Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maintaining Structural Integrity Against Corrosion 12.1 Corrosion Protection Systems
Uploaded by
ObaidUrRehman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageOriginal Title
08
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageMaintaining Structural Integrity Against Corrosion 12.1 Corrosion Protection Systems
Uploaded by
ObaidUrRehmanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
selecting bell-and-spigot (lap) joints or rubber ring jointed pipe.
Butt-welded pipe is the preferred
method in these areas.
c) Specially designed flexible joints shall be provided at all junctions between pipes and rigid structures
(such as reservoirs, pump stations, bridges, and buildings) where pipe flexibility alone is not adequate
to accommodate movement.
d) Where structures are closely spaced such as at pump stations, base isolation of the area may be
considered where minor actions are expected. Connecting to the base isolation area requires a
flexible connection.
e) Flexible connections or other mechanical joints must not be located under any structures and must be
accessible for repair or replacement.
f) Acceptable fuse locations must be designed where service breaks can be easily repaired to minimise
disruption instead of compromising key infrastructure such as pump stations, plants and valve
stations.
12. Maintaining structural integrity against corrosion
12.1 Corrosion protection systems
12.1.1 Tape systems
a) Buried steel pipe shall be tape wrapped with an accepted system to protect the pipe material in the
buried environment.
b) Pipe transitioning into chambers shall be wrapped a minimum of 150mm past the chamber wall and
overlapping onto the painted surface.
c) Pipe transitioning to an above surface pipe shall be wrapped at least 200mm past the soil to surface
interface and onto the painted surface. The tape system shall be over-layered with a UV-stabilised
tape system over the existing tape to 200mm into the buried section and a minimum of 50mm onto
the painted steel.
12.1.2 Paint systems
a) Steel pipe that is exposed, such as in chambers or on pipe bridges shall be painted with a suitable
epoxy corrosion protection system.
b) The appropriate system shall be determined with input from a coatings engineer and identify the site
specific macro and micro environments. The designer must complete the project schedule in the
Material Supply standard and provide this to the coating supplier to support the coating selection.
12.1.3 Cathodic protection systems for metallic pipes
a) For the electrical design of cathodic protection systems refer to the Watercare electrical design
standard. The design must be determined with considerations to the site ground conditions and in
consultation with a cathodic protection designer.
b) All joints of steel pipelines shall be electrically bonded.
c) Isolation joints and test stations shall as far as practicable be located at main line valve installations.
d) Anode beds shall as far as practicable be near main line valve installation.
12.1.4 Internal corrosion protection
a) Internal corrosion protection of pipe and fittings must consider the whole of life of the asset and
choosing the appropriate method that considers re-application or repair of the lining system.
b) Metallic pipe is typically protected using a concrete lining solution.
Ver.1.1 This is an electronic ESF document that
is uncontrolled when copied or printed Page 68 of 70
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Pages From GSM Based Flow metering-IFLM 2Document1 pagePages From GSM Based Flow metering-IFLM 2ObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Bid Submittal Format: Day of May, 2016Document1 pageBid Submittal Format: Day of May, 2016ObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- 2.3 Pressure, Flow and Level Control Valves: Section 2.7.5Document1 page2.3 Pressure, Flow and Level Control Valves: Section 2.7.5ObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Pages From Applsci-09-02703-2 5Document1 pagePages From Applsci-09-02703-2 5ObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- QwedDocument1 pageQwedObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Useful KeltDocument1 pageUseful KeltObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- C. System Installation.: D. BackfillingDocument1 pageC. System Installation.: D. BackfillingObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- 46 2 Hydrogeological Parameters CalculationDocument1 page46 2 Hydrogeological Parameters CalculationObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Laboratory Models-A Scale Model Can Be Built To Reproduce TransientsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Models-A Scale Model Can Be Built To Reproduce TransientsObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- @furqan PKDocument1 page@furqan PKObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
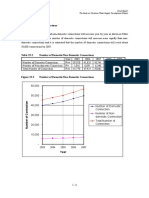
- 2.2.4 Number of Connections: Final Report The Study On Vientiane Water Supply Development ProjectDocument5 pages2.2.4 Number of Connections: Final Report The Study On Vientiane Water Supply Development ProjectObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Vapor Recovery Test Procedure: Adopted: February 1, 2001 Amended: July 3, 2002 Amended: October 8, 2003Document10 pagesVapor Recovery Test Procedure: Adopted: February 1, 2001 Amended: July 3, 2002 Amended: October 8, 2003ObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
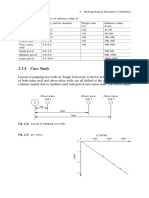
- 2.5.4 Case Study: Observation Well 1 Observation Well 2 Observation Well 3Document1 page2.5.4 Case Study: Observation Well 1 Observation Well 2 Observation Well 3ObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
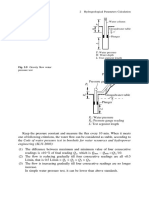
- 50 2 Hydrogeological Parameters Calculation: Water Tank Pipeline Pressure GaugeDocument1 page50 2 Hydrogeological Parameters Calculation: Water Tank Pipeline Pressure GaugeObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Pages From 11822699 - 07Document1 pagePages From 11822699 - 07ObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution (1) Maximum Allowable Standard of Pollution Substance For Immobile Sources in Ambient AirDocument1 pageAir Pollution (1) Maximum Allowable Standard of Pollution Substance For Immobile Sources in Ambient AirObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Punjab Province District Maps: Name of District Maps. Edition. Scale Size (CM) Price (RS.)Document1 pagePunjab Province District Maps: Name of District Maps. Edition. Scale Size (CM) Price (RS.)ObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- GOLDAMATIC Deep Well Injector PumpsDocument3 pagesGOLDAMATIC Deep Well Injector PumpsObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- 96 Pkli AdDocument1 page96 Pkli AdObaidUrRehmanNo ratings yet
- October 2014 1413376166 06 PDFDocument3 pagesOctober 2014 1413376166 06 PDFDineshNo ratings yet
- Agmt - Spa Schedule HDocument20 pagesAgmt - Spa Schedule Hapi-340431954No ratings yet
- Learning Competencies: Table of SpecificationDocument2 pagesLearning Competencies: Table of Specificationyolanda renos0% (1)
- PRP RationaleDocument12 pagesPRP Rationalemarquezjayson548No ratings yet
- Activity 9 Let's Check and Let's AnalyzeDocument3 pagesActivity 9 Let's Check and Let's AnalyzeJean Tronco100% (5)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- STD 12 Accountancy1Document264 pagesSTD 12 Accountancy1Chetan KhonaNo ratings yet
- Ratio & Proportion Part 1Document5 pagesRatio & Proportion Part 1P Singh KarkiNo ratings yet
- Gurdan Saini: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesGurdan Saini: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument2 pagesReflectionBảo HàNo ratings yet
- Senate - Investigating - Committee - On - Education California Textbooks 1948 120pgs GOV EDU - SML PDFDocument115 pagesSenate - Investigating - Committee - On - Education California Textbooks 1948 120pgs GOV EDU - SML PDFdragan346382902No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- VA RESUME HelloracheDocument1 pageVA RESUME HelloracheJessa AbadianoNo ratings yet
- Peter Zumthor - Thinking Architecture PDFDocument33 pagesPeter Zumthor - Thinking Architecture PDFDiana Sterian73% (11)
- Lesson Plan 4Document6 pagesLesson Plan 4Lilay Barambangan100% (3)
- My Kindergarten BookDocument48 pagesMy Kindergarten BookfranciscoNo ratings yet
- QAS M001 SLPS Quality Assurance ManualDocument49 pagesQAS M001 SLPS Quality Assurance ManualMHDNo ratings yet
- Bob Dylan Diskografija Prevodi PesamaDocument175 pagesBob Dylan Diskografija Prevodi PesamaJolanda NešovićNo ratings yet
- Case of Joneja Bright Steels: The Cash Discount DecisionDocument10 pagesCase of Joneja Bright Steels: The Cash Discount DecisionRHEANo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Legal Framework On Sexual Violence in Sri Lanka - Policy BriefDocument4 pagesLegal Framework On Sexual Violence in Sri Lanka - Policy BriefwmcsrilankaNo ratings yet
- Neon Wilderness MenuDocument2 pagesNeon Wilderness MenuAlisa HNo ratings yet
- 1982 B47 Lehigh County Gunsmithing FamiliesDocument12 pages1982 B47 Lehigh County Gunsmithing FamiliesAmr DeabesNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility/Project Study OnDocument14 pagesA Feasibility/Project Study OnWilson Domingo LazarteNo ratings yet
- Talking SwedishDocument32 pagesTalking Swedishdiana jimenezNo ratings yet
- Reflection PseudoscienceDocument3 pagesReflection PseudoscienceSuganthi RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Installing Hyperledger Fabric and Composer: Ser/latest/installing/development-To Ols - HTMLDocument13 pagesInstalling Hyperledger Fabric and Composer: Ser/latest/installing/development-To Ols - HTMLVidhi jainNo ratings yet
- Buyer Behavior ModelDocument1 pageBuyer Behavior ModelraihanulhasanNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Free Download: How To Do Installation of Suspended False CeilingsDocument3 pagesMethod Statement Free Download: How To Do Installation of Suspended False Ceilingsmozartjr22100% (1)
- ACO S Range BrochureDocument20 pagesACO S Range BrochureSyed RaziuddinNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Behavioral Emergencies - Geriatric Psychiatric PatientDocument14 pages2017 - Behavioral Emergencies - Geriatric Psychiatric PatientAna María Arenas DávilaNo ratings yet
- Onechanbara - Bikini Samurai Squad Game GuideDocument83 pagesOnechanbara - Bikini Samurai Squad Game GuideStefan RoscaNo ratings yet
- Motivation MBADocument31 pagesMotivation MBAAkshitaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry, and MetallurgyFrom EverandPrinciples of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry, and MetallurgyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Aqua Group Guide to Procurement, Tendering and Contract AdministrationFrom EverandThe Aqua Group Guide to Procurement, Tendering and Contract AdministrationMark HackettRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsFrom EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (242)