Professional Documents
Culture Documents
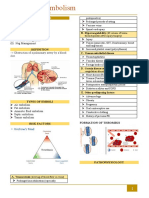
Thromboembolic Disease
Uploaded by
Diana RoseroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thromboembolic Disease
Uploaded by
Diana RoseroCopyright:
Available Formats
UTE UNIVERSITY
Health Sciences Faculty
Medicine
Name: Diana Rosero Date: 16/01/2022
Course: 8 “C” Types :
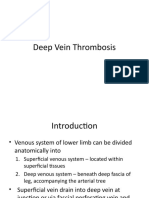
1. Deep vein thrombosis
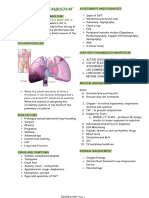
2. Pulmonary thromboembolism
It is a pathological condition caused by the formation of a blood clot (thrombus)
in a blood vessel and its mobilization through circulation with distant
obstruction (embolus) of a blood vessel.
Treatment:
Epidemiology:
- Anticoagulants are the medications
• It is the third most common acute most commonly used to treat DVT or
cardiovascular disease.
Thromboembolic disease PE.
• Morbidity and mortality increase after - Thrombolytics.
40 years of life. - Thrombectomy / embolectomy.
Diagnosis:
Risk Fac tors Signs and Symptoms
Chest X-ray
• Patients older than 40 years old. Deep Venous Thrombosis: Ultrasound
• Obesity.
MRI
• Oral Contraceptives. • Throbbing or cramping pain in 1 leg.
Electrocardiogram
• Family history of thromboembolic • Swelling in 1 leg.
D-dimer
diseases. • Warm skin around the painful area.
Pulmonary angiogram
• Red or darkened skin around the painful area.
Pulmonary Embolism:
• Acute dyspnea.
• Pleuritic chest pain.
• Tachycardia, Tachypnea.
You might also like
- Penyakit VenaDocument37 pagesPenyakit VenaSarah JR Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- IV Surgery PDFDocument265 pagesIV Surgery PDFاللهم أصلح أمريNo ratings yet
- Vte HandoutDocument55 pagesVte HandoutYantoNo ratings yet
- EMPYEMA ReviewDocument95 pagesEMPYEMA ReviewBijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Listeriosis - O&G SeminarDocument17 pagesListeriosis - O&G SeminarFaris Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- TracheaDocument2 pagesTracheaChalsey Jene LorestoNo ratings yet
- Lung TumorDocument36 pagesLung Tumorhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology A. Anatomy & Physiology: ReferenceDocument3 pagesPathophysiology A. Anatomy & Physiology: ReferenceAllana RayosNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Notes PDFDocument39 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Notes PDFrom92100% (1)
- Unusual Presentation of May-Thurner SyndromeDocument5 pagesUnusual Presentation of May-Thurner SyndromeJ. Ruben HermannNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism TransesDocument4 pagesPulmonary Embolism TransesKdamnzNo ratings yet
- Seminar: PathophysiologyDocument12 pagesSeminar: PathophysiologyBeni KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 5. Hemoptysis 王晓龙Document39 pages5. Hemoptysis 王晓龙mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesDeep Vein ThrombosisDoctor MusicNo ratings yet
- DR TahirDocument61 pagesDR TahirRohail GulNo ratings yet
- The Management of DVT: Dr. Heru Sulastomo, SP - JP (K), FIHA Dr. Ahmad Yasa', SP - JP, FIHA, MkesDocument19 pagesThe Management of DVT: Dr. Heru Sulastomo, SP - JP (K), FIHA Dr. Ahmad Yasa', SP - JP, FIHA, MkesDEWI MULYANINo ratings yet
- Deep Vein Thrombosis: EssentialsDocument7 pagesDeep Vein Thrombosis: EssentialsLuthfia RahmaditaNo ratings yet
- Cardiology-7 MEDIASTDocument19 pagesCardiology-7 MEDIASTMahmoud RamadanNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Rays:: Case Studies From The FieldDocument12 pagesChest X-Rays:: Case Studies From The FieldRiki AntoNo ratings yet
- Thoracic TraumaDocument43 pagesThoracic Traumamatrixkhalifa9955No ratings yet
- Aneurysm Final (Bentals Procedure)Document55 pagesAneurysm Final (Bentals Procedure)tejuteju067100% (1)
- Deep Vein Thrombosis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Medical ManagementDocument48 pagesDeep Vein Thrombosis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Medical ManagementasumaacocoNo ratings yet
- 4.18 Mankad Echo in Systemic DiseaseDocument97 pages4.18 Mankad Echo in Systemic DiseaseDiana_anca6No ratings yet
- HIS1-K36 VTE, Diagnosis Klinis DVTDocument26 pagesHIS1-K36 VTE, Diagnosis Klinis DVTPaul Behring ManurungNo ratings yet
- DIGITAL SUBSTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY & INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGYnewDocument79 pagesDIGITAL SUBSTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY & INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGYnewDaniel MontesNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 3: Irwan Surya Angkasa 405150170Document63 pagesPemicu 3: Irwan Surya Angkasa 405150170ElsaNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Document40 pagesNeck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Hauwa shitu.B100% (1)
- Common Respiratory ProblemsDocument10 pagesCommon Respiratory ProblemsNo Saida No LifeNo ratings yet
- Pleual ConditionsDocument61 pagesPleual ConditionsKandarp TrivediNo ratings yet
- Tep PDFDocument8 pagesTep PDFCesar AvilaNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Syllabus PDFDocument3 pagesCardiopulmonary Syllabus PDFsan MunNo ratings yet
- What Is Ultrasound?Document15 pagesWhat Is Ultrasound?Al-Mukashfi TahaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument53 pagesPeripheral Vascular DiseaseShenbagam Mahalingam100% (1)
- Stable Angina AbnetDocument118 pagesStable Angina AbnetAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- Teaching Case Presentation 2Document20 pagesTeaching Case Presentation 2api-347034408No ratings yet
- Respiratory Term 2Document13 pagesRespiratory Term 2Abegail QuintoNo ratings yet
- Venous Thromboembolism DiseaseDocument49 pagesVenous Thromboembolism DiseaseNiko YuandikaNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument29 pagesPericarditisPavin KumarNo ratings yet
- OncologyDocument85 pagesOncologyLhara MañoNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument16 pagesDeep Vein ThrombosisB1 TutorialNo ratings yet
- NoseDocument15 pagesNoseArooshaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesRespiratory SystemMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument16 pagesPulmonary EmbolismEhab Mokhtar WehebaNo ratings yet
- MUAAZDocument16 pagesMUAAZЭламан УрайимовNo ratings yet
- Surgical Conditions of Pleura: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonDocument63 pagesSurgical Conditions of Pleura: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonVincent SerNo ratings yet
- DVT Pulmonary EmbolismDocument40 pagesDVT Pulmonary EmbolismDr. Shatdal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ulcer HX & PExDocument6 pagesUlcer HX & PExAashna JainNo ratings yet
- A. Narrative: Iv. PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesA. Narrative: Iv. Pathophysiologyr_cyrusNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Thrombosis 2015 NNDocument39 pagesKuliah Thrombosis 2015 NNBeladiena Citra SiregarNo ratings yet
- Pulmonory EmbolismDocument39 pagesPulmonory EmbolismLujain M. YumenNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatiDocument42 pagesGambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatisabariaNo ratings yet
- Complications of FracturesDocument19 pagesComplications of Fracturesمحمد رأفتNo ratings yet
- L3 - Hema 2 LecDocument10 pagesL3 - Hema 2 LecJUDEA WILCH ORJENo ratings yet
- Patho 2020Document2 pagesPatho 2020Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer: by Holly Winn and Cathy Mac DonaldDocument49 pagesLung Cancer: by Holly Winn and Cathy Mac DonaldfajarnugrahamulyaNo ratings yet
- Referat HemothoraksDocument28 pagesReferat HemothoraksitsmediNo ratings yet
- ITP 11-9-20-dr - WidiDocument39 pagesITP 11-9-20-dr - WidiWenny TanyawanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuDocument41 pagesDr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuYuni SaviraNo ratings yet
- Seminar W2 Management of Orthopaedic EmergenciesDocument45 pagesSeminar W2 Management of Orthopaedic EmergenciesUN EPNo ratings yet
- Non-Surgical Acute AbdomenDocument1 pageNon-Surgical Acute AbdomenDiana RoseroNo ratings yet
- Purpura and PetechiaeDocument1 pagePurpura and PetechiaeDiana RoseroNo ratings yet
- Secundary InmunodeficiencyDocument1 pageSecundary InmunodeficiencyDiana RoseroNo ratings yet
- Acute Surgical AbdomenDocument1 pageAcute Surgical AbdomenDiana RoseroNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Hypertension: Introduction To Cor PulmonaleDocument16 pagesPulmonary Hypertension: Introduction To Cor PulmonaleJisha JanardhanNo ratings yet
- Right Ovarian Vein Thrombosis (Ovt) - A Rare Presentation of Abdominal PainDocument4 pagesRight Ovarian Vein Thrombosis (Ovt) - A Rare Presentation of Abdominal PainIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Vascular DiseaseDocument4 pagesPulmonary Vascular DiseaseSaima JabbarNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism: Dr. Nurfitriani, SP.PDocument44 pagesPulmonary Embolism: Dr. Nurfitriani, SP.PAfifulichwanNo ratings yet
- Thrombolytic TherapyDocument24 pagesThrombolytic TherapyJayarani Ashok100% (1)
- Critical Care Goals and ObjectivesDocument28 pagesCritical Care Goals and ObjectivesjyothiNo ratings yet
- Acute HF-IAIDocument49 pagesAcute HF-IAIAndita ListyannisaNo ratings yet
- Peripartum Cardiomyopathy ReviewDocument14 pagesPeripartum Cardiomyopathy ReviewWalter Saavedra Yarleque100% (1)
- Ottawas Clerkship GuideDocument44 pagesOttawas Clerkship GuideHugo LuceroNo ratings yet
- Tromboza VenoasaDocument4 pagesTromboza VenoasaDanielaNo ratings yet
- Falla Respiratoria & Embarazo - Lapinsky 2015Document7 pagesFalla Respiratoria & Embarazo - Lapinsky 2015Fabiola Buelna GaxiolaNo ratings yet
- 300 Single Best Answers For The Final FRCR Part ADocument161 pages300 Single Best Answers For The Final FRCR Part Asalah subbah100% (2)
- Option EliteDocument168 pagesOption EliteGoutamSastryNo ratings yet
- Activase (Alteplase) Dosing and Administration: For Acute Ischemic StrokeDocument33 pagesActivase (Alteplase) Dosing and Administration: For Acute Ischemic StrokeThomas HenrryNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE) PDFDocument9 pagesPulmonary Embolism (PE) PDFMileNo ratings yet
- ACCA Toolkit Abridged Version PDFDocument124 pagesACCA Toolkit Abridged Version PDFNur RifqahNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Mbolism: Presented By: Miss. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorDocument9 pagesPulmonary Mbolism: Presented By: Miss. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorKaku ManishaNo ratings yet
- Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) : Quality DepartmentDocument28 pagesVenous Thromboembolism (VTE) : Quality DepartmentDIGITAL 143No ratings yet
- Pulmonary MedicineDocument20 pagesPulmonary Medicineد.سلمان زبيداتNo ratings yet
- CPG Management of Venous TromboemlismDocument63 pagesCPG Management of Venous Tromboemlismapalaginih100% (1)
- Candidate 219 DR Sangeetha Pai-My FRCS Experience PDFDocument10 pagesCandidate 219 DR Sangeetha Pai-My FRCS Experience PDFBintealiNo ratings yet
- Jeaa 243Document10 pagesJeaa 243Mathew McCarthyNo ratings yet
- BLUE-Protocol and FALLS-Protocol: Two Applications of Lung Ultrasound in The Critically IllDocument12 pagesBLUE-Protocol and FALLS-Protocol: Two Applications of Lung Ultrasound in The Critically IllChristiaan CordovaNo ratings yet
- Total Hip Replacement: A Guide For PatientsDocument47 pagesTotal Hip Replacement: A Guide For PatientsSaurabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Usg TemplatesDocument53 pagesUsg Templatessubha1b9448No ratings yet
- Cor PulmonaleDocument14 pagesCor PulmonaleEvangelin MelvinNo ratings yet
- DVTDocument20 pagesDVTNachiket Vijay PotdarNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument27 pagesPulmonary EmbolismEfren Ezekiel AlbiosNo ratings yet
- Deep Venous ThrombosisDocument56 pagesDeep Venous ThrombosisSrikant Konchada100% (1)
- Society of Radiographers - PDFDocument9 pagesSociety of Radiographers - PDFOsama AhmedNo ratings yet