Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry 6E Janice Gorzynski Smith (2018) - EDITED PROPER FORMAT (Pages 199-200) Ch2 Review
Uploaded by
josh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views1 pageThis document discusses methods for determining acidity. It explains that the acidity of a compound increases as the percentage of s-character in the hybridized orbital of its conjugate base increases. This makes the conjugate base more stable. When comparing the acidities of two protons bonded to the same element, the proton attached to an electronegative atom like oxygen will form a more stable conjugate base through resonance and therefore be a stronger acid. Other factors that increase acidity are electron-withdrawing groups and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
Original Description:
Edited with proper format pages 199-200 in Chapter 2 Review for Organic Chemistry 6E Janice Gorzynski Smith (2018); pdf version had images/descriptions cut off from the margins
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses methods for determining acidity. It explains that the acidity of a compound increases as the percentage of s-character in the hybridized orbital of its conjugate base increases. This makes the conjugate base more stable. When comparing the acidities of two protons bonded to the same element, the proton attached to an electronegative atom like oxygen will form a more stable conjugate base through resonance and therefore be a stronger acid. Other factors that increase acidity are electron-withdrawing groups and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views1 pageOrganic Chemistry 6E Janice Gorzynski Smith (2018) - EDITED PROPER FORMAT (Pages 199-200) Ch2 Review
Uploaded by
joshThis document discusses methods for determining acidity. It explains that the acidity of a compound increases as the percentage of s-character in the hybridized orbital of its conjugate base increases. This makes the conjugate base more stable. When comparing the acidities of two protons bonded to the same element, the proton attached to an electronegative atom like oxygen will form a more stable conjugate base through resonance and therefore be a stronger acid. Other factors that increase acidity are electron-withdrawing groups and resonance stabilization of the conjugate base.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
NOTE: EDITED FORMAT - INSERTED W/ORIGINAL PAGES INTACT
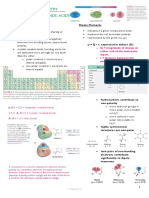
[6] Determining acidity using hybridization effects (2.5D)
[1] Draw the conjugate bases of the follow- [2] Identify the hybridization of the [3] Determine the
ing compounds. carbanions. stronger acid.
• The higher the percent • The acidity of
s-character of the hybrid HA increases as
orbital, the more stable the percent s-
the conjugate base. character of A: -
increases.
See Figure 2.5. Try Problems 2.51d, 2.54d.
Page 86
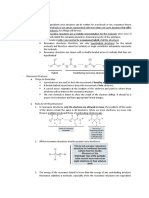
[7] Determining the most acidic proton (2.5E)
[1] Identify the atoms bonded [2] Draw conjugate bases and resonance [3] Determine most acidic
to hydrogen, and use structures. proton
periodic trends to assign
acidity.
• The oxygen anion stabilizes the
conjugate base through resonance
unlike the nitrogen anion. Hence,
the hydrogen atom bound to the
oxygen atom is more acidic.
• If two H atoms in question are
bonded to the same element, draw
• HOR is more acidic than the conjugate bases and look for
H2NR based on other differences:
electronegativity. 1) Do electron-withdrawing
groups stabilize the conjugate
base? If yes, the stronger the acid.
2) Is the conjugate base resonance
stabilized? If yes, the stronger the
acid.
3) How is the conjugate base
hybridized? sp3 has 25% s-
character, sp2 has 33% s-
character, and sp has 50% s-
character; the more s-character,
the more stable the conjugate base
and, therefore, the stronger the
acid
See How To (p. 76), Figure 2.6, Sample Problems 2.7, 2.8. Try Problems 2.43, 2.44, 2.52, 2.64.
You might also like
- Ocr A-Level Chemistry Cheatsheet PDFDocument26 pagesOcr A-Level Chemistry Cheatsheet PDFAhmad Mubashar100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1st Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual DownloadDocument64 pagesOrganic Chemistry Mechanistic Patterns Canadian 1st Edition Ogilvie Solutions Manual DownloadLaura Simpson100% (22)
- A Level Chemistry Notes PDFDocument16 pagesA Level Chemistry Notes PDFRAMAN KUMAR100% (1)
- Chem 221 Name - Organic Chemistry I Quiz #5 (Chapters 1&2)Document3 pagesChem 221 Name - Organic Chemistry I Quiz #5 (Chapters 1&2)mark anjo luyunNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith, ch2Document16 pagesOrganic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith, ch2sungyeon heoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Organic Chemistry KleinDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Organic Chemistry KleinJim XieNo ratings yet
- 25 Buffers - SDocument6 pages25 Buffers - SLeia JonesNo ratings yet
- Nowgong organic notesDocument8 pagesNowgong organic notesjurinlbNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Acid StrengthDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Acid StrengthNarmaNo ratings yet
- 10+2 PCM NOTESDocument33 pages10+2 PCM NOTESMohitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Covalent Bonds Acids & BasesDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Covalent Bonds Acids & BasesPolikNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure - Key NotesDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding & Molecular Structure - Key NotesSagar JaisiNo ratings yet
- Resonance TheoryDocument1 pageResonance TheoryOutward CauseNo ratings yet
- Periodicity Notes - Docx-29Document1 pagePeriodicity Notes - Docx-29Kiều TrangNo ratings yet
- Hard-Soft Acid-Base Theory ExplainedDocument41 pagesHard-Soft Acid-Base Theory Explained김영철No ratings yet
- ACIDS & BASES - InOrg&Org PDFDocument7 pagesACIDS & BASES - InOrg&Org PDFCindy-chan DelfinNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: B.L. Acid-Base Reactions in EquilibriumDocument7 pagesUnit 5: B.L. Acid-Base Reactions in EquilibriumCindy-chan DelfinNo ratings yet
- (Raymond Chang) Chemistry by Raymond Chang (B-Ok - Org) Compressed (1) - 634-640Document7 pages(Raymond Chang) Chemistry by Raymond Chang (B-Ok - Org) Compressed (1) - 634-640Hikma AinazzahraNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and BasesDocument11 pagesHard and Soft Acids and Basesnoor uddinNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC POLAR BONDSDocument12 pagesORGANIC POLAR BONDSelaineustNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part3Document34 pagesUnit 1 Part3Gem khyle VelascoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Acid-Base Reactions and Their Relationship to StructureDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Acid-Base Reactions and Their Relationship to StructureChristine Mae DelimaNo ratings yet
- 4 2024 245 CH 4 AlkenesAlkynes Lecture V1 StudentDocument22 pages4 2024 245 CH 4 AlkenesAlkynes Lecture V1 Studentdingdong19690No ratings yet
- Organic Chemiatry Ch3 KleinDocument41 pagesOrganic Chemiatry Ch3 KleinJonathan ChungNo ratings yet
- Inorganic HSAB 8apr2012Document29 pagesInorganic HSAB 8apr2012اردها نزواNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: ChemistryDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding: ChemistryMuneeb MunawarNo ratings yet
- Hsab DPDocument20 pagesHsab DPShubham Baxla (CSEAIML23310662409:30)No ratings yet
- CHEM231 - Assignment 2 - 2021-KeyDocument12 pagesCHEM231 - Assignment 2 - 2021-Keyzoya attiqueNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Relative Atomic Mass (16 Marks) : 1. A Sample of Zinc Has The Following CompositionDocument7 pages2.1 Relative Atomic Mass (16 Marks) : 1. A Sample of Zinc Has The Following CompositionArian AhmedNo ratings yet
- Resonance Structures and HybridsDocument65 pagesResonance Structures and HybridsamandaNo ratings yet
- Arrhenius Bronsted Lewis Acids: Acids: AcidsDocument3 pagesArrhenius Bronsted Lewis Acids: Acids: AcidsBianca Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- 7 Acid and BasesDocument27 pages7 Acid and BasessemalupurpleNo ratings yet
- Resonance - : Resonance Structures Things To RememberDocument29 pagesResonance - : Resonance Structures Things To RememberDan Sebastian TilaoNo ratings yet
- Coordination Compound: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF FormatDocument7 pagesCoordination Compound: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF Formatjeet VermaNo ratings yet
- 1.7.5 Covalent Bond RevisionDocument3 pages1.7.5 Covalent Bond RevisionTomáš Tommy NagyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- BSPH-1101 Resonance Structure ORGANIC Chemistry Le: Ms. Krishally Joy O. Patalinjug - Feb. 2022Document3 pagesBSPH-1101 Resonance Structure ORGANIC Chemistry Le: Ms. Krishally Joy O. Patalinjug - Feb. 2022Orianna SanoNo ratings yet
- Prep Final-EX CHAP-7Document15 pagesPrep Final-EX CHAP-7dunghd.ba12-056No ratings yet
- Acid-Base ChemistryDocument12 pagesAcid-Base ChemistryNOBLEMANNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Chemistry Notes: Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument3 pagesAIEEE Chemistry Notes: Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureMangesh WajeNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry NotesDocument16 pagesA Level Chemistry NotesPavan кυмαяNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY COMPLETEDDocument10 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY COMPLETEDFa Ti MahNo ratings yet
- 2-HASB Ralph Pearson1968Document6 pages2-HASB Ralph Pearson1968Vasu NagpalNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry 1ed TR WB AnswersDocument113 pagesIB Chemistry 1ed TR WB Answersღ꧁Lizzy X Roxiie꧂ღNo ratings yet
- Seager 10e Ch04 PowerPointDocument71 pagesSeager 10e Ch04 PowerPointHanz Gabriel DegomaNo ratings yet
- Valance bond theory and hybrid orbitals explainedDocument2 pagesValance bond theory and hybrid orbitals explainedHusen HasenNo ratings yet
- Question BanksDocument16 pagesQuestion BanksashNo ratings yet
- HARD - SOFT ACID-2 (Compatibility Mode)Document5 pagesHARD - SOFT ACID-2 (Compatibility Mode)Dhanar ArdikaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic and Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesInorganic and Organic ChemistryValerie BorrioNo ratings yet
- 9 2024 245 CH 9 Aromatics Lecture STUDENTDocument36 pages9 2024 245 CH 9 Aromatics Lecture STUDENTdingdong19690No ratings yet
- d2py01001a (科研通 Ablesci.com)Document13 pagesd2py01001a (科研通 Ablesci.com)z859301254No ratings yet
- Ch02 - Basics2Document44 pagesCh02 - Basics2Saguvij FopoNo ratings yet
- 13H ConjugatedDocument41 pages13H ConjugatedSandipNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersDocument6 pagesChemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersH.sNo ratings yet
- Primary Structure: Beta SheetDocument1 pagePrimary Structure: Beta Sheetthat/niggaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Introduction To Localized & Delocalized BondingDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Introduction To Localized & Delocalized Bondingrabiya fayyaz100% (1)
- CHM574' Inorganic'Chemistry'Ii': Chapter'1:'Molecular'Orbital'Theory'Document29 pagesCHM574' Inorganic'Chemistry'Ii': Chapter'1:'Molecular'Orbital'Theory'Badrudin JundailiNo ratings yet
- Basic Organic ChemistryDocument78 pagesBasic Organic Chemistry2E (04) Ho Hong Tat AdamNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Primary Structure ReviewDocument6 pagesNucleic Acids Primary Structure ReviewGuy CtvNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reviews: The Hard Acids Bases (HSAB) Principle and Organic ChemistryDocument20 pagesChemical Reviews: The Hard Acids Bases (HSAB) Principle and Organic ChemistryPinottoNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 Resonance Structures and Aromatic CompoundsDocument27 pagesCh. 2 Resonance Structures and Aromatic CompoundsCollo KarisNo ratings yet
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases Principle in Organic ChemistryFrom EverandHard and Soft Acids and Bases Principle in Organic ChemistryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Notes Acid BaseDocument7 pagesNotes Acid BaseCherry T CYNo ratings yet
- 1st PU Chemistry Jan 2015 PDFDocument2 pages1st PU Chemistry Jan 2015 PDFPrasad C M100% (4)
- Chem 40.1 Lab PoliciesandBufferReviewDocument12 pagesChem 40.1 Lab PoliciesandBufferReviewYshaReyesNo ratings yet
- Eoy Review Student Questions KeyDocument4 pagesEoy Review Student Questions Keyapi-234918521No ratings yet
- Ionic EqDocument54 pagesIonic EqNurul FarhanaNo ratings yet
- 05 - The Chemistry of Acids and Bases Complete - RevisedDocument63 pages05 - The Chemistry of Acids and Bases Complete - RevisedKabesang TalesNo ratings yet
- Buffers in Our Daily LifeDocument4 pagesBuffers in Our Daily LifeClement CharlesNo ratings yet
- Buffer PreparationDocument3 pagesBuffer PreparationEzzati Aziz0% (2)
- BuffersDocument5 pagesBuffersDiana ZhangNo ratings yet
- HCH111 Quiz 2, Answers, 2019Document2 pagesHCH111 Quiz 2, Answers, 2019Bonita NengweNo ratings yet
- Ch16-Equilibria Weak Acids BasesDocument71 pagesCh16-Equilibria Weak Acids BasesSyafa ArumNo ratings yet
- Tagalog, Christian, Tolentino, Aika Cecille, I., Terrado, Rence, Valencia, IfameDocument10 pagesTagalog, Christian, Tolentino, Aika Cecille, I., Terrado, Rence, Valencia, IfameSenaima Marie Hilario BantosaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Acids and Bases & pH ScaleDocument3 pagesTheories of Acids and Bases & pH ScaleYoviNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument45 pagesAcids and Basesjordanf48922100% (1)
- Acids and BasesDocument82 pagesAcids and BasesKarya mulianaNo ratings yet
- Write Answers To All NCERT Intext Solved & Unsolved Problems. 2. Write Answers To All NCERT Questions in ExercisesDocument2 pagesWrite Answers To All NCERT Intext Solved & Unsolved Problems. 2. Write Answers To All NCERT Questions in ExercisesJagriti DaryaniNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry 11Document12 pagesAnalytical Chemistry 11Rasha HajaratNo ratings yet
- A + B A + B: Mtchem3: Analytical Chemistry For MlsDocument7 pagesA + B A + B: Mtchem3: Analytical Chemistry For MlsJhona Mae CortesNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Worksheet 2Document2 pagesAcid Base Worksheet 2Tutor Academy100% (1)
- Preliminary Chemistry Notes NSWDocument56 pagesPreliminary Chemistry Notes NSWfocuc980% (1)
- Chemistry 12 Notes on Unit 4 TitrationDocument24 pagesChemistry 12 Notes on Unit 4 TitrationBekki VanderlendeNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Chemistry ExamDocument35 pagesAcid Base Chemistry ExamSali IqraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Alcohols, Phenols, and ThiolsDocument19 pagesChapter 7. Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiolshanna liuNo ratings yet
- Monoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria: 1. Strong Acids & Bases: Dilemma in Calculating The PH of Strong Acids & BasesDocument15 pagesMonoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria: 1. Strong Acids & Bases: Dilemma in Calculating The PH of Strong Acids & BasesSkygazerNo ratings yet
- SECOND QUARTER GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 SUMMATIVE TESTDocument2 pagesSECOND QUARTER GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 SUMMATIVE TESTSid Eleazar R. GaffudNo ratings yet
- Acid Base AP Past ExamDocument163 pagesAcid Base AP Past ExamAngela KuoNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases NotesDocument17 pagesAcids and Bases NotesNap DoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical CalculationsDocument29 pagesPharmaceutical CalculationsJai MurugeshNo ratings yet