0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesMedical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of Pangasinan
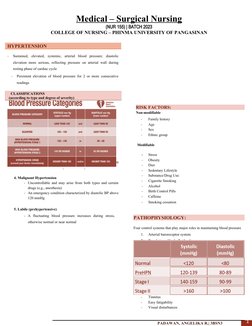
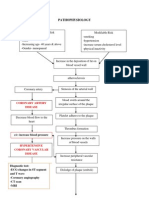
Hypertension is defined as sustained elevated blood pressure with a diastolic pressure over 90 mmHg. It can be classified as primary (essential) hypertension which is idiopathic or secondary caused by other conditions. Risk factors include family history, age, sex, stress, obesity, diet, and substance use. Four systems control blood pressure: the arterial baroreceptor system, body fluid volume regulation, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and vascular autoregulation. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications and medications including diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and ARBs. Careful blood pressure monitoring is needed when taking antihypertensive drugs.
Uploaded by
Rosalinda PerigoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesMedical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of Pangasinan
Hypertension is defined as sustained elevated blood pressure with a diastolic pressure over 90 mmHg. It can be classified as primary (essential) hypertension which is idiopathic or secondary caused by other conditions. Risk factors include family history, age, sex, stress, obesity, diet, and substance use. Four systems control blood pressure: the arterial baroreceptor system, body fluid volume regulation, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, and vascular autoregulation. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications and medications including diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and ARBs. Careful blood pressure monitoring is needed when taking antihypertensive drugs.
Uploaded by
Rosalinda PerigoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd