Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lasix - Drug Study
Uploaded by
Rosalinda PerigoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lasix - Drug Study
Uploaded by
Rosalinda PerigoCopyright:
Available Formats
PHINMA University of Pangasinan
College of Health Sciences
Name of Student Nurse: _________Rosalinda Perigo ____________ Date: ______January 9, 2022___________
Level/block/group: ______3 BSN-08_____________ Hospital/Area: ___Post-Anesthesia Care Unit __________ Clinical Instructor: ___Mr. Raymond Mark A. Mata__________
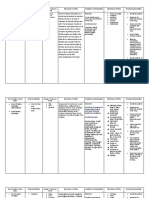
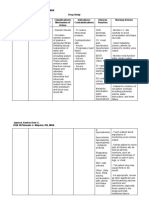
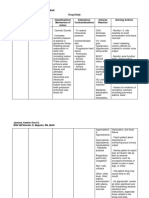
NAME OF DRUG MECHANISM OF ACTION CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
GENERIC NAME Contraindicated in clients Common side effects of bupivacaine Cardio Vascular System: Before:
Furosemide (Lasix) inhibits with the ff. medical include: Postural hypotension -Assess the patient`s history for
the reabsorption of sodium conditions: Increased urination Circulatory collapse hypersensitivity and drug allergies
Furosemide and chloride from the loop Patients with thirst Increase in cholesterol before starting the administration
of henle and distal renal hypersensitivity to muscle cramps and triglyceride serum
BRAND NAME tubule. As a result, renal furosemide or itching or rash levels -Assess patient`s vital signs and
excretion of water, sodium, sulphonamides weakness note the patient`s weight to
Lasix chloride, magnesium, Increasing oliguria, dizziness Gastrointestinal: monitor fluid changes.
potassium and calcium anuria, fluid and spinning sensation Nausea and vomiting
CLASSIFICATION increases. electrolyte depletion diarrhea Oral and gastric burning -Assess the patient for medical
state stomach pain anorexia conditions that are
Hepatic coma constipation Adominal cramping contraindicated to Furosemide
Loop diuretics
Acute pancreatitis
Clay-colored stools During:
INDICATION
Loss of appetite and rapid - Administer oral form early in the
weight loss. day to prevent increased urination
Lasix is indicated to during sleep hour.
post-surgical patient Urinary System:
to enhance urine Dark urine -In patients with Ileostomy, use
output, which can lasix with great care because salt
help to lower blood Integumentary: imbalance and dehydration can
pressure, edema, and Pruritus result from additional fluid loss.
fluid overload. Urticaria
Dermatitis - Check patient's electrolyte levels
DOSAGE & Vasculitis periodically throughout the
FREQUENCY treatment.
Adults: Hematologic: - Assess skin condition to
PO 20-80 mg/day in a Aplastic anemia determine presence of fluid
single dose the first Leukopenia volume deficit or retention
time then repeat it 6-8 Thrombocytopenic After:
purpura - Evaluate the patient`s response
hour.
Children:
PO (Children>
1month) 2mg/kg
single dose.
IM, IV (adults):
20-40 mg repeat 1-2
until response is
obtained. Bolus 0.1
to therapy and any adverse effects
mg/kg followed by 0.1
mg/kg/hr. double q 2
-Instruct patient to avoid sudden
hr to a max of 0.4
consumption of large amounts of
mg/kg/hr
fluid
- Instruct patient to report hearing
IM, IV (children): 1-2
loss and gout symptoms
mg/kg dose q 6-12
hour. 0.05 mg/hr/kg
- Notify provider if gain more than
You might also like
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Salazar DsDocument4 pagesSalazar DsDjayNo ratings yet
- Cyclizine Hydrochloride - Summary of Product CharacteristicsDocument28 pagesCyclizine Hydrochloride - Summary of Product CharacteristicsBrown and Burk UK LtdNo ratings yet
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Insulin Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 pagesInsulin Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Vitamin KDocument2 pagesVitamin KMuvs RazonNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- AmloDocument1 pageAmloamy navajaNo ratings yet
- Methocarbamol (Robaxin)Document1 pageMethocarbamol (Robaxin)ENo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Drug Study - CefradoxilDocument13 pagesDrug Study - CefradoxilJohara G'naid0% (1)
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideDocument6 pagesPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- As Pi LetDocument7 pagesAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Drug study on chemotherapeutic alkylating agentsDocument16 pagesDrug study on chemotherapeutic alkylating agentsPrincess CruzNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Document1 pageErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Activated CharcoalDocument1 pageActivated CharcoalSupreeth PrasadNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- AztreonamDocument2 pagesAztreonamHannahShaeHayesNo ratings yet
- Effects of atracurium besylateDocument3 pagesEffects of atracurium besylateWidya WidyariniNo ratings yet
- Micromonospora Purpurea. Action IsDocument3 pagesMicromonospora Purpurea. Action IsCarlos H. AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesCiprofloxacin Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComAsterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolKay MirandaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesMechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Miglitol (Glyset)Document1 pageMiglitol (Glyset)ENo ratings yet
- JM DrugDocument3 pagesJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities for Salbutamol and PrednisoneDocument7 pagesNursing Responsibilities for Salbutamol and PrednisoneAlvin LimNo ratings yet
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 pagesMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyCen Janber CabrillosNo ratings yet
- Generic Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse ReactionDocument1 pageGeneric Classification Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse ReactionKamille Anne Valdez DavidNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide Drug Study SummaryDocument4 pagesAcetazolamide Drug Study Summarygrail carantesNo ratings yet
- Clotrimazole Cream Lotion Solution Dusting PowderDocument4 pagesClotrimazole Cream Lotion Solution Dusting Powderedy744No ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolNo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- AtroventDocument2 pagesAtroventKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug Study on CelecoxibDocument11 pagesDrug Study on CelecoxibPrincess Brigitte R. PATE�ANo ratings yet
- HydroxyzineDocument4 pagesHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNo ratings yet
- Sal But AmolDocument2 pagesSal But AmolCalimlim KimNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyJoule PeirreNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Sodium BicarbonateDocument7 pagesDrug Study-Sodium BicarbonateTrisha Faye OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationDocument2 pagesDrug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationart_mutantNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)Document3 pagesDrug Study ON Atropine Sulfate: Maa Tripura College of Nursing, Jhabua (M.P.)amitNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyHerwincayeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument18 pagesDrug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsJenica ManuntagNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AtropineDocument3 pagesDrug Study AtropineAerron Severus Secano ShuldbergNo ratings yet
- RifampicinDocument2 pagesRifampicinChaeL90No ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseImnot YouNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: West Visayas State UniversityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: West Visayas State UniversityDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FurosemideDocument2 pagesDrug Study FurosemideAkira Poscablo PiranteNo ratings yet
- DSDocument18 pagesDSAngelica Murillo Ang-AngcoNo ratings yet
- Kedren Drug StudyDocument10 pagesKedren Drug StudyKedren Kent JawoodNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageFurosemide Mechanism of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesPatricia MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Kedren Drug Study.2Document10 pagesKedren Drug Study.2Kedren Kent JawoodNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument11 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Lipospome - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLipospome - Drug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Chapter 3Document24 pagesGroup 4 Chapter 3Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- PHINMA University of Pangasinan College of Health Sciences Student Nurse Clinical ReportDocument2 pagesPHINMA University of Pangasinan College of Health Sciences Student Nurse Clinical ReportRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Open Ended QuestionDocument1 pageOpen Ended QuestionRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument7 pagesPeripheral Vascular DiseaseRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Request LetterDocument1 pageRequest LetterRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Left Vs Right: Heart FailureDocument3 pagesLeft Vs Right: Heart FailureRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument6 pagesOMEPRAZOLERosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Letter of ExplanationDocument2 pagesLetter of ExplanationRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Medical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of PangasinanDocument2 pagesMedical - Surgical Nursing: College of Nursing - Phinma University of PangasinanRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- PERIGO, R - Visual Aids (Hypertension)Document14 pagesPERIGO, R - Visual Aids (Hypertension)Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- ProbsDocument1 pageProbsRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Open Ended QuestionDocument1 pageOpen Ended QuestionRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Request LetterDocument1 pageRequest LetterRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Session 4Document2 pagesSession 4Rosalinda Perigo50% (2)
- Validation Form...Document17 pagesValidation Form...Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Hi, I Hope You Will Succeed Someday! 3Document1 pageHi, I Hope You Will Succeed Someday! 3Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Hi, I Hope You Will Succeed Someday! 3Document1 pageHi, I Hope You Will Succeed Someday! 3Rosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Media ExercisesDocument24 pagesMedia ExercisesMary SyvakNo ratings yet
- Glover U Business Plan 2022 DigitalDocument25 pagesGlover U Business Plan 2022 DigitalJustin CarruthNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 GEC 106Document132 pagesUnit 2 GEC 106fernando.gl559No ratings yet
- Sales Manager or Regional Manager or Senior Sales ExecutiveDocument3 pagesSales Manager or Regional Manager or Senior Sales Executiveapi-77473806No ratings yet
- Module 26Document27 pagesModule 26Ven Zyndryx De JoyaNo ratings yet
- MAXScript EssentialsDocument20 pagesMAXScript EssentialsSebastián Díaz CastroNo ratings yet
- Jerome KaganDocument5 pagesJerome KaganMandeep morNo ratings yet
- Ruibal & Shoemaker 1984 - Osteoders in AnuransDocument17 pagesRuibal & Shoemaker 1984 - Osteoders in AnuransRuivo LucasNo ratings yet
- Verification and Validation in Computational SimulationDocument42 pagesVerification and Validation in Computational SimulationazminalNo ratings yet
- Karl-Fischer TitrationDocument19 pagesKarl-Fischer TitrationSomnath BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Mahaveer Medisales Private LimitedDocument5 pagesMahaveer Medisales Private LimitedvijayNo ratings yet
- English AssignmentDocument79 pagesEnglish AssignmentAnime TubeNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Cooling Technologies For Thermal Management of AvionicsDocument10 pagesActive and Passive Cooling Technologies For Thermal Management of AvionicsdavidNo ratings yet
- HOPE 3A MODULE 1 Introduction To DanceDocument13 pagesHOPE 3A MODULE 1 Introduction To DanceLeo PatrickNo ratings yet
- Burnelli AircraftDocument51 pagesBurnelli Aircraftretread1100% (3)
- 2016 Practical Theory Questions SolutionDocument36 pages2016 Practical Theory Questions Solutionsheeess gaadaNo ratings yet
- Rizal's Extensive Travels Abroad for Education and Revolution (1882-1887Document6 pagesRizal's Extensive Travels Abroad for Education and Revolution (1882-1887Diana JeonNo ratings yet
- Darius Registration Form 201 1623 2nd Semester A.Y. 2021 2022Document1 pageDarius Registration Form 201 1623 2nd Semester A.Y. 2021 2022Kristilla Anonuevo CardonaNo ratings yet
- Tpe Reflection AssignmentDocument5 pagesTpe Reflection Assignmentapi-351869082No ratings yet
- New Life in Christ by Wilson HerreraDocument18 pagesNew Life in Christ by Wilson Herreralesantiago100% (1)
- Narration KIPS Academy (Free Download)Document17 pagesNarration KIPS Academy (Free Download)AyshahNo ratings yet
- Key Responsibilities On Skill.: Curriculum Vitae PersonalDocument3 pagesKey Responsibilities On Skill.: Curriculum Vitae PersonalLAM NYAWALNo ratings yet
- VRF, MPLS and MP-BGP FundamentalsDocument55 pagesVRF, MPLS and MP-BGP FundamentalsIVAN TANEV100% (2)
- A Meta Analysis of Effectiveness of Interventions To I - 2018 - International JoDocument12 pagesA Meta Analysis of Effectiveness of Interventions To I - 2018 - International JoSansa LauraNo ratings yet
- Picture DescriptionDocument7 pagesPicture DescriptionAida Mustafina100% (3)
- QuickZChargerZAC DCDocument2 pagesQuickZChargerZAC DCLucaspasNo ratings yet
- Brochure Manuthera 242 ENDocument4 pagesBrochure Manuthera 242 ENSabau PetricaNo ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 5Document24 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 5Anonymous wirViz1tyoNo ratings yet
- 4880 AnsiDocument0 pages4880 AnsiabualamalNo ratings yet