Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Uploaded by
Rosalinda PerigoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peripheral Vascular Disease
Uploaded by
Rosalinda PerigoCopyright:
Available Formats
Medical – Surgical Nursing
(NUR 155) | BATCH 2023
COLLEGE OF NURSING – PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN
PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASES Nail beds: capillary refill is greater than 3 seconds
Peripheral pulses; may be diminished; audible bruit
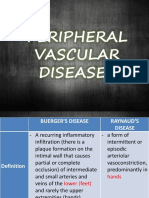
BURGER’S DISEASE
(THROMOANGIITIS OBLITERANS) DIAGNOSTICS:
Physical Examination
- A recurring inflammatory infiltration (there is a plaque formation
Segmental limb pressure
on the intimal wall that causes partial or complete occlusion) of
intermediate and small arteries and veins of the lower (feet) and Doppler ultrasonography
rarely the upper extremities (hands). Arteriography or angiography
Transcutaneous Oximetry
ETIOLOGY: MRI
- Unknown cause (Autoimmune vasculitis but usually associated PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT:
with smoking)
Anticoagulants
INCIDENCE:
Thrombolytics or Fibrolytics
- Men
Vasodilators
- 20-35 years old
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
- All races
Maintain a warm environment
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Legs in slight dependency and avoid elevating the legs
Thrombus formation Avoid vigorous massage of extremities
↓ Advise patient to avoid constrictive clothing and avoid
+ Inflammation crossing of legs
= narrowed lumen Advice to quit smoking
↓
Promote activity or exercise; general exercise; Buerger-Allen
Artery is unable to transport adequate blood volume to the tissue during
exercise
exercise and rest
Maintain skin integrity and prevent infection
↓
Total occlusion = appearance of s/sx
MANIFESTATIONS: SURGICAL MANAGEMENT:
Symptoms resulted from occlusion of arteries, leading to Arterial Bypass Surgery
ischemia, complicated in later stages by infection Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty
(thrombophlebitis) Amputation
PAIN with exercise: most common; usually bilaterally symmetric at
the arch of the foot; RAYNAUD’S DISEASE
-It may occur during rest and sometimes persistent (VASOMOTOR ARTERIAL DISEASE)
Intermittent claudication – most common symptom of - a form of intermittent or episodic arteriolar vasoconstriction,
arterial insufficiency which occurs during exercise predominantly in hands
Skin color and temperature changes
ETIOLOGY:
Ulcers and gangrene
PADAWAN, ANGELIKA R.| 3BSN3 1
Medical – Surgical Nursing
(NUR 155) | BATCH 2023
COLLEGE OF NURSING – PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN
- Unknown cause (autoimmune) but usually associated with Vascular Smooth Muscle Relaxants
emotional stress and hypersensitivity to cold. Vasodilators
INCIDENCE:
NURSING MANAGEMENT:
- Women
(Same as the Burguer’s disease)
- 20-40 years old
Advise the patient to wear gloves and warm socks during
- More on winter months
winter months, in cleaning refrigerator and in handling frozen
foods.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY:
Avoid occupations that require constant exposure to cold.
Cold stress
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT:
↓
Sympathectomy
Episodic arterial spasm
Amputation
↓
Intimal wall thickens because of hypertrophy of medial wall resulting
from constant and repeated spasm or constriction
↓
Sluggish blood flow
↓
Total occlusion = appearance of s/sx
MANIFESTATIONS:
- Symptoms resulted from arterial spasm, leading to ischemia
PAIN with cold stress; usually at fingertips
Skin color and
temperature changes
Ulcers and gangrene
Nail beds: capillary refill is greater than 3 seconds
DIAGNOSTICS:
Physical Examination
Cold stimulation test – fingers are placed in an iced-water bath
for 20 seconds. (+) for Raynaud’s Phenomenon if the
temperature of the fingers did not return to normal after 20
minutes
PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT:
Calcium Antagonist
PADAWAN, ANGELIKA R.| 3BSN3 2
Medical – Surgical Nursing
(NUR 155) | BATCH 2023
COLLEGE OF NURSING – PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN
Other Vascular Disorders:
ANEURYSM SACCULAR ANEURYSM
– a bulbous protrusion of one side of the arterial wall
- Permanent bulging/stretching of an artery in which the dilation
is two times or greater the size of the artery
- 3 sites commonly affected:
a) Aortic Arch
b) Thoracic Aorta
c) Abdominal Aorta
THORACIC AORTIC ANEURYSM
- Approximately 70% of all cases of thoracic aortic aneurysm are DISSECTING ANEURYSM
caused by atherosclerosis. – this is usually a hematoma that splits the layers of the arterial wall
- They occur most frequently in men between the ages of 50 to 70
years, and are estimated to affect 10 of every 100,000 older adults.
- The thoracic area is the most common site for a dissecting ETIOLOGIC CLASSIFICATION OF ANEURYSMS
aneurysm.
• Congenital – primary connective tissue disorders (Marfan
FALSE ANEURYSM Syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome) and other diseases (focal
– actually, a pulsating hematoma
medial agenesis, tuberous sclerosis, Turner syndrome, Menkes
syndrome).
• Mechanical (hemodynamic) – post stenotic and arteriovenous
fistula and amputation related
• Traumatic (pseudoaneurysm) – penetrating arterial injuries,
blunt arterial injuries,
• Inflammatory (non-infectious) – associated with arteritis
TRUE ANEURYSM (Takayasu disease, giant cell arteritis, SLE, Behcet syndrome,
– one, two, or three Arteries are involved. Kawasaki disease) and periarterial inflammation (i.e. pancreatitis)
• Infectious (mycotic) – bacterial, fungal, spirochetal infection
• Pregnancy-related degenerative – non- specific,
inflammatory variant
• Anastomotic (post arteriotomy) and graft aneurysms –
infection, arterial wall failure, suture failure, and graft failure
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
FUSIFORM ANEURYSM • Some patients are asymptomatic.
– symmetric spindle-shaped expansion of entire circumference • Pain is constant and occurs when person is in supine position.
of involved vessel
• Dyspnea
• Paroxysmal cough
• Hoarseness, stridor, weakness or complete loss of voice
(aphonia) – resulting from a pressure in the laryngeal nerve
PADAWAN, ANGELIKA R.| 3BSN3 3
Medical – Surgical Nursing
(NUR 155) | BATCH 2023
COLLEGE OF NURSING – PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN
• Dysphagia • Postimplantation syndrome – typically begins within 24
ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSTIC FINDINGS hours of stent graft placement and consists of
• CXR spontaneously occurring fever, leukocytosis, and
• CT Angiography occasionally transient thrombocytopenia.
• MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiogram) • Check for signs of hemorrhage
• TEE (Transesophageal echocardiography)
MEDICAL/SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
• Controlling BP through anti-hypertensive drugs (e.g. Beta-
blockers, ARBs, ACE inhibitors)
• Repair of aneurysms using endovascular grafts (through CC)
VARICOSE VEINS
- Dilation of veins because of lack of muscle support – results from
prolonged venous stasis
COMMON SITES/RELATED CONDITIONS:
Saphenous vein
Leg vein
Hemorrhoids
Esophageal varices
NURSING MANAGEMENT
• Place patient in supine position after an endovascular
repair.
• V/S and Doppler assessment of peripheral pulses are
monitored every 15 minutes.
• Assess for bleeding, pulsation, swelling, pain and
hematoma formation at the access site.
PREVENTION AND MEDICAL/SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
• Check for signs of embolization such as extremely tender,
• Pt should avoid activities that cause venous stasis such as
irregularly shaped, cyanotic areas, as well as changes in
wearing socks that are too tight at the top, crossing the legs at
v/s, pulse quality, bleeding, swelling, pain, or hematoma.
the thighs, and sitting or standing for long periods.
• Temperature is monitored every 4 hours, and check for
• Change position frequently elevating the legs 3-6 inches
signs of postimplantation syndrome.
higher than the heart.
• Pt is encouraged to walk 30 minutes each day.
PADAWAN, ANGELIKA R.| 3BSN3 4
Medical – Surgical Nursing
(NUR 155) | BATCH 2023
COLLEGE OF NURSING – PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN
• Graduated compression stockings, especially knee-high
stockings are useful.
NURSING MANAGEMENT
• Advise patient that procedures are OPD.
• Patient is advised to walk every hour for 5-10 minutes once
the sedation has worn off.
• Advise the patient that graduated compression stockings are
worn about 1 week after vein stripping.
• Foot of the bed should be elevated.
• Standing and sitting are discouraged.
THERMAL ABLATION
SCLEROTHERAPY
PADAWAN, ANGELIKA R.| 3BSN3 5
Medical – Surgical Nursing
(NUR 155) | BATCH 2023
COLLEGE OF NURSING – PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN
PADAWAN, ANGELIKA R.| 3BSN3 6
Medical – Surgical Nursing
(NUR 155) | BATCH 2023
COLLEGE OF NURSING – PHINMA UNIVERSITY OF PANGASINAN
PADAWAN, ANGELIKA R.| 3BSN3 7
You might also like
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- Buerger'S Disease Raynaud'S Disease Buerger'S Disease Raynaud'S DiseaseDocument4 pagesBuerger'S Disease Raynaud'S Disease Buerger'S Disease Raynaud'S DiseaseJulia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Pediculosis: (Phthipiasis)Document8 pagesPediculosis: (Phthipiasis)Krizelle VaronaNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm Final (Bentals Procedure)Document55 pagesAneurysm Final (Bentals Procedure)tejuteju067100% (1)
- Rabies Laboratory DiagnosisDocument3 pagesRabies Laboratory DiagnosisKoni Oroceo-SacramedNo ratings yet
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Nael HernandezDocument15 pagesType 1 Diabetes Mellitus Nael HernandezShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Pathognomonic Signs of Communicable Diseases: JJ8009 Health & NutritionDocument2 pagesPathognomonic Signs of Communicable Diseases: JJ8009 Health & NutritionMauliza Resky NisaNo ratings yet
- Malnutritiom and Anemia ImciDocument30 pagesMalnutritiom and Anemia ImcibaridacheNo ratings yet
- Otosclerosis and Menieres DiseaseDocument5 pagesOtosclerosis and Menieres DiseaseYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Final Manuscriptcase PresDocument71 pagesFinal Manuscriptcase PresCogie SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Noma Cancrum OrisDocument4 pagesNoma Cancrum OrisAnonymous Syjpyt4MoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence in Elderly: DefinitionDocument13 pagesUrinary Incontinence in Elderly: DefinitionTarek AhmedNo ratings yet
- Health Questionnaire CandidateDocument5 pagesHealth Questionnaire CandidateSaudia Arabia JobsNo ratings yet
- Penetrating Abdominal TraumaDocument67 pagesPenetrating Abdominal TraumarizkaNo ratings yet
- Gerd PresentationDocument44 pagesGerd PresentationMia Mia MiaNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb IschemiaDocument21 pagesAcute Limb IschemiaHina BatoolNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The Objective Structured Clinical Examination OSCE in Nursing Education A Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of The Objective Structured Clinical Examination OSCE in Nursing Education A Literature ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Steven Johnson SyndromeDocument13 pagesSteven Johnson SyndromeKhairul AnwarNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing ReviewerDocument10 pagesCommunity Health Nursing ReviewerNicole CastillaNo ratings yet
- Nootropil: Qualitative and Quantitative CompositionDocument12 pagesNootropil: Qualitative and Quantitative CompositionMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument35 pagesIntestinal Obstructionwht89100% (1)
- Henoch-Schonlein PurpuraDocument10 pagesHenoch-Schonlein PurpurasagameteiroNo ratings yet
- June 2013 NLE Topnotchers and Top SchoolsDocument19 pagesJune 2013 NLE Topnotchers and Top SchoolsCoolbuster.NetNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia SiteDocument23 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia Sitebenypermadi100% (1)
- Analgesics Agents ZJDocument37 pagesAnalgesics Agents ZJDanial HassanNo ratings yet
- Emergency and Disaster NursingDocument9 pagesEmergency and Disaster NursingDempsey AlmirañezNo ratings yet
- Orchitis (Eng)Document15 pagesOrchitis (Eng)Ferzy Awwali FadhilaNo ratings yet
- Papillary CarcinomaDocument7 pagesPapillary Carcinomarazik89No ratings yet
- Rabies: Ragina AguilaDocument55 pagesRabies: Ragina AguilaCharles Lester AdalimNo ratings yet
- Newest Research Paper The Challenges of Student Nurses in Their Clinical Skills Development Using Digital Technology. UwuDocument50 pagesNewest Research Paper The Challenges of Student Nurses in Their Clinical Skills Development Using Digital Technology. UwuMaryan SubaldoNo ratings yet
- Seizure DisordersDocument26 pagesSeizure DisordersMolly NguyenNo ratings yet
- Extrapyramidal Side EffectsDocument15 pagesExtrapyramidal Side EffectsNikhil YadavNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Dysphagia PDFDocument7 pagesApproach To The Patient With Dysphagia PDFHo Yong Wai100% (1)
- Buerger's DiseaseDocument15 pagesBuerger's Diseasezebzeb STEMANo ratings yet
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyDocument8 pagesType 1 Diabetes Mellitus - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyTrifosa Ika Septiana EryaniNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury Case Study (Physical Assessment)Document3 pagesSpinal Cord Injury Case Study (Physical Assessment)TobiDaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Responses To Altered Ventilatory FunctionDocument136 pagesLesson 3 Responses To Altered Ventilatory FunctionMonasque PamelaNo ratings yet
- HERNIORRHAPHYDocument2 pagesHERNIORRHAPHYSheldon Deypalubos Jr.No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument4 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseWidyan Muchzadi AkbarNo ratings yet
- Patient Case Presentation Rabies 28EM29Document36 pagesPatient Case Presentation Rabies 28EM29Viorica Gavriliță100% (1)
- PATHOGNOMONIC SIGNS From Mam Della CruzDocument2 pagesPATHOGNOMONIC SIGNS From Mam Della CruzCiao AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Awareness In, Mogadishu, SomaliaDocument7 pagesInfectious Disease Awareness In, Mogadishu, Somaliashafie Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Airway Emergencies: ORL PostingDocument58 pagesAirway Emergencies: ORL PostingKimberlyLaw95No ratings yet
- Pharma - SkinDocument8 pagesPharma - Skinreference books100% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing 1Document17 pagesPsychiatric Nursing 1Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Medications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMedications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDarla JoyceNo ratings yet
- Acyanotic Disease: Classification of CHDDocument11 pagesAcyanotic Disease: Classification of CHDFenita Renny DinataNo ratings yet
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument6 pagesCase Study PneumoniaBrian CornelNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument22 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- MS2 EarsDocument8 pagesMS2 Earswieka mawieNo ratings yet
- Cestodes: Diphyllobothrium Latum, Broad or FishDocument2 pagesCestodes: Diphyllobothrium Latum, Broad or FishFrance Louie JutizNo ratings yet
- Hansens DiseaseDocument83 pagesHansens DiseaseSajin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- 4 Circulation Disorders PDFDocument69 pages4 Circulation Disorders PDFSetiawan SukmadjaNo ratings yet
- Bullous PemphigoidDocument21 pagesBullous PemphigoidChe Ainil ZainodinNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos Sur Website: MailDocument48 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Tamag, Vigan City 2700 Ilocos Sur Website: MailNo EulNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pleural EffusionDocument46 pagesApproach To Pleural EffusionBaskoro Tri LaksonoNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular Disease-1Document52 pagesPeripheral Vascular Disease-1Johiarra Madanglog Tabigne100% (1)
- Adhesive CapsulitisDocument7 pagesAdhesive CapsulitisMariane GumbanNo ratings yet
- Compartment SyndromeDocument10 pagesCompartment SyndromerobbyNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument11 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- LasixDocument2 pagesLasixRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Lipospome - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLipospome - Drug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Open Ended QuestionDocument1 pageOpen Ended QuestionRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Lasix - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLasix - Drug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Chapter 3Document24 pagesGroup 4 Chapter 3Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Left Vs Right: Heart FailureDocument3 pagesLeft Vs Right: Heart FailureRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Letter of ExplanationDocument2 pagesLetter of ExplanationRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Request LetterDocument1 pageRequest LetterRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument6 pagesOMEPRAZOLERosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Medical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of PangasinanDocument2 pagesMedical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of PangasinanRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Open Ended QuestionDocument1 pageOpen Ended QuestionRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- ProbsDocument1 pageProbsRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Request LetterDocument1 pageRequest LetterRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- PERIGO, R - Visual Aids (Hypertension)Document14 pagesPERIGO, R - Visual Aids (Hypertension)Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Hi, I Hope You Will Succeed Someday! 3Document1 pageHi, I Hope You Will Succeed Someday! 3Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Validation Form...Document17 pagesValidation Form...Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Session 4Document2 pagesSession 4Rosalinda Perigo50% (2)
- Hi, I Hope You Will Succeed Someday! 3Document1 pageHi, I Hope You Will Succeed Someday! 3Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Emergency War Surgery Nato HandbookDocument384 pagesEmergency War Surgery Nato Handbookboubiyou100% (1)
- 3M Window Film PR SeriesDocument3 pages3M Window Film PR SeriesPhan CrisNo ratings yet
- Guarantor Indemnity For Illness or DeathDocument2 pagesGuarantor Indemnity For Illness or Deathlajaun hindsNo ratings yet
- 2.3 & 2.5 Cell DivisionDocument14 pages2.3 & 2.5 Cell DivisionJhonnyNo ratings yet
- Safety at Hand PDFDocument48 pagesSafety at Hand PDFAdesijiBlessingNo ratings yet
- Your Marathon Training PlanDocument16 pagesYour Marathon Training PlanAndrew Richard ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Ott OTT Ecolog 1000 Water Level LoggerDocument3 pagesOtt OTT Ecolog 1000 Water Level LoggerNedimZ1No ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Manual: Proact™ Ii Electric Powered Actuator and DriverDocument32 pagesInstallation and Operation Manual: Proact™ Ii Electric Powered Actuator and DriverDjebali MouradNo ratings yet
- Untitled Form - Google Forms00Document3 pagesUntitled Form - Google Forms00Ericka Rivera SantosNo ratings yet
- BURNS GeneralDocument59 pagesBURNS GeneralValluri MukeshNo ratings yet
- Copy of HW UMTS KPIsDocument18 pagesCopy of HW UMTS KPIsMohamed MoujtabaNo ratings yet
- Helicopter Logging Operations - ThesisDocument7 pagesHelicopter Logging Operations - ThesisAleš ŠtimecNo ratings yet
- Supply ForecastingDocument17 pagesSupply ForecastingBhavesh RahamatkarNo ratings yet
- Concrete and Its PropertiesDocument24 pagesConcrete and Its PropertiesAmila LiyanaarachchiNo ratings yet
- Sample Quantitative Descriptive Paper 1Document20 pagesSample Quantitative Descriptive Paper 1oishimontrevanNo ratings yet
- Traditional Christmas FoodDocument15 pagesTraditional Christmas FoodAlex DumitracheNo ratings yet
- Optimization Process of Biodiesel Production With Ultrasound Assisted by Using Central Composite Design MethodsDocument47 pagesOptimization Process of Biodiesel Production With Ultrasound Assisted by Using Central Composite Design MethodsMiftahFakhriansyahNo ratings yet
- Factors Associated With Early Pregnancies Among Adolescent Girls Attending Selected Health Facilities in Bushenyi District, UgandaDocument12 pagesFactors Associated With Early Pregnancies Among Adolescent Girls Attending Selected Health Facilities in Bushenyi District, UgandaKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledSpace HRNo ratings yet
- Shawarma Refers To The Middle Eastern Method Cooking Where Thin Slices of MeatDocument3 pagesShawarma Refers To The Middle Eastern Method Cooking Where Thin Slices of MeatColai's BcdNo ratings yet
- Ctaa040 - Ctaf080 - Test 4 Solution - 2023Document7 pagesCtaa040 - Ctaf080 - Test 4 Solution - 2023Given RefilweNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource WasNayre JunmarNo ratings yet
- Sasol Polymers PP HNR100Document3 pagesSasol Polymers PP HNR100Albert FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Culturally Safe Classroom Context PDFDocument2 pagesCulturally Safe Classroom Context PDFdcleveland1706No ratings yet
- Final PR 2 CheckedDocument23 pagesFinal PR 2 CheckedCindy PalenNo ratings yet
- WAM IPM Mechanical Pressure Gauge BrochureDocument4 pagesWAM IPM Mechanical Pressure Gauge BrochureOliver ConlonNo ratings yet
- Air MassesDocument22 pagesAir MassesPrince MpofuNo ratings yet
- JAR Part 66 Examination Mod 03Document126 pagesJAR Part 66 Examination Mod 03Shreyas PingeNo ratings yet
- Information HumaLyzer Primus Setting Update and Extension enDocument3 pagesInformation HumaLyzer Primus Setting Update and Extension enluisoft88No ratings yet