Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment No. 1 Thermodynamics Applications
Uploaded by
Vince Romano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThis document provides an assignment to search for and explain 5 practical applications of thermodynamics. It lists heat engines, refrigerators, heat pumps, air conditioners, and electric fans as examples. For each application, it provides a name, image, and brief explanation of how it uses thermodynamics principles to convert various forms of energy and transfer heat.
Original Description:
thermo
Original Title
Assign-1-Thermodynamics-Applications
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an assignment to search for and explain 5 practical applications of thermodynamics. It lists heat engines, refrigerators, heat pumps, air conditioners, and electric fans as examples. For each application, it provides a name, image, and brief explanation of how it uses thermodynamics principles to convert various forms of energy and transfer heat.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesAssignment No. 1 Thermodynamics Applications
Uploaded by
Vince RomanoThis document provides an assignment to search for and explain 5 practical applications of thermodynamics. It lists heat engines, refrigerators, heat pumps, air conditioners, and electric fans as examples. For each application, it provides a name, image, and brief explanation of how it uses thermodynamics principles to convert various forms of energy and transfer heat.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Name: Score:
Course Year Section Date:
Assignment No. 1 Thermodynamics Applications
Search for 5 practical applications of thermodynamics and explain each.
Name of the Technology Image Explanation
Heat engine Heat engines work by
converting a portion of the
energy transferred by heat
from a source into mechanical
energy. Heat transfers energy
from a high-temperature
object to a low-temperature
object while also transferring
unused energy. Heat engines
include gasoline and diesel
engines, jet engines, and
steam turbines that create
electricity.
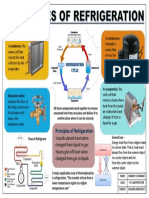
Refrigerator Convection is the most
common process in any
refrigeration device you might
encounter. It is the product of
fluid circulation, which can
occur naturally because of
temperature changes in the
fluid, or in a controlled
manner. Convection is
demonstrated by the heat
exchange that occurs on the
evaporator and condenser.
Heat pump A heat pump is a machine that
transfers heat energy from a
heat source to a thermal
reservoir. Heat pumps take
heat from a cold region and
release it to a warmer one,
moving thermal energy in the
opposite direction of
spontaneous heat transfer. A
heat pump absorbs heat from
the outside air, heats it up
even more, and transfers it
indoors for house heating. For
home cooling, a heat pump
reverses this process,
extracting heat from the
internal air and expelling it to
the outside, much like a
refrigerator or air conditioner,
making the inside air cooler.
Air conditioner Air conditioning (A/C) is a
system that works on the same
basic principles as heat pumps,
but with some differences.
Because they only provide
cooling, air conditioners are
not as versatile as heat pumps.
However, because some places
on Earth do not require
heating, they are more
practical in many cases. They
operate in the same way that
heat pumps do in terms of
cooling.
Electric fan The fan motor converts
incoming electrical energy into
mechanical energy, which is
used to move the fan blades.
However, it does not convert
electricity to motion with 100%
efficiency. The resistance of
the wires in the fan motor
generates heat. As a result,
some of the electricity is
immediately converted into
heat. The remainder of the
electrical energy is converted
to mechanical energy, which is
eventually converted to heat.
You might also like
- Wiley CIA P1 MCQsDocument240 pagesWiley CIA P1 MCQsSameh Saber80% (5)
- 1810 (W 100 CFi - W 120 CFi - W 130 CFi) PDFDocument1 page1810 (W 100 CFi - W 120 CFi - W 130 CFi) PDFadrianNo ratings yet
- Qns Bank For Final Exam FilteredDocument104 pagesQns Bank For Final Exam FilteredPhuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Skills-Based Assessment (Version A) : TopologyDocument5 pagesSkills-Based Assessment (Version A) : TopologyYagui100% (1)
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid SciencesDocument42 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid SciencesMahrukh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Cat 2Document67 pagesCat 2ChinmayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesChapter 6 - Second Law of ThermodynamicsNurshaqina Sufian100% (1)
- Objectives: The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument28 pagesObjectives: The Second Law of ThermodynamicsMohammad RizkyNo ratings yet
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument33 pagesSecond Law of ThermodynamicsZeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lec1Document29 pagesThermodynamics Lec1amir ashrafNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 (The Second Law of Thermodynamics) PDFDocument30 pagesUnit 6 (The Second Law of Thermodynamics) PDFIñigoNo ratings yet
- Thermofluids Ch3 Heat EnginesDocument61 pagesThermofluids Ch3 Heat EnginesAbdallah LotfyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five ThermoDocument31 pagesChapter Five Thermoabene danNo ratings yet
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachDocument31 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachmechgokulNo ratings yet
- The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamicsbenson100% (1)
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid SciencesDocument38 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid SciencesTaha KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Second LawDocument32 pagesWeek 13 Second LawFernando OsorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document39 pagesChapter 6H ANo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Second Law AnalysisDocument30 pagesThermodynamics Second Law AnalysisMetalAnand ChelliahNo ratings yet
- Second Law of Thermodynamics 1Document16 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamics 1Lone KnightNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant - Part 1.1 HeatEngine - 2nd LawDocument17 pagesSteam Power Plant - Part 1.1 HeatEngine - 2nd LawMaznan JaafarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 PDFDocument46 pagesChapter 7 PDFOnur ÖZÇELİKNo ratings yet
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Mehmet KanogluDocument29 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: Mehmet KanogluMalav PurohitNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration components and principlesDocument1 pageRefrigeration components and principlesSharayu DhavaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS5704685Document29 pagesChapter 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS5704685bensonNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Chapter on 2nd Law and ApplicationsDocument39 pagesThermodynamics Chapter on 2nd Law and Applicationsrustam effendyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document49 pagesChapter 05HassanKMNo ratings yet
- Second Law LimitationsDocument16 pagesSecond Law LimitationsCHANDRASEKARANNo ratings yet
- CTDCHA2 - Learning Unit 1C 2019Document63 pagesCTDCHA2 - Learning Unit 1C 2019Brandon GreenwoodNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument41 pagesThermodynamics: The Second Law of ThermodynamicsEgis KrismaNo ratings yet
- CET I 4. Second Law 2021Document63 pagesCET I 4. Second Law 2021Dhruv AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Absorption Chillers Use Heat for Cooling BuildingsDocument2 pagesAbsorption Chillers Use Heat for Cooling Buildingsdalton2004No ratings yet
- The Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument36 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamicshakita86No ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument30 pagesUnit 6 - Second Law of ThermodynamicsIamzura AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 06 - Second Law-8Document38 pagesChapter - 06 - Second Law-8Marviandi EkoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 PDFDocument10 pagesModule 6 PDFTazbir AntuNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Student HandoutDocument39 pagesHeat Exchanger Student HandoutkotiNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document56 pagesCH 5Mintesinot KasaNo ratings yet
- Chap - 5 Second Law of Thermodynamics - Lectureand Pro 2Document41 pagesChap - 5 Second Law of Thermodynamics - Lectureand Pro 2Mulugeta WoldeNo ratings yet
- CHE 325 (Module 3) Second Law of Thermo.Document54 pagesCHE 325 (Module 3) Second Law of Thermo.PreciousNo ratings yet
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument33 pagesSecond Law of ThermodynamicsSInowritaNo ratings yet
- Themodynamics 1 C&o - Heat EnginesDocument4 pagesThemodynamics 1 C&o - Heat EnginesBasil BautistaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PantDocument16 pagesThermal Power PantmehediNo ratings yet
- Topic 2:: Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument28 pagesTopic 2:: Vapor Compression Refrigeration CyclePrince NeoNo ratings yet
- Booklet 10 ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesBooklet 10 ThermodynamicsMark Cidric Roquero IINo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TermsDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Termschristian aldwin canlapanNo ratings yet
- Ekb 1043 Chapter 4 Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument60 pagesEkb 1043 Chapter 4 Second Law of ThermodynamicsAbishree GunasekhranNo ratings yet
- MCH2015 - Int Therm Flu Sci - #05 (11 Nov-2022)Document25 pagesMCH2015 - Int Therm Flu Sci - #05 (11 Nov-2022)yarenonmNo ratings yet
- CHE 325 (Module 3)Document53 pagesCHE 325 (Module 3)Daniel OmolewaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-6-The SECOND LAW of ThermodynamicsDocument38 pagesLecture-6-The SECOND LAW of ThermodynamicsHahshskakagaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: Terminologies Laws of Thermodynamics Heat TransferDocument25 pagesBasic Concepts: Terminologies Laws of Thermodynamics Heat TransferGama AjiyantonoNo ratings yet
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: E233 - ThermofluidsDocument30 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: E233 - ThermofluidsYingyote LubphooNo ratings yet
- Stirling LaboratoryDocument4 pagesStirling LaboratorySilviu DnlNo ratings yet
- Heat Pumps: Basics, Types, and Performance CharacteristicsDocument26 pagesHeat Pumps: Basics, Types, and Performance CharacteristicsilieoniciucNo ratings yet
- lecture 1_ 1.1 to 1.37Document18 pageslecture 1_ 1.1 to 1.37manuj gaikwadNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics FundamentalsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics FundamentalsRitabrataMaitiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document13 pagesLecture 16sanyamjain51150No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Refrigeration: (Heating, Ventilation and Air-Conditioning)Document8 pagesBasic Principles of Refrigeration: (Heating, Ventilation and Air-Conditioning)manish jainNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument5 pagesHandoutsedzeeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 13 - ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 13 - ThermodynamicsGerry Lou QuilesNo ratings yet
- PhyII LPO Chapters 18, 20,21,22Document54 pagesPhyII LPO Chapters 18, 20,21,22Luis PedreroNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4No ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Land As A Sustainable Resource in City Planning The Use of Open Spaces and Drainage Systems To Structure Environmental and Urban NeedsDocument19 pagesLand As A Sustainable Resource in City Planning The Use of Open Spaces and Drainage Systems To Structure Environmental and Urban NeedsVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Computers, Environment and Urban Systems: Cong Cong, Yoonshin Kwak, Brian DealDocument13 pagesComputers, Environment and Urban Systems: Cong Cong, Yoonshin Kwak, Brian DealVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Map of Thi Qar Governorate Using Geographical Information Systems (GIS)Document11 pagesGeotechnical Map of Thi Qar Governorate Using Geographical Information Systems (GIS)Vince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Physiological Responses To Lead Exposure in Wheat, Barley and OatDocument6 pagesPhysiological Responses To Lead Exposure in Wheat, Barley and OatVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Policy Planning To Achieve Sustainable Development Goals For Low-Income NationsDocument10 pagesPolicy Planning To Achieve Sustainable Development Goals For Low-Income NationsVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lec Atn ScriptDocument1 pageAubf Lec Atn ScriptVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 - Reflective EssayDocument3 pagesActivity 5 - Reflective EssayVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Challenges: APA Citation: Souahi, H., Chebout, A., Akrout, K., Massaoud, N., & Gacem, R. (2021Document3 pagesEnvironmental Challenges: APA Citation: Souahi, H., Chebout, A., Akrout, K., Massaoud, N., & Gacem, R. (2021Vince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form: (Buong Pangalan) (Petsa) (Oras) (Kasa/ukuyang Tirahan) : (Numero NG Telepono)Document1 pageHealth Declaration Form: (Buong Pangalan) (Petsa) (Oras) (Kasa/ukuyang Tirahan) : (Numero NG Telepono)Reichmond LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument18 pagesLearning StylesVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- Legal Definitions of DeathDocument5 pagesLegal Definitions of DeathAdelina RotaruNo ratings yet
- Ethics Vs MoralsDocument11 pagesEthics Vs MoralsVince RomanoNo ratings yet
- 6 - Instructional Materials Development For ESPDocument12 pages6 - Instructional Materials Development For ESPMerren Monta100% (1)
- Windows Desktop Interview Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesWindows Desktop Interview Questions and AnswersVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- V2 Progression Pathways by CS IT and DL-with-CT-refs PDFDocument1 pageV2 Progression Pathways by CS IT and DL-with-CT-refs PDFsramsahaNo ratings yet
- BDT QuizDocument4 pagesBDT QuizVani HiremaniNo ratings yet
- PJ1000C-LCD PJ1300C-LCD PJ2000LCD: User ManualDocument44 pagesPJ1000C-LCD PJ1300C-LCD PJ2000LCD: User ManualВладимир100% (1)
- Spec 86569Document17 pagesSpec 86569Tiarnan OKellyNo ratings yet
- Amulet FeliciaDocument103 pagesAmulet FeliciaDaniele PioNo ratings yet
- PDF Vibration Analysis Level 1 CompressDocument3 pagesPDF Vibration Analysis Level 1 CompressMohammad IkbalNo ratings yet
- Bomba JockeyDocument36 pagesBomba Jockeyruben estebanNo ratings yet
- Report Writing - PankajDocument13 pagesReport Writing - PankajPankaj GoyalNo ratings yet
- PDF Photobooth Manual 2023Document24 pagesPDF Photobooth Manual 2023api-725597460No ratings yet
- Production of Coated Detergent Enzyme GranulesDocument121 pagesProduction of Coated Detergent Enzyme Granulesdadang71No ratings yet
- E3tutorial Exercises UsDocument41 pagesE3tutorial Exercises UsKarthik NNo ratings yet
- Valve Material Specification General Notes: Annexure-I (To VMS)Document5 pagesValve Material Specification General Notes: Annexure-I (To VMS)sabareeshNo ratings yet
- MongoDB MonitoringDocument6 pagesMongoDB Monitoringsnet solutionsNo ratings yet
- Surface Vehicle Standard: Rev. AUG2005Document58 pagesSurface Vehicle Standard: Rev. AUG2005Leonardo Gonçalves GomideNo ratings yet
- 2 Classical Detection and Estimation TheoryDocument62 pages2 Classical Detection and Estimation Theorythesunbk25No ratings yet
- Benbri ProfileDocument32 pagesBenbri ProfileOlusola OluwaseunNo ratings yet
- CC Unit4Document8 pagesCC Unit4Harsh RajputNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity (Physics Ch.4 Group 2)Document19 pagesSuperconductivity (Physics Ch.4 Group 2)mnvsptlNo ratings yet
- Line CodingDocument16 pagesLine CodingAitzaz HussainNo ratings yet
- KDS 330 Built for Today, Ready for TomorrowDocument2 pagesKDS 330 Built for Today, Ready for TomorrowBill GetsNo ratings yet
- Seeed Can Bus v2Document20 pagesSeeed Can Bus v2Geo AdmNo ratings yet
- PVS980 - 5MW Pre Commissioning InstructionDocument6 pagesPVS980 - 5MW Pre Commissioning InstructionFrancisco Aguirre VarasNo ratings yet
- HGDGDocument57 pagesHGDGEsperdion Jr GanibeNo ratings yet
- Chap 06Document46 pagesChap 06M. Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet