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworksTejaswi SuryaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationFrom EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Evolved Packet System (EPS): The LTE and SAE Evolution of 3G UMTSFrom EverandEvolved Packet System (EPS): The LTE and SAE Evolution of 3G UMTSNo ratings yet
- 1 Compare I-TCP, S-TCP and M-TCP 2 Understand CO3: Assignment # 2Document8 pages1 Compare I-TCP, S-TCP and M-TCP 2 Understand CO3: Assignment # 2wexidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Introduction To 4GDocument10 pagesChapter 8 - Introduction To 4GwexidaNo ratings yet
- Chapte Rwise Content DocxDocument18 pagesChapte Rwise Content DocxwexidaNo ratings yet
- Why There Is A Need of Mobile IP?Document10 pagesWhy There Is A Need of Mobile IP?wexidaNo ratings yet
- Why There Is A Need of Mobile IP?Document10 pagesWhy There Is A Need of Mobile IP?wexidaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Smartphones (Author: Ahsan Kabir Nuhel)Document7 pagesEvolution of Smartphones (Author: Ahsan Kabir Nuhel)AMMAR AMRANNo ratings yet
- Metrosite 50Document54 pagesMetrosite 50nreyes01No ratings yet
- GSM Signaling SystemDocument27 pagesGSM Signaling SystemabdullaaNo ratings yet
- GSM Overview (Updated)Document174 pagesGSM Overview (Updated)Neeraj MongaNo ratings yet
- Gayathri GSM 2 (1) FinalDocument66 pagesGayathri GSM 2 (1) FinalumasreeNo ratings yet
- GSM Call Drop Problem Analysis - BenDocument80 pagesGSM Call Drop Problem Analysis - BenbeniNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Q&ADocument6 pagesMobile Computing Q&AAnonymous IJAAT2dqBNo ratings yet
- AirScale BSC SW Sales GuideDocument106 pagesAirScale BSC SW Sales GuideAdil Murad100% (1)
- GSM Architecture & InterfaceDocument49 pagesGSM Architecture & InterfaceShivani MehrotraNo ratings yet
- 411 9001 006 - 18.06Document264 pages411 9001 006 - 18.06Mohsin ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- FN1168 Multiple PLMN and Inter-PLMN Handover SupportDocument25 pagesFN1168 Multiple PLMN and Inter-PLMN Handover SupportRazvan Corban50% (2)
- Seminar5 CS Paging Coordination in The BSSDocument122 pagesSeminar5 CS Paging Coordination in The BSSSergio BuonomoNo ratings yet
- About This Chapter: AvailabilityDocument40 pagesAbout This Chapter: Availabilityyaser.ahmedNo ratings yet
- ETSI ES 202 706-1: Final Draft V1.5.0Document49 pagesETSI ES 202 706-1: Final Draft V1.5.0Jose GallardoNo ratings yet
- 10 CDD 20140904 151857Document3,663 pages10 CDD 20140904 151857Opeyemi DadaNo ratings yet
- Asbsc Parameters fp21bDocument27 pagesAsbsc Parameters fp21bHoudaNo ratings yet
- Com5 - Book Final PDFDocument117 pagesCom5 - Book Final PDFAyanle Omer IsmailNo ratings yet
- 09 - RN24041EN14GLN0 - GEMINI in BriefDocument68 pages09 - RN24041EN14GLN0 - GEMINI in Briefazzou dino32No ratings yet
- 2G KPI Improvement PDFDocument57 pages2G KPI Improvement PDFsunil kumarNo ratings yet
- Handover GSMDocument33 pagesHandover GSMShashank Prajapati0% (1)
- GSM Handover, Localisation and Call HandlingDocument17 pagesGSM Handover, Localisation and Call HandlingHrishikesh UgleNo ratings yet
- EEE 264-5: 3G Wireless NetworksDocument102 pagesEEE 264-5: 3G Wireless NetworksSundus Ali100% (1)
- DATAX QB 2G Huawei NBI Data RequirementsDocument9 pagesDATAX QB 2G Huawei NBI Data Requirementsandess_bayNo ratings yet
- 2G Feature G21.Q4 - User Description, Voice Capacity OptimizationDocument21 pages2G Feature G21.Q4 - User Description, Voice Capacity OptimizationAdhi atmaNo ratings yet
- System Architecture of GPRS: Group R1: Xiong Guangyu Nik A. SallehDocument26 pagesSystem Architecture of GPRS: Group R1: Xiong Guangyu Nik A. SallehDinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- TA1 - Mobile Communication - 1688734863912Document111 pagesTA1 - Mobile Communication - 1688734863912j320f samsungNo ratings yet
- Overview of The GSM Cellular System: John ScouriasDocument4 pagesOverview of The GSM Cellular System: John Scouriasdonny_rnpNo ratings yet
- GBSS13-0 Feature Description PDFDocument184 pagesGBSS13-0 Feature Description PDFMartin DiazNo ratings yet
- BSNL Training ReportDocument38 pagesBSNL Training Reportvishal sainiNo ratings yet
- Sys02 GSR7 1760Document564 pagesSys02 GSR7 1760Thiagu ManikandanNo ratings yet