Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cambridge International Examinations: Accounting 0452/22 March 2017
Uploaded by
Mike ChindaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International Examinations: Accounting 0452/22 March 2017
Uploaded by
Mike ChindaCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International Examinations
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
ACCOUNTING 0452/22
Paper 22 March 2017
MARK SCHEME
Maximum Mark: 120
Published
This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates, to indicate the requirements of the
examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were instructed to award marks. It does not indicate the
details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners’ meeting before marking began, which would have
considered the acceptability of alternative answers.
Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for
Teachers.
Cambridge will not enter into discussions about these mark schemes.
Cambridge is publishing the mark schemes for the March 2017 series for most Cambridge IGCSE®,
Cambridge International A and AS Level components and some Cambridge O Level components.
® IGCSE is a registered trademark.
This document consists of 13 printed pages.
© UCLES 2017 [Turn over
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
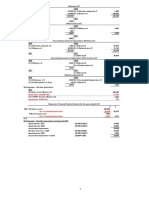
1(a) Mandeep – Cash Book 10
Date Details Discount Cash Bank Date Details Discount Cash Bank
allowed received
2016 $ $ $ 2016 $ $ $
Dec 1 Balance b/d 150 Dec 1 Balance b/d 2 590
11 Jabin (1) 6 294 4 Repairs (1) 387
27 Sales (1) 6 795 15 Rama (1) 18 702
31 Cash c (1)OF 1 745 29 Drawings (1) 5 000
Balance c/d 1 640 31 Bank c (1) 1 745
Balance c/d 200
6 6 945 3 679 18 6 945 3 679
2017 2017
Jan 1 Balance b/d 200 Jan 1 Balance b/d 1 640
(1) (1)OF
+(1) dates
© UCLES 2017 Page 2 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
1(b) Mandeep 14
Inventory account
$ $
2016 2016
Jan 1 Balance b/d 12 650 Dec 31 Income Statement 12 650 (1)
Dec 31 Income Statement 13 420 (1) Dec 31 Balance c/d 13 420
2017
Jan 1 Balance b/d 13 420 (1)
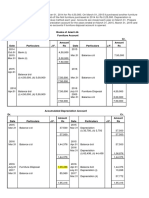
Provision for depreciation of office fixtures account
$ $
2016 2016
Dec 31 Balance c/d 4 636 Jan 1 Balance b/d 3 420
Dec 31 Income Statement 1 216 (1)
4 636 4 636
2017
Jan 1 Balance b/d 4 636 (1)OF
General expenses account
$ $
2016 2016
Dec 31 Total payments 9 475 Dec 31
Balance c/d 375 Income Statement 9 850 (1)
9 850 9 850
2017
Jan 1 Balance b/d 375 (1)
© UCLES 2017 Page 3 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
Rent receivable account
$ $
2016 2016
Dec 31 Jan 1 Total receipts 5 060
Income Statement 5 520 (1) Dec 31 Balance c/d 460
5 520 5 520
2017
Jan 1 Balance b/d 460 (1)
Drawings account
$ $
2016 2016
Dec 31 Total drawings 8 950 Dec 31 Capital 8 950 (1)
8 950 8 950
Capital account
$ $
2016 2016
Dec 31 Drawings 8 950 (1) Jan 1 Balance b/d 63 000
Balance c/d 91 650 Dec 30 Motor vehicle 16 000 (1)
31 Profit for year 21 600 (1)
100 600 100 600
2017
Jan 1 Balance b/d 91 650 (1)OF
© UCLES 2017 Page 4 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
2(a)(i) A statement in which the profit or loss for the year is calculated 1
2(a)(ii) A statement showing the assets and liabilities of a business on a certain date 1
2(a)(iii) Assets which are purchased for use not for resale 2
Assets whose values do not fluctuate frequently
Assets which will be kept by the business for more than 12 months
Assets which are acquired to aid the business earn revenue
Any two statements (1) each
2(a)(iv) Liabilities which are not due for repayment within 12 months 1
2(a)(v) Either The amount the business owes the owner of that business 1
Or Any resources provided for a business by the owner of that business
2(b) Goodwill/patents/trademarks/other suitable example 1
2(c) The current assets are more than three times the current liabilities/it is much higher than the “benchmark” of 2 : 1 2
The current liabilities can easily be paid from the current assets
Funds are not being used very effectively
Any two comments (1) each
2(d) Inventory is excluded from the calculation of the quick ratio (1) 2
Either Inventory is not regarded as a liquid asset (1)
Or The ratio shows whether the business would have surplus liquid funds if the current liabilities were paid
immediately from the liquid assets (1)
2(e) Introduce more cash as capital 2
Obtain long term loans
Sell surplus non-current assets
Reduce drawings
Reduce inventory level
Any two points (1) each
© UCLES 2017 Page 5 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
2(f)(i) Transactions are recorded at actual cost (1) 2
It is difficult to compare transactions taking place at different times (1)
2(f)(ii) Only information which was be expressed in monetary terms is recorded (1) 2
Many important factors which affect the business are not recorded (1)
© UCLES 2017 Page 6 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
3(a) Doshi Manufacturing Company 12
Manufacturing Account for the year ended 31 January 2017
$ $ $
Cost of materials consumed
Opening inventory of raw materials 49 500
Purchases of raw materials 394 600
Less Purchases returns 16 400 378 200 (1) 427 700
Closing inventory of raw materials 41 100
386 600 (1)OF
Direct factory wages 297 100 (1)
Prime cost 683 700 (1)OF
Factory overheads
Factory supervisors' wages
(152 000 (1) + 12 000 (1)) 164 000
General expenses (3/5 × 160 000) 96 000 (1)
Depreciation factory machinery
(20% × (250 000 – 122 000) 25 600 (1)
Depreciation loose tools
(21 150 – 19 050) 2 100 (1) 287 700
971 400 (1)OF
Opening work in progress 28 750 *
1 000 150
Closing work in progress 31 250 *(1) both
Cost of production 968 900 (1)OF
© UCLES 2017 Page 7 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
3(b) Doshi Manufacturing Company 11
Income Statement for the year ended 31 January 2017
$ $ $
Revenue 1 246 850
Less returns inwards 12 250
1 234 600 (1)
Cost of sales
Opening inventory of finished goods 63 100
Cost of production 968 900 (1)OF
Purchases of finished goods 21 700 (1)
Carriage inwards 1 500 (1) 23 200
1 055 200
Closing inventory finished goods 59 100 996 100 (1)OF
Gross profit 238 500 (1)OF
Less Wages of office & sales staff
(108 700 (1) + 4 300 (1)) 113 000
General expenses
(2/5 × 160 000) 64 000 (1)
Depreciation office equipment
(15% × 72 000) 10 800 (1) 187 800
Profit for the year 50 700 (1) OF
3(c) Low value items which are not easy to depreciate separately/Not practical to keep detailed records of such assets/other 1
suitable comment.
© UCLES 2017 Page 8 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
4(a) Purchases ledger 1
4(b) Lahiru has returned goods to Nusrath (1) 2
Credit purchases returns (returns outwards) account (1)
4(c)(i) 2½% 1
4(c)(ii) Prompt payment/payment within the specified period 1
4(d) Set off the amount Lahiru owes Nusrath against the amount Nusrath owes Lahiru/other suitable explanation 1
4(e) 3
Nusrath
Journal
Debit Credit
$ $
Lahiru (purchases ledger) 68 (1)
Lahiru (sales ledger) 68 (1)
Contra entry to set balance in purchases (1)
ledger against balance in sales ledger
4(f)(i) $564 1
4(f)(ii) Current assets 1
© UCLES 2017 Page 9 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
4(g) Lahiru 4
Provision for doubtful debts account
$ $
2017 2016
Feb 28 Balance c/d 716 Mar 1 Balance b/d 500 (1)
2017
Feb 28 Income statement 216 (1)
716 716
2017
Mar 1 Balance b/d 716 (1)OF
+ (1) dates
4(h) The profit for the year is not overstated (1) 2
The trade receivables (current assets) are not overstated (1)
4(i) Either The sales for which a business is unlikely to be paid (1) are regarded as an expense of the year in which those 2
sales are made (1)
Or The provision for doubtful debts is an expense (1) and is matched against the revenue for the year in which
those debts are incurred (1)
© UCLES 2017 Page 10 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
5(a) $ $ 6
Payments to credit suppliers 32 725 (1)
Cash discount received 640 (1)
Trade payables 31 January 2017 5 350 (1) 38 715
Less Trade payables 1 February 2016 4 600 (1)
Interest on overdue account 15 (1) 4 615
Purchases for the year 34 100 (1) OF
Alternative calculation
Total trade payables account
$ $
2017 2016
Jan 31 Bank 32 725 (1) Feb 1 Balance b/d 4 600 (1)
Discount 640 (1) 2017
Balance c/d 5 350 (1) Jan 31 Interest 15 (1)
Purchases 34 100 (1)OF
38 715 38 715
5(b) Jai 7
Income Statement (Trading account section) for the year ended 31 January 2017
$ $
Revenue 42 000 (1) OF
Cost of sales
Inventory 1 February 2016 2 900 (1)
Purchases 34 100 (1)
OF
37 000
Less Inventory 31 January 2017 3 400 (1) 33 600 (1) OF
Gross profit 8 400 }(2) CF/(1) OF
5(c) 33 600 OF } (1) 33 600 2
= = 10.67 times (1) OF
(2900 + 3400) / 2 } 3150
© UCLES 2017 Page 11 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
5(d) Reduce inventory levels 2
More sales activity
Or other suitable points
Any 2 points (1) each
5(e) Prudence 1
5(f) overstated understated 2
Current assets at 31 January 2017 9
Profit for the year ended 31 January 2017 9(1)
Profit for the year ending 31 January 2018 9(1)
5(g) Increase selling price 2
Reduce trade discount allowed to customers
Reduce purchase price
Find cheaper supplier
Obtain better trade discount
Any 2 comments (1) each
© UCLES 2017 Page 12 of 13
0452/22 Cambridge IGCSE – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
6(a) Amina 7
Journal
Debit Credit
$ S
Sales returns 960 (1)
Purchases returns 960 (1)
Suspense 1 920 (1)
No entry – (1)
Suspense 3 000 (1)
AK Stores 330 (1)
Suspense 330 (1)
6(b) 7
Effect on draft profit for the year of correcting the error
Error Increase Decrease No effect
$ $
1 1 000 (1)
2 484 (2)*
3 1 920 (2)*
4 9 (1)
5 9 (1)
* (1) position + (1) amount
© UCLES 2017 Page 13 of 13
You might also like
- 0452 m17 Ms 22Document13 pages0452 m17 Ms 22Mohammed MaGdyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 0452/22 October/November 2017Document12 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 0452/22 October/November 2017pyaaraasingh716No ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Principles of Accounts 7110/22 May/June 2017Document13 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Principles of Accounts 7110/22 May/June 2017Phiri AgnesNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Principles of Accounts 7110/21 May/June 2017Document9 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Principles of Accounts 7110/21 May/June 2017Taha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 0452/21 October/November 2017Document9 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 0452/21 October/November 20171234No ratings yet
- 0452 s17 Ms 23Document12 pages0452 s17 Ms 23Vyakt MehtaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Principles of Accounts 7110/22 October/November 2017Document13 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Principles of Accounts 7110/22 October/November 2017Makanaka MutandariNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument11 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationMandrich AppadooNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Accounting All Mark Scheme 2002 Summer 2018Document1,453 pagesIGCSE Accounting All Mark Scheme 2002 Summer 2018Muhammad Arif100% (2)
- 9706 m17 Ms 32Document16 pages9706 m17 Ms 32FarrukhsgNo ratings yet
- 7110 s19 Ms 21 PDFDocument15 pages7110 s19 Ms 21 PDFkazamNo ratings yet
- 9706 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesDocument5 pages9706 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesMateeh-ur -rehmanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Accounting 0452/11 May/June 2017Document11 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Accounting 0452/11 May/June 2017Ayman ZarifNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 9706/32 October/November 2017Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 9706/32 October/November 2017Phiri Arah RachelNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Accounting 7707/22 October/November 2020Document14 pagesCambridge O Level: Accounting 7707/22 October/November 2020Iman100% (1)
- Accruals Q1 AnswerDocument2 pagesAccruals Q1 AnswerRiyu RimmyNo ratings yet
- 7110 s16 Ms 21Document11 pages7110 s16 Ms 21Muhammad Umair100% (1)
- Cambridge O Level: Accounting 7707/22 May/June 2020Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: Accounting 7707/22 May/June 2020rAJBS;DFNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/22 March 2020Document14 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/22 March 2020FarrukhsgNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 0452/21 May/June 2019Document16 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 0452/21 May/June 2019Shayan KhanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Extra Assessment Material For First Teaching September 2017Document13 pagesMark Scheme: Extra Assessment Material For First Teaching September 2017shamNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Accounting 7707/23 October/November 2020Document14 pagesCambridge O Level: Accounting 7707/23 October/November 2020ImanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 9706/31 October/November 2017Document14 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 9706/31 October/November 2017Phiri Arah RachelNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/22 October/November 2020Document14 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/22 October/November 2020Voon Chen WeiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 9706/23 October/November 2017Document8 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 9706/23 October/November 2017ASHITA AGARWAL-01841No ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Accounting 9706/22 March 2020Document7 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Accounting 9706/22 March 2020Javed MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 03 0452 12 MS Final ScorisDocument10 pages03 0452 12 MS Final ScorisFarman FaheemNo ratings yet
- 2019 May MS 4ac0 1R PDFDocument18 pages2019 May MS 4ac0 1R PDFmahdiarahman10No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/23 October/November 2020Document14 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/23 October/November 2020ATTIQ UR REHMANNo ratings yet
- 0452 w19 Ms 21 PDFDocument17 pages0452 w19 Ms 21 PDFbipin jainNo ratings yet
- 7110 s14 Ms 21Document8 pages7110 s14 Ms 21Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Test Ii Accounts MSDocument10 pagesTest Ii Accounts MSDhrisha GadaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 9706/21 May/June 2018Document15 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Accounting 9706/21 May/June 2018Mayur MandhubNo ratings yet
- Zodeq Vision - Accounting LedgersDocument24 pagesZodeq Vision - Accounting LedgerskeemorodriquezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument9 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Educationcheah_chinNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledTanvi RAMSEWAKNo ratings yet
- Accounting Nov 2017 AddendumDocument16 pagesAccounting Nov 2017 Addendumkwanele andiswaNo ratings yet
- 0452 Specimen Paper Answers Paper 2 (For Examination From 2020)Document26 pages0452 Specimen Paper Answers Paper 2 (For Examination From 2020)Divya SinghNo ratings yet
- 4AC0 01 MSC 20150305 PDFDocument14 pages4AC0 01 MSC 20150305 PDFSabsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: This Document Consists of 19 Printed PagesDocument19 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: This Document Consists of 19 Printed Pagestecho2345No ratings yet
- Accounting - Marking Scheme - Form 3 Secondary - 2016 Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesAccounting - Marking Scheme - Form 3 Secondary - 2016 Page 1 of 3waheeda17No ratings yet
- 0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 SeriesDocument8 pages0452 Accounting: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2014 Seriesaditya agarwalNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/21 May/June 2020Document18 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/21 May/June 2020IronMechKillerNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Accounting 5121Document12 pagesMark Scheme: Accounting 5121SaadArshadNo ratings yet
- 9701 w16 Ms 22Document8 pages9701 w16 Ms 22Praveen PeterNo ratings yet
- Exercises 20.4A Bad DebtsDocument1 pageExercises 20.4A Bad DebtsCarolnesa Dorie Tan Kar MeanNo ratings yet
- Depreciation (110,500 20%) 21,780 Depreciation (3,660 10%) 366Document1 pageDepreciation (110,500 20%) 21,780 Depreciation (3,660 10%) 366Ali MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme PrinciplesDocument23 pagesMark Scheme PrinciplesV-academy MathsNo ratings yet
- Bad Debt Provision: Accounting for Uncollectible Accounts ReceivableDocument4 pagesBad Debt Provision: Accounting for Uncollectible Accounts ReceivableHopeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Accounting 0452/12 March 2017Document8 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Accounting 0452/12 March 2017Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 10 AnswersThe Nightwatchmen100% (1)
- BAFS Mock Paper 2A Set 8 Ans Eng.docDocument9 pagesBAFS Mock Paper 2A Set 8 Ans Eng.dochannahho0723No ratings yet
- Mathematical Literacy P1 Memo 2022Document12 pagesMathematical Literacy P1 Memo 2022oratilerefiloe48No ratings yet
- Depre Sums 2Document6 pagesDepre Sums 2Pradeep NairNo ratings yet
- Daily Fund Report: SeninDocument7 pagesDaily Fund Report: SeninBeriandi RullyNo ratings yet
- 2018 1st S1 簿记与会计答案Document9 pages2018 1st S1 簿记与会计答案伍纹缌-NG WEN XINo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/21 May/June 2020Document18 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/21 May/June 2020Israa MostafaNo ratings yet
- AccgP2 (N12 MS)Document6 pagesAccgP2 (N12 MS)Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Accg P3 (J17 MS)Document7 pagesAccg P3 (J17 MS)Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Accg P3 (N 17 MS)Document8 pagesAccg P3 (N 17 MS)Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Accounts Paper One Form Two Time: 1 Hrs Answer All QuestionsDocument7 pagesAccounts Paper One Form Two Time: 1 Hrs Answer All QuestionsMike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Commerce SolutionsDocument55 pagesCommerce SolutionsMike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Acc P3 J16Document8 pagesAcc P3 J16Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Accounts Form Guide with 40 Accounting QuestionsDocument6 pagesAccounts Form Guide with 40 Accounting QuestionsMike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Accg P2Document8 pagesAccg P2Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument12 pagesZimbabwe School Examinations Council: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelthaboNo ratings yet
- Accounting Study MaterialDocument16 pagesAccounting Study MaterialMike ChindaNo ratings yet
- 6001 Q 02Document16 pages6001 Q 02Masimba Mhangami100% (2)
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationhbuzdarNo ratings yet
- Accounting ReviewDocument4 pagesAccounting ReviewMike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Acc P3 J2018Document6 pagesAcc P3 J2018Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Accounting 9 Final Term 1Document9 pagesAccounting 9 Final Term 1Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Solved Example (1) - Bank Reconciliation Statement: Date Details Payments ($) Receipts ($) Balance ($)Document2 pagesSolved Example (1) - Bank Reconciliation Statement: Date Details Payments ($) Receipts ($) Balance ($)MATIULLAHNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationhbuzdarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Accounting 0452/12 March 2017Document8 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Accounting 0452/12 March 2017Mike ChindaNo ratings yet
- 0452/21/m/j/18 QPDocument20 pages0452/21/m/j/18 QPAnshNo ratings yet
- Accounting Study MaterialDocument64 pagesAccounting Study MaterialMike ChindaNo ratings yet
- Airtel and Vodafone: Comparing India's top telecom brandsDocument82 pagesAirtel and Vodafone: Comparing India's top telecom brandsPia ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of TQMDocument2 pagesBasic Concept of TQMChristian lugtuNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Surmayee UmatheDocument8 pagesPresented By: Surmayee UmatheSurmayee UmatheNo ratings yet
- LEXUSDocument59 pagesLEXUSShubham KhuranaNo ratings yet
- 06-Final Project CharterDocument12 pages06-Final Project Charterapi-555515911No ratings yet
- Contract To SellDocument2 pagesContract To SellMick VelandresNo ratings yet
- BIR Ruling (DA-243-00)Document3 pagesBIR Ruling (DA-243-00)bulasa.jefferson16No ratings yet
- BPR Factors Impact Employee Performance Addis AbabaDocument83 pagesBPR Factors Impact Employee Performance Addis Abababereket tesfayeNo ratings yet
- Invoice 50698496Document1 pageInvoice 50698496monicahmuthee22No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document8 pagesAssignment 2Prakash ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Asia Paci Fic Management Review: Yu-Shun Hung, Yu-Chen ChengDocument14 pagesAsia Paci Fic Management Review: Yu-Shun Hung, Yu-Chen ChenggitaNo ratings yet
- trắc nghiệm quản trị kênh phân phốiDocument14 pagestrắc nghiệm quản trị kênh phân phốiVinh HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Indicators Disclosed in Corporate Sustainability Reports PDFDocument16 pagesAn Analysis of Indicators Disclosed in Corporate Sustainability Reports PDFRahul PramaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Merchandising BSA 101 2015-2016 With SolutionDocument7 pagesQuiz - Merchandising BSA 101 2015-2016 With SolutionNia BranzuelaNo ratings yet
- DIG The UK BIZ Links W Robert Hunter BidenDocument27 pagesDIG The UK BIZ Links W Robert Hunter BidenDGB DGBNo ratings yet
- COA CIRCULAR NO. 2024 006 March 14 2024Document21 pagesCOA CIRCULAR NO. 2024 006 March 14 2024Jen IgnacioNo ratings yet
- MCQ Accounts For 10+2 TS Grewal SirDocument66 pagesMCQ Accounts For 10+2 TS Grewal SirYash ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Accounts Part-II 4 PDFDocument26 pagesAccounts Part-II 4 PDFjibin samuelNo ratings yet
- Kusina 21pblDocument15 pagesKusina 21pblRicky BalatNo ratings yet
- Case No.50 Bearneza Vs DequillaDocument1 pageCase No.50 Bearneza Vs Dequillapaul2574No ratings yet
- Impact of Green Marketing On Customer Satisfaction An Empirical StudyDocument7 pagesImpact of Green Marketing On Customer Satisfaction An Empirical StudyarcherselevatorsNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Handouts: The Nature of Strategy ImplementationDocument4 pagesModule 7 Handouts: The Nature of Strategy ImplementationvivianNo ratings yet
- (VER. 3) TLE-IA6 - q0 - Mod3 - Simple Survey Using Technology - v3Document30 pages(VER. 3) TLE-IA6 - q0 - Mod3 - Simple Survey Using Technology - v3PAUL JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- 17 Mergers LBOs Divestitures and Business FailureDocument2 pages17 Mergers LBOs Divestitures and Business FailureKristel Sumabat100% (1)
- Online Marketing Academy Performance Marketing JobDocument18 pagesOnline Marketing Academy Performance Marketing Jobfoot_musteNo ratings yet
- BNI - 3456789049 - B3 Desember 21Document39 pagesBNI - 3456789049 - B3 Desember 21MOHAMAD IKSAN ABIDINNo ratings yet
- Volvo Group Annual Report 2011-EN PDFDocument166 pagesVolvo Group Annual Report 2011-EN PDFAngelo VillalobosNo ratings yet
- ADJUSTING ENTRIES PPT TacsanDocument31 pagesADJUSTING ENTRIES PPT TacsanDanicaNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues Facing EntrepDocument2 pagesEthical Issues Facing EntrepasdgfhajkalNo ratings yet
- Cost CapitalDocument36 pagesCost CapitalOlivier MNo ratings yet