Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Polysaccharide Notes
Uploaded by
Ryan HaddockOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Polysaccharide Notes
Uploaded by
Ryan HaddockCopyright:
Available Formats
POLYSACCHARIDES:
Polysaccharide formation and break down:
-A polysaccharideis formed when more than two monosaccharides are joined together by
condensation reactions
-A polysaccharide can be broken down into its constituent monosaccharides through hydrolysis
reactions
Functions of Polysaccharides:
-The structure has a direct influence with the function of the following polysaccharides
Starch:
-Cells get any energy from glucose, plants store their addititional glucose as starch
-When a plant need mores glucose for energy, it breaks down starch to release energy/glucose
-Starch is a mixture of two polysaccharides of alpha glucose- amylose and amylopectin
-Amylose is a long unbranched chain of alpha glucose
-The angles of the glycosidic bonds give it a coiled structure
-This makes it very compact, which is ideal for storage as it
becomes very small because you can fit it into a small space
-Amylopectin is a long branched chain of alpha glucose
-Its side branches allow the enzyme that breaks down the
molecule to get access to the glycosidic bonds easier and
more efficiently
-Starch is insoluble in water and does not affect the water potential,
in other words it does not cause water to enter the cell through
osmosis
-If water did enter through osmosis it would cause the cell to swell,
this is another factor that makes it good for storage
Glycogen:
-Animal cells also receive their energy from glucose,
however animals sore their glucose as glycogen
-This is another polysaccharide made up of alpha
glucose monomers
-It has a structure which is similar to amylopectin but has even more side branches coming of it
-The more branches, the quicker the glucose can be accesed and therfore be released at a
quicker rate
-It is also a compact molecule and good for storage
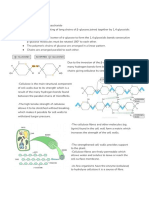
Cellulose:
-It is made of long, unbranched chains of beta
glucose
-When beta glucose molecules bond together,
they form straight cellulose chains
-The cellulose chains are linked together to
form hydorgen bonds (which are weak on their
own but strong together)
-These hydrogen bonds form fibres called
microfibrils
-The strong fibres mean cellulose provides
structural supports for cells e.g. the cell wall in
plants
The Iodine test for starch:
1.) Mix your substance with water unless it is already in liquid form
2.) If there is starch present the substance changes from a browny orange to a blue-black
colour
You might also like
- 1A 3 Carbohydrates 2Document13 pages1A 3 Carbohydrates 2muhammad naufalNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Starch, Glycogen and CelluloseDocument1 page1.4 Starch, Glycogen and CelluloseHroaldrNo ratings yet
- PolyDocument2 pagesPolyapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Biological MoleculesDocument12 pagesLecture 4 Biological MoleculesMuhammad FurrukhNo ratings yet
- Specification NotesDocument1 pageSpecification NotesAdam EchikrNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates - Polysaccharides: Topic A - Structure and Function of Biological MoleculesDocument10 pagesCarbohydrates - Polysaccharides: Topic A - Structure and Function of Biological MoleculesEgamberdi NormurodovNo ratings yet
- Topic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 1-20Document20 pagesTopic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 1-20lisaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Biological Molecule NotesDocument2 pagesTopic 2 Biological Molecule NotesShean LimNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Notes Module 1Document9 pagesCAPE Biology Notes Module 1JordanNo ratings yet
- How Enzymes Break Down Food in the Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesHow Enzymes Break Down Food in the Digestive SystemKatherine NunnNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY Basic Chemistry of A CellDocument22 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Basic Chemistry of A Cellwkwhui100% (2)
- Chapter 5 BayoDocument10 pagesChapter 5 BayoWee-Weh HamjaNo ratings yet
- Water, Biomolecules & Their FunctionsDocument15 pagesWater, Biomolecules & Their FunctionsIshie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BioDocument37 pagesChapter 2 BioEyamgualeleNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Topic 1ADocument10 pagesBiology Notes: Topic 1Alaiba amirNo ratings yet
- L2 CarbohydratesDocument36 pagesL2 CarbohydratesAman ImranNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules RevisionDocument6 pagesBiological Molecules RevisioncocoNo ratings yet
- Carbo Hy DatesDocument18 pagesCarbo Hy DatesVincent Jade SebastianNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument10 pagesCellsRebecca SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Biology As Starch, Glycogen and CelluloseDocument30 pagesBiology As Starch, Glycogen and CelluloseDiddled_skittlesNo ratings yet
- Sheet 13 GhaithDocument15 pagesSheet 13 GhaithСаша ТищенкоNo ratings yet
- 1-6 VocabularyDocument5 pages1-6 VocabularyKate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Starch and Glycogen: Properties of Energy Storage PolysaccharidesDocument3 pagesStarch and Glycogen: Properties of Energy Storage PolysaccharidesKevir ManNo ratings yet
- Random Biology AnswersDocument2 pagesRandom Biology AnswersXavi StanislawskiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates IAL Edexcel ChemistryDocument17 pagesCarbohydrates IAL Edexcel ChemistryIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- PolysaccharidesDocument30 pagesPolysaccharidesbam yeontanieNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 10 Notes (Grade 11)Document12 pagesBio Chapter 10 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (4)
- Biology 20 - Unit D8.1 Nutrients V2Document52 pagesBiology 20 - Unit D8.1 Nutrients V2Najlaa JomhaNo ratings yet
- Anitaatina CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesAnitaatina CarbohydratesR. Ela İrişNo ratings yet
- SStructure Function of Polysaccharides Model AnswerDocument2 pagesSStructure Function of Polysaccharides Model AnswerIkenna UchechukwuNo ratings yet
- L6 Lesson 4Document15 pagesL6 Lesson 4Martyn PereiraNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecule Notes Cie As Biology PDFDocument16 pagesBiological Molecule Notes Cie As Biology PDFKajana Sivarasa Shenthan100% (1)
- Gen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsDocument7 pagesGen Bio - 1 2.5 - The Organic Molecules of Living OrganismsBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Ch 2 SummaryDocument10 pagesMolecular Biology Ch 2 SummaryRafi FarhanNo ratings yet
- Day 04 - Macromolecules (Carbohydrates)Document24 pagesDay 04 - Macromolecules (Carbohydrates)Ryan Wilson - Sandalwood Heights SS (2442)No ratings yet
- AQA AS Biology 3.1.2 CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesAQA AS Biology 3.1.2 CarbohydratesChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates biomoleculeDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates biomoleculeTashi OngNo ratings yet
- 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 Carbohydrates PDFDocument4 pages1.1, 1.2, 1.3 Carbohydrates PDFshahbazhu006No ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument35 pagesBiological MoleculesRavneet KaurNo ratings yet
- HBC 104 Polysaccharides Lecture 4Document21 pagesHBC 104 Polysaccharides Lecture 4craigNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of A Carbon AtomdsdddddddddddDocument3 pagesChemical Properties of A Carbon AtomdsdddddddddddMohammed EbrahimNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Unit 2 Topic 4 Notes Study Revision Guide Summary Edexcel Practice Biodiversity Plant Cell OrganellesDocument50 pagesAS Biology Unit 2 Topic 4 Notes Study Revision Guide Summary Edexcel Practice Biodiversity Plant Cell Organellesshamxrock90% (59)
- Presentation Title: Your SubtitleDocument47 pagesPresentation Title: Your SubtitleDenize Faith Malagday AbellaNo ratings yet
- Before We Study The Digestion System, We Need To Know A Little More About The Food That We Put Into ItDocument25 pagesBefore We Study The Digestion System, We Need To Know A Little More About The Food That We Put Into Itccoleman3No ratings yet
- Biology Notes (Carbohydrates)Document4 pagesBiology Notes (Carbohydrates)Teo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Carbohydrates Notes (2010-2011Document24 pagesGrade 10 Carbohydrates Notes (2010-2011Lonley HumanNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesMabel Lee Shan Shan100% (3)
- Wrtitten .Structure of PolysacDocument4 pagesWrtitten .Structure of PolysacDianne Joy LeybaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Biology Unit 1 Topic 1 - Molecules, Transport and HealthDocument40 pagesEdexcel IAL Biology Unit 1 Topic 1 - Molecules, Transport and HealthEshalNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesCarbohydratesidkmyname100% (5)
- 3.1 - Biological MoleculesDocument24 pages3.1 - Biological Moleculessumanzaib10No ratings yet
- BIO 001 2nd LectDocument62 pagesBIO 001 2nd LectDavid AkinwandeNo ratings yet
- Alevel Biology Notes U1(需修改补充完善的基础资料,仅供自己复习,Notforsale)Document36 pagesAlevel Biology Notes U1(需修改补充完善的基础资料,仅供自己复习,Notforsale)Jerry SongNo ratings yet
- Carbs: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides & PolysaccharidesDocument6 pagesCarbs: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides & PolysaccharidesJada HartNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGICAL-MOLECULESDocument2 pagesBIOLOGICAL-MOLECULEShakdogiklog08No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ClassificationDocument20 pagesCarbohydrates Classificationzikri manggala putraNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Đề bàiDocument3 pagesĐề bàiminhphuongnmh14No ratings yet
- Banned Lists of Chemicals: Cradle To Cradle Certified Product StandardDocument7 pagesBanned Lists of Chemicals: Cradle To Cradle Certified Product StandardVIJAYAKUMAR K ANo ratings yet
- Cysteine, Methionine, ProlineDocument3 pagesCysteine, Methionine, ProlineRio BurlazaNo ratings yet
- General Science (Biological Sciences) : Dr. Sanawar IqbalDocument22 pagesGeneral Science (Biological Sciences) : Dr. Sanawar IqbalAbdullah khalidNo ratings yet
- Penggolongan Obat PDFDocument27 pagesPenggolongan Obat PDFFebiola AnatasyaNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics and Thermosetting PlasticDocument24 pagesThermoplastics and Thermosetting PlasticKAPIL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Gout Presentation Group 2 Defines Metabolic Disorder and ManagementDocument10 pagesGout Presentation Group 2 Defines Metabolic Disorder and ManagementVon Valentine MhuteNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Grignard ReagentsDocument560 pagesHandbook of Grignard Reagentschemgg50% (2)
- Ephoderin BiosynthesisDocument4 pagesEphoderin BiosynthesisHina AftabNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohdrates - 1Document5 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 2 - Analysis of Carbohdrates - 1Juliane JaynNo ratings yet
- Test BankDocument28 pagesTest BankMa Anna Cris Lumongsud50% (2)
- Microbiology Newlab سالى ابو السعود 0864986Document1 pageMicrobiology Newlab سالى ابو السعود 0864986Mohammed TahounNo ratings yet
- 16-31 Look Alike Sound Alike Rev 201503Document4 pages16-31 Look Alike Sound Alike Rev 201503api-249622140No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes PDFDocument101 pagesChemistry Notes PDFahmad.farazNo ratings yet
- Effects of Dietary Flax Seed and Sunflower Seed Supplementation On Normal Canine Serum Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Skin and Hair PDFDocument7 pagesEffects of Dietary Flax Seed and Sunflower Seed Supplementation On Normal Canine Serum Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Skin and Hair PDFjenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 11Document10 pagesChemistry 11catalystgrowthNo ratings yet
- A Convenient Method For The N-Formylation of Secondary Amines and Anilines Using Ammonium FormateDocument3 pagesA Convenient Method For The N-Formylation of Secondary Amines and Anilines Using Ammonium FormateroxdgutNo ratings yet
- Dhisha Jee Mains and Neet-185-206Document22 pagesDhisha Jee Mains and Neet-185-206jeevavelayyaNo ratings yet
- Saturated Versus Unsaturated Hydrocarbons C11-5-10Document10 pagesSaturated Versus Unsaturated Hydrocarbons C11-5-10ALongNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism VijayDocument30 pagesLipid Metabolism VijaytiffNo ratings yet
- Reaction IntermediatesDocument42 pagesReaction IntermediatestareNo ratings yet
- Atc DDD Tablet Buat Pa IjalDocument57 pagesAtc DDD Tablet Buat Pa IjalAriesta PerwitasariNo ratings yet
- 3 s2.0 B9780323511339000073 MainDocument11 pages3 s2.0 B9780323511339000073 MainMuhammad AdeelNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter 11Document34 pages07 Chapter 11M Zia Dogar100% (2)
- Case Study 4Document2 pagesCase Study 4api-305352286100% (1)
- Alkanes Cycloalkanes and AlkenesDocument3 pagesAlkanes Cycloalkanes and AlkenesDorota ZębikNo ratings yet
- LIST HARGA DAN KOMPOSISI 5 Mei 2022Document8 pagesLIST HARGA DAN KOMPOSISI 5 Mei 2022bunda vydaNo ratings yet
- Terpenoids and Steroids - Vol1Document574 pagesTerpenoids and Steroids - Vol1Ngoc Hong TranNo ratings yet
- MON Calculation For Compounds: Motor Octane Factor As Per IS 14861:2000Document2 pagesMON Calculation For Compounds: Motor Octane Factor As Per IS 14861:2000kvsr0205No ratings yet
- Pre Trial MRSM Biology ObjectivesDocument16 pagesPre Trial MRSM Biology ObjectivesKhusyairy Daeng SailendraNo ratings yet