Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-6 Vocabulary
Uploaded by
Kate Copeland0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pagesThis document defines key vocabulary terms related to macromolecules including: monomers, polymers, condensation reactions, carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, enzymes, hormones, proteins, nucleic acids, DNA, RNA, and nucleotides. It describes monomers as small repeating subunits that join to form polymers, and defines carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, DNA, RNA, and their subunits.
Original Description:
Original Title
1-6 Vocabulary - Google Docs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines key vocabulary terms related to macromolecules including: monomers, polymers, condensation reactions, carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, enzymes, hormones, proteins, nucleic acids, DNA, RNA, and nucleotides. It describes monomers as small repeating subunits that join to form polymers, and defines carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, DNA, RNA, and their subunits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views5 pages1-6 Vocabulary
Uploaded by
Kate CopelandThis document defines key vocabulary terms related to macromolecules including: monomers, polymers, condensation reactions, carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, enzymes, hormones, proteins, nucleic acids, DNA, RNA, and nucleotides. It describes monomers as small repeating subunits that join to form polymers, and defines carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, DNA, RNA, and their subunits.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
1-6 Vocabulary
Macromolecule
A molecule made of a very large number of
atoms.
Monomer- Small repeating subunits such as
glucose which join together to form a polymer.
Polymer- Very long, repeating chains of
monomers such as glucose.
Condensation Reaction- The chemical reaction
which forms a polymer, through the removal of
a water molecule from the two connecting
monomers.
Carbohydrate- A category of food molecules
which is used as an energy source.
Monosaccharide- Simple carbohydrates
consisting of one sugar, such
as glucose and fructose.
Disaccharide- Carbohydrates which contain
two sugar molecules joined by a glycosidic
bond.
Polysaccharide- Large carbohydrates which
contain many sugars joined together as either
branched or unbranched chains.
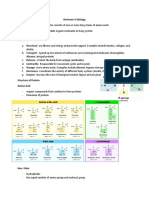
Lipid- A category of food molecules which are
rich in energy and are used for insulation and
to build cell membranes and hormones.
Fatty acid- Molecules which are used to build
lipids.
Amino Acid- The small subunits which make
up proteins.
Enzyme- Proteins which are responsible for
speeding up or slowing down reactions in the
cell.
Hormone- Chemical messengers which are
transported to other parts of the body to
control cell growth or activity.
Protein- Large molecules which are made of
amino acids joined together with a peptide
bond.
Nucleic acid- A long chain of nucleotides
joined together by a phosphate backbone.
DNA- The double stranded molecule which is
found in the nucleus of the cell and contains the
instructions which determine how it functions.
RNA- The smaller, single-stranded molecule
which is able to move from the nucleus of the
cell to the ribosome to manufacture proteins.
Nucleotide- The small subunits which bond
together to form RNA and DNA.
You might also like
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Biochemistry of CellsDocument79 pagesBiochemistry of CellsketakeeNo ratings yet
- MACROmoleculesDocument80 pagesMACROmoleculesMaKenJi EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Handout Biological Macromolecules (2022-2023)Document7 pagesHandout Biological Macromolecules (2022-2023)a c eNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FileDocument17 pagesChemistry FilePrakhar33% (3)
- Chapter 5 VocabDocument2 pagesChapter 5 VocababNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 BayoDocument10 pagesChapter 5 BayoWee-Weh HamjaNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 10 Notes (Grade 11)Document12 pagesBio Chapter 10 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (4)
- Unit 2 - Enzymes and The Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesUnit 2 - Enzymes and The Digestive SystemKatherine NunnNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 1 2nd Quartervanessagaray269No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Reviewer 2324Document7 pagesBiomolecules Reviewer 2324heraloesaNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS Handout Chapter 2Document3 pagesLIPIDS Handout Chapter 2MissNobodyNo ratings yet
- The "Stuff" of LifeDocument46 pagesThe "Stuff" of LifeMarcela UrbnNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument15 pagesBiology ReviewerIshie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Biology 20 - Unit D8.1 Nutrients V2Document52 pagesBiology 20 - Unit D8.1 Nutrients V2Najlaa JomhaNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules and Living Systems: MetabolismDocument2 pagesMacromolecules and Living Systems: MetabolismJohnnyNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES 2nd QuarterDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES 2nd QuarterKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument5 pagesBiology NotesFaith SNNo ratings yet
- Physical Science-Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesPhysical Science-Finals ReviewerPrecious Miracle Lucas SacataniNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 1Document29 pagesBiomolecules 1jefrillevaldezNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument53 pagesDigestive SystemNada DardeerNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument43 pagesScienceK Sai ShankarNo ratings yet
- 1 Macromolecule 2ndQDocument82 pages1 Macromolecule 2ndQAllysa ChanNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsDocument6 pagesMacromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsBon Joey BernestoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of A Carbon AtomdsdddddddddddDocument3 pagesChemical Properties of A Carbon AtomdsdddddddddddMohammed EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Structures of MacromoleculesDocument9 pagesStructures of MacromoleculesArtemist FowlNo ratings yet
- Creating and Breaking Down Polymers:: Inability To Digest The Sugar in MilkDocument3 pagesCreating and Breaking Down Polymers:: Inability To Digest The Sugar in MilkJessa Dela Cruz - RoxasNo ratings yet
- Glossary Key PointsDocument3 pagesGlossary Key PointsbxyrtbgyxcNo ratings yet
- Lecture Outline: Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDocument12 pagesLecture Outline: Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesJumz BoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Molecular Biology IDocument26 pagesLecture Molecular Biology ImartinmulingeNo ratings yet
- Flowchart of Digestion and AbsorptionDocument1 pageFlowchart of Digestion and Absorptionapi-253532759100% (1)
- Annotated GenbioDocument5 pagesAnnotated GenbioJarred HipolitoNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Digestion 1Document28 pagesAbsorption and Digestion 1InaraNo ratings yet
- AP2 Lecture NU2013 Springclass 38 ChemdigstionnotestopostDocument2 pagesAP2 Lecture NU2013 Springclass 38 Chemdigstionnotestopostjchu2919No ratings yet
- Biological Molecules RevisionDocument6 pagesBiological Molecules RevisioncocoNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument19 pagesINTRODUCTIONVatsal BajpaiNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument20 pagesBIOLOGYBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument2 pagesBIOMOLECULESKeith Chastine MiraballesNo ratings yet
- General Biology 11 - ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 11 - ReviewerAnthony OrataNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 NotesDocument15 pagesBiology Unit 1 Notesrizu786_213722545No ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document9 pagesChapter 05hyxuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document47 pagesChapter 1homamunfatNo ratings yet
- BTE101 Lecture3.1 Macromolecules1 MHU BRACU SpringSemester2023 FinalDocument57 pagesBTE101 Lecture3.1 Macromolecules1 MHU BRACU SpringSemester2023 FinalM.H. RafidNo ratings yet
- BiologicalmoleculesDocument58 pagesBiologicalmoleculesrhaineNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Composition, Structure and FunctionDocument50 pagesThe Cell: Composition, Structure and FunctionJally Mae Catam-isanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDocument9 pagesReviewer in Biology Protein-A Large Macromolecules Consists of One or More Long Chains of Amino AcidsDanilo PerezNo ratings yet
- 3 Polysaccharide NotesDocument2 pages3 Polysaccharide NotesRyan HaddockNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingRuskin Jamir AquinoNo ratings yet
- MBC 341 Lecture 1 2023Document16 pagesMBC 341 Lecture 1 2023Jacina AnnNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 4th Quarter Week 3Document12 pagesGrade 10 4th Quarter Week 3KarenNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESjorel marcoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology 1Document2 pagesReviewer in General Biology 1Moy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Absorption and The Products of Digestion1Document55 pagesAbsorption and The Products of Digestion1Abbie WhileyNo ratings yet
- MC3 Midterm ExamDocument1 pageMC3 Midterm ExamgherlethrNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesBiological MacromoleculesHabiba AmrNo ratings yet
- Molecules of LifeDocument5 pagesMolecules of LifeEmmaNo ratings yet
- General Biology: First Stage Lab 6Document13 pagesGeneral Biology: First Stage Lab 6IraqiNo ratings yet
- Basic Biology and Physiology-Lecture 2-Biomacromolecules-NewDocument32 pagesBasic Biology and Physiology-Lecture 2-Biomacromolecules-NewRajdeep PawarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Molecules of LifeDocument8 pagesChapter 3: The Molecules of LifeCourtney FazioNo ratings yet
- Script For BiochemDocument12 pagesScript For Biochemotep freecsNo ratings yet
- 1 4 Exit Quiz TE Chemistry of LifeDocument2 pages1 4 Exit Quiz TE Chemistry of LifeKate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Multiplying by 10: Math Drills WorksheetDocument2 pagesMultiplying by 10: Math Drills WorksheetKate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Sensoryoverload-683x1024 PNGDocument1 pageSensoryoverload-683x1024 PNGKate CopelandNo ratings yet
- 1 5 Guided Notes TE HIGHLIGHTED Google DocsDocument10 pages1 5 Guided Notes TE HIGHLIGHTED Google DocsKate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Who Is A Health Consumer?Document2 pagesWho Is A Health Consumer?Kate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Science Notes #2Document5 pagesScience Notes #2Kate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Science Notes 3Document4 pagesScience Notes 3Kate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Following Message Email: PostsDocument1 pageFollowing Message Email: PostsKate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Group 6 ChinaDocument11 pagesGroup 6 ChinaKate CopelandNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument3 pagesScience NotesKate CopelandNo ratings yet